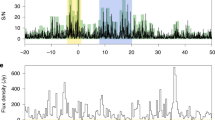
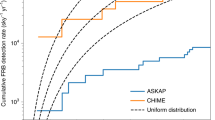
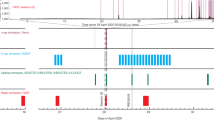
Abstract
Fast radio bursts are mysterious millisecond-duration transients prevalent in the radio sky. Rapid accumulation of data in recent years has facilitated an understanding of the underlying physical mechanisms of these events. Knowledge gained from the neighbouring fields of gamma-ray bursts and radio pulsars has also offered insights. Here I review developments in this fast-moving field. Two generic categories of radiation model invoking either magnetospheres of compact objects (neutron stars or black holes) or relativistic shocks launched from such objects have been much debated. The recent detection of a Galactic fast radio burst in association with a soft gamma-ray repeater suggests that magnetar engines can produce at least some, and probably all, fast radio bursts. Other engines that could produce fast radio bursts are not required, but are also not impossible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other finding of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Lorimer, D. R., Bailes, M., McLaughlin, M. A., Narkevic, D. J. & Crawford, F. A bright millisecond radio burst of extragalactic origin. Science 318, 777–780 (2007). This discovery paper marks the birth of the FRB research field.
Thornton, D. et al. A population of fast radio bursts at cosmological distances. Science 341, 53–56 (2013).
Petroff, E. et al. Identifying the source of perytons at the Parkes radio telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 451, 3933–3940 (2015).
Spitler, L. G. et al. A repeating fast radio burst. Nature 531, 202–205 (2016). This paper reports the discovery of the first repeating FRB source: FRB 121102.
Chatterjee, S. et al. A direct localization of a fast radio burst and its host. Nature 541, 58–61 (2017).
Marcote, B. et al. The repeating fast radio burst FRB 121102 as seen on milliarcsecond angular scales. Astrophys. J. 834, L8 (2017).
Tendulkar, S. P. et al. The host galaxy and redshift of the repeating fast radio burst FRB 121102. Astrophys. J. 834, L7 (2017). This paper reports the discovery of the first host galaxy and redshift of an FRB source: FRB 121102.
Loeb, A., Shvartzvald, Y. & Maoz, D. Fast radio bursts may originate from nearby flaring stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 439, L46–L50 (2014).
Platts, E. et al. A living theory catalogue for fast radio bursts. Phys. Rep. 821, 1–27 (2019).
Kulkarni, S. R. From gamma-ray bursts to fast radio bursts. Nat. Astron. 2, 832–835 (2018).
The CHIME/FRB Collaboration. A bright millisecond-duration radio burst from a Galactic magnetar. Nature http://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2863-y (2020). This paper reports the discovery of an FRB associated with a Galactic SGR, establishing the magnetar origin of at least some FRBs.
Bochenek, C. D. et al. A fast radio burst associated with a Galactic magnetar. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2872-x (2020). This paper also reports the discovery of an FRB associated with a Galactic SGR, establishing the magnetar origin of at least some FRBs.
Li, C. K. et al. Identification of a non-thermal X-ray burst with the Galactic magnetar SGR 1935+2154 and a fast radio burst with Insight-HXMT. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11071 (2020).
Ridnaia, A. et al. A peculiar hard X-ray counterpart of a Galactic fast radio burst. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11178 (2020).
Mereghetti, S. et al. INTEGRAL discovery of a burst with associated radio emission from the magnetar SGR 1935+2154. Astrophys. J. 898, L29 (2020).
Tavani, M. et al. An X-ray burst from a magnetar enlightening the mechanism of fast radio bursts. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12164 (2020).
Petroff, E., Hessels, J. W. T. & Lorimer, D. R. Fast radio bursts. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 27, 4 (2019). This paper is a comprehensive review of the FRB field summarizing observational properties of FRBs as of 2019.
Cordes, J. M. & Chatterjee, S. Fast radio bursts: an extragalactic enigma. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 57, 417–465 (2019). This paper is another comprehensive review of the FRB field summarizing the observational properties of FRBs as of 2019.
Lorimer, D. R. A decade of fast radio bursts. Nat. Astron. 2, 860–864 (2018).
Katz, J. I. Fast radio bursts. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 103, 1–18 (2018).
Popov, S. B., Postnov, K. A. & Pshirkov, M. S. Fast radio bursts. Phys. Uspekhi 61, 965 (2018).
CHIME/FRB Collaboration. A second source of repeating fast radio bursts. Nature 566, 235–238 (2019).
The CHIME/FRB Collaboration. CHIME/FRB detection of eight new repeating fast radio burst sources. Astrophys. J. 885, L24 (2019).
Kumar, P. et al. Faint repetitions from a bright fast radio burst source. Astrophys. J. 887, L30 (2019).
Luo, R. et al. Diverse polarisation angle swings from a repeating fast radio burst source. Nature (in the press).
Ravi, V. The prevalence of repeating fast radio bursts. Nat. Astron. 3, 928–931 (2019).
Lu, W., Piro, A. L. & Waxman, E. Implications of CHIME repeating fast radio bursts. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.12581 (2020).
Petroff, E. et al. A survey of FRB fields: limits on repeatability. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 454, 457–462 (2015).
Palaniswamy, D., Li, Y. & Zhang, B. Are there multiple populations of fast radio bursts? Astrophys. J. 854, L12 (2018).
Caleb, M., Stappers, B. W., Rajwade, K. & Flynn, C. Are all fast radio bursts repeating sources? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 484, 5500–5508 (2019).
Zhang, Y. G. et al. Fast radio burst 121102 pulse detection and periodicity: a machine learning approach. Astrophys. J. 866, 149 (2018).
The CHIME/FRB Collaboration. Periodic activity from a fast radio burst source. Nature 582, 351–355 (2020).
Rajwade, K. M. et al. Possible periodic activity in the repeating FRB 121102. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 495, 3551–3558 (2020).
Ioka, K. & Zhang, B. A binary comb model for periodic fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 893, L26 (2020).
Lyutikov, M., Barkov, M. V. & Giannios, D. FRB periodicity: mild pulsars in tight O/B-star binaries. Astrophys. J. 893, L39 (2020).
Dai, Z. G. & Zhong, S. Q. Periodic fast radio bursts as a probe of extragalactic asteroid belts. Astrophys. J. 895, L1 (2020).
Levin, Y., Beloborodov, A. M. & Bransgrove, A. Precessing flaring magnetar as a source of repeating FRB 180916.J0158+65. Astrophys. J. 895, L30 (2020).
Zanazzi, J. J. & Lai, D. Periodic fast radio bursts with neutron star free precession. Astrophys. J. 892, L15 (2020).
Yang, H. & Zou, Y.-C. Orbit-induced spin precession as a possible origin for periodicity in periodically repeating fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 893, L31 (2020).
Luan, J. & Goldreich, P. Physical constraints on fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 785, L26 (2014).
Cordes, J. M., Wharton, R. S., Spitler, L. G., Chatterjee, S. & Wasserman, I. Radio wave propagation and the provenance of fast radio bursts. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05890 (2016).
Xu, S. & Zhang, B. On the origin of the scatter broadening of fast radio burst pulses and astrophysical implications. Astrophys. J. 832, 199 (2016).
Hessels, J. W. T. et al. FRB 121102 bursts show complex time-frequency structure. Astrophys. J. 876, L23 (2019).
Petroff, E. et al. FRBCAT: the fast radio burst catalogue. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 33, 45 (2016).
Bannister, K. W. et al. A single fast radio burst localized to a massive galaxy at cosmological distance. Science 365, 565–570 (2019).
Ravi, V. et al. A fast radio burst localized to a massive galaxy. Nature 572, 352–354 (2019).
Marcote, B. et al. A repeating fast radio burst source localized to a nearby spiral galaxy. Nature 577, 190–194 (2020).
Prochaska, J. X. et al. The low density and magnetization of a massive galaxy halo exposed by a fast radio burst. Science 366, 231–234 (2019).
Macquart, J. P. et al. A census of baryons in the Universe from localized fast radio bursts. Nature 581, 391–395 (2020).
Li, Z. et al. Cosmology-insensitive estimate of IGM baryon mass fraction from five localized fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 496, L28–L32 (2020).
Zhang, B. Fast radio burst energetics and detectability from high redshifts. Astrophys. J. 867, L21 (2018).
Lin, L. et al. No pulsed radio emission during a bursting phase of a Galactic magnetar. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2839-y (2020). This paper reports the non-detection of FRBs from many SGR bursts, suggesting that the FRB–SGR associations are rather rare.
Kellermann, K. I. & Pauliny-Toth, I. I. K. The spectra of opaque radio sources. Astrophys. J. 155, L71 (1969).
Chawla, P. et al. Detection of repeating FRB 180916.J0158+65 down to frequencies of 300 MHz. Astrophys. J. 896, L41 (2020).
Gajjar, V. et al. Highest frequency detection of FRB 121102 at 4–8 GHz using the Breakthrough Listen digital backend at the Green Bank Telescope. Astrophys. J. 863, 2 (2018).
Law, C. J. et al. A multi-telescope campaign on FRB 121102: implications for the FRB population. Astrophys. J. 850, 76 (2017).
Karastergiou, A. et al. Limits on fast radio bursts at 145 MHz with ARTEMIS, a real-time software backend. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 452, 1254–1262 (2015).
Michilli, D. et al. An extreme magneto-ionic environment associated with the fast radio burst source FRB 121102. Nature 553, 182–185 (2018).
Cho, H. et al. Spectropolarimetric analysis of FRB 181112 at microsecond resolution: implications for fast radio burst emission mechanism. Astrophys. J. 891, L38 (2020).
Day, C. K. et al. High time resolution and polarisation properties of ASKAP-localised fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 497, 3335–3350 (2020) (2020).
Lorimer, D. R. & Kramer, M. Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2012). This is a comprehensive book on pulsar astronomy, enabling comparison of FRB phenomenology with pulsar phenomenology.
Radhakrishnan, V. & Cooke, D. J. Magnetic poles and the polarization structure of pulsar radiation. Astrophys. Lett. 3, 225 (1969).
Ravi, V. et al. The magnetic field and turbulence of the cosmic web measured using a brilliant fast radio burst. Science 354, 1249–1252 (2016).
Margalit, B. & Metzger, B. A concordance picture of FRB 121102 as a flaring magnetar embedded in a magnetized ion-electron wind nebula. Astrophys. J. 868, L4 (2018).
Yang, Y.-P., Li, Q.-C. & Zhang, B. Are persistent emission luminosity and rotation measure of fast radio bursts related? Astrophys. J. 895, 7 (2020).
Petroff, E. et al. A real-time fast radio burst: polarization detection and multiwavelength follow-up. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 447, 246–255 (2015).
Yi, S.-X., Gao, H. & Zhang, B. Multi-wavelength afterglows of fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 792, L21 (2014).
Bannister, K. W., Murphy, T., Gaensler, B. M. & Reynolds, J. E. Limits on prompt, dispersed radio pulses from gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 757, 38 (2012).
DeLaunay, J. J. et al. Discovery of a transient gamma-ray counterpart to FRB 131104. Astrophys. J. 832, L1 (2016).
Cunningham, V. et al. A search for high-energy counterparts to fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 879, 40 (2019).
Metzger, B. D., Berger, E. & Margalit, B. Millisecond magnetar birth connects FRB 121102 to superluminous supernovae and long-duration gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 841, 14 (2017). This paper proposes that young magnetars born in extreme explosions such as GRBs and superluminous supernovae are the engines of repeating FRBs.
Law, C. J. et al. A search for late-time radio emission and fast radio bursts from superluminous supernovae. Astrophys. J. 886, 24 (2019).
Men, Y. et al. Non-detection of fast radio bursts from six gamma-ray burst remnants with possible magnetar engines. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 489, 3643–3647 (2019).
Wang, X.-G. et al. Is GRB 110715A the progenitor of FRB 171209? Astrophys. J. 894, L22 (2020).
Bhandari, S. et al. The SUrvey for Pulsars and Extragalactic Radio Bursts—II. New FRB discoveries and their follow-up. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 475, 1427–1446 (2018).
Luo, R., Lee, K., Lorimer, D. R. & Zhang, B. On the normalized FRB luminosity function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 481, 2320–2337 (2018).
Lu, W. & Piro, A. L. Implications from ASKAP fast radio burst statistics. Astrophys. J. 883, 40 (2019).
Luo, R. et al. On the FRB luminosity function. II. Event rate density. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 494, 665–679 (2020).
Lu, W., Kumar, P. & Zhang, B. A unified picture of Galactic and cosmological fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 498, 1397–1405 (2020). (2020).
Nicholl, M. et al. Empirical constraints on the origin of fast radio bursts: volumetric rates and host galaxy demographics as a test of millisecond magnetar connection. Astrophys. J. 843, 84 (2017).
Bhandari, S. et al. The host galaxies and progenitors of fast radio bursts localized with the Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder. Astrophys. J. 895, L37 (2020).
Li, Y. & Zhang, B. A comparative study of host galaxy properties between fast radio bursts and stellar transients. Astrophys. J. 899, L6 (2020).
Totani, T. Cosmological fast radio bursts from binary neutron star mergers. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 65, L12 (2013).
Zhang, B. A possible connection between fast radio bursts and gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 780, L21 (2013).
Wang, J.-S., Yang, Y.-P., Wu, X.-F., Dai, Z.-G. & Wang, F.-Y. Fast radio bursts from the inspiral of double neutron stars. Astrophys. J. 822, L7 (2016).
Margalit, B., Berger, E. & Metzger, B. D. Fast radio bursts from magnetars born in binary neutron star mergers and accretion induced collapse. Astrophys. J. 886, 110 (2019).
Wang, F. Y. et al. Fast radio bursts from activity of neutron stars newborn in BNS mergers: offset, birth rate, and observational properties. Astrophys. J. 891, 72 (2020).
Zhang, B. Fast radio bursts from interacting binary neutron star systems. Astrophys. J. 890, L24 (2020).
Zhang, B. The Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2018). This is a comprehensive book on GRB phenomenology and theoretical models, enabling cross-comparison of the FRB and the GRB fields.
Popov, S. B. & Postnov, K. A. Hyperflares of SGRs as an engine for millisecond extragalactic radio bursts. In Evolution of Cosmic Objects through their Physical Activity (eds Harutyunian, H. A., Mickaelian, A. M. & Terzian, Y.) 129–132 (2010). This paper was the first to propose that SGRs are the sources of FRBs, an idea recently proved by the FRB 200428–SGR 1935+2154 association.
Kulkarni, S. R., Ofek, E. O., Neill, J. D., Zheng, Z. & Juric, M. Giant sparks at cosmological distances? Astrophys. J. 797, 70 (2014).
Katz, J. I. How soft gamma repeaters might make fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 826, 226 (2016).
Lyubarsky, Y. A model for fast extragalactic radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 442, L9–L13 (2014). This paper first proposes the synchrotron maser coherent mechanism to interpret FRBs.
Beloborodov, A. M. A flaring magnetar in FRB 121102? Astrophys. J. 843, L26 (2017).
Kumar, P., Lu, W. & Bhattacharya, M. Fast radio burst source properties and curvature radiation model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 468, 2726–2739 (2017).
Yang, Y.-P. & Zhang, B. Bunching coherent curvature radiation in three-dimensional magnetic field geometry: application to pulsars and fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 868, 31 (2018).
Wadiasingh, Z. et al. The fast radio burst luminosity function and death line in the low-twist magnetar model. Astrophys. J. 891, 82 (2020).
Nemiroff, R. J. A century of gamma ray burst models. AIP Conf. Proc. 307, 730 (1994).
Waxman, E. On the origin of fast radio bursts (FRBs). Astrophys. J. 842, 34 (2017).
Plotnikov, I. & Sironi, L. The synchrotron maser emission from relativistic shocks in fast radio bursts: 1D PIC simulations of cold pair plasmas. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 485, 3816–3833 (2019).
Metzger, B. D., Margalit, B. & Sironi, L. Fast radio bursts as synchrotron maser emission from decelerating relativistic blast waves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 485, 4091–4106 (2019).
Beloborodov, A. M. Blast waves from magnetar flares and fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 896, 142 (2020).
Melrose, D. B. Coherent emission mechanisms in astrophysical plasmas. Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 1, 5 (2017). This is a comprehensive review for coherent radio emission models for the sources in the Universe other than FRBs.
Harding, A. K. Gamma-ray pulsar light curves as probes of magnetospheric structure. J. Plasma Phys. 82, 635820306 (2016).
Rankin, J. M. Toward an empirical theory of pulsar emission. VI. The geometry of the conal emission region. Astrophys. J. 405, 285 (1993).
Ruderman, M. A. & Sutherland, P. G. Theory of pulsars—polar caps, sparks, and coherent microwave radiation. Astrophys. J. 196, 51–72 (1975).
Camilo, F. et al. The magnetar XTE J1810–197: variations in torque, radio flux density, and pulse profile morphology. Astrophys. J. 663, 497–504 (2007).
Zhang, B. Mergers of charged black holes: gravitational-wave events, short gamma-ray bursts, and fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 827, L31 (2016).
Levin, J., D’Orazio, D. J. & Garcia-Saenz, S. Black hole pulsar. Phys. Rev. D 98, 123002 (2018).
Long, K. & Pe’er, A. Synchrotron maser from weakly magnetized neutron stars as the emission mechanism of fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 864, L12 (2018).
Katz, J. I. Coherent emission in fast radio bursts. Phys. Rev. D 89, 103009 (2014).
Lu, W. & Kumar, P. On the radiation mechanism of repeating fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 477, 2470–2493 (2018). This paper is a comprehensive survey of many coherent emission models and a critical assessment of the validity of these models for FRBs.
Ghisellini, G. Synchrotron masers and fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 465, L30–L33 (2017).
Lu, W., Kumar, P. & Narayan, R. Fast radio burst source properties from polarization measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 483, 359–369 (2019).
Lyubarsky, Y. Induced scattering of short radio pulses. Astrophys. J. 682, 1443–1449 (2008).
Murase, K., Kashiyama, K. & Mészáros, P. A burst in a wind bubble and the impact on baryonic ejecta: high-energy gamma-ray flashes and afterglows from fast radio bursts and pulsar-driven supernova remnants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 461, 1498–1511 (2016).
Kumar, P. & Lu, W. Radiation forces constrain the FRB mechanism. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 494, 1217–1228 (2020).
Piro, A. L. The impact of a supernova remnant on fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 824, L32 (2016).
Yang, Y.-P. & Zhang, B. Dispersion measure variation of repeating fast radio burst sources. Astrophys. J. 847, 22 (2017).
Yang, Y.-P., Zhang, B. & Dai, Z.-G. Synchrotron heating by a fast radio burst in a self-absorbed synchrotron nebula and its observational signature. Astrophys. J. 819, L12 (2016).
Goldreich, P. & Julian, W. H. Pulsar electrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 157, 869 (1969).
Lyubarsky, Y. Fast radio bursts from reconnection in a magnetar magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 897, 1 (2020).
Melrose, D. B. Amplified linear acceleration emission applied to pulsars. Astrophys. J. 225, 557–573 (1978).
Melikidze, G. I., Gil, J. A. & Pataraya, A. D. The spark-associated soliton model for pulsar radio emission. Astrophys. J. 544, 1081–1096 (2000).
Yang, Y.-P., Zhu, J.-P., Zhang, B. & Wu, X.-F. Pair separation in parallel electric field in magnetar magnetosphere and narrow spectra of fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 901, L13 (2020). (2020).
Kumar, P. & Bošnjak, Ž. FRB coherent emission from decay of Alfvén waves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 494, 2385–2395 (2020).
Zhang, B. A “cosmic comb” model of fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 836, L32 (2017).
Wang, W., Zhang, B., Chen, X. & Xu, R. On the time-frequency downward drifting of repeating fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 876, L15 (2019).
Usov, V. V. & Katz, J. I. Low frequency radio pulses from gamma-ray bursts? Astron. Astrophys. 364, 655–659 (2000).
Sagiv, A. & Waxman, E. Collective processes in relativistic plasma and their implications for gamma-ray burst afterglows. Astrophys. J. 574, 861–872 (2002).
Kaspi, V. M. & Beloborodov, A. M. Magnetars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 55, 261–301 (2017).
Thompson, C. & Duncan, R. C. Neutron star dynamos and the origins of pulsar magnetism. Astrophys. J. 408, 194–217 (1993).
Beniamini, P., Hotokezaka, K., van der Horst, A. & Kouveliotou, C. Formation rates and evolution histories of magnetars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 487, 1426–1438 (2019).
Vink, J. & Kuiper, L. Supernova remnant energetics and magnetars: no evidence in favour of millisecond proto-neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 370, L14–L18 (2006).
Tendulkar, S. P., Kaspi, V. M. & Patel, C. Radio nondetection of the SGR 1806–20 giant flare and implications for fast radio bursts. Astrophys. J. 827, 59 (2016).
Li, Y., Zhang, B., Nagamine, K. & Shi, J. The FRB 121102 host is atypical among nearby FRBs. Astrophys. J. 884, L26 (2019 (2019).
Thompson, C. & Duncan, R. C. The soft gamma repeaters as very strongly magnetized neutron stars—I. Radiative mechanism for outbursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 275, 255–300 (1995).
Margalit, B., Beniamini, P., Sridhar, N. & Metzger, B. D. implications of a “fast radio burst” from a galactic magnetar. Astrophys. J. 899, L27 (2020).
Katz, J. I. The FRB-SGR connection. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03468 (2020).
Yu, Y.-W., Zou, Y.-C., Dai, Z.-G. & Yu, W.-F. Revisiting the confrontation of the shock-powered synchrotron maser model with the Galactic FRB 200428. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.00484 (2020).
Connor, L., Sievers, J. & Pen, U.-L. Non-cosmological FRBs from young supernova remnant pulsars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 458, L19–L23 (2016).
Cordes, J. M. & Wasserman, I. Supergiant pulses from extragalactic neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 457, 232–257 (2016).
Katz, J. I. Are fast radio bursts made by neutron stars? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 494, L64–L68 (2020).
Gu, W.-M., Dong, Y.-Z., Liu, T., Ma, R. & Wang, J. A neutron star-white dwarf binary model for repeating fast radio burst 121102. Astrophys. J. 823, L28 (2016).
Zhang, B. FRB 121102: a repeatedly combed neutron star by a nearby low-luminosity accreting supermassive black hole. Astrophys. J. 854, L21 (2018).
Katz, J. I. Searching for Galactic micro-FRB with lunar scattering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 494, 3464–3468 (2020).
Dai, Z. G., Wang, J. S., Wu, X. F. & Huang, Y. F. Repeating fast radio bursts from highly magnetized pulsars traveling through asteroid belts. Astrophys. J. 829, 27 (2016).
Smallwood, J. L., Martin, R. G. & Zhang, B. Investigation of the asteroid-neutron star collision model for the repeating fast radio bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 485, 1367–1376 (2019).
Dai, Z. G. A magnetar-asteroid impact model for FRB 200428 associated with an X-ray burst from SGR 1935+2154. Astrophys. J. 897, L40 (2020).
Falcke, H. & Rezzolla, L. Fast radio bursts: the last sign of supramassive neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 562, A137 (2014).
Ai, S., Gao, H. & Zhang, B. On the true fractions of repeating and non-repeating FRB sources. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.02400 (2020).
Wang, M.-H. et al. Testing the hypothesis of a compact-binary-coalescence origin of fast radio bursts using a multimessenger approach. Astrophys. J. 891, L39 (2020).
Acknowledgements
I thank P. Kumar, W. Lu, J. I. Katz. Y.-P. Yang and Z.-G. Dai for comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B. The physical mechanisms of fast radio bursts. Nature 587, 45–53 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2828-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2828-1
This article is cited by
-
Integrated microcavity electric field sensors using Pound-Drever-Hall detection
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Science with a Small Two-Band UV-Photometry Mission I: Mission Description and Follow-up Observations of Stellar Transients
Space Science Reviews (2024)
-
Pose optimization of the FAST feed support system based on the new feed cabin mechanism
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
-
Repeating fast radio burst 20201124A originates from a magnetar/Be star binary
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Magnetic reconnection in the era of exascale computing and multiscale experiments
Nature Reviews Physics (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.