Abstract
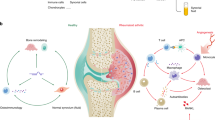
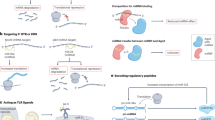
Non-coding RNAs have distinct regulatory roles in the pathogenesis of joint diseases including osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As the amount of high-throughput profiling studies and mechanistic investigations of microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs in joint tissues and biofluids has increased, data have emerged that suggest complex interactions among non-coding RNAs that are often overlooked as critical regulators of gene expression. Identifying these non-coding RNAs and their interactions is useful for understanding both joint health and disease. Non-coding RNAs regulate signalling pathways and biological processes that are important for normal joint development but, when dysregulated, can contribute to disease. The specific expression profiles of non-coding RNAs in various disease states support their roles as promising candidate biomarkers, mediators of pathogenic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. This Review synthesizes literature published in the past 2 years on the role of non-coding RNAs in OA and RA with a focus on inflammation, cell death, cell proliferation and extracellular matrix dysregulation. Research to date makes it apparent that ‘non-coding’ does not mean ‘non-essential’ and that non-coding RNAs are important parts of a complex interactome that underlies OA and RA.
Key points
-
An increasing body of literature on non-coding RNAs in joint health and disease has revealed important regulatory functions that indicate that ‘non-coding’ does not equate to ‘non-essential’.
-
Non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs, can directly interact and have co-regulatory functions.
-
In osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, non-coding RNAs are important contributors to pathogenesis and serve as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
-
With the emergence of data from high-throughput studies, detailed reporting and accurate annotation of results are required to integrate individual studies and enable interrogation of the non-coding RNA interactome.
-
An expanded understanding of the non-coding RNA interactome could reveal essential regulatory mechanisms and novel therapeutic opportunities for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and other related joint diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palazzo, A. F. & Lee, E. S. Non-coding RNA: what is functional and what is junk? Front. Genet. 6, 2 (2015).
Rice, S. J., Beier, F., Young, D. A. & Loughlin, J. Interplay between genetics and epigenetics in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 16, 268–281 (2020).
Reynard, L. N. & Barter, M. J. Osteoarthritis year in review 2019: genetics, genomics and epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 28, 275–284 (2020).
Vicente, R., Noel, D., Pers, Y. M., Apparailly, F. & Jorgensen, C. Deregulation and therapeutic potential of microRNAs in arthritic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 12, 211–220 (2016).
Zhang, P., Wu, W., Chen, Q. & Chen, M. Non-coding RNAs and their integrated networks. J. Integr. Bioinform 16, 20190027 (2019).
Ren, S. et al. Circular RNAs: promising molecular biomarkers of human aging-related diseases via functioning as an miRNA sponge. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 18, 215–229 (2020).
Chillon, I. & Marcia, M. The molecular structure of long non-coding RNAs: emerging patterns and functional implications. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 55, 662–690 (2020).
Jiang, S., Liu, Y., Xu, B., Zhang, Y. & Yang, M. Noncoding RNAs: new regulatory code in chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 11, e1584 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. The role of lncRNAs in osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15, 243–249 (2020).
Della Bella, E. et al. Differential regulation of circRNA, miRNA, and piRNA during early osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Cells 9, 398 (2020).
Inui, M., Martello, G. & Piccolo, S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 11, 252–263 (2010).
Feng, L. et al. MicroRNA-378 suppressed osteogenesis of MSCs and impaired bone formation via inactivating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 21, 1017–1028 (2020).
Ohba, S. Hedgehog signaling in endochondral ossification. J. Dev. Biol. 4, 20 (2016).
Chen, T. et al. MicroRNA-1 promotes cartilage matrix synthesis and regulates chondrocyte differentiation via post-transcriptional suppression of Ihh expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 22, 2404–2414 (2020).
Lin, A. C. et al. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat. Med. 15, 1421–1425 (2009).
Zhang, H. et al. MicroRNA-30a regulates chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through targeting Sox9. Exp. Ther. Med. 18, 4689–4697 (2019).
Cai, W. L. et al. LncRNA LINC00707 promotes osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway activated by LINC00707/miR-145/LRP5 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 18–28 (2020).
Huang, M. J. et al. lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 controls human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and functions as a ceRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 18, 533–545 (2019).
Huang, X. et al. Prospect of circular RNA in osteogenesis: a novel orchestrator of signaling pathways. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 21450–21459 (2019).
Liu, X., Yan, C., Deng, X. & Jia, J. Hsa_circularRNA_0079201 suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and endochondral ossification by regulating the microRNA1403p/SMAD2 signaling pathway in idiopathic short stature. Int. J. Mol. Med. 46, 1993–2006 (2020).
Tavallaee, G., Rockel, J. S., Lively, S. & Kapoor, M. MicroRNAs in synovial pathology associated with osteoarthritis. Front. Med. 7, 376 (2020).
Endisha, H., Rockel, J., Jurisica, I. & Kapoor, M. The complex landscape of microRNAs in articular cartilage: biology, pathology, and therapeutic targets. JCI Insight 3, e121630 (2018).
Qiu, W. J., Xu, M. Z., Zhu, X. D. & Ji, Y. H. MicroRNA-27a alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammatory response and articular cartilage degradation via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in articular chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 76, 105839 (2019).
Xiang, Y. et al. miR-142-5p as a CXCR4-targeted microRNA attenuates SDF-1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation via inactivating MAPK signaling pathway. Biochem. Res. Int. 2020, 4508108 (2020).
Luo, X., Wang, J., Wei, X., Wang, S. & Wang, A. Knockdown of lncRNA MFI2-AS1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoarthritis progression by miR-130a-3p/TCF4. Life Sci. 240, 117019 (2020).
Chen, K., Fang, H. & Xu, N. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 is transcriptionally activated by JUND and contributes to osteoarthritis progression via targeting the miR-423-5p/KDM5C axis. Life Sci. 258, 118095 (2020).
Green, J. A., Ansari, M. Y., Ball, H. C. & Haqqi, T. M. tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs) regulate post-transcriptional gene expression via AGO-dependent mechanism in IL-1β stimulated chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 28, 1102–1110 (2020).
Ripmeester, E. G. J. et al. Impaired chondrocyte U3 snoRNA expression in osteoarthritis impacts the chondrocyte protein translation apparatus. Sci. Rep. 10, 13426 (2020).
Nanus, D. E. et al. Regulation of the inflammatory synovial fibroblast phenotype by metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 long noncoding RNA in obese patients with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 609–619 (2020).
Tu, Y. et al. MicroRNA-377-3p alleviates IL-1β-caused chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis in part by downregulating ITGA6. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 523, 46–53 (2020).
Tang, J., Yi, S. & Liu, Y. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 can regulate the proliferation and inflammatory responses of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting microRNA-145-5p. Hum. Cell 33, 1081–1090 (2020).
Alnajjar, F. A. et al. The expression and function of metastases associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript-1 long non-coding RNA in subchondral bone and osteoblasts from patients with osteoarthritis. Cells 10, 786 (2021).
Wang, Y. et al. LncRNA NEAT1 targets fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via the miR-410-3p/YY1 Axis. Front. Immunol. 11, 1975 (2020).
Sun, J. L. et al. MicroRNA-29b promotes subchondral bone loss in TMJ osteoarthritis. J. Dent. Res. 99, 1469–1477 (2020).
Wang, P. et al. Genome-wide microRNA screening reveals miR-582-5p as a mesenchymal stem cell-specific microRNA in subchondral bone of the human knee joint. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 21877–21888 (2019).
Zhao, C. et al. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells promote chondrogenesis and suppress inflammation by upregulating miR145 and miR221. Mol. Med. Rep. 21, 1881–1889 (2020).
Zhao, J. et al. Identification of lncRNA and mRNA biomarkers in osteoarthritic degenerative meniscus by weighted gene coexpression network and competing endogenous RNA network analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2123787 (2020).
Liu, C., Gao, J., Su, G., Xiang, Y. & Wan, L. MicroRNA-1202 plays a vital role in osteoarthritis via KCNQ1OT1 has-miR-1202-ETS1 regulatory pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 15, 130 (2020).
Zhang, P. et al. lncRNA IGHCγ1 acts as a ceRNA to regulate macrophage inflammation via the miR-6891-3p/TLR4 axis in osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020, 9743037 (2020).
Soul, J. et al. Stratification of knee osteoarthritis: two major patient subgroups identified by genome-wide expression analysis of articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 77, 423 (2018).
Coutinho de Almeida, R. et al. Identification and characterization of two consistent osteoarthritis subtypes by transcriptome and clinical data integration. Rheumatology 60, 1166–1175 (2021).
Coutinho de Almeida, R. et al. RNA sequencing data integration reveals an miRNA interactome of osteoarthritis cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78, 270–277 (2019).
Zhou, Y. et al. Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and mRNAs in synovial of osteoarthritis via RNA-sequencing. BMC Med. Genet. 21, 46 (2020).
Wang, H. et al. Prediction of microRNA and gene target in synovium-associated pain of knee osteoarthritis based on canonical correlation analysis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 4506876 (2019).
Ormseth, M. J. et al. Development and validation of a microRNA panel to differentiate between patients with rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus and controls. J. Rheumatol. 47, 188–196 (2020).
Ormseth, M. J. et al. The endogenous plasma small RNAome of rheumatoid arthritis. ACR Open. Rheumatol. 2, 97–105 (2020).
Zhang, C. et al. miR-22 inhibits synovial fibroblasts proliferation and proinflammatory cytokine production in RASF via targeting SIRT1. Gene 724, 144144 (2020).
Jin, Z., Ren, J. & Qi, S. Human bone mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes overexpressing microRNA-26a-5p alleviate osteoarthritis via down-regulation of PTGS2. Int. Immunopharmacol. 78, 105946 (2020).
Xie, F. et al. Role of microRNA, lncRNA, and exosomes in the progression of osteoarthritis: a review of recent literature. Orthop. Surg. 12, 708–716 (2020).
Alevizos, I. & Illei, G. G. MicroRNAs as biomarkers in rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 6, 391–398 (2010).
Wang, S. et al. Expression of Dicer in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with disease activity and balances the production of TNF-α. Mol. Med. Rep. 16, 1590–1595 (2017).
Ormseth, M. J. et al. Circulating microbial small RNAs are altered in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 79, 1557–1564 (2020).
Lai, Z. & Cao, Y. Plasma miR-200c-3p, miR-100-5p, and miR-1826 serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers for knee osteoarthritis: randomized controlled trials. Medicine 98, e18110 (2019).
Feng, L. et al. Circulating microRNA let7e is decreased in knee osteoarthritis, accompanied by elevated apoptosis and reduced autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 45, 1464–1476 (2020).
Giordano, R. et al. Preoperative serum circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for chronic postoperative pain after total knee replacement. Mol. Pain. 16, 1744806920962925 (2020).
Rousseau, J. C. et al. Association of circulating microRNAs with prevalent and incident knee osteoarthritis in women: the OFELY study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 22, 2 (2020).
Ali, S. A. et al. Sequencing identifies a distinct signature of circulating microRNAs in early radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 28, 1471–1481 (2020).
Aae, T. F. et al. Evaluating plasma extracellular vesicle microRNAs as possible biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage Open 1, 100018 (2020).
Potla, P., Ali, S. A. & Kapoor, M. A bioinformatics approach to microRNA-sequencing analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage Open 3, 100131 (2021).
Kwak, Y. H. et al. Significant changes in synovial fluid microRNAs after high tibial osteotomy in medial compartmental knee osteoarthritis: identification of potential prognostic biomarkers. PLoS ONE 15, e0227596 (2020).
Li, Y. H. et al. Identification of synovial fluid microRNA signature in knee osteoarthritis: differentiating early- and late-stage knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 24, 1577–1586 (2016).
Ehrlich, G. D. Circular RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 23, 701–702 (2019).
Qi, K. et al. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) CAIF is downregulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits LPS-induced interleukin 6 (IL-6) upregulation by downregulation of miR-1246. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 8019–8024 (2019).
Ni, S. et al. LncRNA LUADT1 regulates miR-34a/SIRT1 to participate in chondrocyte apoptosis. J. Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29637 (2020).
Zhang, H., Li, J., Shao, W. & Shen, N. LncRNA SNHG9 is downregulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis by downregulating miR-34a through methylation. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 21, 511 (2020).
Zhang, H., Li, J., Shao, W. & Shen, N. LncRNA CTBP1-AS2 is upregulated in osteoarthritis and increases the methylation of miR-130a gene to inhibit chondrocyte proliferation. Clin. Rheumatol. 39, 3473–3478 (2020).
Gao, Y., Zhao, H. & Li, Y. LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 regulates miR-142-3p/HMGB1 to promote LPS-induced chondrocyte apoptosis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 20, 605 (2019).
Sun, Y., Kang, S., Pei, S., Sang, C. & Huang, Y. MiR93-5p inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting lncRNA CASC2. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 21, 26 (2020).
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Jia, D., Zheng, J. & Wang, G. Correlation between single nucleotide polymorphisms in CXCR4 microRNA binding site and the susceptibility to knee osteoarthritis in Han Chinese population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 35, e23600 (2021).
Weng, K., Luo, M. & Dong, D. Elucidation of the mechanism by which a ADAMTS5 gene microRNA-binding site single nucleotide polymorphism affects the risk of osteoarthritis. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 24, 467–477 (2020).
Cao, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, L. & Li, J. miR-940 regulates the inflammatory response of chondrocytes by targeting MyD88 in osteoarthritis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 461, 183–193 (2019).
Najm, A. et al. MicroRNA-17-5p reduces inflammation and bone erosions in mice with collagen-induced arthritis and directly targets the JAK/STAT pathway in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 2030–2039 (2020).
Wu, S., Wang, J., Li, J. & Li, F. microRNA-21 aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in MH7A cells through targeting SNF5. Inflammation 43, 441–454 (2020).
Jiang, F. et al. MicroRNA-421 promotes inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting SPRY1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 8186–8193 (2019).
Zhang, M. et al. Identification of microRNA-363-3p as an essential regulator of chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting NRF1 through the p53-signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 21, 1077–1088 (2020).
Wang, Y. et al. miR-410-3p regulates proliferation and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting YY1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 119, 109426 (2019).
Huang, Y. et al. Up-regulated microRNA-411 or declined RIPK1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis mice via decreased NF-κB pathway. Cell Cycle 19, 666–683 (2020).
Wang, X. et al. Up-regulation of miR-365 promotes the apoptosis and restrains proliferation of synoviocytes through downregulation of IGF1 and the inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in mice with rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 79, 106067 (2020).
Zhang, Y. et al. miR-137 suppresses cell growth and extracellular matrix degradation through regulating ADAMTS-5 in chondrocytes. Am. J. Transl Res. 11, 7027–7034 (2019).
Bai, Y., Chen, K., Zhan, J. & Wu, M. miR-122/SIRT1 axis regulates chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biosci. Rep. 40, BSR20191908 (2020).
Liu, H. & Luo, J. miR-211-5p contributes to chondrocyte differentiation by suppressing fibulin-4 expression to play a role in osteoarthritis. J. Biochem. 166, 495–502 (2019).
Cheleschi, S. et al. Hydrostatic pressure regulates oxidative stress through microRNA in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 3653 (2020).
Li, H. et al. MicroRNA-375 exacerbates knee osteoarthritis through repressing chondrocyte autophagy by targeting ATG2B. Aging 12, 7248–7261 (2020).
He, B. & Jiang, D. HOTAIR-induced apoptosis is mediated by sponging miR-130a-3p to repress chondrocyte autophagy in knee osteoarthritis. Cell Biol. Int. 44, 524–535 (2020).
Tian, F., Wang, J., Zhang, Z. & Yang, J. LncRNA SNHG7/miR-34a-5p/SYVN1 axis plays a vital role in proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Biol. Res. 53, 9 (2020).
Lei, J., Fu, Y., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, K. & Lu, D. LncRNA SNHG1 alleviates IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting miR-16-5p-mediated p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Biosci. Rep. 39, BSR20191523 (2019).
An, Y. et al. Down-regulation of microRNA-203a suppresses IL-1β-induced inflammation and cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes through Smad3 signaling. Biosci. Rep. 40, BSR20192723 (2020).
Li, Y., Nie, J. & Jiang, P. Oleanolic acid mitigates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte dysfunction by regulating miR-148-3p-modulated FGF2 expression. J. Gene Med. 22, e3169 (2020).
Shi, F. L. & Ren, L. X. Up-regulated miR-374a-3p relieves lipopolysaccharides induced injury in CHON-001 cells via regulating Wingless-type MMTV integration site family member 5B. Mol. Cell Probes 51, 101541 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Forkhead box C1 promotes the pathology of osteoarthritis by upregulating β-catenin in synovial fibroblasts. FEBS J. 287, 3065–3087 (2020).
Dinesh, P., Kalaiselvan, S., Sujitha, S. & Rasool, M. MiR-145-5p mitigates dysregulated Wnt1/β-catenin signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 82, 106328 (2020).
Shui, X. et al. Identification and functional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in the synovial membrane of osteoarthritis patients. Cell Biochem. Funct. 38, 460–471 (2020).
Zhu, S., Deng, Y., Gao, H., Huang, K. & Nie, Z. miR-877-5p alleviates chondrocyte dysfunction in osteoarthritis models via repressing FOXM1. J. Gene Med. 22, e3246 (2020).
Wei, H. et al. MicroRNA-15a/16/SOX5 axis promotes migration, invasion and inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Aging 12, 14376–14390 (2020).
Chen, J. & Wu, X. MicroRNA-103 contributes to osteoarthritis development by targeting Sox6. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109186 (2019).
Chunlei, H. et al. Down-regulation of mir-138-5p protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1 β-induced inflammation via up-regulating SOX9. Curr. Pharm. Des. 25, 4613–4621 (2020).
Guo, Y., Tian, L., Du, X. & Deng, Z. MiR-203 regulates estrogen receptor α and cartilage degradation in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes. J. Bone Min. Metab. 38, 346–356 (2020).
Tian, L., Su, Z., Ma, X., Wang, F. & Guo, Y. Inhibition of miR-203 ameliorates osteoarthritis cartilage degradation in the postmenopausal rat model: involvement of estrogen receptor α. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 30, 160–168 (2019).
Zhu, J. et al. lncRNAs: function and mechanism in cartilage development, degeneration, and regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 10, 344 (2019).
Yang, Y. et al. A long non-coding RNA, HOTAIR, promotes cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting WIF-1 expression and activating Wnt pathway. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 53 (2020).
Wang, H., Li, J., Cheng, Y. & Yao, J. Association of long-chain noncoding RNA H19 and MEG3 gene polymorphisms and their interaction with risk of osteoarthritis in a Chinese Han population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomarkers 24, 328–337 (2020).
Zhang, L. et al. Yeast cell wall particle mediated nanotube-RNA delivery system loaded with miR365 antagomir for post-traumatic osteoarthritis therapy via oral route. Theranostics 10, 8479–8493 (2020).
Wang, Q., Wang, W., Zhang, F., Deng, Y. & Long, Z. NEAT1/miR-181c Regulates osteopontin (OPN)-mediated synoviocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. J. Cell Biochem. 118, 3775–3784 (2017).
Nakamura, A., Ali, S. A. & Kapoor, M. Antisense oligonucleotide-based therapies for the treatment of osteoarthritis: opportunities and roadblocks. Bone 138, 115461 (2020).
Chen, Y. et al. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) alleviates osteoarthritis progression by regulation of extracellular matrix homeostasis. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, e923868 (2020).
Chen, H., Yang, S. & Shao, R. Long non-coding XIST raises methylation of TIMP-3 promoter to regulate collagen degradation in osteoarthritic chondrocytes after tibial plateau fracture. Arthritis Res. Ther. 21, 271 (2019).
Pan, H. et al. MicroRNA-410-3p modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation by targeting high mobility group Box 1 (HMGB1) in an osteoarthritis mouse model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 21, 486 (2020).
Zhao, H. & Gong, N. miR-20a regulates inflammatory in osteoarthritis by targeting the IκBβ and regulates NK-κB signaling pathway activation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 518, 632–637 (2019).
Lei, J., Fu, Y., Zhuang, Y., Zhang, K. & Lu, D. miR-382-3p suppressed IL-1β induced inflammatory response of chondrocytes via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway by directly targeting CX43. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 23160–23168 (2019).
Si, H. B. et al. miR-140 attenuates the progression of early-stage osteoarthritis by retarding chondrocyte senescence. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 19, 15–30 (2020).
Papathanasiou, I., Balis, C., Trachana, V., Mourmoura, E. & Tsezou, A. The synergistic function of miR-140-5p and miR-146a on TLR4-mediated cytokine secretion in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 522, 783–791 (2020).
Pearson, M. J. et al. Long intergenic noncoding RNAs mediate the human chondrocyte inflammatory response and are differentially expressed in osteoarthritis cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68, 845–856 (2016).
Yang, P. et al. Th17 cell pathogenicity and plasticity in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 106, 1233–1240 (2019).
Shui, X. et al. Knockdown of lncRNA NEAT1 inhibits Th17/CD4(+) T cell differentiation through reducing the STAT3 protein level. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 22477–22484 (2019).
Yang, P. et al. MicroRNA let-7g-5p alleviates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 174, 113822 (2020).
Alivernini, S. et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Med. 26, 1295–1306 (2020).
Paoletti, A. et al. Monocyte/macrophage abnormalities specific to rheumatoid arthritis are linked to miR-155 and are differentially modulated by different TNF inhibitors. J. Immunol. 203, 1766–1775 (2019).
Quero, L. et al. miR-221-3p drives the shift of M2-macrophages to a pro-inflammatory function by suppressing JAK3/STAT3 activation. Front. Immunol. 10, 3087 (2019).
Ma, F., Li, G., Yu, Y., Xu, J. & Wu, X. MiR-33b-3p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation by targeting DNMT3A in osteoarthritis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 519, 430–437 (2019).
Chen, H., Yang, J. & Tan, Z. Upregulation of microRNA-9-5p inhibits apoptosis of chondrocytes through downregulating Tnc in mice with osteoarthritis following tibial plateau fracture. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 23326–23336 (2019).
Liu, W., Zha, Z. & Wang, H. Upregulation of microRNA-27a inhibits synovial angiogenesis and chondrocyte apoptosis in knee osteoarthritis rats through the inhibition of PLK2. J. Cell Physiol. 234, 22972–22984 (2019).
Chang, Q., Ji, M., Li, C. & Geng, R. Downregulation of miR4865p alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury, oxidative stress and apoptosis in chondrogenic cell ATDC5 by targeting NRF1. Mol. Med. Rep. 22, 2123–2131 (2020).
Cheng, F., Hu, H., Sun, K., Yan, F. & Geng, Y. miR-455-3p enhances chondrocytes apoptosis and inflammation by targeting COL2A1 in the in vitro osteoarthritis model. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 84, 695–702 (2020).
Wen, X. et al. MiR-455-3p reduces apoptosis and alleviates degeneration of chondrocyte through regulating PI3K/AKT pathway. Life Sci. 253, 117718 (2020).
Tao, H., Cheng, L. & Yang, R. Downregulation of miR-34a promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of rat osteoarthritic cartilage cells by activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Clin. Interv. Aging 15, 373–385 (2020).
Chen, S. & Li, B. MiR-128-3p post-transcriptionally inhibits WISP1 to suppress apoptosis and inflammation in human articular chondrocytes via the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Transpl. 29, 963689720939131 (2020).
Fan, Z. et al. MiR-155 promotes interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and catabolic activity by targeting PIK3R1-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24, 8441–8451 (2020).
Wang, W. T. et al. microRNA-1236 promotes chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis via direct suppression of PIK3R3. Life Sci. 253, 117694 (2020).
Li, F., Yao, J., Hao, Q. & Duan, Z. miRNA-103 promotes chondrocyte apoptosis by down-regulation of sphingosine kinase-1 and ameliorates PI3K/AKT pathway in osteoarthritis. Biosci. Rep. 39, BSR20191255 (2019).
Dong, C. et al. microRNA-mediated GAS1 downregulation promotes the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts by PI3K-Akt signaling in osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 18, 4273–4286 (2019).
Shirdel, E. A., Xie, W., Mak, T. W. & Jurisica, I. NAViGaTing the micronome — using multiple microRNA prediction databases to identify signalling pathway-associated microRNAs. PLoS ONE 6, e17429 (2011).
Liu, X. C. et al. MiR-1207-5p/CX3CR1 axis regulates the progression of osteoarthritis via the modulation of the activity of NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 23, 1057–1065 (2020).
Li, L., Lv, G., Wang, B. & Kuang, L. XIST/miR-376c-5p/OPN axis modulates the influence of proinflammatory M1 macrophages on osteoarthritis chondrocyte apoptosis. J. Cell Physiol. 235, 281–293 (2020).
Wang, Y. et al. miR-483-3p promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting IGF-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 130, 110519 (2020).
Rao, Y. et al. Delivery of long non-coding RNA NEAT1 by peripheral blood mononuclear cells-derived exosomes promotes the occurrence of rheumatoid arthritis via the microRNA-23a/MDM2/SIRT6 axis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 551681 (2020).
Xiao, P. et al. MicroRNA-613 alleviates IL-1β-induced injury in chondrogenic CHON-001 cells by targeting fibronectin 1. Am. J. Transl Res. 12, 5308–5319 (2020).
Yang, B., Xu, L. & Wang, S. Regulation of lncRNA-H19/miR-140-5p in cartilage matrix degradation and calcification in osteoarthritis. Ann. Palliat. Med. 9, 1896–1904 (2020).
Wei, W. et al. LINC01534 promotes the aberrant metabolic dysfunction and inflammation in IL-1β-simulated osteoarthritic chondrocytes by targeting miR-140-5p. Cartilage https://doi.org/10.1177/1947603519888787 (2019).
Duan, L., Liang, Y., Xu, X., Xiao, Y. & Wang, D. Recent progress on the role of miR-140 in cartilage matrix remodelling and its implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 22, 194 (2020).
Balaskas, P. et al. Small non-coding RNAome of ageing chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5675 (2020).
Peffers, M. J. et al. SnoRNA signatures in cartilage ageing and osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 10, 10641 (2020).
Liu, D. et al. Synovial fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-106b suppresses chondrocyte proliferation and migration in rheumatoid arthritis via down-regulation of PDK4. J. Mol. Med. 98, 409–423 (2020).
Chen, J. et al. Exosomal miRNA-486-5p derived from rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes induces osteoblast differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad pathway. Biomater. Sci. 8, 3430–3442 (2020).
Esmaeili, A., Hosseini, S. & Baghaban Eslaminejad, M. Engineered-extracellular vesicles as an optimistic tool for microRNA delivery for osteoarthritis treatment. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 78, 79–91 (2020).
Asghar, S., Litherland, G. J., Lockhart, J. C., Goodyear, C. S. & Crilly, A. Exosomes in intercellular communication and implications for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology 59, 57–68 (2020).
Wu, X. et al. Extracellular vesicles: potential role in osteoarthritis regenerative medicine. J. Orthop. Transl 21, 73–80 (2020).
Zhang, G., Zhou, Y., Su, M., Yang, X. & Zeng, B. Inhibition of microRNA-27b-3p relieves osteoarthritis pain via regulation of KDM4B-dependent DLX5. Biofactors 46, 788–802 (2020).
Hoshikawa, N., Sakai, A., Takai, S. & Suzuki, H. Targeting extracellular miR-21-TLR7 signaling provides long-lasting analgesia in osteoarthritis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 19, 199–207 (2020).
Bai, J. et al. LncRNA MM2P-induced, exosome-mediated transfer of Sox9 from monocyte-derived cells modulates primary chondrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 11, 763 (2020).
Jiang, L. & Cao, S. Role of microRNA-26a in cartilage injury and chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis rats by regulating expression of CTGF. J. Cell Physiol. 235, 979–992 (2020).
Meng, Q. & Qiu, B. Exosomal microRNA-320a derived from mesenchymal stem cells regulates rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte activation by suppressing CXCL9 expression. Front. Physiol. 11, 441 (2020).
Zheng, J. et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomal microRNA-192-5p delays inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 78, 105985 (2020).
Sun, W. et al. Resolvin D1 suppresses pannus formation via decreasing connective tissue growth factor caused by upregulation of miRNA-146a-5p in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 22, 61 (2020).
Wang, J. et al. Identification of a novel microRNA-141-3p/Forkhead box C1/β-catenin axis associated with rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast function in vivo and in vitro. Theranostics 10, 5412–5434 (2020).
Liang, Y. et al. Chondrocyte-targeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 36938–36947 (2020).
Lv, S. et al. MicroRNA-27b targets CBFB to inhibit differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hypertrophic chondrocytes. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 392 (2020).
Geng, Y. et al. Intra-articular injection of hUC-MSCs expressing miR-140-5p induces cartilage self-repairing in the rat osteoarthritis. J. Bone Min. Metab. 38, 277–288 (2020).
Abbasi Pashaki, P., Rahim, F., Habibi Roudkenar, M., Razavi-Toosi, S. & Ebrahimi, A. MicroRNA tough decoy knockdowns miR-195 and represses hypertrophy in chondrocytes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 191, 1056–1071 (2020).
Nakamura, A. et al. microRNA-181a-5p antisense oligonucleotides attenuate osteoarthritis in facet and knee joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 78, 111–121 (2019).
Endisha, H. et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p promotes joint destruction during osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 73, 426–439 (2020).
Lee, W. S. et al. MicroRNA-9 ameliorates destructive arthritis through down-regulation of NF-κB1-RANKL pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin. Immunol. 212, 108348 (2020).
Rai, M. F. et al. Applications of RNA interference in the treatment of arthritis. Transl Res. 214, 1–16 (2019).
Wang, T. et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 11, 598 (2020).
Ying, H. et al. Cancer therapy using a self-replicating RNA vaccine. Nat. Med. 5, 823–827 (1999).
Ragni, E. et al. miR-22-5p and miR-29a-5p are reliable reference genes for analyzing extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and are stable under inflammatory priming mimicking osteoarthritis condition. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 15, 743–754 (2019).
Martinez-Sanchez, A., Lazzarano, S., Sharma, E., Lockstone, H. & Murphy, C. L. High-throughput identification of miR-145 targets in human articular chondrocytes. Life 10, 58 (2020).
Lu, J. et al. MiR-520d-5p modulates chondrogenesis and chondrocyte metabolism through targeting HDAC1. Aging 12, 18545–18560 (2020).
Ross, A. K. et al. The miRNA-mRNA interactome of murine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived chondrocytes in response to inflammatory cytokines. FASEB J. 34, 11546–11561 (2020).
Skrzypa, M. et al. miRNA-146a-5p is upregulated in serum and cartilage samples of patients with osteoarthritis. Pol. Przegl. Chir. 91, 1–5 (2019).
Kolarz, B., Ciesla, M., Dryglewska, M., Rosenthal, A. K. & Majdan, M. Hypermethylation of the miR-155 gene in the whole blood and decreased plasma level of miR-155 in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 15, e0233897 (2020).
Shao, L. & Hou, C. miR-138 activates NF-κB signaling and PGRN to promote rheumatoid arthritis via regulating HDAC4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 519, 166–171 (2019).
Rezaeepoor, M. et al. Altered expression of microRNAs may predict therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 83, 106404 (2020).
Stypinska, B. et al. The serum cell-free microRNA expression profile in MCTD, SLE, SSc, and RA patients. J. Clin. Med. 9, 161 (2020).
Romo-Garcia, M. F. et al. Identification of putative miRNA biomarkers in early rheumatoid arthritis by genome-wide microarray profiling: a pilot study. Gene 720, 144081 (2019).
Guo, D. et al. Study of miRNA interactome in active rheumatoid arthritis patients reveals key pathogenic roles of dysbiosis in the infection-immune network. Rheumatology 60, 1512–1522 (2021).
Lim, M. K. et al. Serum exosomal miRNA-1915-3p is correlated with disease activity of Korean rheumatoid arthritis. Vivo 34, 2941–2945 (2020).
Mu, N. et al. Blockade of discoidin domain receptor 2 as a strategy for reducing inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis via altered interleukin-15 and Dkk-1 signaling in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72, 943–956 (2020).
Wang, J. & Zhao, Q. LncRNA LINC-PINT increases SOCS1 expression by sponging miR-155-5p to inhibit the activation of ERK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts induced by TNF-α. Int. Immunopharmacol. 84, 106497 (2020).
Wang, J., Kong, X., Hu, H. & Shi, S. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating miR-543-dependent SCUBE2 in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 15, 142 (2020).
Li, Z. et al. Circ_0136474 and MMP-13 suppressed cell proliferation by competitive binding to miR-127-5p in osteoarthritis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 23, 6554–6564 (2019).
Chen, C., Yin, P., Hu, S., Sun, X. & Li, B. Circular RNA-9119 protects IL-1β-treated chondrocytes from apoptosis in an osteoarthritis cell model by intercepting the microRNA-26a/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 256, 117924 (2020).
Shen, P. et al. CircCDK14 protects against osteoarthritis by sponging miR-125a-5p and promoting the expression of Smad2. Theranostics 10, 9113–9131 (2020).
Wu, Q., Yuan, Z. H., Ma, X. B. & Tang, X. H. Low expression of CircRNA HIPK3 promotes osteoarthritis chondrocyte apoptosis by serving as a sponge of miR-124 to regulate SOX8. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 7937–7945 (2020).
Ma, H. R. et al. CircVCAN regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocyte through NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 6517–6525 (2020).
Chen, G., Liu, T., Yu, B., Wang, B. & Peng, Q. CircRNA-UBE2G1 regulates LPS-induced osteoarthritis through miR-373/HIF-1a axis. Cell Cycle 19, 1696–1705 (2020).
Ni, J. L., Dang, X. Q. & Shi, Z. B. CircPSM3 inhibits the proliferation and differentiation of OA chondrocytes by targeting miRNA-296-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 3467–3475 (2020).
Zhang, W. et al. Circular RNA-CDR1as acts as the sponge of microRNA-641 to promote osteoarthritis progression. J. Inflamm. 17, 8 (2020).
Bai, Z. M., Kang, M. M., Zhou, X. F. & Wang, D. CircTMBIM6 promotes osteoarthritis-induced chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation via miR-27a/MMP13 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 7927–7936 (2020).
Zhu, H., Hu, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, X. & He, D. CircGCN1L1 promotes synoviocyte proliferation and chondrocyte apoptosis by targeting miR-330-3p and TNF-α in TMJ osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. 11, 284 (2020).
Zhong, S. et al. Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes the proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miR-140-3p and upregulating SIRT 1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 125, 131–139 (2020).
Yang, J. et al. CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis. 11, 833 (2020).
Li, X. et al. Promising targets and drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: a module-based and cumulatively scoring approach. Bone Jt. Res. 9, 501–514 (2020).
Xiang, S., Li, Z., Bian, Y. & Weng, X. RNA sequencing reveals the circular RNA expression profiles of osteoarthritic synovium. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 18031–18040 (2019).
Xiao, K. et al. Circular RNA expression profile of knee condyle in osteoarthritis by illumina HiSeq platform. J. Cell Biochem. 120, 17500–17511 (2019).
Wang, Y. et al. Screening for differentially expressed circular RNAs in the cartilage of osteoarthritis patients for their diagnostic value. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 23, 706–716 (2019).
Chen, H. & Chen, L. An integrated analysis of the competing endogenous RNA network and co-expression network revealed seven hub long non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Bone Jt. Res. 9, 90–98 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The work of M.J.P. is supported by a Wellcome Trust Intermediate Clinical Fellowship (107471/Z/15/Z) and by the Medical Research Council and Versus Arthritis as part of the Medical Research Council Versus Arthritis Centre for Integrated Research into Musculoskeletal Ageing (MR/R502182/1). The work of M.J.O. is supported by the Veterans Health Administration CDA (IK2CX001269) and by an Arthritis Foundation Delivering on Discovery grant. I.J. is also at the Departments of Medical Biophysics and Computer Science, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada and the Institute of Neuroimmunology, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovakia. The work of I.J. was funded in part by the Ontario Research Fund (no. 34876 and GL2-01-030), the Natural Sciences Research Council (NSERC no. 203475), Genome Canada (DIG2 no. 14408), the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI no. 29272, no. 225404, no. 33536) and the Canada Research Chair Program (CRC no. 203373 and no. 225404). Additional support is provided by the Schroeder Arthritis Institute via the Toronto General and Western Hospital Foundation, University Health Network. The work of M.K. is supported by the Canadian Institute of Health Research Operating grant (no. 156299) and the Tier 1 Canada Research Chair Award (no. 950-232237).
Review criteria
A literature search was performed in PubMed for articles published in the past 2 years using combinations of the following key words: “osteoarthritis”, “rheumatoid arthritis”, “microRNA”, “long non-coding RNA”, “circular RNA”, “small nucleolar RNAs” and “transfer RNAs”. Some highly relevant papers outside the search criteria were also included.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
S.A.A. and M.K. declare that they have filed a US Provisional Patent Application no. 63/033,463 titled “Circulating MicroRNAs in Knee Osteoarthritis and Uses Thereof”. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Disclaimer
None of the funders had a role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Rheumatology thanks S. Jones and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
circAtlas: http://159.226.67.237:8080/new/index.php
circBase: http://www.circbase.org/
DIANA-lncBase: https://diana.e-ce.uth.gr/lncbasev3
EMBL-EBI European Nucleotide Archive: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/home
Enrichr: https://maayanlab.cloud/Enrichr/
Gene Ontology Resource: http://geneontology.org
Hugo Gene Nomenclature: https://www.genenames.org/
miRanda: https://bioweb.pasteur.fr/packages/pack@miRanda@3.3a
miRbase: http://www.mirbase.org/
miRDB: http://mirdb.org/
miRDeep2: https://github.com/rajewsky-lab/mirdeep2
mirDIP: http://ophid.utoronto.ca/mirDIP/
NCBI Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gap/
NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus repository: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds
NCBI Sequence Read Archive: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra
pathDIP: http://ophid.utoronto.ca/pathDIP/
TargetScan: http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, S.A., Peffers, M.J., Ormseth, M.J. et al. The non-coding RNA interactome in joint health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 17, 692–705 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-021-00687-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-021-00687-y
This article is cited by
-
Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates hypoxia-induced proliferation, migration, and inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via inhibiting the HIF-1α- circCDC42BPB pathway
Advances in Rheumatology (2024)
-
Non-coding RNA in the gut of the blood-feeding parasitic worm, Haemonchus contortus
Veterinary Research (2024)
-
Circular RNAs and cervical cancer: friends or foes? A landscape on circRNA-mediated regulation of key signaling pathways involved in the onset and progression of HPV-related cervical neoplasms
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Non-coding RNAs in disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics
Nature Reviews Genetics (2024)
-
LncRNA CARMN inhibits abdominal aortic aneurysm formation and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic transformation by interacting with SRF
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2024)