Abstract
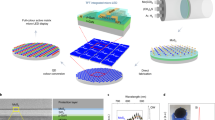
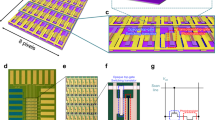
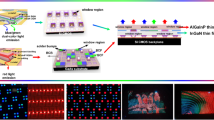
Two-dimensional materials are promising candidates for future electronics due to unmatched device performance at atomic limit and low-temperature heterogeneous integration. To adopt these emerging materials in computing and optoelectronic systems, back end of line (BEOL) integration with mainstream technologies is needed. Here, we show the integration of large-area MoS2 thin-film transistors (TFTs) with nitride micro light-emitting diodes (LEDs) through a BEOL process and demonstrate high-resolution displays. The MoS2 transistors exhibit median mobility of 54 cm2 V−1s −1, 210 μA μm−1 drive current and excellent uniformity. The TFTs can drive micrometre-sized LEDs to 7.1 × 107 cd m−2 luminance under low voltage. Comprehensive analysis on driving capability, response time, power consumption and modulation scheme indicates that MoS2 TFTs are suitable for a range of display applications up to the high resolution and brightness limit. We further demonstrate prototypical 32 × 32 active-matrix displays at 1,270 pixels-per-inch resolution. Moreover, our process is fully monolithic, low-temperature, scalable and compatible with microelectronic processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other finding of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
All code used in this work is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Nakamura, S., Senoh, M. & Mukai, T. High‐power InGaN/GaN double‐heterostructure violet light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 62, 2390–2392 (1993).
Li, G. et al. GaN-based light-emitting diodes on various substrates: a critical review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 79, 056501 (2016).
Global Packaged GaN LED Market Report (Market Reports World, 2019); https://www.marketreportsworld.com/-global-packaged-gan-led-market-14194592
Jin, S. X., Li, J., Li, J. Z., Lin, J. Y. & Jiang, H. X. GaN microdisk light emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 631–633 (2000).
Yuan, Y. F. et al. Potential key technologies for 6G mobile communications. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 63, 183301 (2020).
Lin, J. Y. & Jiang, H. X. Development of microLED. Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, 100502 (2020).
Wong, M. S., Nakamura, S. & DenBaars, S. P. Review—progress in high performance III-nitride micro-light-emitting diodes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 9, 015012 (2019).
Huang, Y., Hsiang, E.-L., Deng, M.-Y. & Wu, S.-T. Mini-LED, micro-LED and OLED displays: present status and future perspectives. Light Sci. Appl. 9, 105 (2020).
Liu, Z., Chong, W. C., Wong, K. M. & Lau, K. M. GaN-based LED micro-displays for wearable applications. Microelectron. Eng. 148, 98–103 (2015).
Park, S.-I. et al. Printed assemblies of inorganic light-emitting diodes for deformable and semitransparent displays. Science 325, 977–981 (2009).
Liu, Z. J., Chong, W. C., Wong, K. M. & Lau, K. M. 360 PPI flip-chip mounted active matrix addressable light emitting diode on silicon (LEDoS) micro-displays. J. Disp. Technol. 9, 678–682 (2013).
Cok, R. S. et al. Inorganic light-emitting diode displays using micro-transfer printing. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 25, 589–609 (2017).
Zhang, L., Ou, F., Chong, W. C., Chen, Y. & Li, Q. Wafer-scale monolithic hybrid integration of Si-based IC and III–V epi-layers—a mass manufacturable approach for active matrix micro-LED micro-displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 26, 137–145 (2018).
Tull, B. R. et al. 26.2: Invited paper: high brightness, emissive microdisplay by integration of III‐V LEDs with thin film silicon transistors. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 46, 375–377 (2015).
Akinwande, D. et al. Graphene and two-dimensional materials for silicon technology. Nature 573, 507–518 (2019).
Liu, C. et al. Two-dimensional materials for next-generation computing technologies. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 545–557 (2020).
Manzeli, S., Ovchinnikov, D., Pasquier, D., Yazyev, O. V. & Kis, A. 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17033 (2017).
Fiori, G. et al. Electronics based on two-dimensional materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 768–779 (2014).
Yu, Z. et al. Realization of room-temperature phonon-limited carrier transport in monolayer MoS2 by dielectric and carrier screening. Adv. Mater. 28, 547–552 (2016).
Li, W. et al. Uniform and ultrathin high-κ gate dielectrics for two-dimensional electronic devices. Nat. Electron. 2, 563–571 (2019).
Zhou, J. et al. A library of atomically thin metal chalcogenides. Nature 556, 355–359 (2018).
Wang, Q. et al. Wafer-scale highly oriented monolayer MoS2 with large domain sizes. Nano Lett. 20, 7193–7199 (2020).
Kang, Kibum et al. High-mobility three-atom-thick semiconducting films with wafer-scale homogeneity. Nature 520, 656–660 (2015).
Tang, H. W. et al. Recent progress in devices and circuits based on wafer-scale transition metal dichalcogenides. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 62, 220401 (2019).
Goossens, S. et al. Broadband image sensor array based on graphene–CMOS integration. Nat. Photonics 11, 366–371 (2017).
Choi, M. et al. Full-color active-matrix organic light-emitting diode display on human skin based on a large-area MoS2 backplane. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb5898 (2020).
Liu, Y., Huang, Y. & Duan, X. Van der Waals integration before and beyond two-dimensional materials. Nature 567, 323–333 (2019).
Yu, J. et al. Van der Waals epitaxy of III‐nitride semiconductors based on 2D materials for flexible applications. Adv. Mater. 32, 1903407 (2020).
Akinwande, D., Petrone, N. & Hone, J. Two-dimensional flexible nanoelectronics. Nat. Commun. 5, 5678 (2014).
Zhuang, Z. et al. High color rendering index hybrid III-nitride/nanocrystals white light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 36–43 (2016).
Li, T. et al. Epitaxial growth of wafer-scale molybdenum disulfide semiconductor single crystals on sapphire. Nat. Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00963-8 (2021).
Pirkle, A. et al. The effect of chemical residues on the physical and electrical properties of chemical vapor deposited graphene transferred to SiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 122108 (2011).
Liu, Y. et al. Approaching the Schottky–Mott limit in van der Waals metal–semiconductor junctions. Nature 557, 696–700 (2016).
Huang, Y. et al. Universal mechanical exfoliation of large-area 2D crystals. Nat. Commun. 11, 2453 (2020).
Struthers, J. D. Solubility and diffusivity of gold, iron, and copper in silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 27, 1560 (1956).
Day, Jacob et al. III-Nitride full-scale high-resolution microdisplays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 031116 (2011).
Smets, Q. et al. Sources of variability in scaled MoS2 FETs. In Proc. 2020 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) 3.1.1–3.1.4 (IEEE, 2020).
Smithe, K. K. H., Suryavanshi, S. V., Muñoz Rojo, M., Tedjarati, A. D. & Pop, E. Low variability in synthetic monolayer MoS2 devices. ACS Nano 11, 8456–8463 (2017).
Huo, N. et al. High carrier mobility in monolayer CVD-grown MoS2 through phonon suppression. Nanoscale 10, 15071–15077 (2018).
Yu, L. et al. Design, modeling, and fabrication of chemical vapor deposition grown MoS2 circuits with E-mode FETs for large-area electronics. Nano Lett. 16, 6349–6356 (2016).
Polyushkin, D. et al. Analogue two-dimensional semiconductor electronics. Nat. Electron. 3, 486–491 (2020).
Sebastian, A. et al. Benchmarking monolayer MoS2 and WS2 field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun. 12, 693 (2021).
Nomura, K. et al. Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004).
Wager, J. F. TFT technology: advancements and opportunities for improvement. Info Disp. 36, 9–13 (2020).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Leading-edge Technology Programme of Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (grant no. BK20202005); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 61927808, 61521001, 61734003, 61861166001, 61851401, 51861145202, 62004104, 61974062, 61921005, 91964202); the Strategic Priority Research Programme of Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. XDB30000000); the National Key Research and Development Programme of China (grant no. 2016YFB0404101); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant no. BK20202005); the Collaborative Innovation Center of Solid-State Lighting and Energy-Saving Electronics, Research Funds from NJU-Yangzhou Institute of Opto-electronics and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.W. conceived the research and supervised the project with B.L., R.Z. and Y.S. W.M, F.X., Z.Y., T.T. developed the MoS2 TFT fabrication and monolithic integration process, fabricated micro-LED structures, conducted electrical measurements and demonstrated AM displays. L.S., W.L., H.N. and N.D. contributed to MoS2 TFT fabrication. L.L. and T.L. performed MoS2 CVD growth and characterizations. F.X., K.W. and J.W. performed LED brightness measurements. L.H. and L.S. performed TEM and data analysis. F.Q., X.T. and D.P. contributed to micro-LED fabrication. S.H. designed peripheral circuits and programs. D.L, Y.Z and Y.L. contributed to data analysis. W.M., Z.Y., B.L. and X.W. co-wrote the manuscript with input from other authors. All authors contributed to discussions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Nanotechnology thanks Deji Akinwande and Deep Jariwala for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Text 1, Figs. 1–14 and Tables 1 and 2.
Supplementary Video 1
Scanning the QR code by smart phone to get the word ‘MoS2 LED NJU’.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, W., Xu, F., Yu, Z. et al. Three-dimensional monolithic micro-LED display driven by atomically thin transistor matrix. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1231–1236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00966-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-021-00966-5
This article is cited by
-
Phase dimensions resolving of efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes at high brightness
Nature Photonics (2024)
-
The Roadmap of 2D Materials and Devices Toward Chips
Nano-Micro Letters (2024)
-
Low-thermal-budget synthesis of monolayer MoS2
Science China Materials (2024)
-
Vapour-phase deposition of two-dimensional layered chalcogenides
Nature Reviews Materials (2023)
-
Low-thermal-budget synthesis of monolayer molybdenum disulfide for silicon back-end-of-line integration on a 200 mm platform
Nature Nanotechnology (2023)