Abstract
Surface acoustic waves are commonly used in classical electronics applications, and their use in quantum systems is beginning to be explored, as evidenced by recent experiments using acoustic Fabry–Pérot resonators. Here we explore their use for quantum communication, where we demonstrate a single-phonon surface acoustic wave transmission line, which links two physically separated qubit nodes. Each node comprises a microwave phonon transducer, an externally controlled superconducting variable coupler, and a superconducting qubit. Using this system, precisely shaped individual itinerant phonons are used to coherently transfer quantum information between the two physically distinct quantum nodes, enabling the high-fidelity node-to-node transfer of quantum states as well as the generation of a two-node Bell state. We further explore the dispersive interactions between an itinerant phonon emitted from one node and interacting with the superconducting qubit in the remote node. The observed interactions between the phonon and the remote qubit promise future quantum-optics-style experiments with itinerant phonons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Quantum communication is of significant interest for the generation of remote entanglement and the secure transmission of information, as well as for distributed quantum computing1,2,3,4,5,6,7. There are several demonstrations of long-distance quantum communication protocols using optical methods, in parallel with demonstrations of similar protocols using microwave-frequency photons, including Bell state entanglement of remote qubits as well as the transmission of multi-qubit entangled states8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16. Microwave-frequency phonons, as opposed to photons, can also be used for quantum communication as well as for coupling hybrid quantum systems17,18,19,20, in the latter case taking advantage of the strong strain coupling in some optical as well as atomic-scale systems. Microwave-frequency acoustic resonators may be able to serve as very long-lived quantum memories21. Quantum communication protocols implemented with phonons are thus of significant scientific as well as practical interest. Recent advances in the quantum control of phonons include the creation and measurement of stationary phonon quantum states22,23,24, the emission and absorption of phonons in an acoustic resonator25, and the generation of entangled phonons in a phonon-mediated quantum eraser experiment26.
Here we report the experimental realization of a phonon-based quantum communication channel, enabling the communication of quantum states via traveling phonons linking two physically distinct quantum nodes. The phonons are emitted in the communication channel as short-duration acoustic pulses, sufficiently brief that the extent of the acoustic pulses is significantly less than the length of the channel, such that the phonons travel in a particle-like fashion along the channel, which we term itinerant.
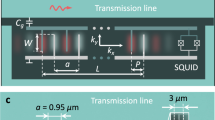
The experimental system is shown schematically in Fig. 1, with the physical setup in Fig. 1a and the circuit schematic in Fig. 1b. The 2-mm-long phonon communication channel (500 ns single-trip time) is terminated at each end by a specially designed unidirectional interdigitated transducer (IDT), which is in turn connected to a superconducting qubit via a superconducting tunable coupler. The unidirectional transducers (UDTs) differ from conventional acoustic transducers, here emitting itinerant phonons in only one direction, as opposed to more standard bidirectional transducers, which emit excitations equally in two opposing directions (see Supplementary Note 1; a related but distinct design appears in ref. 27). We note this device differs from the experimental construction in e.g. ref. 25, which uses a single bidirectional transducer in a Fabry–Pérot cavity. In that experiment, a single phonon comprises acoustic excitations that travel in two opposing directions to distant acoustic mirrors, from which the excitations reflect and return to interfere constructively at the emitting transducer, where the excitation can be intercepted by one of two qubits. In the experiment here, two distinct UDTs are used to link two physically separate nodes. Each transducer is constructed to emit an acoustic excitation in only one direction, creating a significantly more flexible and general-purpose design, with physically separate and distinct phonon emitter and receiver.
a Schematic representation of the two quantum communication nodes and the phononic quantum channel. Each node comprises a superconducting qubit, a tunable coupler that allows shaping phonon release and capture, and a unidirectional phonon transducer. Details in the Methods section. b Circuit diagram of the assembled device. Each qubit Qj is excited through its dedicated Qxyj microwave line and frequency-controlled through a separate Qz j flux-bias line, and each tunable coupler Gk is controlled via its associated Gz k flux-bias line.
We use this device to demonstrate two-node quantum state transfers as well as the phonon-mediated deterministic generation of an entangled Bell state, representing a significant advance over prior work, in which a single transducer was coupled to a Fabry–Pérot acoustic cavity formed by two acoustic mirrors22,23,24,25,26. We also realize a single-phonon interferometer, using one qubit to emit and detect a traveling phonon, where the phonon is used to probe the state of the second qubit, effectively demonstrating the dispersive interaction of a photon (localized in the remote qubit) and a traveling phonon. Finally, we demonstrate a Ramsey interferometer, using the second qubit to detect the presence of a traveling phonon emitted by the first qubit, thus interchanging the roles of the qubits in the previous experiment and demonstrating the versatility of this architecture.
Results
Phonon-mediated quantum state transfer
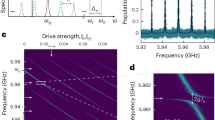
We first probe the interaction between the qubits and the phonon channel, as shown in Fig. 2a. We excite Q1 with a π pulse, then set its coupler G1 to an intermediate coupling, sufficient that Q1’s relaxation is dominated by phonon emission. We set Q2’s coupler G2 off during this measurement so that Q2 does not interact with the traveling phonon. For frequencies inside the transducer’s active band, from 3.87 to 4.01 GHz, where the emission is almost entirely unidirectional itinerant phonons, we observe a time-delayed revival of qubit Q1’s excited state population \({P}_{e}^{{Q}_{1}}\) at times that are multiples of the phonon round-trip time τRT ~ 1 μs, each revival corresponding to the traveling phonon reflecting off the other transducer before re-exciting Q1. Outside the unidirectional band, we see a complex structure in Pe as a function of frequency and interaction time, with broad swings of width ~150 MHz superposed with narrow oscillations of width ~7 MHz. The broad swings and finer details are in accordance with expectations (see Supplementary Note 1)28.
a Measured Q1 excited state population \({P}_{e}^{{Q}_{1}}\) as a function of time and Q1 bare frequency, with coupler G1 at an intermediate coupling κ1/2π = 2.4 MHz (measured at 3.976 GHz) and G2 set to zero coupling. In this configuration, Q1’s energy relaxation is dominated by phonon emission via UDT1, followed by traveling phonon dynamics. The white and red dashed lines indicate the unidirectional and bidirectional working frequencies, respectively (see text); inset shows the qubit excitation and measurement pulse sequence. b Quantum state transfer via a traveling phonon at the unidirectional (left) and bidirectional (right) operating frequencies. Q2’s final population is 4.5 times smaller for the bidirectional transfer compared to the unidirectional transfer, in line with simulations. Green solid lines are from a master equation simulation. Inset: pulse sequence. For either process, Q1’s emission rate is set to \({\kappa }_{c}^{{{{{{\rm{uni| bi}}}}}}}/2\pi =10| \,{{\mbox{6}}}\,\ \,{{\mbox{MHz}}}\,\), corresponding to a 81∣138 ns full-width-at-half-maximum (FWHM) phonon wave packet. c Quantum process tomography for the unidirectional and bidirectional regimes, with process fidelities of \({{{{{{\mathcal{F}}}}}}}_{{{{{{\rm{uni}}}}}}}={{{{{\rm{Tr}}}}}}\,({\chi }_{\exp } \cdot {\chi }_{{{{{{\rm{ideal}}}}}}})=82\pm \,{{\rm{0.3}}}{\%}\) and \({{{{{{\mathcal{F}}}}}}}_{{{{{{\rm{bi}}}}}}}=39\pm \,{{\rm{0.3}}}{{{\%}}}\,\), respectively. Red solid lines show values expected for an ideal transfer; black dashed lines show master equation simulations, taking into account finite qubit coherence and phonon channel losses. Uncertainties are standard deviations from the mean.
The itinerant phonon experiments are performed at the working frequency \({\omega }_{{Q}_{1,2}}^{{{{{{\rm{uni}}}}}}}/2\pi =\,{{\mbox{3.976}}}\,\ \,{{\mbox{GHz}}}\,\), inside the unidirectional band. By working outside this band, we can explore the regime where the transducers are effectively bidirectional, using the second working frequency \({\omega }_{{Q}_{1,2}}^{{{{{{\rm{bi}}}}}}}/2\pi =\,{{\mbox{4.102}}}\,\ \,{{\mbox{GHz}}}\,\). These frequencies are marked by the dashed white and red lines, respectively, in Fig. 2a.
To maximize the efficiency of phonon-mediated quantum state transfers, we need to carefully shape the emission and absorption of the phonon wave packet, which is done by time-dependent control of the coupling between the qubit and its transducer11,12,13,14,15,25,29. We experimentally optimize the transfer efficiency, with results shown in Fig. 2b for both the unidirectional (left) and bidirectional (right) regimes. The transfer starts with the shaped emission of a phonon, shown by the decrease of Q1’s excited state population with the expected time dependence. Both qubits then remain in their ground states until the phonon reaches Q2, which absorbs the itinerant phonon, following the expected time dependence, and ultimately reaching a plateau once the transfer is complete. The total transfer takes ~700 ns, including the ~500 ns phonon travel time. The final Q2 population reaches a maximum of 68% for the unidirectional transfer, limited mostly by phonon loss in the channel. For the bidirectional transfer, the final Q2 population reaches 15%, 4.5 times less than the unidirectional population, which is 12% higher than the ideal value, demonstrating good agreement with theory and excellent unidirectionality for the transducer design. We simulate the transfer process using a cascaded quantum input-output model25 (solid green line). From this model, we estimate that phonon loss reduces the final unidirectional transfer efficiency by 27%, and the finite Q1 and Q2 coherence times reduce the fidelity by 1 and 2%, respectively. We note that an equivalent photon travel time would require a ~100-m-long coaxial cable, illustrating the very long delays achievable with phonon-based quantum channels.
In Fig. 2c, we show quantum process tomography for both regimes. For the unidirectional process, we find a process fidelity of \({{{{{{\mathcal{F}}}}}}}^{{{{{{\rm{uni}}}}}}}=\,({{\rm{82.0}}}\,\pm \,{\rm{0.3}}){{\%}}\), while for the bidirectional regime, the process fidelity is limited to \({{{{{{\mathcal{F}}}}}}}^{{{{{{\rm{bi}}}}}}}=\,({{\rm{39.0}}}\,\pm\,{{\rm{0.3}}}){{{\%}}}\). We compare these experimental process fidelities with predictions and find trace distances \(d=\sqrt{{{{{{\rm{Tr}}}}}}\,{({\chi }_{\exp }-{\chi }_{{{{{{\rm{sim}}}}}}})}^{2}}=0.07\) and 0.3 for the unidirectional and bidirectional regimes. The contrast in fidelities and trace distances underlines the importance of the UDTs.
Traveling phonon-mediated remote entanglement
We further explore the capabilities of itinerant phonon communication by performing a phonon-mediated remote entanglement of the two qubits, shown in Fig. 3. The protocol is similar to that for the quantum state transfer, except here we calibrate the emission pulse to only emit Q1’s excitation as a phonon with a probability of 1/2, meaning that immediately following the “half-emission,” with qubit Q2 in the ground state, the system is ideally in the state \((\left|e0g\right\rangle +\left|g1g\right\rangle )/\sqrt{2}\) (writing the state \(\left|{Q}_{1}\ \gamma \ {Q}_{2}\right\rangle\) where γ represents the itinerant phonon). During the time the emitted “half-phonon” travels along the phonon channel, Q1’s remaining excitation decays following Q1’s intrinsic T1 time, with Q1’s coupling to the channel set to zero. The traveling half-phonon is then captured by Q2, generating a Bell state \(\left|\psi \right\rangle =(\left|eg\right\rangle +{e}^{i\varphi }\left|ge\right\rangle )/\sqrt{2}\) between the two qubits, with φ a relative phase.
a Inset: pulse sequence for Bell state generation. Main panel: excited state probabilities for Q1 (red) and Q2 (blue) as a function of time. Green lines are results from a master equation simulation. The final state is analyzed at tm = 725 ns (gray dashed line). b Bell state density matrix, absolute values, without readout correction, measured at tm. Red solid lines show values expected for an ideal Bell state; black dashed lines show simulation results including qubit coherence and phonon channel losses.
Figure 3a shows the time-dependent qubit state populations Pe for each qubit, which agrees well with a master equation simulation. Following the capture of the half-phonon, we perform quantum state tomography at time tm = 750 ns; these measurements are used to reconstruct the two-qubit density matrix ρ shown in Fig. 3b. We find a Bell state fidelity \({{{{{{\mathcal{F}}}}}}}_{{{{{{\rm{Bell}}}}}}}={{{{{\rm{Tr}}}}}}\,({\rho }_{{{{{{\rm{ideal}}}}}}}\cdot \rho )=\,{{\rm{72}}}{{{\%}}}\,\) and a concurrence \({{{{{\mathcal{C}}}}}}=\,{{\mbox{0.53}}}\,\), close to the master equation simulation results, with a trace distance \({d}^{{{{{{\rm{Bell}}}}}}}=\sqrt{{{{{{\rm{Tr}}}}}}\,{({\rho }_{\exp }-{\rho }_{{{{{{\rm{sim}}}}}}})}^{2}}=\,{{\mbox{0.13}}}\,\).
Phonon-qubit dispersive interaction
Sensing traveling phonons without absorbing them would provide a highly useful capability, as would being able to use a traveling phonon as a probe of a remote quantum system, which we explore in a pair of related experiments. First, we use a traveling phonon as a probe of a remote quantum two-level system, shown in Fig. 4a. We use qubit Q1 as the emitter and receiver of a “half-phonon” that is detected interferometrically25,26 when returning to Q1. This allows us to measure how the phase of the traveling phonon is affected by interacting dispersively with qubit Q2, which serves as a stand-in for a generic quantum system.
Dispersive state-dependent interferometric probe. a Schematic roles played by each element. b Blue (salmon) points show the φ dependence of Q1’s final Pe when Q2 is in \(\left|g\right\rangle\) (\(\left|e\right\rangle\)), showing a dependence of the phonon phase on Q2’s state, with a shift of ~0.4π rad. c Qubit pulse sequences (see text for details). d Schematic roles played by each element for the dispersive phase-dependent interferometric probe. e Ramsey interference in Q2 (blue circles) reveals Q2’s dependence on the relative phase with the phonon. When repeating the same protocol with no initial π pulse on Q1, we measure the Ramsey interference of Q2 (salmon squares), shifted by π compared to the first measurement. Blue (salmon) points show the φ dependence of Q1’s final Pe when Q2 is in \(\left|g\right\rangle\) (\(\left|e\right\rangle\)), showing a dependence of the phonon phase on Q2’s state, with a shift of ~0.4π rad. f Qubit pulse sequences, similar to c except Q2 is always placed in \((\left|g\right\rangle +{e}^{{{{{{\rm{i}}}}}}\theta }\left|e\right\rangle )/\sqrt{2}\) and the θ-dependent \({P}_{e}^{Q2}\) is measured.
The pulse sequence for this state detection is shown to the right in Fig. 4a. We first prepare Q1 in its excited state and emit a half-phonon, which reflects from the distant transducer, whose coupling to Q2 is turned on during the reflection process, and the half-phonon interacts with Q1 on its return. During the half-phonon transit, we briefly shift Q1’s frequency so that Q1’s excited state acquires a relative phase φ, yielding an interferometric interaction with the returning half-phonon, either interfering constructively to return Q1 toward its excited state, or destructively and having Q1 emit its remaining energy and relax to its ground state. In Fig. 4a, we show the final Q1 population as a function of the phase φ (blue points), showing a characteristic interference pattern with a visibility of 32%.
We repeat the experiment with Q2 excited by a π pulse at the beginning of the experiment, with the experiment otherwise unchanged; the results are shown in Fig. 4a (salmon points). There are three effects on the oscillation pattern: a slight increase in the oscillation minima, attributed to a decrease of the phonon coherence25 in its interaction with Q2; a more marked reduction of visibility attributed to inadequate absorption of the phonon wave packet; and, most significantly, a phase shift of \({{\Delta }}{\varphi }_{\exp }=0.40\pi\) attributed to the dispersive interaction between Q2 and the traveling half-phonon, close to our fit-free simulated value of \({{\Delta }}{\varphi }_{{{{{{\rm{sim}}}}}}}=0.41\pi\) (see Supplementary Note 9). This last effect points to the interesting possibility of using phonons as dispersive probes of other quantum systems.
In a separate experiment, shown in Fig. 4b, we swap the roles of the qubits, so Q2 is now used as a dispersive probe for the phonon released by Q1, using a Ramsey fringe measurement of Q2. The pulse sequence is shown to the right in Fig. 4b, where Q2 is placed in the state \((\left|g\right\rangle +{e}^{{{{{{\rm{i}}}}}}\theta }\left|e\right\rangle )/\sqrt{2}\) by the initial π/2 rotation, performed about an axis rotated in the x – y plane of the Bloch sphere by θ, and the θ-dependent evolution of Q2 is compared for where Q1 is not excited (no probe phonon) to where Q1 is excited and Q2 interacts with the subsequently released traveling phonon. In the latter case, the Ramsey fringe visibility is reduced, which we attribute to leakage from Q2 into the phononic channel, but we again observe a significant phase shift, here as high as \({{\Delta }}{\theta }_{\exp }=0.95\ \pi\) close to our simulation \({{\Delta }}{\theta }_{{{{{{\rm{sim}}}}}}}=0.99\ \pi\).
Discussion
In conclusion, we demonstrate controlled phonon-mediated quantum state transfer and remote entanglement between two quantum nodes, each node comprising a superconducting qubit with a time-variable coupler, using individual itinerant SAW phonons traveling in an acoustic transmission line after a controlled, on-demand release, followed by capture. Using this architecture, we also demonstrate the dispersive interaction between an itinerant phonon and a superconducting qubit. These results have been made possible by the integration of broadband, highly UDT in a 2-mm-long phonon communication channel, as well as the use of a quantum state protocol requiring tunable coupling to each qubit node2. Achieving a quite impressive quantum state transfer fidelity of 82.0(2)%, limited by the loss in the phonon channel, this platform paves the way for quantum-optics-like experiments realized with individual phonons instead of photons.
Methods
Device fabrication and characterization
The device used in these experiments comprises two dies, a sapphire die with the two superconducting qubits (Q1 and Q2), and their associated tunable couplers (G1 and G2, respectively), as well as control and readout wiring, and a lithium niobate die with the phononic channel and the two UDTs. The two dies are fabricated separately then flip-chip assembled30. The full circuit schematic is shown in Fig. 1b.
The acoustic die is fabricated using a single layer of ~25-nm-thick aluminum patterned by PMMA liftoff on a LiNbO3 wafer, 500 μm thick. The central part of the acoustic device is the ℓ = 2-mm-long phononic channel, with width W = 150 μm, terminated at each end by a UDT (UDT1,2).
The UDTs are described more completely in Supplementary Note 1. Briefly, the two (nominally identical) UDTs each comprise a standard bidirectional IDT combined with an acoustic mirror (a reflective grating). The IDT emits equal-amplitude acoustic excitations in opposite directions, one toward and the other away from the second UDT. The acoustic mirror, placed immediately adjacent to the IDT on the side opposite the second UDT, reflects its incident excitation back toward the second UDT, such that it interferes constructively with the other excitation. Each UDT is coupled inductively to one of the two qubits.
We have separately characterized similar IDT-mirror designs, wherein the frequency band from about 3.85–4 GHz, excellent directionality is achieved, with emission from the UDT almost entirely directed away from the mirror. Typical directivities are greater than 20 dB. Outside this unidirectional band, the mirrors are less effective and the devices emit more strongly in both directions27.
The superconducting qubit die is fabricated on 430-μm-thick sapphire using standard lithographic processing15. The qubits Q1,2 are tunable xmon-style qubits31,32, where each qubit’s frequency is controlled by a flux line Qz1,z2, and excited using a capacitively coupled microwave line Qxy1,xy2. Each qubit is coupled to the SAW chip through a superconducting tunable coupler G1,2, whose coupling is controlled33 using external flux lines Gz1,z2. Qubit states are inferred from standard dispersive measurements using a separate readout resonator for each qubit. The readout resonators are connected to a common readout line; more details are given in Supplementary Note 1.
The qubits are characterized with their couplers turned off (see Supplementary Notes 6 and 7). At the qubit idle frequency ωidle/(2π) ~4.3 GHz, we find the qubits have an energy relaxation time T1 = 57 μs (Q1) and 38 μs (Q2), with a coherence time \({T}_{2}^{{{{{{\rm{Ramsey}}}}}}}\)= 1.11 μs (Q1) and 0.88 μs (Q2) (most likely limited by flux noise as the qubits are tuned far away from their flux-insensitive point). These times demonstrate the potential for excellent qubit coherence when using a flip-chip assembly30.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to A. N. Cleland (anc@uchicago.edu).
References
Bennett, C. H. et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895–1899 (1993).
Cirac, J. I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H. J. & Mabuchi, H. Quantum state transfer and entanglement distribution among distant nodes in a quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221–3224 (1997).
Bouwmeester, D. et al. Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390, 575–579 (1997).
Gottesman, D. & Chuang, I. L. Demonstrating the viability of universal quantum computation using teleportation and single-qubit operations. Nature 402, 390–393 (1999).
Duan, L. M., Lukin, M. D., Cirac, J. I. & Zoller, P. Long-distance quantum communication with atomic ensembles and linear optics. Nature 414, 413–417 (2001).
Jiang, L., Taylor, J., Sörensen, A. & Lukin, M. Distributed quantum computation based-on small quantum registers. Phys. Rev. A 76, 062323 (2007).
Kimble, H. J. The quantum internet. Nature 453, 1023–1030 (2008).
Yin, J. et al. Entanglement-based secure quantum cryptography over 1,120 kilometres. Nature 582, 1–5 (2020).
Xu, F., Ma, X., Zhang, Q., Lo, H.-K. & Pan, J.-W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 92, 025002 (2020).
Chang, H.-S. et al. Remote entanglement via adiabatic passage using a tunably dissipative quantum communication system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 240502 (2020).
Kurpiers, P. et al. Deterministic quantum state transfer and remote entanglement using microwave photons. Nature 558, 264–267 (2018).
Axline, C. J. et al. On-demand quantum state transfer and entanglement between remote microwave cavity memories. Nat. Phys. 14, 705–710 (2018).
Campagne-Ibarcq, P. et al. Deterministic remote entanglement of superconducting circuits through microwave two-photon transitions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 200501 (2018).
Leung, N. et al. Deterministic bidirectional communication and remote entanglement generation between superconducting qubits. npj Quantum Inf. 5, 18 (2019).
Zhong, Y. P. et al. Violating Bell’s inequality with remotely connected superconducting qubits. Nat. Phys. 15, 741–744 (2019).
Zhong, Y. P. et al. Deterministic multi-qubit entanglement in a quantum network. Nature 590, 571–575 (2021).
Vainsencher, A., Satzinger, K. J., Peairs, G. A. & Cleland, A. N. Bi-directional conversion between microwave and optical frequencies in a piezoelectric optomechanical device. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 033107 (2016).
Whiteley, S. J. et al. Spin-phonon interactions in silicon carbide addressed by Gaussian acoustics. Nat. Phys. 15, 490–495 (2019).
Peairs, G. A. et al. Bi-directional conversion between microwave and optical frequencies in a piezoelectric optomechanical device. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 061001 (2020).
Mirhosseini, M., Sipahigil, A., Kalaee, M. & Painter, O. Superconducting qubit to optical photon transduction. Nature 588, 599–603 (2020).
MacCabe, G. S. et al. Nano-acoustic resonator with ultralong phonon lifetime. Science 370, 840–843 (2020).
Chu, Y. et al. Quantum acoustics with superconducting qubits. Science 358, 199–202 (2017).
Chu, Y. et al. Creation and control of multi-phonon fock states in a bulk acoustic-wave resonator. Nature 563, 666–670 (2018).
Satzinger, K. J. et al. Quantum control of surface acoustic-wave phonons. Nature 563, 661–665 (2018).
Bienfait, A. et al. Phonon-mediated quantum state transfer and remote qubit entanglement. Science 364, 368–371 (2019).
Bienfait, A. et al. Quantum erasure using entangled surface acoustic phonons. Phys. Rev. X 10, 021055 (2020).
Dumur, É. et al. Unidirectional distributed acoustic reflection transducers for quantum applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 114, 223501 (2019).
Morgan, D. Surface Acoustic Wave Filters (Elsevier Ltd., 2007).
Korotkov, A. N. Flying microwave qubits with nearly perfect transfer efficiency. Phys. Rev. B 84, 014510 (2011).
Satzinger, K. J. et al. Simple non-galvanic flip-chip integration method for hybrid quantum systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 114, 173501 (2019).
Koch, J. et al. Charge-insensitive qubit design derived from the Cooper pair box. Phys. Rev. A 76, 042319 (2007).
Barends, R. et al. Coherent Josephson qubit suitable for scalable quantum integrated circuits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 080502 (2013).
Chen, Y. et al. Qubit architecture with high coherence and fast tunable coupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 220502 (2014).
Acknowledgements
Devices and experiments were supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the Army Research Laboratory, and material for this work was supported by the Department of Energy (DOE). É. D. was supported by LDRD funds from Argonne National Laboratory. K. J. S. was supported by NSF GRFP (NSF DGE-1144085) and A. N. C. was supported by the DOE, Office of Basic Energy Sciences. This work was partially supported by the UChicago MRSEC (NSF DMR-2011854), AFOSR under award FA9550-20-1-0270, the NSF QLCI for HQAN (NSF Award 2016136), and made use of the Pritzker Nanofabrication Facility, which receives support from SHyNE, a node of the National Science Foundation’s National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NSF NNCI ECCS-2025633).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
É. D. designed and fabricated the devices, performed the experiment, and analyzed the data. K. J. S., G. A. P., and M.-H. C. participated to the design process of the unidirectional transducer. É. D., K. J. S., A. B., H.-S. C., J. G., and Y. P. Z. developed the fabrication process of the superconducting circuit. É. D., K. J. S., and A. B. wrote code to model surface acoustic waves. A. N. C. advised on all efforts. All authors contributed to the discussion and production of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Dumur, É., Satzinger, K.J., Peairs, G.A. et al. Quantum communication with itinerant surface acoustic wave phonons. npj Quantum Inf 7, 173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00511-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00511-1
This article is cited by
-
Deterministic generation of multidimensional photonic cluster states with a single quantum emitter
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Unlocking phonon properties of a large and diverse set of cubic crystals by indirect bottom-up machine learning approach
Communications Materials (2023)
-
Phononic bath engineering of a superconducting qubit
Nature Communications (2023)