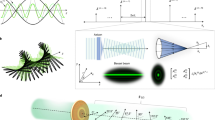
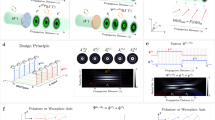
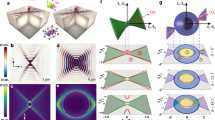
Abstract
Optical communications, laser science, microscopy and metrology demand control of light polarization, which is also used as a probe of chemical and biological systems. Typically, certain polarization states of light are achieved using macroscopic anisotropic crystals. Metamaterials and metasurfaces have recently been developed to act as efficient passive polarization components of subwavelength dimensions1,2,3,4. However, active polarization control has so far been mainly limited to microwave and terahertz wavelengths5,6,7. Here, we demonstrate all-optical switching of visible light polarization, achieving up to 60° rotation of the polarization ellipse at picosecond timescales. This is accomplished both under control illumination and in a self-phase modulation regime, where the intensity of light affects its own polarization state, by exploiting the strong anisotropy and nonlinear response of a hyperbolic metamaterial3,8,9,10. The effects are general for any resonant, anisotropic, nonlinear nanoantennas and metasurfaces and are suited to numerous photonic applications and material characterization techniques where ultrafast polarization shaping is required.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gansel, J. K. et al. Gold helix photonic metamaterial as broadband circular polarizer. Science 325, 1513–1515 (2009).
Plum, E. et al. Metamaterial with negative index due to chirality. Phys. Rev. B 79, 035407 (2009).
Ginzburg, P. et al. Manipulating polarization of light with ultrathin epsilon-near-zero metamaterials. Opt. Express 21, 14907–14917 (2013).
Zhao, Y. & Alù, A. Manipulating light polarization with ultrathin plasmonic metasurfaces. Phys. Rev. B 84, 205428 (2011).
Mousavi, S. A., Plum, E., Shi, J. H. & Zheludev, N. I. Coherent control of optical polarization effects in metamaterials. Sci. Rep. 5, 8977 (2015).
Zhang, S. et al. Photoinduced handedness switching in terahertz chiral metamolecules. Nat. Commun. 3, 942 (2012).
Kamaraju, N. et al. Subcycle control of terahertz waveform polarization using all-optically induced transient metamaterials. Light Sci. Appl. 3, e155 (2014).
Poddubny, A., Iorsh, I., Belov, P. & Kivshar, Y. Hyperbolic metamaterials. Nat. Photon. 7, 948–957 (2013).
Wurtz, G. A. et al. Designed ultrafast optical nonlinearity in a plasmonic nanorod metamaterial enhanced by nonlocality. Nat. Nanotech. 6, 107–111 (2011).
Neira, A. D. et al. Eliminating material constraints for nonlinearity with plasmonic metamaterials. Nat. Commun. 6, 7757 (2015).
Schäferling, M., Dregely, D., Hentschel, M. & Giessen, H. Tailoring enhanced optical chirality: design principles for chiral plasmonic nanostructures. Phys. Rev. X 2, 031010 (2012).
Zhao, R., Zhang, L., Zhou, J., Koschny, T. & Soukoulis, C. M. Conjugated gammadion chiral metamaterial with uniaxial optical activity and negative refractive index. Phys. Rev. B 83, 035105 (2011).
Decker, M., Zhao, R., Soukoulis, C. M., Linden, S. & Wegener, M. Twisted split-ring-resonator photonic metamaterial with huge optical activity. Opt. Lett. 35, 1593–1595 (2010).
Zhu, H., Yin, X., Chen, L., Zhu, Z. & Li, X. Manipulating light polarizations with a hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide. Opt. Lett. 40, 4595–4598 (2015).
Ren, M., Plum, E., Xu, J. & Zheludev, N. I. Giant nonlinear optical activity in a plasmonic metamaterial. Nat. Commun. 3, 833 (2012).
Genevet, P. et al. Ultra-thin plasmonic optical vortex plate based on phase discontinuities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 013101 (2012).
Yu, N. et al. A broadband, background-free quarter-wave plate based on plasmonic metasurfaces. Nano Lett. 12, 6328–6333 (2012).
Ding, F., Wang, Z., He, S., Shalaev, V. M. & Kildishev, A. V. Broadband high-efficiency half-wave plate: a supercell-based plasmonic metasurface approach. ACS Nano 9, 4111–4119 (2015).
Zhu, B. et al. Polarization modulation by tunable electromagnetic metamaterial reflector/absorber. Opt. Express 18, 23196–23203 (2010).
Cui, J. H. et al. Dynamical manipulation of electromagnetic polarization using anisotropic meta-mirror. Sci. Rep. 6, 30771 (2016).
Wang, D. C. et al. Switchable ultrathin quarter-wave plate in terahertz using active phase-change metasurface. Sci. Rep. 5, 15020 (2015).
Kan, T. et al. Enantiomeric switching of chiral metamaterial for terahertz polarization modulation employing vertically deformable MEMS spirals. Nat. Commun. 6, 8422 (2015).
Born, M. & Wolf, E. Principles of Optics: Electromagnetic Theory of Propagation, Interference and Diffraction of Light 7th edn (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK, 1999).
Vasilantonakis, N., Nasir, M. E., Dickson, W., Wurtz, G. A. & Zayats, A. V. Bulk plasmon–polaritons in hyperbolic nanorod metamaterial waveguides. Laser Photon. Rev. 9, 345–353 (2015).
Markowicz, P. P. et al. Phase-sensitive time-modulated surface plasmon resonance polarimetry for wide dynamic range biosensing. Opt. Express 15, 1745–1754 (2007).
Svedendahl, M., Verre, R. & Kall, M. Refractometric biosensing based on optical phase flips in sparse and short-range-ordered nanoplasmonic layers. Light Sci. Appl. 3, e220 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported, in part, by the EPSRC (UK) and the ERC iPLASMM project (321268). A.V.Z. acknowledges support from the Royal Society and the Wolfson Foundation. G.A.W. acknowledges support from the EC FP7 project 304179 (Marie Curie Actions). F.J.R.-F. acknowledges financial support from the ERC-2016-StG-714151 PSINFONI project. R.M.C.-C acknowledges the support of CONACyT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.H.N., F.J.R.-F. and A.V.Z. developed the idea and designed the experiments. L.H.N., G.A.W. and N.O. performed the experiments. L.H.N. and F.J.R.-F. performed numerical simulations and data processing. M.E.N. and R.M.C.-C. fabricated the metamaterial samples. L.H.N., F.J.R.-F. and A.V.Z. wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information
Additional fabrication, measurement, modelling and other details.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicholls, L.H., Rodríguez-Fortuño, F.J., Nasir, M.E. et al. Ultrafast synthesis and switching of light polarization in nonlinear anisotropic metamaterials. Nature Photon 11, 628–633 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-017-0002-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-017-0002-6
This article is cited by
-
Visible to mid-infrared giant in-plane optical anisotropy in ternary van der Waals crystals
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Single-shot polarimetry of vector beams by supervised learning
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Clamping effect driven design and fabrication of new infrared birefringent materials with large optical anisotropy
Science China Chemistry (2023)
-
Cavity-enhanced linear dichroism in a van der Waals antiferromagnet
Nature Photonics (2022)
-
Development of polarization modulator using MXene thin film
Scientific Reports (2022)