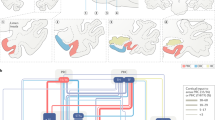
Abstract
Standard models of episodic memory focus on hippocampal–parahippocampal interactions, with the neocortex supplying sensory information and providing a final repository of mnemonic representations. However, recent advances have shown that other regions make distinct and equally critical contributions to memory. In particular, there is growing evidence that the anterior thalamic nuclei have a number of key cognitive functions that support episodic memory. In this article, we describe these findings and argue for a core, tripartite memory system, comprising a ‘temporal lobe’ stream (centred on the hippocampus) and a ‘medial diencephalic’ stream (centred on the anterior thalamic nuclei) that together act on shared cortical areas. We demonstrate how these distributed brain regions form complementary and necessary partnerships in episodic memory formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eichenbaum, H. A cortical–hippocampal system for declarative memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 1, 41–50 (2000).
Manns, J. R. & Eichenbaum, H. Evolution of declarative memory. Hippocampus 16, 795–808 (2006).
Squire, L. R. Memory and brain systems: 1969–2009. J. Neurosci. 29, 12711–12716 (2009).
Bellmund, J. L., Gärdenfors, P., Moser, E. I. & Doeller, C. F. Navigating cognition: spatial codes for human thinking. Science 362, 6415 (2018).
Ekstrom, A. D. & Ranganath, C. Space, time, and episodic memory: the hippocampus is all over the cognitive map. Hippocampus 28, 680–687 (2018).
Gudden, H. Klinische und anatommische beitrage zur kenntnis der multiplen alkoholneuritis nebst bemerzungen uber die regenerationsvorgange im peripheren nervensystem. Arch. Psychiat. 28, 643–741 (1896).
Gamper, E. Zur Frage der Polioencephalitis hæmorrhagica der chronischen Alkoholiker: Anatomische Befund beim alkoholischen Korsakow und ihre Beziehungen zum klinischen Bild. Dtsch. Ztschr. Nervenh 102, 122 (1928).
Kopelman, M. D. What does a comparison of the alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome and thalamic infarction tell us about thalamic amnesia? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 46–56 (2015).
Gabriel, M. in Neurobiology of Cingulate Cortex and Limbic Thalamus (eds. Vogt, B. A. & Gabriel, M.) 478–523 (Birkhäuser, 1993).
Wright, N. F., Vann, S. D., Aggleton, J. P. & Nelson, A. J. A critical role for the anterior thalamus in directing attention to task-relevant stimuli. J. Neurosci. 35, 5480–5488 (2015).
Aggleton, J. P. & Nelson, A. J. Why do lesions in the rodent anterior thalamic nuclei cause such severe spatial deficits? Neurosc. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 131–144 (2015).
Aggleton, J. P. et al. Hippocampal–anterior thalamic pathways for memory: uncovering a network of direct and indirect actions. Eur. J. Neurosci. 31, 2292–2307 (2010).
Aggleton, J. P. & Pearce, J. M. Neural systems underlying episodic memory: insights from animal research. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 356, 1467–1482 (2001).
Bird, C. M. & Burgess, N. The hippocampus and memory: insights from spatial processing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 182–194 (2008).
Barry, D. N. & Maguire, E. A. Remote memory and the hippocampus: a constructive critique. Trends Cogn. Sci. 23, 128–142 (2019).
Yonelinas, A. P., Ranganath, C., Ekstrom, A. D. & Wiltgen, B. J. A contextual binding theory of episodic memory: systems consolidation reconsidered. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20, 364–375 (2019).
Yamawaki, N. et al. Long-range inhibitory intersection of a retrosplenial thalamocortical circuit by apical tuft-targeting CA1 neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 618–626 (2019).
Taube, J. S. The head direction signal: origins and sensory-motor integration. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 181–207 (2007).
Goodridge, J. P. & Taube, J. S. Interaction between the postsubiculum and anterior thalamus in the generation of head direction cell activity. J. Neurosci. 17, 9315–9330 (1997).
Winter, S. S., Clark, B. J. & Taube, J. S. Disruption of the head direction cell network impairs the parahippocampal grid cell signal. Science 347, 870–874 (2015).
Nelson, A. J., Kinnavane, L., Amin, E., O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. Deconstructing the direct reciprocal hippocampal-anterior thalamic pathways for spatial learning. J. Neurosci. 40, 6978–6990 (2020).
Bourbon-Teles, J. et al. Thalamic control of human attention driven by memory and learning. Curr. Biol. 24, 993–999 (2014).
Lawson, R. On the symptomatology of alcoholic brain disorders. Brain 1, 182–194 (1878).
Korsakoff, S. S. Ob alkogol’nom paraliche (Of alcoholic paralysis: disturbance of psychic activity and its relation to the disturbance of the psychic sphere in multiple neuritis of nonalcoholic origin). Vestnick. Klin. Psychiat. Neurol. 4, 1–102 (1887).
Harding, A., Halliday, G., Caine, D. & Kril, J. Degeneration of anterior thalamic nuclei differentiates alcoholics with amnesia. Brain 123, 141–154 (2000).
Guillery, R. W. A quantitative study of the mamillary bodies and their connexions. J. Anat. 89, 19–32 (1955).
Takeuchi, Y., Allen, G. V. & Hopkins, D. A. Transnuclear transport and axon collateral projections of the mamillary nuclei in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 14, 453–468 (1985).
von Bekhterev, M. Demonstration eines Gehirns mit Zerstö rung der vorderen und inneren Theile der Hirnrinde beider Schlä fenlappen. Neurologisches Zeitblatt 19, 990–991 (1900).
Clark, R. E. & Squire, L. R. An animal model of recognition memory and medial temporal lobe amnesia: history and current issues. Neuropsychologia 48, 2234–2244 (2010).
Scoville, W. B. & Milner, B. Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 20, 11–21 (1957).
Zola-Morgan, S., Squire, L. R. & Amaral, D. G. Human amnesia and the medial temporal region: enduring memory impairment following a bilateral lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 6, 2950–2967 (1986).
Rempel-Clower, N. L., Zola, S. M., Squire, L. R. & Amaral, D. G. Three cases of enduring memory impairment after bilateral damage limited to the hippocampal formation. J. Neurosci. 16, 5233–5255 (1996).
Spiers, H. J., Maguire, E. A. & Burgess, N. Hippocampal amnesia. Neurocase 7, 357–382 (2001).
Papez, J. W. A proposed mechanism of emotion. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. 38, 725–743 (1937).
Bastin, C. et al. An integrative memory model of recollection and familiarity to understand memory deficits. Behav. Brain Sci. 42, e281 (2019).
Delay, J. & Brion, S. Le Syndrome de Korsakoff (Masson, 1969).
Aggleton, J. P. & Brown, M. W. Episodic memory, amnesia and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav. Brain Sci. 22, 425–444 (1999).
O’Keefe, J. & Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map: preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 34, 171–174 (1971).
Bliss, T. V. & Lømo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. 232, 331–356 (1973).
Morris, R. G., Garrud, P., Rawlins, J. A. & O’Keefe, J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 297, 681–683 (1982).
Eichenbaum, H. Prefrontal–hippocampal interactions in episodic memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 547–558 (2017).
Korotkova, T. et al. Reconciling the different faces of hippocampal theta: the role of theta oscillations in cognitive, emotional and innate behaviors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 85, 65–80 (2018).
Watrous, A. J. et al. A comparative study of human and rat hippocampal low-frequency oscillations during spatial navigation. Hippocampus 23, 656–661 (2013).
Addante, R. J., Watrous, A. J., Yonelinas, A. P., Ekstrom, A. D. & Ranganath, C. Prestimulus theta activity predicts correct source memory retrieval. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 10702–10707 (2011).
Horner, A. J. & Doeller, C. F. Plasticity of hippocampal memories in humans. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 43, 102–109 (2017).
Kota, S., Rugg, M. D. & Lega, B. C. Hippocampal theta oscillations support successful associative memory formation. J. Neurosci. 40, 9507–9518 (2020).
Zeidman, P. & Maguire, E. A. Anterior hippocampus: the anatomy of perception, imagination and episodic memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 173–182 (2016).
Nadel, L., Samsonovich, A., Ryan, L. & Moscovitch, M. Multiple trace theory of human memory: computational, neuroimaging, and neuropsychological results. Hippocampus 10, 352–368 (2000).
Squire, L. R., Genzel, L., Wixted, J. T. & Morris, R. G. Memory consolidation. Cold Spring Harb. Persp. Biol. 7, a021766 (2015).
Ritchey, M., Libby, L. A. & Ranganath, C. Cortico-hippocampal systems involved in memory and cognition: the PMAT framework. Progr. Brain Res. 219, 45–64 (2015).
Fama, R. & Sullivan, E. V. Thalamic structures and associated cognitive functions: relations with age and aging. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 29–37 (2015).
Alderson, T. et al. Disrupted thalamus white matter anatomy and posterior default mode network effective connectivity in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 9, 370 (2017).
Aggleton, J. P., Pralus, A., Nelson, A. J. & Hornberger, M. Thalamic pathology and memory loss in early Alzheimer’s disease: moving the focus from the medial temporal lobe to Papez circuit. Brain 139, 1877–1890 (2016).
Braak, H. & Braak, E. Alzheimer’s disease affects limbic nuclei of the thalamus. Acta Neuropath 81, 261–268 (1991).
Forno, G., Lladó, A. & Hornberger, M. Going round in circles — the Papez circuit in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 54, 7668–7687 (2021).
Elvsåshagen, T. et al. The genetic architecture of the human thalamus and its overlap with ten common brain disorders. Nat. Commun. 12, 2909 (2021).
Siniatchkin, M., Coropceanu, D., Moeller, F., Boor, R. & Stephani, U. EEG-fMRI reveals activation of brainstem and thalamus in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Epilepsia 52, 766–774 (2011).
Perry, J. C., Pakkenberg, B. & Vann, S. D. Striking reduction in neurons and glial cells in anterior thalamic nuclei of older patients with Down syndrome. Neurobiol. Aging 75, 54–61 (2019).
O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. Space and memory (far) beyond the hippocampus: many subcortical structures also support cognitive mapping and mnemonic processing. Front. Neur. Circ. 13, 52 (2019).
Wright, N. F., Vann, S. D., Erichsen, J. T., O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. Segregation of parallel inputs to the anteromedial and anteroventral thalamic nuclei of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 521, 2966–2986 (2013).
Christiansen, K. et al. Complementary subicular pathways to the anterior thalamic nuclei and mammillary bodies in the rat and macaque monkey brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 43, 1044–1061 (2016).
Mathiasen, M. L., Nelson, A. J., Amin, E., O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. A direct comparison of afferents to the rat anterior thalamic nuclei and nucleus reuniens: overlapping but different. eNeuro 8, https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0103-20.2021 (2021).
Shibata, H. Direct projections from the anterior thalamic nuclei to the retrohippocampal region in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 337, 431–445 (1993).
Bubb, E. J., Kinnavane, L. & Aggleton, J. P. Hippocampal–diencephalic–cingulate networks for memory and emotion: an anatomical guide. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 1, 2398212817723443 (2017).
Cenquizca, L. A. & Swanson, L. W. Analysis of direct hippocampal cortical field CA1 axonal projections to diencephalon in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 497, 101–114 (2006).
Vetere, G. et al. An inhibitory hippocampal–thalamic pathway modulates remote memory retrieval. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 685–693 (2021).
Ferguson, M. A. et al. A human memory circuit derived from brain lesions causing amnesia. Nat. Commun. 10, 3497 (2019).
Wolff, M. & Vann, S. D. The cognitive thalamus as a gateway to mental representations. J. Neurosci. 39, 3–14 (2019).
Mitchell, A. S. & Chakraborty, S. What does the mediodorsal thalamus do? Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7, 37 (2013).
Perry, B. A., Lomi, E. & Mitchell, A. S. Thalamocortical interactions in cognition and disease: the mediodorsal and anterior thalamic nuclei. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 130, 162–177 (2021).
Mathiasen, M. L., O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. The anterior thalamic nuclei and nucleus reuniens: so similar but so different. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 119, 268–280 (2020).
Moreau, P. H. et al. Lesions of the anterior thalamic nuclei and intralaminar thalamic nuclei: place and visual discrimination learning in the water maze. Brain Struct. Funct. 218, 657–667 (2013).
Warburton, E. C. & Aggleton, J. P. Differential deficits in the Morris water maze following cytotoxic lesions of the anterior thalamus and fornix transection. Behav. Brain Res. 98, 27–38 (1998).
Dolleman-van der Weel, M. J., Morris, R. G. & Witter, M. P. Neurotoxic lesions of the thalamic reuniens or mediodorsal nucleus in rats affect non-mnemonic aspects of watermaze learning. Brain Struct. Funct. 213, 329–342 (2009).
Loureiro, M. et al. The ventral midline thalamus (reuniens and rhomboid nuclei) contributes to the persistence of spatial memory in rats. J. Neurosci. 32, 9947–9959 (2012).
McKenna, J. T. & Vertes, R. P. Afferent projections to nucleus reuniens of the thalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 480, 115–142 (2004).
Mathiasen, M. L. et al. Separate cortical and hippocampal cell populations target the rat nucleus reuniens and mammillary bodies. Eur. J. Neurosci. 49, 1649–1672 (2019).
Prasad, J. A. & Chudasama, Y. Viral tracing identifies parallel disynaptic pathways to the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 33, 8494–8503 (2013).
Griffin, A. L. The nucleus reuniens orchestrates prefrontal-hippocampal synchrony during spatial working memory. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 128, 415–420 (2021).
Cassel, J. C. et al. The reuniens and rhomboid nuclei of the thalamus: a crossroads for cognition-relevant information processing? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 126, 338–360 (2021).
Mitchell, A. S. The mediodorsal thalamus as a higher order thalamic relay nucleus important for learning and decision-making. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 76–88 (2015).
Hunt, P. R. & Aggleton, J. P. Medial dorsal thalamic lesions and working memory in the rat. Behav. Neural Biol. 55, 227–246 (1991).
Aggleton, J. P., Dumont, J. R. & Warburton, E. C. Unraveling the contributions of the diencephalon to recognition memory: a review. Learn. Mem. 18, 384–400 (2011).
Segobin, S. et al. Dissociating thalamic alterations in alcohol use disorder defines specificity of Korsakoff’s syndrome. Brain 142, 1458–1470 (2019).
Van der Werf, Y. D. et al. Deficits of memory, executive functioning and attention following infarction in the thalamus; a study of 22 cases with localised lesions. Neuropsychologia 41, 1330–1344 (2003).
Carlesimo, G. A., Lombardi, M. G. & Caltagirone, C. Vascular thalamic amnesia: a reappraisal. Neuropsychologia 49, 777–789 (2011).
Mair, R. G., Burk, J. A. & Porter, M. C. Impairment of radial maze delayed nonmatching after lesions of anterior thalamus and parahippocampal cortex. Behav. Neurosci. 117, 596–605 (2003).
Mitchell, A. S. & Dalrymple-Alford, J. C. Lateral and anterior thalamic lesions impair independent memory systems. Learn. Mem. 13, 388–396 (2006).
Clark, B. J. & Harvey, R. E. Do the anterior and lateral thalamic nuclei make distinct contributions to spatial representation and memory? Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 133, 69–78 (2016).
Aggleton, J. P., Vann, S. D., Oswald, C. J. & Good, M. Identifying cortical inputs to the rat hippocampus that subserve allocentric spatial processes: a simple problem with a complex answer. Hippocampus 10, 466–474 (2000).
Moran, J. P. & Dalrymple-Alford, J. C. Perirhinal cortex and anterior thalamic lesions: comparative effects on learning and memory. Behav. Neurosci. 117, 1326–1341 (2003).
Cassel, J. C., Duconseille, E., Jeltsch, H. & Will, B. The fimbria-fornix/cingular bundle pathways: a review of neurochemical and behavioural approaches using lesions and transplantation techniques. Progr. Neurobiol. 51, 663–716 (1997).
Aggleton, J. P. & Brown, M. W. in Neuropsychology of Memory (eds. Squire, L. R. & Schacter, D. L.) 377–394 (Guilford, 2002).
Aggleton, J. P., Neave, N., Nagle, S. & Hunt, P. R. A comparison of the effects of anterior thalamic, mamillary body and fornix lesions on reinforced spatial alternation. Behav. Brain Res. 68, 91–101 (1995).
Parker, A. & Gaffan, D. The effect of anterior thalamic and cingulate cortex lesions on object-in-place memory in monkeys. Neuropsychologia 35, 1093–1102 (1997).
Gaffan, D. Scene-specific memory for objects: a model of episodic memory impairment in monkeys with fornix transection. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 6, 305–320 (1994).
Sutherland, R. J. & Rodriguez, A. J. The role of the fornix/fimbria and some related subcortical structures in place learning and memory. Behav. Brain Res. 32, 265–277 (1989).
Aggleton, J. P., Keith, A. B. & Sahgal, A. Both fornix and anterior thalamic, but not mammillary, lesions disrupt delayed non-matching-to-position memory in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 44, 151–161 (1991).
Dumont, J. R., Wright, N. F., Pearce, J. M. & Aggleton, J. P. The impact of anterior thalamic lesions on active and passive spatial learning in stimulus controlled environments: geometric cues and pattern arrangement. Behav. Neurosci. 128, 161–177 (2014).
Pearce, J. M., Good, M. A., Jones, P. M. & McGregor, A. Transfer of spatial behavior between different environments: implications for theories of spatial learning and for the role of the hippocampus in spatial learning. J. Exp. Psych. Anim. Behav. Proc. 30, 135 (2004).
Aggleton, J. P., Keith, A. B., Rawlins, J. N. P., Hunt, P. R. & Sahgal, A. Removal of the hippocampus and transection of the fornix produce comparable deficits on delayed non-matching to position by rats. Behav. Brain Res. 52, 61–71 (1992).
Song, D. et al. Extraction and restoration of hippocampal spatial memories with non-linear dynamical modeling. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 8, 97 (2014).
Morris, R. G. M., Schenk, F., Tweedie, F. & Jarrard, L. E. Ibotenate lesions of hippocampus and/or subiculum: dissociating components of allocentric spatial learning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2, 1016–1028 (1990).
Jarrard, L. E. What does the hippocampus really do? Behav. Brain Res. 71, 1–10 (1995).
Taube, J. S. Head direction cells recorded in the anterior thalamic nuclei of freely moving rats. J. Neurosci. 15, 70–86 (1995).
Calton, J. L. et al. Hippocampal place cell instability after lesions of the head direction cell network. J. Neurosci. 23, 9719–9731 (2003).
Moser, E. I. et al. Grid cells and cortical representation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 15, 466–481 (2014).
Golob, E. J. & Taube, J. S. Head direction cells and episodic spatial information in rats without a hippocampus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7645–7650 (1997).
Safari, V. et al. Individual subnuclei of the rat anterior thalamic nuclei differently affect spatial memory and passive avoidance tasks. Neuroscience 444, 19–32 (2020).
Vann, S. D. Transient spatial deficit associated with bilateral lesions of the lateral mammillary nuclei. Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 820–824 (2005).
Dillingham, C. M. & Vann, S. D. Why isn’t the head direction system necessary for direction? lessons from the lateral mammillary nuclei. Front. Neur. Circ. 13, 60 (2019).
van Groen, T., Kadish, I. & Wyss, J. M. Role of the anterodorsal and anteroventral nuclei of the thalamus in spatial memory in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 132, 19–28 (2002).
Moser, E. I., Moser, M. B. & McNaughton, B. L. Spatial representation in the hippocampal formation: a history. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 1448–1464 (2017).
Matulewicz, P. et al. Proximal perimeter encoding in the rat rostral thalamus. Sci. Rep. 9, 2568 (2019).
Jankowski, M. M. et al. Evidence for spatially-responsive neurons in the rostral thalamus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 9, 256 (2015).
Tsanov, M. et al. Theta-modulated head direction cells in the rat anterior thalamus. J. Neurosci. 31, 9489–9502 (2011).
Horikawa, K., Kinjo, N., Stanley, L. C. & Powell, E. W. Topographic organization and collateralization of the projections of the anterior and laterodorsal thalamic nuclei to cingulate areas 24 and 29 in the rat. Neurosci. Res. 6, 31–44 (1988).
Gibson, W. S. et al. Anterior thalamic deep brain stimulation: functional activation patterns in a large animal model. Brain Stim 9, 770–773 (2016).
Horner, A. J., Bisby, J. A., Wang, A., Bogus, K. & Burgess, N. The role of spatial boundaries in shaping long-term event representations. Cognition 154, 151–164 (2016).
Tsanov, M. et al. Differential regulation of synaptic plasticity of the hippocampal and the hypothalamic inputs to the anterior thalamus. Hippocampus 21, 1–8 (2011).
Bauch, E. M. et al. Theta oscillations underlie retrieval success effects in the nucleus accumbens and anterior thalamus: evidence from human intracranial recordings. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 155, 104–112 (2018).
Sweeney-Reed, C. M. et al. Corticothalamic phase synchrony and cross-frequency coupling predict human memory formation. Elife 3, e05352 (2014).
Sweeney-Reed, C. M. et al. Thalamic theta phase alignment predicts human memory formation and anterior thalamic cross-frequency coupling. Elife 4, e07578 (2015).
Sweeney-Reed, C. M. et al. The role of the anterior nuclei of the thalamus in human memory processing. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 126, 146–158 (2021).
Li, A. W. & King, J. Spatial memory and navigation in ageing: a systematic review of MRI and fMRI studies in healthy participants. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 103, 33–49 (2019).
Fritch, H. A. et al. The anterior hippocampus is associated with spatial memory encoding. Brain Res. 1732, 146696 (2020).
Petersen, R. C. et al. Memory and MRI-based hippocampal volumes in aging and AD. Neurology 54, 581–581 (2000).
Rugg, M. D. et al. Item memory, context memory and the hippocampus: fMRI evidence. Neuropsychologia 50, 3070–3079 (2012).
Hou, M., De Chastelaine, M., Jayakumar, M., Donley, B. E. & Rugg, M. D. Recollection-related hippocampal fMRI effects predict longitudinal memory change in healthy older adults. Neuropsychologia 146, 107537 (2020).
Geier, K. T., Buchsbaum, B. R., Parimoo, S. & Olsen, R. K. The role of anterior and medial dorsal thalamus in associative memory encoding and retrieval. Neuropsychologia 148, 107623 (2020).
Spets, D. S. & Slotnick, S. D. Thalamic functional connectivity during spatial long-term memory and the role of sex. Brain Sci. 10, 898 (2020).
Kafkas, A., Mayes, A. R. & Montaldi, D. Thalamic-medial temporal lobe connectivity underpins familiarity memory. Cereb. Cortex 30, 3827–3837 (2020).
Pergola, G., Ranft, A., Mathias, K. & Suchan, B. The role of the thalamic nuclei in recognition memory accompanied by recall during encoding and retrieval: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 74, 195–208 (2013).
Su, J. H. et al. Thalamus optimized multi atlas segmentation (Thomas): fast, fully automated segmentation of thalamic nuclei from structural MRI. Neuroimage 194, 272–282 (2019).
Choi, S. H., Kim, Y. B., Paek, S. H. & Cho, Z. H. Papez circuit observed by in vivo human brain with 7.0T MRI super-resolution track density imaging and track tracing. Front. Neuroanat. 13, 17 (2019).
Iglehart, C., Monti, M., Cain, J., Tourdias, T. & Saranathan, M. A systematic comparison of structural-, structural connectivity-, and functional connectivity-based thalamus parcellation techniques. Brain Struct. Funct. 225, 1631–1642 (2020).
Albo, Z., Di Prisco, G. V. & Vertes, R. P. Anterior thalamic unit discharge profiles and coherence with hippocampal theta rhythm. Thal. Relat. Syst. 2, 133–144 (2003).
Phillips, J. W. et al. A repeated molecular architecture across thalamic pathways. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1925–1935 (2019).
Aggleton, J. P., Hunt, P. R., Nagle, S. & Neave, N. The effects of selective lesions within the anterior thalamic nuclei on spatial memory in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 81, 189–198 (1996).
Byatt, G. & Dalrymple-Alford, J. C. Both anteromedial and anteroventral thalamic lesions impair radial-maze learning in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 110, 1335–1348 (1996).
Wilton, L. A. K., Baird, A. L., Muir, J. L., Honey, R. C. & Aggleton, J. P. Loss of the thalamic nuclei for “head direction” impairs performance on spatial memory tasks in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 115, 861–869 (2001).
Cullen, K. E. & Taube, J. S. Our sense of direction: progress, controversies and challenges. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 1465–1473 (2017).
Viejo, G. & Peyrache, A. Precise coupling of the thalamic head-direction system to hippocampal ripples. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–14 (2020).
van Groen, T., Kadish, I. & Wyss, J. M. Efferent connections of the anteromedial nucleus of the thalamus of the rat. Brain Res. Rev. 30, 1–26 (1999).
Barbas, H., Henion, T. H. & Dermon, C. R. Diverse thalamic projections to the prefrontal cortex in the rhesus monkey. J. Comp. Neurol. 313, 65–94 (1991).
Shibata, H. & Naito, J. Organization of anterior cingulate and frontal cortical projections to the anterior and laterodorsal thalamic nuclei in the rat. Brain Res. 1059, 93–103 (2005).
Wolff, M., Gibb, S. J. & Dalrymple-Alford, J. C. Beyond spatial memory: the anterior thalamus and memory for the temporal order of a sequence of odor cues. J. Neurosci. 26, 2907–2913 (2006).
Dumont, J. R. & Aggleton, J. P. Dissociation of recognition and recency memory judgments after anterior thalamic nuclei lesions in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 127, 415–431 (2013).
Bubb, E. J., Aggleton, J. P., O’Mara, S. M. & Nelson, A. J. Chemogenetics reveal an anterior cingulate–thalamic pathway for attending to task-relevant information. Cereb. Cortex 31, 2169–2186 (2021).
Kim, S. M., Ganguli, S. & Frank, L. M. Spatial information outflow from the hippocampal circuit: distributed spatial coding and phase precession in the subiculum. J. Neurosci. 32, 11539–11558 (2012).
Poulter, S., Lee, S. A., Dachtler, J., Wills, T. J. & Lever, C. Vector trace cells in the subiculum of the hippocampal formation. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 266–275 (2021).
Tsanov, M. et al. Hippocampal inputs mediate theta-related plasticity in anterior thalamus. Neuroscience 187, 52–62 (2011).
Dillingham, C. M. et al. Mammillothalamic disconnection alters hippocampocortical oscillatory activity and microstructure: implications for diencephalic amnesia. J. Neurosci. 39, 6696–6713 (2019).
Frost, B. E. et al. Anterior thalamic function is required for spatial coding in the subiculum and is necessary for spatial memory. J. Neurosci. 41, 6511–6525 (2021).
Hani, S. A. H. B., Al-Haidari, M. H. & Saboba, M. M. Neuronal types in the human anterior ventral thalamic nucleus: a Golgi study. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 27, 745–755 (2007).
Gaffan, D. & Gaffan, E. A. Amnesia in man following transection of the fornix: a review. Brain 114, 2611–2618 (1991).
Aggleton, J. P. et al. Differential cognitive effects of colloid cysts in the third ventricle that spare or compromise the fornix. Brain 123, 800–815 (2000).
Warburton, E. C., Baird, A. L., Morgan, A., Muir, J. L. & Aggleton, J. P. Disconnecting hippocampal projections to the anterior thalamus produces deficits on tests of spatial memory in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 12, 1714–1726 (2000).
Henry, J., Petrides, M., St-Laurent, M. & Sziklas, V. Spatial conditional associative learning: effects of thalamo-hippocampal disconnection in rats. Neuroreport 15, 2427–2431 (2004).
Kitanishi, T., Umaba, R. & Mizuseki, K. Robust information routing by dorsal subiculum neurons. Sci. Adv. 7, eabf1913 (2021).
Rudebeck, S. R. et al. Fornix microstructure correlates with recollection but not familiarity memory. J. Neurosci. 29, 14987–14992 (2009).
Metzler-Baddeley, C., Jones, D. K., Belaroussi, B., Aggleton, J. P. & O’Sullivan, M. J. Frontotemporal connections in episodic memory and aging: a diffusion MRI tractography study. J. Neurosci. 31, 13236–13245 (2011).
Hartopp, N. et al. A key role for subiculum-fornix connectivity in recollection in older age. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 12, 70 (2019).
Hodgetts, C. J. et al. The role of the fornix in human navigational learning. Cortex 124, 97–110 (2020).
Christiansen, K. et al. The status of the precommissural and postcommissural fornix in normal ageing and mild cognitive impairment: an MRI tractography study. NeuroImage 130, 35–47 (2016).
Coad, B. M. et al. Precommissural and postcommissural fornix microstructure in healthy aging and cognition. Brain Neurosci. Adv. 4, 2398212819899316 (2020).
Commins, S., Gigg, J., Anderson, M. & O’Mara, S. M. Interaction between paired-pulse facilitation and long-term potentiation in the projection from hippocampal area CA1 to the subiculum. Neuroreport 9, 4109–4113 (1998).
Liu, J. et al. Anterior thalamic stimulation improves working memory precision judgments. Brain Stim 14, 1073–1080 (2021).
Xiao, D. & Barbas, H. Pathways for emotions and memory II. Afferent input to the anterior thalamic nuclei from prefrontal, temporal, hypothalamic areas and the basal ganglia in the rhesus monkey. Thal. Relat. Syst. 2, 33–48 (2002).
Jones, B. F. & Witter, M. P. Cingulate cortex projections to the parahippocampal region and hippocampal formation in the rat. Hippocampus 17, 957–976 (2007).
Sugar, J., Witter, M. P., van Strien, N. & Cappaert, N. The retrosplenial cortex: intrinsic connectivity and connections with the (para) hippocampal region in the rat. An interactive connectome. Front. Neuroinf. 5, 7 (2011).
Dillingham, C. M., Milczarek, M. M., Perry, J. C. & Vann, S. D. Time to put the mammillothalamic pathway into context. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 121, 60–74 (2021).
Poirier, G. L. et al. Anterior thalamic lesions produce chronic and profuse transcriptional de-regulation in retrosplenial cortex: a model of retrosplenial hypoactivity and covert pathology. Thal. Relat. Syst. 4, 59–77 (2008).
Poirier, G. L. & Aggleton, J. P. Post-surgical interval and lesion location within the limbic thalamus determine extent of retrosplenial cortex hypoactivity. Neuroscience 160, 452–469 (2009).
Vann, S. D. Dismantling the Papez circuit for memory in rats. Elife 2, e00736 (2013).
Yamawaki, N., Corcoran, K. A., Guedea, A. L., Shepherd, G. M. & Radulovic, J. Differential contributions of glutamatergic hippocampal→retrosplenial cortical projections to the formation and persistence of context memories. Cereb. Cortex 29, 2728–2736 (2019).
Aggleton, J. P. Multiple anatomical systems embedded within the primate medial temporal lobe: implications for hippocampal function. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36, 1579–1596 (2012).
Jay, T. M. & Witter, M. P. Distribution of hippocampal CA1 and subicular efferents in the prefrontal cortex of the rat studied by means of anterograde transport of Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin. J. Comp. Neurol. 313, 574–586 (1991).
Raichle, M. E. The brain’s default mode network. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 38, 433–447 (2015).
Mak, L. E. et al. The default mode network in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Conn. 7, 25–33 (2017).
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Reidler, J. S., Sepulcre, J., Poulin, R. & Buckner, R. L. Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain’s default network. Neuron 65, 550–562 (2010).
Wen, T., Mitchell, D. J. & Duncan, J. The functional convergence and heterogeneity of social, episodic, and self-referential thought in the default mode network. Cereb. Cortex 30, 5915–5929 (2020).
Yeshurun, Y., Nguyen, M. & Hasson, U. The default mode network: where the idiosyncratic self meets the shared social world. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 181–192 (2021).
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R. & Schacter, D. L. in The Year in Cognitive Neuroscience (eds. Kingstone, A. & Miller, M. B.) 1–38 (Blackwell, 2008).
Schacter, D. L., Addis, D. R. & Buckner, R. L. Remembering the past to imagine the future: the prospective brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 657–661 (2007).
Schacter, D. L. et al. The future of memory: remembering, imagining, and the brain. Neuron 76, 677–694 (2012).
Alves, P. N. et al. An improved neuroanatomical model of the default-mode network reconciles previous neuroimaging and neuropathological findings. Comm. Biol. 2, 370 (2019).
Li, J. et al. Mapping the subcortical connectivity of the human default mode network. NeuroImage 245, 118758 (2021).
Jones, D. T., Mateen, F. J., Lucchinetti, C. F., Jack, C. R. & Welker, K. M. Default mode network disruption secondary to a lesion in the anterior thalamus. Arch. Neurol. 68, 242–247 (2011).
Middlebrooks, E. H. et al. Functional activation patterns of deep brain stimulation of the anterior nucleus of the thalamus. World Neurosurg. 136, 357–363 (2020).
Kaboodvand, N., Bäckman, L., Nyberg, L. & Salami, A. The retrosplenial cortex: a memory gateway between the cortical default mode network and the medial temporal lobe. Hum. Brain Map. 39, 2020–2034 (2018).
Garden, D. L. et al. Anterior thalamic lesions stop synaptic plasticity in retrosplenial cortex slices: expanding the pathology of diencephalic amnesia. Brain 132, 1847–1857 (2009).
Williams, A. N. et al. The role of the pre-commissural fornix in episodic autobiographical memory and simulation. Neuropsychologia 142, 107457 (2020).
Corkin, S. Beware of frontal lobe deficits in hippocampal clothing. Trends Cogn. Sci. 5, 321–323 (2001).
Hermann, B. & Seidenberg, M. Executive system dysfunction in temporal lobe epilepsy: effects of nociferous cortex versus hippocampal pathology. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsych 17, 809–819 (1995).
Pearce, J. M. & Mackintosh, N. J. in Attention and Associative Learning: From Brain to Behaviour (eds. Mitchell, C. & Le Pelley, M.) 11–39 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2010).
Dias, R., Robbins, T. W. & Roberts, A. C. Dissociation in prefrontal cortex of affective and attentional shifts. Nature 380, 69–72 (1996).
Birrell, J. M. & Brown, V. J. Medial frontal cortex mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in the rat. J. Neurosci. 20, 4320–4324 (2000).
Barbas, H. & Zikopoulos, B. The prefrontal cortex and flexible behavior. Neuroscientist 13, 532–545 (2007).
Marquis, J. P., Goulet, S. & Doré, F. Y. Neonatal ventral hippocampus lesions disrupt extra-dimensional shift and alter dendritic spine density in the medial prefrontal cortex of juvenile rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 90, 339–346 (2008).
Nelson, A. J. The anterior thalamic nuclei and cognition: a role beyond space? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 126, 1–11 (2021).
Wolff, M., Alcaraz, F., Marchand, A. R. & Coutureau, E. Functional heterogeneity of the limbic thalamus: from hippocampal to cortical functions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 120–130 (2015).
Albasser, M. M., Amin, E., Lin, T. C. E., Iordanova, M. D. & Aggleton, J. P. Evidence that the rat hippocampus has contrasting roles in object recognition memory and object recency memory. Behav. Neurosci. 126, 659–669 (2012).
Dupire, A. et al. A role for anterior thalamic nuclei in affective cognition: interaction with environmental conditions. Hippocampus 23, 392–404 (2013).
Gabriel, M. & Talk, A. C. in Model Systems and the Neurobiology of Associative Learning: A Festschrift in Honor of Richard F. Thompson (eds. Steinmetz, J. E. Gluck, M. A. & Solomon, P. R.) 149–185 (Lawrence Erlbaum, 2001).
Shin, J. N., Doron, G. & Larkum, M. E. Memories off the top of your head. Science 374, 538–539 (2021).
Witter, M. P. & Groenewegen, H. J. Connections of the parahippocampal cortex in the cat. III. Cortical and thalamic efferents. J. Comp. Neurol. 252, 1–31 (1986).
Brennan, E. K. et al. Thalamus and claustrum control parallel layer 1 circuits in retrosplenial cortex. eLife 10, e62207 (2021).
Kinnavane, L., Vann, S. D., Nelson, A. J., O’Mara, S. M. & Aggleton, J. P. Collateral projections innervate the mammillary bodies and retrosplenial cortex: a new category of hippocampal cells. eNeuro 5, ENEURO.0383-17.2018 2018.
Zoppelt, D., Koch, B., Schwarz, M. & Daum, I. Involvement of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in mediating recollection and familiarity. Neuropsychologia 41, 1160–1170 (2003).
Danet, L. et al. Medial thalamic stroke and its impact on familiarity and recollection. Elife 6, e28141 (2017).
Carlesimo, G. A., Lombardi, M. G., Caltagirone, C. & Barban, F. Recollection and familiarity in the human thalamus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 54, 18–28 (2015).
Grodd, W., Kumar, V. J., Schüz, A., Lindig, T. & Scheffler, K. The anterior and medial thalamic nuclei and the human limbic system: tracing the structural connectivity using diffusion-weighted imaging. Sci. Rep. 10, 10957 (2020).
Gagnepain, P. et al. Collective memory shapes the organization of individual memories in the medial prefrontal cortex. Nat. Hum. Behav. 4, 189–200 (2020).
Barnett, S. C. et al. Anterior thalamic nuclei neurons sustain memory. Curr. Res. Neurobiol. 2, 100022 (2021).
Swanson, L. W. & Cowan, W. M. An autoradiographic study of the organization of the efferent connections of the hippocampal formation in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 172, 49–84 (1977).
van Groen, T. & Wyss, J. M. Connections of the retrosplenial granular a cortex in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 300, 593–606 (1990).
van Groen, T. & Wyss, J. M. Connections of the retrosplenial dysgranular cortex in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 315, 200–216 (1992).
Shibata, H. Topographic organization of subcortical projections to the anterior thalamic nuclei in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 323, 117–127 (1992).
Lozsádi, D. A. Organization of connections between the thalamic reticular and the anterior thalamic nuclei in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 358, 233–246 (1995).
Bartsch, T. & Butler, C. Transient amnesic syndromes. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 9, 86–97 (2013).
Jankowski, M. M. et al. The anterior thalamus provides a subcortical circuit supporting memory and spatial navigation. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 7, 45 (2013).
Acknowledgements
J.P.A. and S.M.O’M. are supported in the work described here by the Wellcome Trust (103722/Z14/Z). We thank S. Commins, S. Martin, A. Nelson and C. Ranganath for very helpful feedback on a prior version of the manuscript. We also thank M. M. Jankowski for assistance with Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Neuroscience thanks J. Dalrymple-Alford, M. Wolff and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggleton, J.P., O’Mara, S.M. The anterior thalamic nuclei: core components of a tripartite episodic memory system. Nat Rev Neurosci 23, 505–516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-022-00591-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-022-00591-8
This article is cited by
-
Comparing episodic memory outcomes from walking augmented reality and stationary virtual reality encoding experiences
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Sensory and behavioral modulation of thalamic head-direction cells
Nature Neuroscience (2024)
-
Lateralized brunt of sleep deprivation on white matter injury in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease
GeroScience (2023)
-
The human thalamus orchestrates neocortical oscillations during NREM sleep
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Characterizing functional modules in the human thalamus: coactivation-based parcellation and systems-level functional decoding
Brain Structure and Function (2022)