Abstract
Electrophysiological data from implanted electrodes in the human brain are rare, and therefore scientific access to such data has remained somewhat exclusive. Here we present a freely available curated library of implanted electrocorticographic data and analyses for 16 behavioural experiments, with 204 individual datasets from 34 patients recorded with the same amplifiers and at the same settings. For each dataset, electrode positions were carefully registered to brain anatomy. A large set of fully annotated analysis scripts with which to interpret these data is embedded in the library alongside them. All data, anatomical locations and analysis files (MATLAB code) are provided in a shared file structure at https://searchworks.stanford.edu/view/zk881ps0522.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


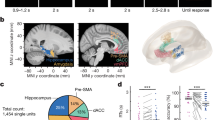
Panel b was adapted from Ramon y Cajal’s cortex drawings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katzner, S. et al. Local origin of field potentials in visual cortex. Neuron 61, 35–41 (2009).
Miller, K. J. Broadband spectral change: evidence for a macroscale correlate of population firing rate? J. Neurosci. 30, 6477 (2010).
Miller, K. J. et al. Broadband changes in the cortical surface potential track activation of functionally diverse neuronal populations. Neuroimage 85(Pt 2), 711–720 (2014).
Miller, K. J., Sorensen, L. B., Ojemann, J. G. & den Nijs, M. Power-law scaling in the brain surface electric potential. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000609 (2009).
Manning, J. R., Jacobs, J., Fried, I. & Kahana, M. J. Broadband shifts in LFP power spectra are correlated with single-neuron spiking in humans. J. Neurosci. 29, 13613–13620 (2009).
Gazzaniga, M. S. The Cognitive Neurosciences (MIT Press, 2009).
Miller, K. J., Zanos, S., Fetz, E. E., den Nijs, M. & Ojemann, J. G. Decoupling the cortical power spectrum reveals real-time representation of individual finger movements in humans. J. Neurosci. 29, 3132 (2009).
Miller, K. J., Hermes, D., Witthoft, N., Rao, R. P. & Ojemann, J. G. The physiology of perception in human temporal lobe is specialized for contextual novelty. J. Neurophysiol. 114, 256–263 (2015).
Miller, K. J., Makeig, S., Hebb, A. O., Rao, R. P. & Ojemann, J. G. Cortical electrode localization from X-rays and simple mapping for electrocorticographic research: The “Location on Cortex” (LOC) package for MATLAB. J. Neurosci. Methods 162, 303–308 (2007).
Hermes, D., Miller, K. J., Noordmans, H. J., Vansteensel, M. J. & Ramsey, N. F. Automated electrocorticographic electrode localization on individually rendered brain surfaces. J. Neurosci. Methods 185, 293–298 (2010).
Crone, N. E. et al. Functional mapping of human sensorimotor cortex with electrocorticographic spectral analysis. I. Alpha and beta event-related desynchronization. Brain 121, 2271–2299 (1998).
Crone, N. E., Miglioretti, D. L., Gordon, B. & Lesser, R. P. Functional mapping of human sensorimotor cortex with electrocorticographic spectral analysis. II. Event-related synchronization in the gamma band. Brain 121, 2301–2315 (1998).
Miller, K. J. et al. Spectral changes in cortical surface potentials during motor movement. J. Neurosci. 27, 2424–2432 (2007).
Miller, K. J., Sorensen, L. B., Ojemann, J. G. & Nijs, M. D. ECoG observations of power-law scaling in the human cortex. Preprint at arXiv https://arxiv.org/abs/0712.0846v1 (2007).
Miller, K. J. et al. Dynamic modulation of local population activity by rhythm phase in human occipital cortex during a visual search task. Front Hum. Neurosci. 4, 197 (2010).
Miller, K. J., Hermes, D., Pestilli, F., Wig, G. S. & Ojemann, J. G. Face percept formation in human ventral temporal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 118, 2614–2627 (2017).
Miller, K. J., Abel, T. J., Hebb, A. O. & Ojemann, J. G. Rapid online language mapping with electrocorticography. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 7, 482–490 (2011).
Miller, K. J. et al. Human motor cortical activity is selectively phase-entrained on underlying rhythms. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8, e1002655 (2012).
Hermes, D. et al. Cortical theta wanes for language. Neuroimage 85, 738–748 (2014).
Hanslmayr, S. et al. Alpha phase reset contributes to the generation of ERPs. Cereb. Cortex 17, 1–8 (2006).
Schalk, G. A general framework for dynamic cortical function: the function-through-biased-oscillations (FBO) hypothesis. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9, 352 (2015).
Jensen, O. & Mazaheri, A. Shaping functional architecture by oscillatory alpha activity: gating by inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 4, 186 (2010).
Hermes, D., Miller, K., Wandell, B. & Winawer, J. Stimulus dependence of gamma oscillations in human visual cortex. Cereb. Cortex 25, 2951–2959 (2014).
Davis, P. A. Effects of acoustic stimuli on the waking human brain. J. Neurophysiol. 2, 494–499 (1939).
Jasper, H. & Penfield, W. Electrocorticograms in man: effect of voluntary movement upon the electrical activity of the precentral gyrus. Arch. f.ür. Psychiatr. und Nervenkrankh. 183, 163–174 (1949).
Miller, K. J., Schalk, G., Hermes, D., Ojemann, J. G. & Rao, R. P. Spontaneous decoding of the timing and content of human object perception from cortical surface recordings reveals complementary information in the event-related potential and broadband spectral change. PLoS Comput. Biol. 12, e1004660 (2016).
University of Pennsylvania. Restoring Active Memory (RAM) http://memory.psych.upenn.edu/RAM (2018).
Paulson, T. Thought powers computer, Seattle Post-Intelligencer (16 December 2004).
Schalk, G., McFarland, D. J., Hinterberger, T., Birbaumer, N. & Wolpaw, J. R. BCI2000: a general-purpose brain-computer interface (BCI) system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51, 1034–1043 (2004).
Ojemann, G., Ojemann, J., Lettich, E. & Berger, M. Cortical language localization in left, dominant hemisphere. An electrical stimulation mapping investigation in 117 patients. J. Neurosurg. 71, 316 (1989).
Ojemann, G. A. Models of the brain organization for higher integrative functions derived with electrical stimulation techniques. Hum. Neurobiol. 1, 243 (1982).
Fox, P. T., Perlmutter, J. S. & Raichle, M. E. A stereotactic method of anatomical localization for positron emission tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 9, 141–153 (1985).
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B. & Sereno, M. I. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9, 179–194 (1999).
Ashburner, J. & Friston, K. J. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26, 839–851 (2005).
Friston, K. J. et al. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2, 189–210 (1995).
Miller, K. J. et al. Brain surface electrode co-registration using MRI and X-ray. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE 6015–6018 (IEEE, 2010).
Porat, B. A Course in Digital Signal Processing (Wiley, 1997).
Goupillaud, P., Grossmann, A. & Morlet, J. Cycle-octave and related transforms in seismic signal analysis. Geoexploration 23, 85–102 (1984).
Pakkenberg, B. & Gundersen, H. J. G. Neocortical neuron number in humans: effect of sex and age. J. Comp. Neurol. 384, 312–320 (1997).
Mitzdorf, U. Current source-density method and application in cat cerebral cortex: investigation of evoked potentials and EEG phenomena. Physiol. Rev. 65, 37–100 (1985).
Schalk, G. et al. Two-dimensional movement control using electrocorticographic signals in humans. J. Neural Eng. 5, 75–84 (2008).
Miller, K. J. et al. Cortical activity during motor execution, motor imagery, and imagery-based online feedback. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4430–4435 (2010).
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to J. Ojemann, M. den Nijs, R. Rao and G. Schalk for many years of selfless mentorship during the development of this library. D. Hermes, R. Eisinger and B. Wandell provided many helpful discussions about open data and helped with critical readings of this manuscript. The scientific value of the time spent by our patients at Harborview Hospital in Seattle is immense and I am thankful for their enthusiastic participation. I am financially supported by the Van Wagenen Foundation. Data collection was supported by NSF grant no. BCS-0642848 and NIH grant no. RO1NS065186. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author has no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information: Primary Handling Editor: Marike Schiffer.
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, K.J. A library of human electrocorticographic data and analyses. Nat Hum Behav 3, 1225–1235 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-019-0678-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-019-0678-3
This article is cited by
-
Face-Specific Activity in the Ventral Stream Visual Cortex Linked to Conscious Face Perception
Neuroscience Bulletin (2024)
-
A motor association area in the depths of the central sulcus
Nature Neuroscience (2023)
-
AJILE12: Long-term naturalistic human intracranial neural recordings and pose
Scientific Data (2022)
-
Open multimodal iEEG-fMRI dataset from naturalistic stimulation with a short audiovisual film
Scientific Data (2022)
-
Neural silences can be localized rapidly using noninvasive scalp EEG
Communications Biology (2021)