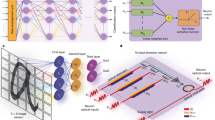
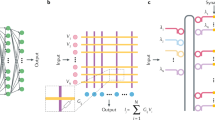
Abstract
Research in photonic computing has flourished due to the proliferation of optoelectronic components on photonic integration platforms. Photonic integrated circuits have enabled ultrafast artificial neural networks, providing a framework for a new class of information processing machines. Algorithms running on such hardware have the potential to address the growing demand for machine learning and artificial intelligence in areas such as medical diagnosis, telecommunications, and high-performance and scientific computing. In parallel, the development of neuromorphic electronics has highlighted challenges in that domain, particularly related to processor latency. Neuromorphic photonics offers sub-nanosecond latencies, providing a complementary opportunity to extend the domain of artificial intelligence. Here, we review recent advances in integrated photonic neuromorphic systems, discuss current and future challenges, and outline the advances in science and technology needed to meet those challenges.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y. & Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444 (2015).
Wu, Y. et al. Google’s neural machine translation system: bridging the gap between human and machine translation. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1609.08144 (2016).
Capper, D. et al. DNA methylation-based classification of central nervous system tumours. Nature 555, 469–474 (2018).
Merolla, P. A. et al. A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 345, 668–673 (2014).
Davies, M. et al. Loihi: a neuromorphic manycore processor with on-chip learning. IEEE Micro 38, 82–99 (2018).
Keyes, R. W. Optical logic-in the light of computer technology. Opt. Acta 32, 525–535 (1985).
Prucnal, P. R. & Shastri, B. J. Neuromorphic Photonics (CRC, 2017).
Magesan, E., Gambetta, J. M., Corcoles, A. D. & Chow, J. M. Machine learning for discriminating quantum measurement trajectories and improving readout. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 200501 (2015).
Radovic, A. et al. Machine learning at the energy and intensity frontiers of particle physics. Nature 560, 41–48 (2018).
Duarte, J. et al. Fast inference of deep neural networks in FPGAs for particle physics. J. Instrum. 13, P07027 (2018).
Kates-Harbeck, J., Svyatkovskiy, A. & Tang, W. Predicting disruptive instabilities in controlled fusion plasmas through deep learning. Nature 568, 526–531 (2019).
Ferreira de Lima, T. et al. Machine learning with neuromorphic photonics. J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 1515–1534 (2019).
Han, J., Jentzen, A. & Weinan, E. Solving high-dimensional partial differential equations using deep learning. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 8505–8510 (2018).
Shen, Y. et al. Deep learning with coherent nanophotonic circuits. Nat. Photon. 11, 441–446 (2017).
Jouppi, N. P. et al. In-datacenter performance analysis of a tensor processing unit. In Proc. 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture 1–12 (Association for Computing Machinery, 2017).
Hughes, T. W., Minkov, M., Shi, Y. & Fan, S. Training of photonic neural networks through in situ backpropagation and gradient measurement. Optica 5, 864–871 (2018).
Tait, A. N. et al. Demonstration of multivariate photonics: blind dimensionality reduction with integrated photonics. J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 5996–6006 (2019).
Huang, C. et al. Demonstration of photonic neural network for fiber nonlinearity compensation in long-haul transmission systems. In Optical Fiber Communication Conference Th4C–6 (Optical Society of America, 2020).
Zhang, S. et al. Field and lab experimental demonstration of nonlinear impairment compensation using neural networks. Nat. Commun. 10, 3033 (2019).
Kravtsov, K. S., Fok, M. P., Prucnal, P. R. & Rosenbluth, D. Ultrafast all-optical implementation of a leaky integrate-and-fire neuron. Opt. Express 19, 2133–2147 (2011).
Tait, A. N., Nahmias, M. A., Shastri, B. J. & Prucnal, P. R. Broadcast and weight: an integrated network for scalable photonic spike processing. J. Lightwave Technol. 32, 4029–4041 (2014).
Shainline, J. M., Buckley, S. M., Mirin, R. P. & Nam, S. W. Superconducting optoelectronic circuits for neuromorphic computing. Phys. Rev. Appl. 7, 034013 (2017).
Bangari, V. et al. Digital electronics and analog photonics for convolutional neural networks (DEAP-CNNs). IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 7701213 (2020).
Feldmann, J., Youngblood, N., Wright, C. D., Bhaskaran, H. & Pernice, W. H. P. All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities. Nature 569, 208–214 (2019).
Goodman, J. W., Dias, A. R. & Woody, L. M. Fully parallel, high-speed incoherent optical method for performing discrete Fourier transforms. Opt. Lett. 2, 1–3 (1978).
Goodman, J. W., Leonberger, F. J., Kung, S.-Y. & Athale, R. A. Optical interconnections for VLSI systems. Proc. IEEE 72, 850–866 (1984).
Miller, D. A. B. Rationale and challenges for optical interconnects to electronic chips. Proc. IEEE 88, 728–749 (2000).
Psaltis, D. & Farhat, N. Optical information processing based on an associative-memory model of neural nets with thresholding and feedback. Opt. Lett. 10, 98–100 (1985).
Soref, R. & Bennett, B. Electrooptical effects in silicon. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 23, 123–129 (1987).
Tait, A. N. et al. Neuromorphic photonic networks using silicon photonic weight banks. Sci. Rep. 7, 7430 (2017).
Bogaerts, W. & Chrostowski, L. Silicon photonics circuit design: methods, tools and challenges. Laser Photon. Rev. 12, 1700237 (2018).
Nozaki, K. et al. Femtofarad optoelectronic integration demonstrating energy-saving signal conversion and nonlinear functions. Nat. Photon. 13, 454–459 (2019).
Nahmias, M. A. et al. Photonic multiply-accumulate operations for neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 7701518 (2020).
Ríos, C. et al. In-memory computing on a photonic platform. Sci. Adv. 5, eaau5759 (2019).
Ríos, C. et al. Integrated all-photonic non-volatile multi-level memory. Nat. Photon. 9, 725–732 (2015).
Lecun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y. & Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86, 2278–2324 (1998).
Tait, A., Ferreira de Lima, T., Nahmias, M., Shastri, B. & Prucnal, P. Continuous calibration of microring weights for analog optical networks. Photon. Technol. Lett. 28, 887–890 (2016).
Tait, A. N. et al. Microring weight banks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 22, 312–325 (2016).
Shi, B., Calabretta, N. & Stabile, R. Deep neural network through an InP SOA-based photonic integrated cross-connect. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 7701111 (2020).
Xu, X. et al. Photonic perceptron based on a Kerr microcomb for high-speed, scalable, optical neural networks. Laser Photon. Rev. 14, 2000070 (2020).
Reck, M., Zeilinger, A., Bernstein, H. J. & Bertani, P. Experimental realization of any discrete unitary operator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 58–61 (1994).
Carolan, J. et al. Universal linear optics. Science 349, 711–716 (2015).
Shainline, J. M. et al. Superconducting optoelectronic loop neurons. J. Appl. Phys. 126, 044902 (2019).
Chiles, J., Buckley, S. M., Nam, S. W., Mirin, R. P. & Shainline, J. M. Design, fabrication, and metrology of 10 × 100 multi-planar integrated photonic routing manifolds for neural networks. APL Photon. 3, 106101 (2018).
Buckley, S. et al. All-silicon light-emitting diodes waveguide-integrated with superconducting single-photon detectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 141101 (2017).
Harris, N. C. et al. Efficient, compact and low loss thermo-optic phase shifter in silicon. Opt. Express 22, 10487–10493 (2014).
Jayatilleka, H. et al. Wavelength tuning and stabilization of microring-based filters using silicon in-resonator photoconductive heaters. Opt. Express 23, 25084–25097 (2015).
Tait, A. N. et al. Feedback control for microring weight banks. Opt. Express 26, 26422–26443 (2018).
Patel, D. et al. Design, analysis, and transmission system performance of a 41 GHz silicon photonic modulator. Opt. Express 23, 14263 (2015).
Komljenovic, T. et al. Heterogeneous silicon photonic integrated circuits. J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 20–35 (2016).
He, M. et al. High-performance hybrid silicon and lithium niobate Mach–Zehnder modulators for 100 Gbit s−1 and beyond. Nat. Photon. 13, 359–364 (2019).
Sorianello, V. et al. Graphene–silicon phase modulators with gigahertz bandwidth. Nat. Photon. 12, 40–44 (2018).
Gholipour, B. et al. Amorphous metal-sulphide microfibers enable photonic synapses for brain-like computing. Adv. Opt. Mater. 3, 635–641 (2015).
Goodman, J. W. Fan-in and fan-out with optical interconnections. Opt. Acta 32, 1489–1496 (1985).
Nahmias, M. A., Shastri, B. J., Tait, A. N. & Prucnal, P. R. A leaky integrate-and-fire laser neuron for ultrafast cognitive computing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 19, 1800212 (2013).
Romeira, B. et al. Excitability and optical pulse generation in semiconductor lasers driven by resonant tunneling diode photo-detectors. Opt. Express 21, 20931–20940 (2013).
Tait, A. N. et al. Silicon photonic modulator neuron. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 064043 (2019).
Amin, R. et al. ITO-based electro-absorption modulator for photonic neural activation function. APL Mater. 7, 081112 (2019).
George, J. K. et al. Neuromorphic photonics with electro-absorption modulators. Opt. Express 27, 5181–5191 (2019).
Nahmias, M. A. et al. An integrated analog O/E/O link for multi-channel laser neurons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 151106 (2016).
Williamson, I. A. D. et al. Reprogrammable electro-optic nonlinear activation functions for optical neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 7700412 (2020).
McCaughan, A. N. et al. A superconducting thermal switch with ultrahigh impedance for interfacing superconductors to semiconductors. Nat. Electron. 2, 451–456 (2019).
Mourgias-Alexandris, G. et al. An all-optical neuron with sigmoid activation function. Opt. Express 27, 9620–9630 (2019).
Hill, M., Frietman, E. E. E., de Waardt, H., Khoe, G.-D. & Dorren, H. All fiber-optic neural network using coupled SOA based ring lasers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 13, 1504–1513 (2002).
Rosenbluth, D., Kravtsov, K., Fok, M. P. & Prucnal, P. R. A high performance photonic pulse processing device. Opt. Express 17, 22767–22772 (2009).
Sebastian, A. et al. Tutorial: brain-inspired computing using phase-change memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 111101 (2018).
Selmi, F. et al. Relative refractory period in an excitable semiconductor laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 183902 (2014).
Peng, H. T. et al. Neuromorphic photonic integrated circuits. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 24, 6101715 (2018).
Romeira, B., Avo, R., Figueiredo, J. M. L., Barland, S. & Javaloyes, J. Regenerative memory in time-delayed neuromorphic photonic resonators. Sci. Rep. 6, 19510 (2016).
Shastri, B. J. et al. Spike processing with a graphene excitable laser. Sci. Rep. 6, 19126 (2016).
Coomans, W., Gelens, L., Beri, S., Danckaert, J. & Van der Sande, G. Solitary and coupled semiconductor ring lasers as optical spiking neurons. Phys. Rev. E 84, 036209 (2011).
Brunstein, M. et al. Excitability and self-pulsing in a photonic crystal nanocavity. Phys. Rev. A 85, 031803 (2012).
Robertson, J., Deng, T., Javaloyes, J. & Hurtado, A. Controlled inhibition of spiking dynamics in VCSELS for neuromorphic photonics: theory and experiments. Opt. Lett. 42, 1560–1563 (2017).
Hopfield, J. J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79, 2554–2558 (1982).
Stewart, T. C. & Eliasmith, C. Large-scale synthesis of functional spiking neural circuits. Proc. IEEE 102, 881–898 (2014).
Bueno, J. et al. Reinforcement learning in a large-scale photonic recurrent neural network. Optica 5, 756–760 (2018).
Lin, X. et al. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks. Science 361, 1004–1008 (2018).
Zuo, Y. et al. All-optical neural network with nonlinear activation functions. Optica 6, 1132–1137 (2019).
Xu, S., Wang, J., Wang, R., Chen, J. & Zou, W. High-accuracy optical convolution unit architecture for convolutional neural networks by cascaded acousto-optical modulator arrays. Opt. Express 27, 19778–19787 (2019).
Mehrabian, A., Miscuglio, M., Alkabani, Y., Sorger, V. J. & El-Ghazawi, T. A Winograd-based integrated photonics accelerator for convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 6100312 (2020).
McMahon, P. L. et al. A fully programmable 100-spin coherent Ising machine with all-to-all connections. Science 354, 614–617 (2016).
Roques-Carmes, C. et al. Heuristic recurrent algorithms for photonic Ising machines. Nat. Commun. 11, 249 (2020).
Tang, P. T. P., Lin, T.-H. & Davies, M. Sparse coding by spiking neural networks: convergence theory and computational results. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.05475 (2017).
Davies, M. Benchmarks for progress in neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 386–388 (2019).
Maass, W. Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 10, 1659–1671 (1997).
Peng, H. et al. Temporal information processing with an integrated laser neuron. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 5100209 (2020).
Robertson, J., Hejda, M., Bueno, J. & Hurtado, A. Ultrafast optical integration and pattern classification for neuromorphic photonics based on spiking VCSEL neurons. Sci. Rep. 10, 6098 (2020).
Chakraborty, I., Saha, G., Sengupta, A. & Roy, K. Toward fast neural computing using all-photonic phase change spiking neurons. Sci. Rep. 8, 12980 (2018).
Fok, M. P., Tian, Y., Rosenbluth, D. & Prucnal, P. R. Pulse lead/lag timing detection for adaptive feedback and control based on optical spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Opt. Lett. 38, 419–421 (2013).
Toole, R. et al. Photonic implementation of spike-timing-dependent plasticity and learning algorithms of biological neural systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 34, 470–476 (2016).
Xiang, S. et al. STDP-based unsupervised spike pattern learning in a photonic spiking neural network with VCSELs and VCSOAs. IEEE J. Sel.Top. Quantum Electron. 25, 1700109 (2019).
Larger, L. et al. Photonic information processing beyond Turing: an optoelectronic implementation of reservoir computing. Opt. Express 20, 3241–3249 (2012).
Paquot, Y. et al. Optoelectronic reservoir computing. Sci. Rep. 2, 287 (2012).
Duport, F., Schneider, B., Smerieri, A., Haelterman, M. & Massar, S. All-optical reservoir computing. Opt. Express 20, 22783–22795 (2012).
Brunner, D., Soriano, M. C., Mirasso, C. R. & Fischer, I. Parallel photonic information processing at gigabyte per second data rates using transient states. Nat. Commun. 4, 1364 (2013).
Vandoorne, K. et al. Experimental demonstration of reservoir computing on a silicon photonics chip. Nat. Commun. 5, 3541 (2014).
Brunner, D. et al. Tutorial: Photonic neural networks in delay systems. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 152004 (2018).
Brunner, D., Soriano, M. C. & der Sande, G. V. Photonic Reservoir Computing (De Gruyter, 2019).
Antonik, P., Marsal, N., Brunner, D. & Rontani, D. Human action recognition with a large-scale brain-inspired photonic computer. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 530–537 (2019).
Sun, C. et al. Single-chip microprocessor that communicates directly using light. Nature 528, 534–538 (2015).
Stojanovic, V. et al. Monolithic silicon-photonic platforms in state-of-the-art CMOS SOI processes [Invited]. Opt. Express 26, 13106 (2018).
Jha, A. et al. Lateral bipolar junction transistor on a silicon photonics platform. Opt. Express 28, 11692–11704 (2020).
Giewont, K. et al. 300-mm monolithic silicon photonics foundry technology. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 25, 8200611 (2019).
Zhou, Z., Yin, B. & Michel, J. On-chip light sources for silicon photonics. Light Sci. Appl. 4, e358 (2015).
Song, B., Stagarescu, C., Ristic, S., Behfar, A. & Klamkin, J. 3d integrated hybrid silicon laser. Opt. Express 24, 10435–10444 (2020).
Mack, M. et al. Luxtera’s silicon photonics platform for transceiver manufacturing. In 2014 International Conference on Solid State Devices and Materials 506–507 (Luxtera, Inc., 2014).
Billah, M. R. et al. Hybrid integration of silicon photonics circuits and inp lasers by photonic wire bonding. Optica 5, 876–883 (2018).
Liang, D. & Bowers, J. E. Recent progress in lasers on silicon. Nat. Photon. 4, 511–517 (2010).
Chen, S. et al. Electrically pumped continuous-wave III–V quantum dot lasers on silicon. Nat. Photon. 10, 307–311 (2016).
Berggren, K. et al. Roadmap on emerging hardware and technology for machine learning. Nanotechnology 32, 012002 (2021).
Ambrogio, S. et al. Equivalent-accuracy accelerated neural-network training using analogue memory. Nature 558, 60–67 (2018).
Li, C. et al. Long short-term memory networks in memristor crossbar arrays. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 49–57 (2019).
Sze, V., Chen, Y., Yang, T. & Emer, J. S. Efficient processing of deep neural networks: a tutorial and survey. Proc. IEEE 105, 2295–2329 (2017).
Cheng, Z. et al. Device-level photonic memories and logic applications using phase-change materials. Adv. Mater. 30, 1802435 (2018).
Zhang, Y. et al. Broadband transparent optical phase change materials for high-performance nonvolatile photonics. Nat. Commun. 10, 4279 (2019).
Cheng, Z., Ríos, C., Pernice, W. H. P., Wright, C. D. & Bhaskaran, H. On-chip photonic synapse. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700160 (2017).
Bogaerts, W. et al. Silicon microring resonators. Laser Photon. Rev. 6, 47–73 (2012).
Schrauwen, J., Van Thourhout, D. & Baets, R. Trimming of silicon ring resonator by electron beam induced compaction and strain. Opt. Express 16, 3738 (2008).
Prorok, S., Petrov, A. Y., Eich, M., Luo, J. & Jen, A. K.-Y. Trimming of high-Q-factor silicon ring resonators by electron beam bleaching. Opt. Lett. 37, 3114 (2012).
Milosevic, M. M. et al. Ion implantation in silicon for trimming the operating wavelength of ring resonators. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 24, 8200107 (2018).
Harris, N. C. et al. Linear programmable nanophotonic processors. Optica 5, 1623–1631 (2018).
Perez, D., Gasulla, I., Mahapatra, P. D. & Capmany, J. Principles, fundamentals, and applications of programmable integrated photonics. Adv. Opt. Photon. 12, 709–786 (2020).
Gaeta, A. L., Lipson, M. & Kippenberg, T. J. Photonic-chip-based frequency combs. Nat. Photon. 13, 158–169 (2019).
Kippenberg, T. J., Holzwarth, R. & Diddams, S. A. Microresonator-based optical frequency combs. Science 332, 555–559 (2011).
Del’Haye, P. et al. Optical frequency comb generation from a monolithic microresonator. Nature 450, 1214–1217 (2007).
Turner, E. H. High-frequency electro-optic coefficients of lithium niobate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 8, 303–304 (1966).
Wang, C., Zhang, M., Stern, B., Lipson, M. & Loncar, M. Nanophotonic lithium niobate electro-optic modulators. Opt. Express 26, 1547–1555 (2018).
Mercante, A. J. et al. 110 GHz CMOS compatible thin film LiNbO3 modulator on silicon. Opt. Express 24, 15590–15595 (2016).
Wang, C. et al. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature 562, 101–104 (2018).
Sun, J. et al. A 128 Gb/s PAM4 silicon microring modulator with integrated thermo-optic resonance tuning. J. Lightwave Technol. 37, 110–115 (2019).
Patel, D., Samani, A., Veerasubramanian, V., Ghosh, S. & Plant, D. V. Silicon photonic segmented modulator-based electro-optic dac for 100 gb/s pam-4 generation. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 27, 2433–2436 (2015).
Meng, J., Miscuglio, M., George, J. K., Babakhani, A. & Sorger, V. J. Electronic bottleneck suppression in next-generation networks with integrated photonic digital-to-analog converters. Adv. Photon. Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/adpr.202000033 (2021).
Gelens, L et al. Excitability in semiconductor microring lasers: experimental and theoretical pulse characterization. Phys. Rev. A 82, 063841 (2010).
Beri, S. et al. Excitability in optical systems close to Z2-symmetry. Phys. Lett. A 374, 739–743 (2010).
Bogaerts, W. & Rahim, A. Programmable photonics: an opportunity for an accessible large-volume PIC ecosystem. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 26, 8302517 (2020).
Acknowledgements
B.J.S. acknowledges support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). T.F.d.L. and P.R.P. acknowledge support from the Office of Naval Research (ONR), Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and National Science Foundation (NSF). We thank J. Shainline, P. Kuo and N. Sanford for editorial contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Photonics thanks Yichen Shen and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shastri, B.J., Tait, A.N., Ferreira de Lima, T. et al. Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat. Photonics 15, 102–114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-00754-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-020-00754-y
This article is cited by
-
Conflict-free joint decision by lag and zero-lag synchronization in laser network
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
History-dependent nano-photoisomerization by optical near-field in photochromic single crystals
Communications Materials (2024)
-
High-speed and energy-efficient non-volatile silicon photonic memory based on heterogeneously integrated memresonator
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Multichannel meta-imagers for accelerating machine vision
Nature Nanotechnology (2024)
-
Fiber optic computing using distributed feedback
Communications Physics (2024)