Abstracte
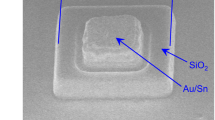
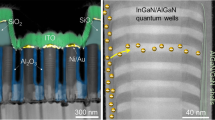
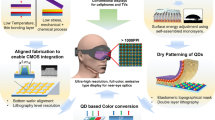
InGaN-based blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs), with their high efficiency and brightness, are entering the display industry. However, a significant gap remains between the expectation of highly efficient light sources and their experimental realization into tiny pixels for ultrahigh-density displays for augmented reality. Herein, we report using tailored ion implantation (TIIP) to fabricate highly efficient, electrically-driven pixelated InGaN micro-LEDs (μLEDs) at the mid-submicrometre scale (line/space of 0.5/0.5 μm), corresponding to 8,500 pixels per inch (ppi) (RGB). Creating a laterally confined non-radiative region around each pixel with a controlled amount of mobile vacancies, TIIP pixelation produces relatively invariant luminance, and high pixel distinctiveness, at submicrometre-sized pixels. Moreover, with the incomparable integration capability of TIIP pixelation due to its planar geometry, we demonstrate 2,000 ppi μLED displays with monolithically integrated thin-film transistor pixel circuits, and 5,000 ppi compatible core technologies. We expect that the demonstrated method will pave the way toward high-performance μLED displays for seamless augmented-reality glasses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Choi, J. H. et al. Nearly single-crystalline GaN light-emitting diodes on amorphous glass substrates. Nat. Photon. 5, 763–769 (2011).
Choi, J. H. et al. Fully flexible GaN light‐emitting diodes through nanovoid‐mediated transfer. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2, 267–274 (2014).
Ding, K., Avrutin, V., Izyumskaya, N., Özgür, Ü. & Morkoç, H. Micro-LEDs, a manufacturability perspective. Appl. Sci. 9, 1206 (2019).
Kang, C. et al. Monolithic integration of AlGaInP-based red and InGaN-based green LEDs via adhesive bonding for multicolor emission. Sci. Rep. 7, 10333 (2017).
Kang, C.-M. et al. Fabrication of a vertically-stacked passive-matrix micro-LED array structure for a dual color display. Opt. Express 25, 2489–2495 (2017).
Yadavalli, K., Chuang, C.-L. & El-Ghoroury, H. S. Monolithic and heterogeneous integration of RGB micro-LED arrays with pixel-level optics array and CMOS image processor to enable small form-factor display applications. Proc. SPIE 11310, 113100Z (2020).
Gou, F. et al. High performance color‐converted micro‐LED displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 27, 199–206 (2019).
Na, J.-S., Hong, S.-K. & Kwon, O.-K. A 4410-ppi resolution pixel circuit for high luminance uniformity of OLEDOS microdisplays. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 7, 1026–1032 (2019).
Huang, Y., Liao, E., Chen, R. & Wu, S.-T. Liquid-crystal-on-silicon for augmented reality displays. Appl. Sci. 8, 2366 (2018).
Olivier, F., Daami, A., Licitra, C. & Templier, F. Shockley–Read–Hall and Auger non-radiative recombination in GaN based LEDs: a size effect study. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 022104 (2017).
Kou, J. et al. Impact of the surface recombination on InGaN/GaN-based blue micro-light emitting diodes. Opt. Express 27, A643–A653 (2019).
Qian, F. et al. Multi-quantum-well nanowire heterostructures for wavelength-controlled lasers. Nat. Mater. 7, 701–706 (2008).
Lim, W. et al. SiO2 nanohole arrays with high aspect ratio for InGaN/GaN nanorod-based phosphor-free white light-emitting-diodes. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 34, 042204 (2016).
Kum, H. et al. Wafer-scale thermodynamically stable GaN nanorods via two-step self-limiting epitaxy for optoelectronic applications. Sci. Rep. 7, 40893 (2017).
Hook, T. B. et al. Lateral ion implant straggle and mask proximity effect. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 50, 1946–1951 (2003).
Sheu,Y.-M. et al. Modeling the well edge proximity effect in highly-scaled MOSFETs. In Proc. Custom Integrated Circuits Conference 831–834 (IEEE, 2005).
Polishchuk, I., Mathur, N., Sandstrom, C., Manos, P. & Pohland O. CMOS Vt-control improvement through implant lateral scatter elimination. In IEEE International Symposium on Semiconductor Manufacturing (IEEE, 2005).
Lulli, G. Two-dimensional simulation of undermask penetration in 4H-SiC implanted with Al+ ions. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 58, 190–194 (2011).
Lazar, M., Laariedh, F., Cremillieu, P., Planson, D. & Leclercq, J.-L. The channeling effect of Al and N ion implantation in 4H–SiC during JFET integrated device processing. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 365, 256–259 (2015).
Müting, J., Bobal, V., Azarov, A., Svensson, B. G. & Grossner, U. Lateral straggling of ion implantation distributions in 4H-SiC investigated by SIMS. Mater. Sci. Forum 963, 437–440 (2019).
Müting, J., Bobal, V., Sky, T. N., Vines, L. & Grossner, U. Lateral straggling of implanted aluminum in 4H-SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, 012101 (2020).
Majid, A., Zhu, J. J., Rana, U. A. & Khan, S. U.-D. Resonant Raman scattering study of V, Cr and Co ions implanted into GaN. RSC Adv. 6, 73589–73594 (2016).
Kucheyev, S. O. et al. Cathodoluminescence depth profiling of ion-implanted GaN. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 34–36 (2001).
Slotte, J. et al. Fluence, flux, and implantation temperature dependence of ion-implantation-induced defect production in 4H–SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 033513 (2005).
Kucheyev, O. J., Williams, S., Jagadish, C., Zou, J. & Li, G. Surface disordering and nitrogen loss in GaN under ion bombardment. Phys. Rev. B 62, 7510–7522 (2000).
Liu, Z., Ma, J., Huang, T., Liu, C. & Lau, K. M. Selective epitaxial growth of monolithically integrated GaN-based light emitting diodes with AlGaN/GaN driving transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 091103 (2014).
Hwang, I. et al. p-GaN gate HEMTS with tungsten gate metal for high threshold voltage and low gate current. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 34, 202–204 (2013).
Chung, D.-S. et al. Carbon nanotube electron emitters with a gated structure using backside exposure processes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 4045–4047 (2002).
Ramm, P. et al. (eds) Handbook of Wafer Bonding (Wiley, 2012).
Kim, J.-H., Lee, S.-J. & Park, S.-H. InGaN-based resonant-cavity light-emitting diodes with a ZrO2/SiO2 distributed Bragg reflector and metal reflector. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 49, 122102 (2010).
Won, Y. et al. Highly efficient and stable InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature 575, 634–638 (2019).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Lee, K. Kim and S. Heo for the 2D SIMS, XRD and DLTS analyses for characterizing ion-implanted samples, respectively, and useful discussions. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (no. 2017R1A2B3011629 and no. 2020R1A5A6017701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.P. performed the main IIP experiment and characterization. J.H.C. designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. K.K. designed the pixel-driving circuitry. J.H.H., J.H.P., N.K., E.L., D.K., J.K., D.C. and S.J. fabricated and characterized the EL devices. M.K. guided the theoretical investigations and edited the manuscript. E.Y. guided the experimental investigations. J.S. and S.H. designed the project. All authors provided feedback.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Photonics thanks Ulrich Schwarz and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figs. 1–13, discussion and Tables 1 and 2.
Supplementary Video 1
Moving image 1 of 300 ppi prototype.
Supplementary Video 2
Moving image 2 of 300 ppi prototype.
Supplementary Video 3
Moving image 3 of 2,000 ppi prototype.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Choi, J.H., Kong, K. et al. Electrically driven mid-submicrometre pixelation of InGaN micro-light-emitting diode displays for augmented-reality glasses. Nat. Photonics 15, 449–455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00783-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00783-1
This article is cited by
-
Improved electrical properties of micro light-emitting diode displays by ion implantation technology
Discover Nano (2023)
-
Ultra-low-current driven InGaN blue micro light-emitting diodes for electrically efficient and self-heating relaxed microdisplay
Nature Communications (2023)
-
MicroLEDs get in line
Nature Electronics (2023)
-
Monolithic full-color active-matrix micro-LED micro-display using InGaN/AlGaInP heterogeneous integration
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
3.5 × 3.5 μm2 GaN blue micro-light-emitting diodes with negligible sidewall surface nonradiative recombination
Nature Communications (2023)