Abstract
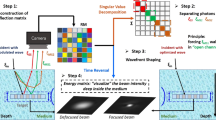
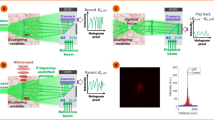
The efficient delivery of light energy is a prerequisite for the non-invasive imaging and stimulating of target objects embedded deep within a scattering medium. However, the injected waves experience random diffusion by multiple light scattering, and only a small fraction reaches the target object. Here, we present a method to counteract wave diffusion and to focus multiple-scattered waves at the deeply embedded target. To realize this, we experimentally inject light into the reflection eigenchannels of a specific flight time to preferably enhance the intensity of those multiple-scattered waves that have interacted with the target object. For targets that are too deep to be visible by optical imaging, we demonstrate a more than tenfold enhancement in light energy delivery in comparison with ordinary wave diffusion cases. This work will lay a foundation to enhance the working depth of imaging, sensing and light stimulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeremy, C. H., Simon, R. A. & David, T. D. Optical imaging in medicine: I. Experimental techniques. Phys. Med. Biol. 42, 825–840 (1997).
Huang, X. & El-Sayed, M. A. Gold nanoparticles: optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 1, 13–28 (2010).
Packer, A. M., Roska, B. & Hausser, M. Targeting neurons and photons for optogenetics. Nat. Neurosci. 16, 805–815 (2013).
Vellekoop, I. M. & Mosk, A. P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media. Opt. Lett. 32, 2309–2311 (2007).
Katz, O., Small, E., Bromberg, Y. & Silberberg, Y. Focusing and compression of ultrashort pulses through scattering media. Nat. Photon. 5, 372–377 (2011).
Aulbach, J., Gjonaj, B., Johnson, P. & Lagendijk, A. Spatiotemporal focusing in opaque scattering media by wave front shaping with nonlinear feedback. Opt. Express 20, 29237–29251 (2012).
Mounaix, M. et al. Spatiotemporal coherent control of light through a multiple scattering medium with the multispectral transmission matrix. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 253901 (2016).
Kim, M. et al. Maximal energy transport through disordered media with the implementation of transmission eigenchannels. Nat. Photon. 6, 581–585 (2012).
Goetschy, A. & Stone, A. D. Filtering random matrices: the effect of incomplete channel control in multiple scattering. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 063901 (2013).
Kim, M. et al. Exploring anti-reflection modes in disordered media. Opt. Express 23, 12740–12749 (2015).
Sarma, R., Yamilov, A. G., Petrenko, S., Bromberg, Y. & Cao, H. Control of energy density inside a disordered medium by coupling to open or closed channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 086803 (2016).
Hsu, C. W., Liew, S. F., Goetschy, A., Cao, H. & Stone, A. D. Correlation-enhanced control of wave focusing in disordered media. Nat. Phys. 13, 497–502 (2017).
Mounaix, M., de Aguiar, H. B. & Gigan, S. Temporal recompression through a scattering medium via a broadband transmission matrix. Optica 4, 1289–1292 (2017).
Marsh, P. N., Burns, D. & Girkin, J. M. Practical implementation of adaptive optics in multiphoton microscopy. Opt. Express 11, 1123–1130 (2003).
Ji, N., Milkie, D. E. & Betzig, E. Adaptive optics via pupil segmentation for high-resolution imaging in biological tissues. Nat. Methods 7, 141–147 (2010).
Fiolka, R., Si, K. & Cui, M. Complex wavefront corrections for deep tissue focusing using low coherence backscattered light. Opt. Express 20, 16532–16543 (2012).
Wang, C. et al. Multiplexed aberration measurement for deep tissue imaging in vivo. Nat. Methods 11, 1037–1040 (2014).
Park, J. H., Sun, W. & Cui, M. High-resolution in vivo imaging of mouse brain through the intact skull. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 9236–9241 (2015).
Vellekoop, I. M., van Putten, E. G., Lagendijk, A. & Mosk, A. P. Demixing light paths inside disordered metamaterials. Opt. Express 16, 67–80 (2008).
Xu, X. A., Liu, H. L. & Wang, L. V. Time-reversed ultrasonically encoded optical focusing into scattering media. Nat. Photon. 5, 154–157 (2011).
Judkewitz, B., Wang, Y. M., Horstmeyer, R., Mathy, A. & Yang, C. H. Speckle-scale focusing in the diffusive regime with time reversal of variance-encoded light (TROVE). Nat. Photon. 7, 300–305 (2013).
Popoff, S. M. et al. Exploiting the time-reversal operator for adaptive optics, selective focusing, and scattering pattern analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 263901 (2011).
Prada, C., Wu, F. & Fink, M. The iterative time-reversal mirror—a solution to self-focusing in the pulse echo mode. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 90, 1119–1129 (1991).
Prada, C. & Fink, M. Eigenmodes of the time-reversal operator—a solution to selective focusing in multiple-target media. Wave Motion 20, 151–163 (1994).
Kang, S. et al. Imaging deep within a scattering medium using collective accumulation of single-scattered waves. Nat. Photon. 9, 253–258 (2015).
Kang, S. et al. High-resolution adaptive optical imaging within thick scattering media using closed-loop accumulation of single scattering. Nat. Commun. 8, 2157 (2017).
Choi, Y. et al. Measurement of the time-resolved reflection matrix for enhancing light energy delivery into a scattering medium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 243901 (2013).
Badon, A. et al. Smart optical coherence tomography for ultra-deep imaging through highly scattering media. Sci. Adv. 2, e1600370 (2016).
Wang, L., Ho, P. P., Liu, C., Zhang, G. & Alfano, R. R. Ballistic 2-D imaging through scattering walls using an ultrafast optical Kerr gate. Science 253, 769–771 (1991).
Goto, K., Nakagawa, T., Nakamura, O. & Kawata, S. An implantable power supply with an optically rechargeable lithium battery. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 48, 830–833 (2001).
Choi, W., Mosk, A. P., Park, Q. H. & Choi, W. Transmission eigenchannels in a disordered medium. Phys. Rev. B 83, 134207 (2011).
Choi, W., Park, Q. H. & Choi, W. Perfect transmission through Anderson localized systems mediated by a cluster of localized modes. Opt. Express 20, 20721–20729 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by IBS-R023-D1 and the Global Frontier Program (2014M3A6B3063710) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning. It was also supported by the Korea Health Technology R&D Project (HI14C0748) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea. H.-G.P. acknowledges support from an NRF grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (no. 2009-0081565).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wonshik C., S.J., S.K. and Y.-R.L. conceived the experiment, and S.J. carried out the measurements. Experimental data were analysed by S.J., Y.-R.L. and Wonshik C. Y.-R.L. developed the theoretical framework and analysed FDTD simulation results with Wonshik C. Wonjun C. constructed the FDTD platform for computing the time-resolved reflection matrix and its eigenchannels, and ran the FDTD simulations. Y.-S.L. assisted in the design of the optical set-up. J.H.H. prepared biological tissues. J.-S.P. and H.-G.P. provided silver disks. S.J., Y.-R.L. and Wonshik C. prepared the manuscript. All authors contributed to finalizing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Numerical and theoretical analyses, additional experimental data analysis, comparison of experimental data with the theoretical results, and further discussion on the proposed method.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, S., Lee, YR., Choi, W. et al. Focusing of light energy inside a scattering medium by controlling the time-gated multiple light scattering. Nature Photon 12, 277–283 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-018-0120-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-018-0120-9
This article is cited by
-
Tracing multiple scattering trajectories for deep optical imaging in scattering media
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Exploiting volumetric wave correlation for enhanced depth imaging in scattering medium
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Shaping the propagation of light in complex media
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Anti-reflection structure for perfect transmission through complex media
Nature (2022)
-
High-throughput volumetric adaptive optical imaging using compressed time-reversal matrix
Light: Science & Applications (2022)