Abstract
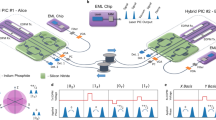
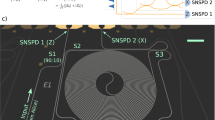
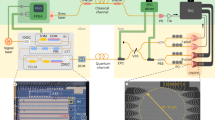
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a quantum communication technology that promises unconditional communication security. High-performance and cost-effective QKD systems are essential for the establishment of quantum communication networks1,2,3. By integrating all the optical components (except the laser source) on a silicon photonic chip, we have realized a stable, miniaturized and low-cost system for continuous-variable QKD (CV-QKD) that is compatible with the existing fibre optical communication infrastructure4. Here, the integrated silicon photonic chip is demonstrated for CV-QKD. It implements the widely studied Gaussian-modulated coherent state protocol that encodes continuous distributed information on the quadrature of laser light5,6. Our proof-of-principle chip-based CV-QKD system is capable of producing a secret key rate of 0.14 kbps (under collective attack) over a simulated distance of 100 km in fibre, offering new possibilities for low-cost, scalable and portable quantum networks.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Lo, H. K., Curty, M. & Tamaki, K. Secure quantum key distribution. Nat. Photon. 8, 595–604 (2014).
Scarani, V. et al. The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301–1350 (2009).
Orieux, A. & Diamanti, E. Recent advances on integrated quantum communications. J. Opt. 18, 083002 (2016).
Diamanti, E., Lo, H. K., Qi, B. & Yuan, Z. L. Practical challenges in quantum key distribution. npj Quant. Inf. 2, 16025 (2016).
Grosshans, F. & Grangier, P. Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002).
Grosshans, F. et al. Quantum key distribution using Gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 421, 238–241 (2003).
Sibson, P. et al. Chip-based quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 8, 13984 (2017).
Zhang, P. et al. Reference-frame-independent quantum-key-distribution server with a telecom tether for an on-chip client. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 130501 (2014).
Tanzilli, S. et al. On the genesis and evolution of integrated quantum optics. Laser Photon. Rev. 6, 115–143 (2012).
Politi, A., Cryan, M. J., Rarity, J. G., Yu, S. Y. & O’Brien, J. L. Silica-on-silicon waveguide quantum circuits. Science 320, 646–649 (2008).
Davis, K. M., Miura, K., Sugimoto, N. & Hirao, K. Writing waveguides in glass with a femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 21, 1729–1731 (1996).
Huang, J. G. et al. Torsional frequency mixing and sensing in optomechanical resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 111102 (2017).
Shi, Y. Z. et al. Sculpting nanoparticle dynamics for single-bacteria-level screening and direct binding-efficiency measurement. Nat. Commun. 9, 815 (2018).
Shi, Y. et al. Nanometer-precision linear sorting with synchronized optofluidic dual barriers. Sci. Adv. 4, eaao0773 (2018).
Boaron, A. et al. Secure quantum key distribution over 421 km of optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 190502 (2018).
Yin, H. L. et al. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 190501 (2016).
Ma, C. X. et al. Silicon photonic transmitter for polarization-encoded quantum key distribution. Optica 3, 1274–1278 (2016).
Ding, Y. H. et al. High-dimensional quantum key distribution based on multicore fiber using silicon photonic integrated circuits. npj Quant. Inf. 3, 25 (2017).
Sibson, P. et al. Integrated silicon photonics for high-speed quantum key distribution. Optica 4, 172–177 (2017).
Najafi, F. et al. On-chip detection of non-classical light by scalable integration of single-photon detectors. Nat. Commun. 6, 5873 (2015).
Pernice, W. H. P. et al. High-speed and high-efficiency travelling wave single-photon detectors embedded in nanophotonic circuits. Nat. Commun. 3, 1325 (2012).
Lodewyck, J. et al. Quantum key distribution over 25 km with an all-fiber continuous-variable system. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042305 (2007).
Ziebell, M. et al. Towards on-chip continuous-variable quantum key distribution. In Conf. Lasers Electro-Optics (CLEO) Europe JSV-4.2 (Optical Society of America, 2015).
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Leverrier, A., Grangier, P. & Diamanti, E. Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photon. 7, 378–381 (2013).
Huang, D., Huang, P., Lin, D. K. & Zeng, G. H. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 6, 19201 (2016).
Rude, M. et al. Interferometric photodetection in silicon photonics for phase diffusion quantum entropy sources. Opt. Express 26, 31957–31964 (2018).
Raffaelli, F. et al. Generation of random numbers by measuring phase fluctuations from a laser diode with a silicon-on-insulator chip. Opt. Express 26, 19730–19741 (2018).
Abellan, C. et al. Quantum entropy source on an InP photonic integrated circuit for random number generation. Optica 3, 989–994 (2016).
Raffaelli, F. et al. A homodyne detector integrated onto a photonic chip for measuring quantum states and generating random numbers. Quantum Sci. Technol. 3, 025003 (2018).
Lance, A. M. et al. No-switching quantum key distribution using broadband modulated coherent light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 180503 (2005).
Shen, Y., Zou, H. X., Tian, L. A., Chen, P. X. & Yuan, J. M. Experimental study on discretely modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 82, 022317 (2010).
Wang, X. Y., Zhang, Y. C., Yu, S. & Guo, H. High speed error correction for continuous-variable quantum key distribution with multi-edge type LDPC code. Sci. Rep. 8, 10543 (2018).
Milicevic, M., Feng, C., Zhang, L. M. & Gulak, P. G. Quasi-cyclic multi-edge LDPC codes for long-distance quantum cryptography. npj Quant. Inf. 4, 21 (2018).
Jouguet, P., Kunz-Jacques, S., Diamanti, E. & Leverrier, A. Analysis of imperfections in practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 032309 (2012).
Qi, B., Lougovski, P., Pooser, R., Grice, W. & Bobrek, M. Generating the local oscillator “locally” in continuous-variable quantum key distribution based on coherent detection. Phys. Rev. X 5, 041009 (2015).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE) Tier 3 grant (MOE2017-T3-1-001), the Singapore National Research Foundation (NRF) National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) joint grant (NRF2017NRF-NSFC002-014) and the Singapore National Research Foundation under the Competitive Research Program (NRF-CRP13-2014-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.Z., L.C.K. and A.Q.L. jointly conceived the idea. G.Z. and H.C. designed and fabricated the silicon photonic chip. G.Z., Y.Z., S.Y., J.W., W.S., F.X. and X.Z. performed the experiments. J.Y.H., S.M.A., J.F.F. and L.C.K. assisted with the theory. All authors contributed to the discussion of experimental results. F.X., L.C.K. and A.Q.L. supervised and coordinated all the work. G.Z., F.X., L.C.K. and A.Q.L. wrote the manuscript with contributions from all co-authors.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary notes and figures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Haw, J.Y., Cai, H. et al. An integrated silicon photonic chip platform for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 13, 839–842 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0504-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0504-5
This article is cited by
-
Inorganic perovskite-based active multifunctional integrated photonic devices
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Prospects and applications of on-chip lasers
eLight (2023)
-
Recent progress in quantum photonic chips for quantum communication and internet
Light: Science & Applications (2023)
-
Provably-secure quantum randomness expansion with uncharacterised homodyne detection
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A hybrid integrated quantum key distribution transceiver chip
npj Quantum Information (2023)