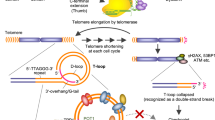
Abstract
Quadruplex nucleic acids — helical four-stranded structures known to form from guanine-rich nucleic acid sequences through Hoogsteen-type hydrogen bonding — were once just laboratory curiosities. However, they are now emerging from this rather obscure status to become important targets for small-molecule drugs, which can stabilize the quadruplex structures and thereby promote selective downregulation of gene expression and telomerase inhibition, and also activate DNA damage responses. Most of these quadruplex-binding small molecules can stabilize a range of cellular quadruplexes, as well as clusters of quadruplexes within a single gene or telomere, which could be an advantage. This widespread stabilization can generate a polygene response, and thus is able to simultaneously affect several key driver genes in human cancers, with potential therapeutic benefit.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hargrove, A. E. et al. Tumor repression of VCaP xenografts by a pyrrole–imidazole polyamide. PLoS ONE 10, e0143161 (2015).
Flynn, M. J. et al. ADCT-301, a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer-containing antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) targeting CD25-expressing hematological malignancies. Mol. Cancer Ther. 15, 2709–2721 (2016).
Gellert, M., Lipsett, M. N. & Davies, D. R. Helix formation by guanylic acid. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 48, 2013–2018 (1962).
Bhattacharyya, D., Mirihana Arachchilage, G. & Basu, S. Metal cations in G-quadruplex folding and stability. Front. Chem. 4, 38 (2016).
Henderson, E., Hardin, C. C., Walk, S. K., Tinoco, I. Jr & Blackburn, E. H. Telomeric DNA oligonucleotides form novel intramolecular structures containing guanine–guanine base pairs. Cell 51, 899–908 (1987).
Sen, D. & Gilbert, W. Formation of parallel four-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature 334, 364–366 (1988).
Sundquist, W. I. & Klug, A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature 342, 825–829 (1989).
Simonsson, T., Pecinka, P. & Kubista, M. DNA tetraplex formation in the control region of c-myc. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 1167–1172 (1998).
Laughlan, G. et al. The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex. Science 265, 520–524 (1994).
Wang, Y. & Patel, D. J. Solution structure of the human telomeric repeat d[AG3(T2AG3)3] G-tetraplex. Structure 1, 263–282 (1993).
Burge, S., Parkinson, G. N., Hazel, P., Todd, A. K. & Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 5402–5415 (2006).
Adrian, M., Heddi, B. & Phan, A. T. NMR spectroscopy of G-quadruplexes. Methods 57, 11–24 (2012).
Parkinson, G. N., Lee, M. P. & Neidle, S. Crystal structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA. Nature 417, 876–880 (2002).
Luu, K. N. et al. Structure of the human telomere in K+ solution: an intramolecular (3 + 1) G-quadruplex scaffold. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 9963–9970 (2006).
Brcˇic´, J. & Plavec, J. Solution structure of a DNA quadruplex containing ALS and FTD related GGGGCC repeat stabilized by 8-bromodeoxyguanosine substitution. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 8590–8600 (2015).
Vasilyev, N. et al. Crystal structure reveals specific recognition of a G-quadruplex RNA by a β-turn in the RGG motif of FMRP. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 5391–5400 (2015).
De Nicola, B. et al. Structure and possible function of a G-quadruplex in the long terminal repeat of the proviral HIV-1 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 6442–6451 (2016).
Dai, J., Carver, M., Punchihewa, C., Jones, R. A. & Yang, D. Structure of the hybrid-2 type intramolecular human telomeric G-quadruplex in K+ solution: insights into structure polymorphism of the human telomeric sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 4927–4740 (2007).
Lim, K. W. et al. Structure of the human telomere in K+ solution: a stable basket-type G-quadruplex with only two G-tetrad layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 4301–4309 (2009).
Heddi, B. & Phan, A. T. Structure of human telomeric DNA in crowded solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 9824–9833 (2013).
Monchaud, D. & Teulade-Fichou, M.-P. A hitchhiker's guide to G-quadruplex ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 6, 627–636 (2008).
Müller, S. & Rodriguez, R. G-Quadruplex interacting small molecules and drugs: from bench towards bedside. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 7, 663–679 (2014).
Islam, M. K., Jackson, P. J., Rahman, K. M. & Thurston, D. E. Recent advances in targeting the telomeric G-quadruplex DNA sequence with small molecules as a strategy for anticancer therapies. Future Med. Chem. 8, 1259–1290 (2016).
Kejnovská, I., Vorlícˇková, M., Brázdová, M. & Sagi, J. Stability of human telomere quadruplexes at high DNA concentrations. Biopolymers 101, 428–438 (2014).
Liu, H. Y. et al. Conformation selective antibody enables genome profiling and leads to discovery of parallel G-quadruplex in human telomeres. Cell Chem. Biol. 23, 1261–1270 (2016).
Moye, A. L. et al. Telomeric G-quadruplexes are a substrate and site of localization for human telomerase. Nat. Commun. 6, 7643 (2015).
Wright, W. E., Tesmer, V. M., Huffman, K. E., Levene, S. D. & Shay, J. W. Normal human chromosomes have long G-rich telomeric overhangs at one end. Genes Dev. 11, 2801–2809 (1997).
Zaug, A. J. Podell, E. R. & Cech, T. R. Human POT1 disrupts telomeric G-quadruplexes allowing telomerase extension in vitro .. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10864–10869 (2005).
Yu, H. Q., Miyoshi, D. & Sugimoto, N. Characterization of structure and stability of long telomeric DNA G-quadruplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 15461–15468 (2006).
Bugaut, A. & Alberti, P. Understanding the stability of DNA G-quadruplex units in long human telomeric strands. Biochimie 113, 125–133 (2015).
Haider, S. M. & Neidle, S. A molecular model for drug binding to tandem repeats of telomeric G-quadruplexes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 37, 583–588 (2009).
Petraccone, L. et al. Structure and stability of higher-order human telomeric quadruplexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 20951–20961 (2011).
Sun, D. et al. Inhibition of human telomerase by a G-quadruplex-interactive compound. J. Med. Chem. 40, 2113–2116 (1997).
Campbell, N. H., Parkinson, G. N., Reszka, A. P. & Neidle, S. Structural basis of DNA quadruplex recognition by an acridine drug. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 6722–6724 (2008).
Burger, A. M. et al. The G-quadruplex-interactive molecule BRACO-19 inhibits tumor growth, consistent with telomere targeting and interference with telomerase function. Cancer Res. 65, 1489–1496 (2005).
Zhou, G. et al. Telomere targeting with a novel G-quadruplex-interactive ligand BRACO-19 induces T-loop disassembly and telomerase displacement in human glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 7, 14925–14939 (2016).
Brown, J. S., O'Carrigan, B., Jackson, S. P. & Yap, T. A. Targeting DNA repair in cancer: beyond PARP inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 7, 20–37 (2017).
Cookson, J. C. et al. Pharmacodynamics of the G-quadruplex-stabilizing telomerase inhibitor 3,11-difluoro-6,8,13-trimethyl-8H-quino[4,3,2-kl] acridinium methosulfate (RHPS4) in vitro: activity in human tumor cells correlates with telomere length and can be enhanced, or antagonized, with cytotoxic agents. Mol. Pharmacol. 68, 1551–1558 (2005).
Salvati, E. et al. Telomere damage induced by the G-quadruplex ligand RHPS4 has an antitumor effect. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 3236–3247 (2007).
Salvati, E. et al. PARP1 is activated at telomeres upon G4 stabilization: possible target for telomere-based therapy. Oncogene 29, 6280–6293 (2010).
Rodriguez, R. et al. A novel small molecule that alters shelterin integrity and triggers a DNA-damage response at telomeres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 15758–15759 (2008).
Rodriguez, R. et al. Small-molecule-induced DNA damage identifies alternative DNA structures in human genes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 8, 301–310 (2012).
Müller, S. et al. Pyridostatin analogues promote telomere dysfunction and long-term growth inhibition in human cancer cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 10, 6537–6546 (2012).
Iachettini, S. et al. On and off-target effects of telomere uncapping G-quadruplex selective ligands based on pentacyclic acridinium salts. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 32, 68 (2013).
Rizzo, A. et al. Identification of novel RHPS4-derivative ligands with improved toxicological profiles and telomere-targeting activities. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 33, 81 (2014).
Chung, W. J. et al. Solution structure of an intramolecular (3 + 1) human telomeric G-quadruplex bound to a telomestatin derivative. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 13495–13501 (2013).
Siddiqui-Jain, A., Grand, C. L., Bearss, D. J. & Hurley, L. H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 11593–11598 (2002).
Balasubramanian, S., Hurley, L. H. & Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: a novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 10, 261–275 (2011).
Rigo, R., Palumbo, M. & Sissi, C. G-Quadruplexes in human promoters: a challenge for therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 4165, 30518–30519 (2016).
Todd, A. K., Johnston, M. & Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 2901–2907 (2005).
Huppert, J. L. & Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 2908–2916 (2005).
Bedrat, A., Lacroix, L. & Mergny, J.-L. Re-evaluation of G-quadruplex propensity with G4Hunter. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 1746–1759 (2016).
Chambers, V. S. et al. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 877–881 (2015).
Huppert, J. L. & Balasubramanian, S. G-Quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 406–413 (2007).
Bugaut, A. & Balasubramanian, S. 5′-UTR RNA G-quadruplexes: translation regulation and targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 4727–4741 (2012).
Maizels, N. & Gray, L. T. The G4 genome. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003468 (2013).
Murat, P. & Balasubramanian, S. Existence and consequences of G-quadruplex structures in DNA. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 25, 22–29 (2014).
Rhodes, D. & Lipps, H. J. G-Quadruplexes and their regulatory roles in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 8627–8637 (2015).
Bochman, M. L., Paeschke, K. & Zakian, V. A. DNA secondary structures: stability and function of G-quadruplex structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 770–780 (2012).
Hänsel-Hertsch, R. et al. G-Quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 48, 1267–1272 (2016).
Guo, J. U. & Bartel, D. P. RNA G-quadruplexes are globally unfolded in eukaryotic cells and depleted in bacteria. Science http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf5371 (2016).
Dai, J., Carver, M., Hurley, L. H. & Yang, D. Solution structure of a 2:1 quindoline–c-MYC G-quadruplex: insights into G-quadruplex interactive small molecule drug design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 17673–17680 (2011).
Schaffitzel, C. et al. In vitro generated antibodies specific for telomeric guanine-quadruplex DNA react with Stylonychia lemnae macronuclei. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8572–8577 (2001).
Lam, E. Y. N., Beraldi, D., Tannahill, D. & Balasubramanian, S. G-Quadruplex structures are stable and detectable in human genomic DNA. Nat. Commun. 4, 1796–1780 (2013).
Biffi, G., Tannahill, D., McCafferty, J. & Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nat. Chem. 5, 182–186 (2013).
Henderson, A. et al. Detection of G-quadruplex DNA in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, 860–869 (2013).
Biffi, G., Di Antonio, M., Tannahill, D. & Balasubramanian, S. Visualization and selective chemical targeting of RNA G-quadruplex structures in the cytoplasm of human cells. Nat. Chem. 6, 75–80 (2014).
Biffi, G., Tannahill, D., Miller, J., Howat, W. J. & Balasubramanian, S. Elevated levels of G-quadruplex formation in human stomach and liver cancer tissues. PLoS ONE 9, e102711 (2014).
Mendoza, O., Bourdoncle, A., Boulé, J.-B., Brosh, R. M. Jr & Mergny, J.-L. G-Quadruplexes and helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 1989–2006 (2016).
Tseng, T.-Y. et al. Fluorescent probe for visualizing guanine-quadruplex DNA by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 18, 101309 (2013).
Laguerre, A. et al. Visualization of RNA-quadruplexes in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 8521–8525 (2015).
Shivalingam, A. et al. The interactions between a small molecule and G-quadruplexes are visualized by fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. Nat. Commun. 6, 8178 (2015).
Doria, F. et al. A red-NIR fluorescent dye detecting nuclear DNA G-quadruplexes: in vitro analysis and cell imaging. Chem. Commun. 53, 2268–2271 (2017).
Cogoi, S. & Xodo, L. E. G4 DNA in ras genes and its potential in cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1859, 663–674 (2016).
Paulo, A. & Francisco, A. P. Oncogene expression modulation in cancer cell lines by DNA G-quadruplex-interactive small molecules. Curr. Med. Chem. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160829145055 (2016).
Phan, A. T., Kuryavyi, V., Burge, S., Neidle, S. & Patel, D. J. Structure of an unprecedented G-quadruplex scaffold in the human c-kit promoter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4386–4392 (2007).
Hsu, S. T. et al. G-Rich sequence within the c-kit oncogene promoter forms a parallel G-quadruplex having asymmetric G-tetrad dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 13399–13409 (2009).
Kuryavyi, V., Phan, A. T. & Patel, D. J. Solution structures of all parallel-stranded monomeric and dimeric G-quadruplex scaffolds of the human c-kit2 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 6757–6773 (2010).
Dai, J., Chen, D., Jones, R. A., Hurley, L. H. & Yang, D. NMR solution structure of the major G-quadruplex structure formed in the human BCL2 promoter region. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 5133–5144 (2006).
Agrawal, P., Lin, C., Mathad, R. I., Carver, M. & Yang, D. The major G-quadruplex formed in the human BCL-2 proximal promoter adopts a parallel structure with a 13-nt loop in K+ solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 1750–1753 (2014).
Agrawal, P., Hatzakis, E., Guo, K., Carver, M. & Yang, D. Solution structure of the major G-quadruplex formed in the human VEGF promoter in K+: insights into loop interactions of the parallel G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 10584–10592 (2013).
Kerkour, A. et al. High-resolution 3D NMR structure of the KRAS proto-oncogene promoter reveals key features of a G-quadruplex involved in transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.781906 (2017).
Wei, D., Parkinson, G. N., Reszka, A. P. & Neidle, S. Crystal structure of a c-kit promoter quadruplex reveals the structural role of metal ions and water molecules in maintaining loop conformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 4691–4700 (2012).
Wei, D., Husby, J. & Neidle, S. Flexibility and structural conservation in a c-KIT G-quadruplex. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 629–644 (2015).
Martino, L., Pagano, B., Fotticchia, I., Neidle, S. & Giancola, C. Shedding light on the interaction between TMPyP4 and human telomeric quadruplexes. J. Phys. Chem. B. 113, 14779–14786 (2009).
Guédin, A., Lacroix, L. & Mergny, J.-L. Thermal melting studies of ligand DNA interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 613, 25–35 (2010).
Jana, J. et al. Chelerythrine down regulates expression of VEGFA, BCL2 and KRAS by arresting G-quadruplex structures at their promoter regions. Sci. Rep. 7, 40706 (2017).
Boddupally, P. V. et al. Anticancer activity and cellular repression of c-MYC by the G-quadruplex-stabilizing 11-piperazinylquindoline is not dependent on direct targeting of the G-quadruplex in the c-MYC promoter. J. Med. Chem. 55, 6076–6086 (2012).
Brown, R. V., Danford, F. L., Gokhale, V., Hurley, L. H. & Brooks, T. A. Demonstration that drug-targeted down-regulation of MYC in non-Hodgkins lymphoma is directly mediated through the promoter G-quadruplex. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 41018–41027 (2011).
Franceschin, M. et al. Aromatic core extension in the series of N-cyclic bay-substituted perylene G-quadruplex ligands: increased telomere damage, antitumor activity, and strong selectivity for neoplastic over healthy cells. ChemMedChem 7, 2144–2154 (2012).
Porru, M. et al. Targeting G-quadruplex DNA structures by EMICORON has a strong antitumor efficacy against advanced models of human colon cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 14, 2541–2551 (2015).
Micheli, E. et al. Perylene and coronene derivatives binding to G-rich promoter oncogene sequences efficiently reduce their expression in cancer cells. Biochimie 125, 223–231 (2016).
Zimmer, J. et al. Targeting BRCA1 and BRCA2 deficiencies with G-quadruplex-interacting compounds. Mol. Cell 61, 449–460 (2016).
Micco, M. et al. Structure-based design and evaluation of naphthalene diimide G-quadruplex ligands as telomere targeting agents in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 56, 2959–2974 (2013).
Nadai, M. et al. Assessment of gene promoter G-quadruplex binding and modulation by a naphthalene diimide derivative in tumor cells. Int. J. Oncol. 46, 369–380 (2015).
Ohnmacht, S. A. et al. A G-quadruplex-binding compound showing anti-tumour activity in an in vivo model for pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 5, 11385 (2015).
Alizadeh, A. A. et al. Toward understanding and exploiting tumor heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 21, 846–853 (2015).
Jamal-Hanjani, M., Quezada, S. A., Larkin, J. & Swanton, C. Translational implications of tumor heterogeneity. Clin. Cancer Res. 21, 1258–1266 (2015).
Hänsel-Hertsch, R., Di Antonio, M. & Balasubramanian, S. DNA G-quadruplexes in the human genome: detection, functions and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.3 (2017).
Drygin, D. et al. Anticancer activity of CX-3543: a direct inhibitor of rRNA biogenesis. Cancer Res. 69, 7653–7661 (2009).
Xu, H. et al. CX-5461 is a DNA G-quadruplex stabilizer with selective lethality in BRCA1/2 deficient tumours. Nat. Commun. 8, 14432 (2017).
Workman, P., Draetta, G. F., Schellens, J. H. & Bernards, R. How much longer will we put up with $100,000 cancer drugs? Cell 168, 579–583 (2017).
Yu, H., Gu, X., Nakano, S. I., Miyoshi, D. & Sugimoto, N. Beads-on-a-string structure of long telomeric DNAs under molecular crowding conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 20060–20069 (2012).
Cousins, A. R. et al. Ligand selectivity in stabilising tandem parallel folded G-quadruplex motifs in human telomeric DNA sequences. Chem. Commun. 50, 15202–15205 (2014).
Vilar, R. et al. Dinickel–salphen complexes as binders of human telomeric dimeric G-quadruplexes. Chem. Eur. J. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/chem.201700276 (2017).
Reed, J. E., Arnal, A. A., Neidle, S. & Vilar, R. Stabilization of G-quadruplex DNA and inhibition of telomerase activity by square-planar nickel(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 5992–5993 (2006).
Funke, A., Dickerhoff, J. & Weisz, K. Towards the development of structure-selective G-quadruplex-binding indolo[3,2-b]quinolines. Chem. Eur. J. 22, 3170–3181 (2016).
Felsenstein, K. M. et al. Small molecule microarrays enable the identification of a selective, quadruplex-binding inhibitor of MYC expression. ACS Chem. Biol. 11, 139–148 (2016).
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges support from the Pancreatic Cancer Research Fund, the Medical Research Council (UK), the Wellcome Trust, Johnson & Johnson and the University College London Technology Fund, and thanks a number of colleagues for useful discussions, especially R. Angell, S. Haider, R. Vilar and S. Balasubramanian.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neidle, S. Quadruplex nucleic acids as targets for anticancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Chem 1, 0041 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-017-0041
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-017-0041
This article is cited by
-
Development and application of metallo-phthalocyanines as potent G-quadruplex DNA binders and photosensitizers
JBIC Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry (2023)
-
Improving the accuracy of the FMO binding affinity prediction of ligand-receptor complexes containing metals
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2023)
-
RHAU Peptides Specific for Parallel G-Quadruplexes: Potential Applications in Chemical Biology
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Hormonal regulation of telomerase activity and hTERT expression in steroid-regulated tissues and cancer
Cancer Cell International (2022)