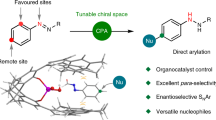
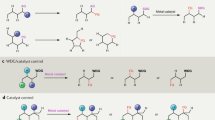
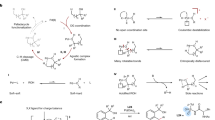
Abstract
C–H functionalization represents a promising approach for the synthesis of complex molecules. Instead of relying on modifying the functional groups present in a molecule, the synthetic sequence is achieved by carrying out selective reactions on the C–H bonds, which traditionally would have been considered to be the unreactive components of a molecule. A major challenge is to design catalysts to control both the site- and stereoselectivity of the C–H functionalization. We have been developing dirhodium catalysts with different selectivity profiles in C–H functionalization reactions with donor/acceptor carbenes as reactive intermediates. Here we describe a new dirhodium catalyst capable of the functionalization of non-activated primary C–H bonds with high levels of site selectivity and enantioselectivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Godula, K. & Sames, D. C–H bond functionalization in complex organic synthesis. Science 312, 67–72 (2006).
Gutekunst, W. R. & Baran, P. S. C–H functionalization logic in total synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 1976–1991 (2011).
Wencel-Delord, J. & Glorius, F. C–H bond activation enables the rapid construction and late-stage diversification of functional molecules. Nat. Chem. 5, 369–375 (2013).
Fier, P. S. & Hartwig, J. F. Synthesis and late-stage functionalization of complex molecules through C–H fluorination and nucleophilic aromatic substitution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 10139–10147 (2014).
Noisier, A. F. & Brimble, M. A. C–H functionalization in the synthesis of amino acids and peptides. Chem. Rev. 114, 8775–8806 (2014).
Romero, N. A., Margrey, K. A., Tay, N. E. & Nicewicz, D. A. Site-selective arene C–H amination via photoredox catalysis. Science 349, 1326–1330 (2015).
Cuthbertson, J. D. & MacMillan, D. W. The direct arylation of allylic sp 3 C–H bonds via organic and photoredox catalysis. Nature 519, 74–77 (2015).
Jin, J. & MacMillan, D. W. Alcohols as alkylating agents in heteroarene C–H functionalization. Nature 525, 87–90 (2015).
Davies, H. M. L. & Hansen, T. Asymmetric intermolecular carbenoid C−H insertions catalyzed by rhodium(ii) (S)-N-(p-dodecylphenyl)sulfonylprolinate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 9075–9076 (1997).
Davies, H. M. L., Antoulinakis, E. G. & Hansen, T. Catalytic asymmetric synthesis of syn-aldol products from intermolecular C−H insertions between allyl silyl ethers and methyl aryldiazoacetates. Org. Lett. 1, 383–386 (1999).
Davies, H. M. L. & Antoulinakis, E. G. Asymmetric catalytic C−H activation applied to the synthesis of syn-aldol products. Org. Lett. 2, 4153–4156 (2000).
Chan, K. H., Guan, X., Lo, V. K. & Che, C. M. Elevated catalytic activity of ruthenium(ii)-porphyrin-catalyzed carbene/nitrene transfer and insertion reactions with N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 2982–2987 (2014).
Li, Y., Huang, J. S., Zhou, Z. Y., Che, C. M. & You, X. Z. Remarkably stable iron porphyrins bearing nonheteroatom-stabilized carbene or (alkoxycarbonyl)carbenes: isolation, X-ray crystal structures, and carbon atom transfer reactions with hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 13185–13193 (2002).
Suematsu, H. & Katsuki, T. Iridium(iii) catalyzed diastereo- and enantioselective C−H bond functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 14218–14219 (2009).
Axten, J. M., Ivy, R., Krim, L. & Winkler, J. D. Enantioselective synthesis of d-threo-methylphenidate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 6511–6512 (1999).
Davies, H. M. L., Hansen, T., Hopper, D. W. & Panaro, S. A. Highly regio-, diastereo-, and enantioselective C−H insertions of methyl aryldiazoacetates into cyclic N-Boc-protected amines. Asymmetric synthesis of novel C2-symmetric amines and threo-methylphenidate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 6509–6510 (1999).
Lyons, T. W. & Sanford, M. S. Palladium-catalyzed ligand-directed C–H functionalization reactions. Chem. Rev. 110, 1147–1169 (2010).
Simmons, E. M. & Hartwig, J. F. Catalytic functionalization of unactivated primary C–H bonds directed by an alcohol. Nature 483, 70–73 (2012).
Liu, Y. J. et al. Overcoming the limitations of directed C–H functionalizations of heterocycles. Nature 515, 389–393 (2014).
Dick, A. R., Hull, K. L. & Sanford, M. S. A highly selective catalytic method for the oxidative functionalization of C−H bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 2300–2301 (2004).
Desai, L. V., Malik, H. A. & Sanford, M. S. Oxone as an inexpensive, safe, and environmentally benign oxidant for C−H bond oxygenation. Org. Lett. 8, 1141–1144 (2006).
Kalyani, D. & Sanford, M. S. Regioselectivity in palladium-catalyzed C−H activation/oxygenation reactions. Org. Lett. 7, 4149–4152 (2005).
Hwang, S. J., Cho, S. H. & Chang, S. Synthesis of condensed pyrroloindoles via Pd-catalyzed intramolecular C–H bond functionalization of pyrroles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16158–16159 (2008).
McQuaid, K. M. & Sames, D. C–H bond functionalization via hydride transfer: Lewis acid catalyzed alkylation reactions by direct intramolecular coupling of sp 3 C–H bonds and reactive alkenyl oxocarbenium intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 402–403 (2009).
He, G., Zhao, Y., Zhang, S., Lu, C. & Chen, G. Highly efficient syntheses of azetidines, pyrrolidines, and indolines via palladium catalyzed intramolecular amination of C(sp 3)−H and C(sp 2)−H bonds at gamma and delta positions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 3–6 (2012).
Doyle, M. P., Duffy, R., Ratnikov, M. & Zhou, L. Catalytic carbene insertion into C−H bonds. Chem. Rev. 110, 704–724 (2010).
Doyle, M. P., Kalinin, A. V. & Ene, D. G. Chiral catalyst controlled diastereoselection and regioselection in intramolecular carbon−hydrogen insertion reactions of diazoacetates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 8837–8846 (1996).
Taber, D. F. & Stiriba, S. E. Synthesis of natural products by rhodium-mediated intramolecular C−H insertion. Chem. Eur. J. 4, 990–992 (1998).
Breslow, R. & Gellman, S. H. Intramolecular nitrene carbon–hydrogen insertions mediated by transition-metal complexes as nitrogen analogs of cytochrome P-450 reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 6728–6729 (1983).
Espino, C. G., Wehn, P. M., Chow, J. & Du Bois, J. Synthesis of 1,3-difunctionalized amine derivatives through selective C−H bond oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 6935–6936 (2001).
Sigman, M. S. & Werner, E. W. Imparting catalyst control upon classical palladium-catalyzed alkenyl C−H bond functionalization reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 45, 874–884 (2012).
Hickman, A. J. & Sanford, M. S. Catalyst control of site selectivity in the Pdii/iv-catalyzed direct arylation of naphthalene. ACS Catal. 1, 170–174 (2011).
Hartwig, J. F. Catalyst-controlled site-selective bond activation. Acc. Chem. Res. 50, 549–555 (2017).
Dydio, P. et al. An artificial metalloenzyme with the kinetics of native enzymes. Science 354, 102–106 (2016).
Thu, H. Y., Yu, W. Y. & Che, C. M. Intermolecular amidation of unactivated sp 2 and sp 3 C–H bonds via palladium-catalyzed cascade C–H activation/nitrene insertion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 9048–9049 (2006).
Espino, C. G., Fiori, K. W., Kim, M. & Du Bois, J. Expanding the scope of C–H amination through catalyst design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 15378–15379 (2004).
Bois, J. D. Rhodium-catalyzed C–H amination—an enabling method for chemical synthesis. Org. Process Res. Dev. 15, 758–762 (2011).
Huang, X., Bergsten, T. M. & Groves, J. T. Manganese-catalyzed late-stage aliphatic C–H azidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 5300–5303 (2015).
Sharma, A. & Hartwig, J. F. Metal-catalysed azidation of tertiary C–H bonds suitable for late-stage functionalization. Nature 517, 600–604 (2015).
Chen, H., Schlecht, S., Semple, T. C. & Hartwig, J. F. Thermal, catalytic, regiospecific functionalization of alkanes. Science 287, 1995–1997 (2000).
Schmidt, V. A., Quinn, R. K., Brusoe, A. T. & Alexanian, E. J. Site-selective aliphatic C–H bromination using N-bromoamides and visible light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 14389–14392 (2014).
Davies, H. M. & Manning, J. R. Catalytic C–H functionalization by metal carbenoid and nitrenoid insertion. Nature 451, 417–424 (2008).
Davies, H. M. & Morton, D. Guiding principles for site selective and stereoselective intermolecular C–H functionalization by donor/acceptor rhodium carbenes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 1857–1869 (2011).
Liao, K., Negretti, S., Musaev, D. G., Bacsa, J. & Davies, H. M. L. Site-selective and stereoselective functionalization of unactivated C–H bonds. Nature 533, 7602–7606 (2016).
Liao, K. et al. Site-selective and stereoselective functionalization of non-activated tertiary C–H bonds. Nature 551, 609–613 (2017).
Thu, H. Y. et al. Highly selective metal catalysts for intermolecular carbenoid insertion into primary C–H bonds and enantioselective C−C bond formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 9747–9751 (2008).
Davies, H. M. L. & Venkataramani, C. Kinetic resolution and double stereodifferentiation in catalytic asymmetric C−H activation of 2-substituted pyrrolidines. Org. Lett. 3, 1773–1775 (2001).
Liao, K. et al. Site-selective carbene-induced C–H functionalization catalyzed by dirhodium tetrakis(triarylcyclopropanecarboxylate) complexes. ACS Catal. 8, 678–682 (2018).
Hansen, J. H., Autsbach, J. & Davies, H. M. L. Computational study on the selectivity of donor/acceptor-substituted rhodium carbenoids. J. Org. Chem. 74, 6555–6563 (2009).
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided by the National Science Foundation (NSF) via the CCI Center for Selective C–H Functionalization (CHE-1700982). D.G.M. acknowledges NSF MRI-R2 grant CHE-0958205 and the use of the resources of the Cherry Emerson Center for Scientific Computation. Funds to purchase the NMR and X-ray spectrometers used in these studies were supported by the NSF (CHE 1531620 and CHE 1626172). The authors thank J. Bacsa for the X-ray structure determinations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.L. and H.M.L.D. designed the synthetic experiments, K.L. performed the synthetic experiments, Y.-F.Y., Y.L., J.S., D.G.M. and K.N.H. conducted the computational studies, and K.L., K.N.H and H.M.L.D. prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
H.M.L.D. is a named inventor on a patent entitled ‘Dirhodium catalyst compositions and synthetic processes related thereto’ (US 8,974,428, issued March 10, 2015). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary experimental and computational details
Crystallographic data
CIF for compound 11; CCDC reference: 1551026
Crystallographic data
Structure factors for compound 11; CCDC reference 1551026
Crystallographic data
CIF for catalyst F; CCDC reference: 1552206
Crystallographic data
Structure factors for catalyst F; CCDC reference 1552206
Computational data
Calculated C2 symmetric structure for catalyst I
Computational data
Calculated C4 symmetric structure for catalyst I
Computational data
Calculated C4a symmetric structure for catalyst I
Computational data
Calculated D2 symmetric structure for catalyst I
Computational data
Calculated C2 symmetric carbene structure
Computational data
Calculated C4 symmetric carbene structure for catalyst
Computational data
Calculated transition state TS1
Computational data
Calculated transition state TS2
Computational data
Calculated transition state TS3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, K., Yang, YF., Li, Y. et al. Design of catalysts for site-selective and enantioselective functionalization of non-activated primary C–H bonds. Nature Chem 10, 1048–1055 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0087-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-018-0087-7
This article is cited by
-
Regioselective aliphatic C–H functionalization using frustrated radical pairs
Nature (2023)
-
A tautomerized ligand enabled meta selective C–H borylation of phenol
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Computational Study of Key Mechanistic Details for a Proposed Copper (I)-Mediated Deconstructive Fluorination of N-Protected Cyclic Amines
Topics in Catalysis (2022)
-
Marine furanocembranoids-inspired macrocycles enabled by Pd-catalyzed unactivated C(sp3)-H olefination mediated by donor/donor carbenes
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Organocatalyst-controlled site-selective arene C–H functionalization
Nature Chemistry (2021)