Abstract
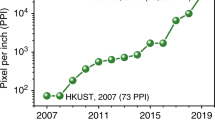
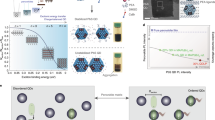
With the ever-growing demand for a greater number of pixels, next-generation displays have challenging requirements for resolution as well as colour gamut. Here, to meet this need, quantum-dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) with an ultrahigh pixel resolution of 9,072–25,400 pixels per inch are realized via transfer printing combined with the Langmuir–Blodgett film technology. To reduce the leakage current of the devices, a honeycomb-patterned layer of wide-bandgap quantum dots is embedded between the light-emitting quantum-dot pixels as a non-emitting charge barrier layer. Red and green QLEDs are demonstrated. Notably, the red devices achieve a brightness of up to 262,400 cd m−2 at an applied voltage of 8 V and a peak external quantum efficiency of 14.72%. This work provides a promising way for achieving ultrahigh-resolution QLED devices with high performance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271, 933–937 (1996).
Bae, W. K. et al. Highly efficient green-light-emitting diodes based on CdSe@ZnS quantum dots with a chemical-composition gradient. Adv. Mater. 21, 1690–1694 (2009).
Chen, O. et al. Compact high-quality CdSe–CdS core–shell nanocrystals with narrow emission linewidths and suppressed blinking. Nat. Mater. 12, 445–451 (2013).
Cho, K. S. et al. High-performance crosslinked colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat. Photon. 3, 341–345 (2009).
Dai, X., Deng, Y., Peng, X. & Jin, Y. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for large-area displays: towards the dawn of commercialization. Adv. Mater. 29, 1607022 (2017).
Li, X. Y. et al. Bright colloidal quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by efficient chlorination. Nat. Photon. 12, 159–164 (2018).
Shirasaki, Y., Supran, G. J., Bawendi, M. G. & Bulovic, V. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nat. Photon. 7, 13–23 (2013).
Yang, Y. X. et al. High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nat. Photon. 9, 259–266 (2015).
Dai, X. L. et al. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 515, 96–99 (2014).
Liu, Y. et al. Highly efficient all-solution processed inverted quantum dots based light emitting diodes. ACS Nano 12, 1564–1570 (2018).
Shen, P. Y. et al. Solution-processed double-junction quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with an EQE of over 40%. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 1065–1070 (2019).
Yang, L. Q. et al. High-performance red quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on organic electron transporting layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007686 (2021).
Zhang, Z. X. et al. High-performance, solution-processed, and insulating-layer-free light-emitting diodes based on colloidal quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 30, 1801387 (2018).
Zhu, Y. B. et al. Ultrahighly efficient white quantum dot light-emitting diodes operating at low voltage. Adv. Optical Mater. 8, 2001479 (2020).
Yang, J. et al. Toward full-color electroluminescent quantum dot displays. Nano Lett. 21, 26–33 (2021).
Mei, W. et al. High-resolution, full-color quantum dot light-emitting diode display fabricated via photolithography approach. Nano Res. 13, 2485–2491 (2020).
Kim, T.-H. et al. Full-colour quantum dot displays fabricated by transfer printing. Nat. Photon. 5, 176–182 (2011).
Yang, P., Zhang, L., Kang, D. J., Strahl, R. & Kraus, T. High-resolution inkjet printing of quantum dot light-emitting microdiode arrays. Adv. Optical Mater. 8, 1901429 (2020).
Kim, B. H. et al. High-resolution patterns of quantum dots formed by electrohydrodynamic jet printing for light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett. 15, 969–973 (2015).
Liu, Y. et al. Efficient all-solution processed quantum dot light emitting diodes based on inkjet printing technique. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 25506–25512 (2017).
Zhao, J. Y. et al. Full-color laser displays based on organic printed microlaser arrays. Nat. Commun. 10, 870 (2019).
Keum, H. et al. Photoresist contact patterning of quantum dot films. ACS Nano 12, 10024–10031 (2018).
Park, J. S. et al. Alternative patterning process for realization of large-area, full-color, active quantum dot display. Nano Lett. 16, 6946–6953 (2016).
Yang, J. et al. High-resolution patterning of colloidal quantum dots via non-destructive, light-driven ligand crosslinking. Nat. Commun. 11, 2874 (2020).
Cho, H. et al. Soft contact transplanted nanocrystal quantum dots for light-emitting diodes: effect of surface energy on device performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 10828–10833 (2015).
Choi, M. K. et al. Wearable red-green-blue quantum dot light-emitting diode array using high-resolution intaglio transfer printing. Nat. Commun. 6, 7149 (2015).
Kim, B. H. et al. Multilayer transfer printing for pixelated, multicolor quantum dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Nano 10, 4920–4925 (2016).
Linghu, C., Zhang, S., Wang, C. & Song, J. Transfer printing techniques for flexible and stretchable inorganic electronics. npj Flex. Electron. 2, 26 (2018).
Li, X., Hu, B., Du, Z., Wu, Y. & Jiang, L. Asymmetric wettability interfaces induced a large-area quantum dot microstructure toward high-resolution quantum dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 28520–28526 (2019).
Nam, T. W. et al. Thermodynamic-driven polychromatic quantum dot patterning for light-emitting diodes beyond eye-limiting resolution. Nat. Commun. 11, 3040 (2020).
Kim, L. et al. Contact printing of quantum dot light-emitting devices. Nano Lett. 8, 4513–4517 (2008).
Bourvon, H. et al. Langmuir–Schaeffer monolayers of colloidal nanocrystals for cost-efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 24, 4414–4418 (2012).
Lambert, K. et al. Langmuir−Schaefer deposition of quantum dot multilayers. Langmuir 26, 7732–7736 (2010).
Ariga, K. Don’t forget Langmuir–Blodgett films 2020: interfacial nanoarchitectonics with molecules, materials, and living objects. Langmuir 36, 7158–7180 (2020).
Lunz, M. et al. Influence of quantum dot concentration on Förster resonant energy transfer in monodispersed nanocrystal quantum dot monolayers. Phys. Rev. B 81, 205316 (2010).
Lunz, M. et al. Concentration dependence of Förster resonant energy transfer between donor and acceptor nanocrystal quantum dot layers: effect of donor-donor interactions. Phys. Rev. B 83, 115423 (2011).
Shen, T. L. et al. Coherent Förster resonance energy transfer: a new paradigm for electrically driven quantum dot random lasers. Sci. Adv. 6, 1705 (2020).
Zhu, Y. B. et al. Light-emitting memristors for optoelectronic artificial efferent nerve. Nano Lett. 21, 6087–6094 (2021).
Mashford, B. S. et al. High-efficiency quantum-dot light-emitting devices with enhanced charge injection. Nat. Photon. 7, 407–412 (2013).
Zhang, H., Su, Q. & Chen, S. Suppressing Förster resonance energy transfer in close‐packed quantum‐dot thin film: toward efficient quantum‐dot light‐emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency over 21.6%. Adv. Optical Mater. 8, 1902092 (2020).
Song, J. J. et al. Over 30% external quantum efficiency light-emitting diodes by engineering quantum dot-assisted energy level match for hole transport layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1808377 (2019).
Kim, T. H. et al. Heterogeneous stacking of nanodot monolayers by dry pick-and-place transfer and its applications in quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 4, 2637 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62075043) and Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China (2021ZZ126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F.L. conceived the core strategy of the patterning method and designed the experiment. T.M., Y. Zheng., D.Z. and Y. Zhu. carried out the patterning experiment and film characterizations. T.M., Z.X., S.J., J.J., X.C. and H.G. fabricated the QLEDs and analysed their performance. F.L., H.H., K.Y., T.G. and L.Q. discussed the experimental results. F.L., T.M. and H.H. prepared the manuscript. F.L., J.F. and L.Q. revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Photonics thanks Zhaojun Liu, Manuel Alejandro Triana Valencia and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, T., Zheng, Y., Zhao, D. et al. Ultrahigh-resolution quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat. Photon. 16, 297–303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-022-00960-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-022-00960-w
This article is cited by
-
Stable and efficient pure blue quantum-dot LEDs enabled by inserting an anti-oxidation layer
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Body-conformable light-emitting materials and devices
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
Efficient blue electroluminescence from reduced-dimensional perovskites
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
High-performance all-solution-processed inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes enabled by water treatment
Nano Research (2023)
-
High-resolution light-emitting devices for display applications
Science China Materials (2023)