Abstract
Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores are key iron sources for modern industry, yet their origin remains controversial. Diverse ore-forming processes have been discussed, comprising low-temperature hydrothermal processes versus a high-temperature origin from magma or magmatic fluids. We present an extensive set of new and combined iron and oxygen isotope data from magnetite of Kiruna-type ores from Sweden, Chile and Iran, and compare them with new global reference data from layered intrusions, active volcanic provinces, and established low-temperature and hydrothermal iron ores. We show that approximately 80% of the magnetite from the investigated Kiruna-type ores exhibit δ56Fe and δ18O ratios that overlap with the volcanic and plutonic reference materials (> 800 °C), whereas ~20%, mainly vein-hosted and disseminated magnetite, match the low-temperature reference samples (≤400 °C). Thus, Kiruna-type ores are dominantly magmatic in origin, but may contain late-stage hydrothermal magnetite populations that can locally overprint primary high-temperature magmatic signatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
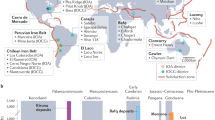
Apatite-iron oxide ore is by far the biggest source of iron in Europe and one of the main iron sources worldwide1. In Europe, these magnetite-dominated ores have traditionally been sourced from two principal regions, the Bergslagen ore province in south central Sweden and the Kiruna-Malmberget region in northern Sweden (Fig. 1)2. The apatite-iron oxide ores from these localities are internationally renowned and similar ores elsewhere are usually referred to as being of Kiruna-type3,4,5. While the Grängesberg and Kiruna deposits are Palaeoproterozoic in age6, similar apatite-iron oxide deposits along the American Cordilleras are much younger and range in age from Jurassic to Neogene, like the Pliocene El Laco deposit in Chile7,8,9. Together with the occurrences of Paleozoic apatite-iron oxide ores in Turkey, Iran, and China, and Triassic examples from Korea10,11,12,13, apatite-iron oxide ores have repeatedly formed across the globe and throughout geological time.
The origin of the Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores remains ambiguous, however, despite a long history of study and a concurrently intense scientific debate. Several fundamentally different modes of formation have been proposed. Today two broad schools of thought prevail, represented by either direct magmatic formation processes, such as segregation or crystallization, or by hydrothermal replacement processes, including hydrothermal precipitation in the sense of iron-oxide-copper-gold (IOCG) deposits3,4,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31. Specifically, the discussion revolves around a direct magmatic origin (ortho-magmatic) from volatile- and Fe–P-rich magmas or high-temperature magmatic fluids1,5,18,31, versus a purely hydrothermal one, where circulating, metal-rich fluids replace original host rock mineralogy with apatite-iron-oxide mineralizations at medium to low temperature4,19,28,29,30,32. An ortho-magmatic origin is generally understood to be either formation by direct crystallization from a magma or from high-temperature magmatic fluids (e.g. ≥800 °C), or via high-temperature liquid immiscibility and physical separation of an iron oxide-dominated melt from a silicate-dominated magma, where the former may subsequently crystallize as a separate body17,18,33,34,35,36,37,38. Hydrothermal processes, in turn, encompass transport and precipitation, including replacement-type reactions, by means of aqueous fluids at more moderate to low temperatures (typically ≤400 °C)27,29,30,32. Both the magmatic and the hydrothermal hypotheses are supported in part by field observations, textural relationships, and mineral chemistry, however, petrological field evidence and chemical trends of major and trace elements have frequently been interpreted in different ways5,14,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,28,29,30,31,32. Moreover, many of previous investigations have focused on one case study only and frequently present a range of various data, with individual data sets often being relatively restricted in respect to data volume. What has so far been missing is a broad and decisive geochemical approach to distinguish between these two rival formation hypotheses on an across-deposit scale. To date no systematic stable isotope study employing several distinct Kiruna–type apatite iron oxide ore deposits is available and, importantly, no systematic comparison with accepted magmatic and hydrothermal rock and ore suites has previously been presented in the literature.
Results
Scientific rationale and sample selection
Here we use the isotopes of iron and oxygen, the two essential elements in magnetite (Fe3O4), on magnetite samples from four major Kiruna-type ore provinces. Magnetite is the main iron-bearing component in Kiruna-type deposits and our approach therefore utilizes highly reliable major elements as petrogenetic tracers, as opposed to, e.g., traditional minor element approaches that rely on low-concentration constituents in these ores and their host rocks. We present an extensive set of new Fe and O isotope data of magnetite from a suite of world-class Kiruna-type ores from three continents, represented by Sweden, Chile, and Iran, and complement these data by a large suite of new comparative data on accepted magmatic and hydrothermal reference samples (54 new Fe–O coupled isotope ratios and another 12 individual ratios, totaling 120 new individual isotope ratios). In addition, the four different regions of Kiruna-type deposits investigated are separated in space and time, as are the extensive suite of volcanic, plutonic, and low-temperature reference materials that we employ to define the endmember processes reflected in our ore deposit data (see Fig. 1 and Supplementary Table 1). We use these data to address whether Kiruna-type apatite-iron oxide ores form primarily through direct magmatic processes (magma and magmatic fluids) at high temperatures (≥800 °C), or alternatively, through precipitation from hydrothermal fluids at considerably lower temperatures (≤400 °C). The comparative aspect of our work is a particular strength and to the best of our knowledge, no other systematic study with such global coverage has been performed to date. In addition, we offer the first substantial data sets for coupled Fe and O isotopes for the world famous Kiruna, Grängesberg, and Bafq deposits, plus new comparative data for El Laco that are consistent with published data for this deposit5,14,17,18,32. The study’s global extent, its systematic approach, its large data volume, and most crucially, the global Fe–O isotope correlation permits a decisive conclusion, which allows us to advance our understanding of the relationship between magmatic and hydrothermal processes in the genesis of Kiruna-type iron-oxide ore deposits. The use of a broad set of Fe–O isotope data is especially useful as it establishes not only genetic similarities between different deposits, but also provides constrains on the formation temperatures1,5,39 and allows us to identify a high-temperature versus a low-temperature origin of individual ore deposits.
To facilitate a widely applicable comparison of apatite-iron-oxide ores, analyses of iron and oxygen isotope ratios of magnetite from massive apatite-iron-oxide ores from the Kiruna Mining District in northern Sweden (n = 14), the Grängesberg Mining District and the nearby Blötberget ore body in central Sweden (n = 16), the El Laco district in Chile (n = 6), and the Bafq Mining District in central Iran (n = 6; Figs. 1 and 2) were performed. These ore provinces and regions are briefly introduced below, and full details are given in Supplementary Note 1.
Images of apatite-iron oxide ores in this study. False-color BSE images of massive magnetite ore samples from a, b Kiruna; c, d Grängesberg; e, f Bafq; and g, h El Laco. Kiruna, Grängesberg, and Bafq magnetite samples are homogeneous and commonly lack zonation or signs of alteration. El Laco (g, h), is exceptional in this respect as for some samples intra-crystal zonation is observed. As a supplement, regular greyscale BSE images for these samples are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1
The study of apatite-iron-oxide mineralizations began at the iconic deposits of the Kiruna Mining District3. The present Kiruna mine at Kiirunavaara is the largest deposit of its type, and is the main supplier of iron ore in Europe. This deposit alone represents a pre-mining reserve of ≥2 billion tons of high grade ore. The ores in Kiruna and similar Palaeoproterozoic deposits in the district (Supplementary Table 1) are dominated by magnetite and contain between 50 and 70% Fe with a P content of, commonly, up to 2 wt.% that is mainly hosted by fluorapatite and subordinate monazite-(Ce)25. Additional gangue minerals that can occur in small proportions are Mg-rich actinolite, phlogopite, chlorite, titanite, talc, feldspar, quartz, carbonates, sulfides, sulfates, and clays3,5,25.
The apatite-iron-oxide ores of the Grängesberg and the nearby Blötberget deposits represent the largest iron-ore accumulation in the Bergslagen ore province, a classic mining region in central Sweden considered to represent a Palaeoproterozoic continental rift or back arc basin40. A historic production of 156 Mt of ore, averaging 60% Fe and 0.81% P, is documented from Grängesberg. In addition to iron oxides (dominantly magnetite), the presence of phosphates such as fluorapatite, monazite-(Ce), and xenotime-(Y), together with REE-silicates constitute a potentially significant P and REE resource1,41.
The El Laco apatite-iron-oxide ore deposit at the Pico Laco volcanic complex in northern Chile consists of seven individual ore bodies which together comprise ~500 Mt of mainly magnetite-dominated ore with an average grade of 60% Fe5,18,26,30. The Plio- to Pleistocene El Laco deposit is part of the young apatite-iron-oxide mineralizations that characterize the eastern high Andes and is separate from the Cretaceous apatite-iron-oxide ores of the so-called Chilean Iron Belt7,14,17,18.
The Bafq Mining District in Central Iran comprises 34 documented iron ore mineralizations with a total reserve of ~2 billion tons of iron ore with grades between 53 and 65%11,42. The apatite-iron oxide ores of the Bafq region are coeval with their early Cambrian andesitic and rhyolitic host rocks that formed in a volcanic arc setting43. Samples from the Bafq Mining District were collected from the Sechahun, Lakkeh Siah, Chadormalu, and Esfordi deposits42.
Analyzed plutonic reference samples (Fig. 1) include magnetite from the layered igneous intrusion of Panzhihua in China (n = 2), the Bushveld igneous complex in South Africa (n = 1), and the layered intrusions of Taberg (n = 1), Ulvön (n = 1), and Ruoutevare (n = 1) in Sweden and an iron-rich gabbro nodule from Iceland (n = 1). Samples representative of magmatic magnetites of volcanic derivation were chosen from basalts and dolerite from the Canary Islands (n = 3), recent basaltic andesites from Indonesia (n = 6), dacites from New Zealand (n = 2) and a hypabyssal dolerite from Cyprus (n = 1; Supplementary Table 1). Reference samples for low-temperature or hydrothermal iron ore deposits include magnetite from the polymetallic magnetite-skarn deposit at Dannemora (n = 4), the banded iron formation at Striberg (n = 1), and the marble-hosted iron oxide deposit at Björnberget (n = 1), all situated in Bergslagen, Central Sweden (Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Note 1).
Our interpretations are based on the combination of new iron (n = 63) and oxygen (n = 57) isotope ratios combined with literature data for magnetite from apatite-iron-oxide ores and available volcanic, plutonic and the low-temperature or hydrothermal reference materials1,5,14,31,32,44,45,46,47,48. Notably, the literature data for low-temperature or hydrothermal magnetite include a sample from the north-American Mineville apatite-iron-oxide deposit, which has been extensively overprinted by later hydrothermal processes14,49.
Iron and oxygen isotope results
Magnetite from massive apatite-iron-oxide ores from Kiruna have a relatively restricted δ56Fe range of +0.12 to +0.41‰ (n = 11) (Supplementary Table 1, Fig. 3). The Grängesberg and Blötberget magnetite samples show δ56Fe-values mainly between +0.11 and +0.40‰ (n = 16). However, one sample from Grängesberg shows an exceptionally high value of +1.0‰. Apatite-iron-oxide ores from El Laco yield δ56Fe-values between +0.24 and +0.36‰ (n = 6). Magnetite from Bafq have a range in the +0.20 to +0.32‰ interval (n = 6).
Iron isotope results. Shown is a the distribution of iron isotopes in magnetites from the Kiruna and Grängesberg districts, El Laco, and the Bafq district from this study, and b our data together with available literature data14,45,47,48. Reference fields for common hydrothermal and magmatic magnetites are shown for comparison39,45,46,47,51,69,70. Magnetites from apatite-iron oxide ores show a clear distinction from low-temperature or hydrothermal magnetites and overlap with the layered intrusions and volcanic reference magnetites (i.e. in the magmatic reference field). Data from Wang et al.45 show the effects of a progressive transgression from ortho-magmatic processes to hydrothermal fluid evolution from originally higher to lower δ56Fe values and an originally magmatic fluid may thus evolve into a hydrothermal fluid. One hydrothermal sample from the highly altered, remobilized, and recrystallized Mineville deposit in the USA (δ56Fe = −0.92‰, δ18O = −0.79)14 is not shown for simplification. Ve-Di samples represent vein and disseminated magnetites
Magnetite samples from the plutonic and volcanic reference suites show δ56Fe-values from +0.11 to +0.61‰ (n = 5) and from +0.06 to +0.46‰ (n = 13), respectively, consistent with iron isotope values for magmatic rock suites elsewhere (e.g. Figure 3)39,46.
The low-temperature deposit group, i.e., the Dannemora iron oxide skarn samples and the Björnberget and the Striberg samples, on the other side, show relatively low δ56Fe-values that range from −0.57 to +0.01‰. The magnetite compositions in the low-temperature group form a separate group (Fig. 3) that does not overlap with the reported range of igneous magnetites (+0.06 to +0.49‰)39,46, but with low-temperature hydrothermal samples from elsewhere (e.g., Mineville, USA and Xinqiao, China)14,45,49.
Magnetite separates from the Kiruna Mining District range in δ18O value from −1.0‰ to +4.1‰ (n = 14), and those from Grängesberg and Blötberget are between −1.1 and +2.8‰ (n = 16). (Supplementary Table 1, Fig. 4). Magnetite from El Laco shows a large range in δ18O values from −4.3 to +4.4‰ (n = 6), whereas magnetite samples from Bafq give a smaller range of +0.6 to +3.4‰ (n = 6).
Oxygen isotope results. a Oxygen isotopes of magnetite samples from Kiruna, Grängesberg, El Laco, and the Bafq district from this study are compared to reference samples from layered igneous intrusions, recent volcanic magnetites, and low-temperature or hydrothermal ore deposits as well as b data from the Chilean Iron Belt14, the Pea Ridge and Pilot Knob deposits48. The range of typical igneous magnetite is outlined in the reference box50. The majority of magnetite samples from apatite-iron oxide ores plot within the reference field for common magmatic δ18O-values and overlap with magnetite values from recent volcanic rocks and layered intrusions. The low-temperature or hydrothermal reference suite, together with low-temperature magnetite literature data14,44, plot dominantly to the left of the magmatic magnetite field, with only one exception, a magnetite from the Fe-skarn deposit at Dannemora. This particular outlier comes from a part of the deposit (Konstäng) which itself represents a geochemical anomaly within the Dannemora deposit. Our values for El Laco overlap with results from previous studies5,14,17,18,32
Magnetites from the plutonic reference samples (Panzhihua, Bushveld, Taberg, Ulvön, Ruoutevare, and Iceland gabbro bomb; n = 7), and from recent volcanic provinces (New Zealand, Indonesia and Tenerife, n = 3) show exclusively positive δ18O-values between +1.8 and +4.8‰, and +3.7 to +3.9‰ respectively, which is within or near the commonly accepted range of igneous magnetites (δ18O = +1.0 to +4.0‰)50. The low-temperature and hydrothermal reference ore samples (e.g. Dannemora, Björnberget, and Striberg), have low δ18O values (−1.2 to −0.4‰; n = 5) with one exception; a skarn sample from Dannemora that has a δ18O-value of +2.1‰ (Supplementary Table 1). This particular sample, however, comes from a part of the deposit (Konstäng) which itself is reported to be geochemically anomalous with respect to the deposit as a whole (see Supplementary Note 1).
Comparing the oxygen and iron isotope data of magnetite samples from Kiruna, Grängesberg, El Laco, and Bafq, we find that they overlap with the magnetite data from the plutonic and recent volcanic reference samples. Recognized low-temperature or hydrothermal deposits, such as Striberg, Björnberget, and Dannemora record magnetite isotope values that, in turn, differ distinctly in their Fe and O isotope signatures from magmatic values (Figs. 3 and 4). We note that the oxygen isotope data from two vein and disseminated (Ve-Di) magnetite samples from Grängesberg, three samples from Kiruna, as well as magnetite from two samples from El Laco overlap with the low-temperature and hydrothermal reference group. However, these samples still show Fe isotope signatures that are similar to our magmatic reference suite and are hence assumed to reflect originally igneous sources.
The compositional overlap between Kiruna-type magnetite and the plutonic and volcanic reference suite for Fe and O isotopes is consistent with an ortho-magmatic (magma or highest-temperature magmatic-fluids) origin for the Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide samples in this study. Low-temperature processes are reflected in a small number of the Kiruna-type ore samples (n = 7) represented by vein- and disseminated-type magnetite samples. The exceptionally high Fe-value for one Grängesberg sample, in turn, is in agreement with the “ultra-magmatic” Fe isotope composition recorded in magnetite from the Bushveld complex (Fig. 3)51. In contrast, the lower δ56Fe- and δ18O-values in Figs. 3 and 4 then either reflect the lower end of the magmatic temperature range, or secondary effects, such as alteration, as well as leaching and subsequent re-precipitation at temperatures below 400 °C, which postdates an initial high-temperature (magmatic) stage of formation (Fig. 5). Therefore, the oxygen and iron isotope data for the massive apatite-iron oxide magnetites indicate an originally high-temperature magmatic signature that, most clearly for oxygen isotopes, transitions to lower temperature values indicating a gradual cooling trend. One critical issue, especially for the Palaeoproterozoic Swedish deposits, which have gone through variable grades of metamorphism, is that post-depositional processes (e.g., fluid overprint, re-heating) might have affected the primary isotope composition of the ore and cannot be entirely excluded. Yet, since the same trends in isotope signatures are observed for both the older and younger, less geologically overprinted deposits, we argue that post-depositional changes in isotope composition was negligible in respect to the Fe–O isotope chemistry of our magnetite samples. This is particularly the case for the massive magnetite ores, where this overall chemically inert and refractory mineral would provide local buffering with regards to post-depositional re-equilibration1.
Distribution of Fe and O isotope values of magnetite samples used in this study. a The various magnetite samples can be divided into three groups according to their Fe–O isotope composition; (i) high-temperature magmatic magnetites, (ii) hydrothermal magnetite samples, and (iii) low-temperature magnetite samples. b Most of the magnetite compositions of the apatite-iron-oxide ores in this study lie within, or near, the reference field for igneous magnetite, and overlap with the plutonic and volcanic magnetite samples analysed as reference suite. See also Supplementary Note 1 and Supplementary Fig. 2 for a detailed assessment of temperature-dependent equilibrium compositions. Reference field for common igneous and hydrothermal magnetites are based on literature data14,39,44,46,47,50,51
Discussion
Based on fluid and melt inclusion studies and isotope compositions of mineral pairs, high temperatures of ore formation have been proposed for various apatite-iron oxide ores. For instance, temperature determinations for equilibrium magnetite–quartz pairs and magnetite–pyroxene pairs from Kiruna, El Laco, and Grängesberg yield temperatures that consistently exceed 600 °C1,5. Such crystallization temperatures are further supported by, e.g., the occurrence of high-temperature actinolite in, e.g., the Los Colorados and Kiruna deposits14,34,52 by Ti exsolution textures in magnetite from Kiruna52, and by Zr in titanite studies at Kiruna that suggest 750–800 °C53. These temperature determinations provide independent support for a high-temperature (ortho-magmatic) origin of these ore assemblages. Using these temperatures as a reference point and employing appropriate equilibrium fractionation factors, we modeled the isotope compositions of respective equilibrium sources to test the mineralization conditions of our sample suite (Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Fig. 2). We applied available fractionation factors between magnetite and andesite/dacite magma (T~1000 °C) as well as between an equilibrium aqueous magmatic fluid phase at temperatures between 600 and 800 °C for both iron and oxygen isotopes (see Supplementary Tables 2, 3, 4, 5).
For oxygen isotopes, the calculations indicate that magnetite samples from apatite-iron oxide ores with δ18O ≥ 0, corresponding to over 80% of our sample set, reflect equilibrium with either an intermediate magma (δ18O of +5.7 to +8.7‰) or a high-temperature magmatic fluid (δ18O of +5.2 to +9.6‰; Supplementary Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5, Supplementary Fig. 2). Although equilibrium with ortho-magmatic, high-temperature sources are found for most of our samples, it naturally remains difficult to distinguish between a magma or a very high-temperature, magmatically derived aqueous fluid as the initial magnetite source. This realization is highlighted by the fact that our oxygen isotope values from Kiruna-type magnetite samples overlap with oxygen isotopes from the Granisle porphyry copper deposit presented in Bilenker et al.14, which is proposed to have formed entirely from expelled ortho-magmatic fluids. For the same samples, iron isotope equilibrium source calculations yield values that correspond to magmas and modeled magmatic fluids with δ56Fe values from +0.08 to +0.38‰, and −0.13 to +0.17‰, respectively, which plot partly above the reported array of intermediate magmas and magmatic waters (Supplementary Fig. 2)39,54. This suggests that the metal sources of the samples that exceed the range were likely enriched in the heavy iron isotope (56Fe) already at the time of magnetite formation39,46, which we refer to as ultra-magmatic. Such 56Fe enrichment may be caused by magmatic degassing, which is common in many volcanic systems39, or more likely represents the result of iron oxide-enriched melts acting as an iron sink55. Notably, this enrichment is also seen in some samples of our magmatic (plutonic and volcanic) reference suite (Supplementary Table 4, Supplementary Fig. 2), as well as in several Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide derived magnetite samples in other studies (Supplementary Table 5, Supplementary Fig. 2)14,48. Magma degassing may preferentially remove the lighter Fe isotopes39, increasing the δ56Fe in the melt. Alternatively, the iron-sink scenario is possibly caused by the tendency for magnetite to incorporate the heavy Fe isotopes over the lighter ones either during crystallization or during silicate-metal immiscibility. This could lead to ultra-magmatic signals following prolonged crystallization of silicate phases from a basaltic magma. Specifically, the heavier iron isotope that partitions into the melt due to removal of early Fe-fractionating minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene, will deplete the melt in the isotopically lighter Fe2+ and will leave Fe3+ preferentially in the residual magma46. When magnetite becomes the dominant iron-bearing phase later in the crystallization sequence it will consequently reflect the isotopically heavy melt signature46. Finally, the high Fe3+/Fetot and the strong bonding in the tetrahedral site for Fe3+ in magnetite make it a highly suitable host for the heavier iron isotope46. The combined effects of magma degassing, prolonged fractional crystallization leading to more andesitic to dacitic melts, and the preference of magnetite for the heavy iron isotope are the likely reasons for the ultra-magmatic signature in several magnetite samples from the plutonic-volcanic reference suite as well as from some apatite-iron-oxide ore samples.
The key concepts proposed by the magmatic school of thought are formation of Kiruna-type ores by either liquid immiscibility or separation of magnetite cumulates (by sinking or flotation/frothing) from a silicate melt5,17,18,31,38,48. To evaluate which magmatic process is dominantly responsible for the formation of the massive magnetite bodies has proven difficult and while some petrological and experimental studies favor the concept of liquid immiscibility18,38, other workers suggest cumulate-type processes14,31. Unfortunately, the currently available experiments that support liquid immiscibility are not truly representative of nature (e.g. 40 wt.% P2O5 in a starting melt)36,38. Such a composition contrasts with the host rocks to actual Kiruna-type deposits at Bafq, El Laco, Grängesberg, and Kiruna. Using our new data to assess formation mechanisms, we can employ the isotope fractionation between immiscible Fe-rich melts and their silicate counterparts35,56. Assuming a hydrous system, the maximum fractionation for oxygen isotopes between an iron-rich melt and a silicate melt is 0.8‰35. Testing if our massive magnetite samples are representative of an Fe-rich melt that formed from immiscibility would require associated equilibrium silicate melts with δ18O between −3.5 and +5.2‰. These values are out of the range of common intermediate igneous rocks57,58. Testing the same approach for the plutonic reference material (n = 7) produces two equilibrium melts (δ18O = +5.4 and +5.6‰) that both match a basaltic igneous composition (MORB = +5.7 ± 0.4‰). The formation of Kiruna-type ores by liquid immiscibility is therefore not fully aligned with our data. Although this would, at first glance, favor cumulate processes over liquid immiscibility, there is probably uncertainty as to the natural fractionation of δ18O during liquid immiscibility and, to date, little information is available for Fe–isotopes in such situations. This leads us to encourage further tests in order to verify which of these two magmatic processes is more dominant in the formation of apatite-iron oxide systems. Future developments in the field of in-situ analysis of Fe–O isotope composition may hopefully help resolve small features such as thin, Ti-poor outer alteration rims as reported by e.g., Knipping et al.31 on magnetite samples from the Los Colorados apatite-iron-oxide deposit that these authors interpret to have bearing on the ore formation process. However, such textures cannot yet be analyzed for Fe and O isotopes in situ59, and in respect to our whole-grain results, such volumetrically small features would have a minimal effect on the bulk isotope signature of our samples.
In contrast to the massive ore samples, the vein and disseminated magnetites associated with apatite-iron oxide ores and low-δ18O massive magnetite ores from Kiruna, Grängesberg, and El Laco (i.e. δ18Omgt < 0‰, n = 7) are not in equilibrium with recognized magmatic sources at the previously established temperatures. For these samples equilibrium with magmatic sources would only be obtained at temperatures below 400 °C (Supplementary Table 6). Notably, Fe–P-rich magmas can only be liquid down to ~600 °C34 implying that these magnetite samples cannot have formed directly from a magma. Moreover, the O isotope signatures in these magnetites overlap with those of our low-temperature and hydrothermal reference group and they can either be explained by a cooling magmatic fluid, or by a low-temperature hydrothermal system with external fluid influx. For El Laco, disequilibrium between high-temperature magmatic sources and a sub-set of low-δ18O samples has previously been discussed and is attributed to late-stage or secondary processes5,32. The low-δ18O magnetite samples from El Laco are also associated with considerable amounts of hematite that probably formed as a result of oxidation of magnetite by low-δ18O, possibly meteoric-dominated, hydrothermal fluids at temperatures of ≤150 °C5,32. Meteoric fluids, particularly from higher altitudes such as the Andes, could cause such a negative shift in oxygen isotopes. However, these fluids would be Fe poor and may thus have only limited effect on iron isotope composition. For the isotope analysis great care was taken to avoid any direct hematite contamination of the samples, yet minor hematite formation along fractures in discrete magnetite grains is seen in some El Laco samples and may in part explain the larger spread in oxygen isotope data5,14,17,18,32. Our iron isotope data, on the other hand, confirm a magmatic isotope signal throughout, i.e., even in the low-δ18O samples. The low-δ18O but magmatic δ56Fe magnetite compositions at El Laco are thus likely to represent overprint, remobilization, and reprecipitation of an originally magmatic iron and oxygen signal by hydrothermal fluids that strongly affected oxygen isotopes in the magnetite, but had little effect on the iron isotopes14,31. The fluids affecting the ores may either have been derived from the cooling magmatic system or from an external fluid contribution during the evolution of the mineralization. Remarkably, hydrothermal overprint in the Kiruna Mining District in Sweden, for instance, has now been suggested to post-date ore formation with up to 250 My52. If this is correct, it implies that some non-magmatic (i.e. hydrothermal) isotope signals in apatite-iron-oxide ores may be entirely unrelated to the original mode of formation.
The Fe–O isotope data obtained on magnetite samples from apatite-iron oxide ores from Sweden, Chile, and Iran are thus broadly consistent with the few available Fe–O isotope values from (a) the literature (apatite-iron-oxide ores from USA and the Chilean iron belt), and (b) the volcanic and plutonic reference data in this study from various layered igneous intrusions (from China, South Africa and Sweden) and from recent volcanic provinces (Indonesia, Canary Islands, New Zealand, and Iceland). Moreover, the iron and oxygen isotopes of magnetite samples from apatite-iron oxide ores differ, for most samples, from magnetites produced by low temperature or hydrothermal processes (≤400 °C). The iron and oxygen isotope data together with the calculated equilibrium sources are therefore in agreement with a predominantly (ortho-)magmatic origin (magma and high temperature magmatic fluids) for the investigated Kiruna-type deposits, rather than of a low-temperature hydrothermal one. While our data are very well suited to distinguish these broad formation conditions, they are not ideally suited to resolve the precise formation process and agent, i.e, we cannot distinguish magma versus high-temperature fluid or liquid immiscibility processes versus magnetite accumulation (Supplementary Fig. 2). Accepting an essentially magmatic nature of these deposits, a local hydrothermal overprint and replacement within a volcanic to sub-volcanic system would naturally be expected (Fig. 6), and will involve localized late-stage or secondary hydrothermal alteration and overprint1,18,32,41. Hydrothermal alteration might locally be pronounced and may seem pervasive in places, as is known from many volcanic provinces60,61. This by-product of otherwise ortho-magmatic formation processes must, however, not be confused with the main source signal of most Kiruna-type magnetite samples revealed in our study (Figs. 5 and 6).
Schematic representation of magmatic stages for Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores from this and other studies, and from the analyzed reference materials. Stages II and III comprise ortho-magmatic ore formation: with decreasing temperature and on-going crystallization in the melt, the volatile/fluid pressure will increase and magmatic fluids are being expelled into the surrounding rocks. Below ~600 °C (towards the end of stage III), the magmatic-derived volatile pressure may begin to decrease, allowing progressively more of available external fluids into the system that initiate hydrothermal activity (<400 °C). Massive apatite-iron oxide ores appear to commence crystallization in the ortho-magmatic stages (Stages II and III), whereas vein and disseminated magnetites formed mainly during Stage IV (hydrothermal precipitation and replacement). This implies that the commonly observed hydrothermal signals in apatite-iron oxide ores are late-stage products that are results of syn- to post-magmatic hydrothermal processes active during the cooling of the volcanic system, or in some cases possibly reprecipitation during later overprints
Hydrothermally formed magnetite is isotopically distinct and appears subordinate in our sample suite. The bulk of the Kiruna-type ore investigated thus formed in sub-volcanic environments under essentially high-temperature magmatic conditions, in line with the magmatic school of thought3,5,14,17,18,31,62. Precipitation of magnetite was either from iron-oxide-saturated intermediate magmas or from immiscible Fe-rich melts that separated from broadly andesitic to dacitic parent magmas and subsequent physical (either gravity or gas-driven) magnetite segregation to form massive magnetite melts and mushes18,24,31,35,63. Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores are hence dominantly a magmatic phenomenon and they presumably continue to form in active arc- and back-arc type sub-volcanic environments up to the present day. Our combined isotope data and calculations represent a significant advance in the understanding of Kiruna-type ore deposits and over-rules most arguments for a completely hydrothermal mode of formation. Moreover, we provide a reference system for Fe–O isotopes in Kiruna-type ores against which future research can test genetic concepts for low- versus high-temperature origin of as yet underexplored Kiruna-type deposits.
Methods
Sampling
Samples from the Kiruna Mining District (n = 11) come from the type locality for Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores at Kiirunavaara, Sweden, as well as from other apatite-iron-oxide deposits in the district, including magnetite dykes in the footwall of the smaller deposit at Luossavaara, as well as massive ore from the Mertainen and Rektorn deposits. Mineralized samples from the Grängesberg Mining District (GMD) were collected from three drillcores (DC), DC 690 (n = 7), DC 717 (n = 3), and DC 575 (n = 3) that transect the deposit with a shallow plunge (<20 °) and were drilled at 650 m (n = 2) and 570 m below the surface respectively. In addition to massive apatite-iron-oxide samples, two Grängesberg samples were selected from magnetite veins and disseminations in the host rocks. One sample was collected from the smaller Blötberget apatite-iron-oxide deposit within the greater Grängesberg area and another from the nearby but contrasting marble-hosted hydrothermal/low-temperature iron oxide deposit at Björnberget (n = 1). Samples from El Laco (n = 6) were sampled at the surface and come from Laco Sur, the southern deposit in the area. To obtain a meaningful and widely applicable comparison of the apatite-iron-oxide ores with hydrothermal and magmatic reference samples, oxygen, and iron isotope values were also determined on magnetite from massive ore from the iron oxide-polymetallic skarn deposit at Dannemora in Sweden (n = 4), the banded iron formation at Striberg in Sweden (n = 1), the layered igneous intrusion of Panzhihua in China (n = 2), the Bushveld igneous complex in South Africa (n = 1), the Swedish layered igneous intrusions of Taberg (n = 1), Ulvön (n = 1), and Ruoutevare (n = 1), and from a gabbro bomb from Skjaldbreiður in Iceland (n = 1). Samples representative of recent igneous magnetites were chosen from basaltic andesites from Indonesia (n = 6), basalts, and dolerite from the Canary Islands (n = 3), dacites from New Zealand (n = 2), and a dolerite from Troodos massif in Cyprus (n = 1). An overview of the samples used in this study and details on their mineral assemblage and provenance is given in Supplementary Table 1. An outline of the geological setting of our sample suite is given in the Supplementary Information.
Iron isotope analysis
Analysis of the individual magnetite samples for Fe isotopes was dominantly carried out at the Victoria University in Wellington, New Zealand (n = 47). The crystals were digested and chemically purified with concentrated HF and HNO3 acid and the analysis was then done using a 57Fe– 58Fe double spike and a Nu Plasma MC-ICP-MS (Multicollector-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer). As a standard the international IRMM-014 CRM material was used. Full details on the Fe isotope analysis are given in Millet et al.64. All iron isotope data were recorded as δ56Fe, which is the deviation of 56Fe/54Fe relative to the IRMM-014 CRM standard material. The average 2σ error during iron isotope analysis was 0.03‰.
A set of magnetite samples (n = 11) was analysed for iron-isotopes by ALS Scandinavia Ltd. in Luleå, Sweden. The magnetite samples were prepared for analysis by microwave-assisted digestion in a HNO3 + HCl + HF mixture according to the method described in Ingri et al.65. The isotope analysis was then carried out with a Thermo Scientific Neptune MC-ICP mass spectrometer. The δ56Fe-values were calculated with relation to the IRMM-014 CRM standard. The 2σ error was calculated from two independent consecutive measurements and was on average also about 0.03‰. Six further magnetite samples were analyzed at the Vegacenter at the Swedish Museum of Natural History in Stockholm. The crystals were digested and chemically purified using concentrated HF and HNO3 and 10 M HCl acid following the procedures of Borrok et al.66 and Millet et al.64. The samples were diluted with 0.3 M HNO3 to a concentration of 2–3 ppm before measurement. The Fe isotope analyses were performed on a Nu Plasma II HR-MC-ICP-MS in pseudo-high-resolution mode to resolve interfering species. The samples were corrected for mass bias using the standard-sample bracketing technique, normalizing to the IRMM-014 standard. The average 2σ external reproducibility for the samples was 0.06‰ for δ56Fe.
Oxygen isotope analysis
The analysis for oxygen isotopes was carried out at the University of Cape Town (South Africa) using a Finnigan DeltaXP dual inlet gas source mass spectrometer (n = 59). For the oxygen analysis the magnetite samples were prepared by laser fluorination67, whereby they were reacted with 10 kPa of BrF5, and the purified O2 was collected onto a 5 Å molecular sieve in a glass storage bottle. As a reference and calibration standard Monastery garnet was used68. All oxygen data were recorded in the usual δ18O notation relative to SMOW where δ18O = (Rsample/Rstandard − 1)×1000, and R = the measured ratio 18O/16O. All oxygen isotope data were obtained with a 2σ error of ≤0.2‰.
Data availability
The authors declare that all relevant data are available within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Jonsson, E. et al. Magmatic origin of giant ‘Kiruna-type’ apatite-iron-oxide ores in Central Sweden. Sci. Rep. 3, 1644 (2013).
Williams, P. & Barton, M. Iron oxide copper-gold deposits: Geology, space-time distribution, and possible modes of origin. Econ. Geol. 100th Anniversary Volume, 371–405 (2005).
Geijer, P. I gneous rocks and iron ores of Kiirunavaara, Luossavaara and Tuollavaara. Scientific and practical researches in Lapland arranged by the Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara Aktiebolag, Geology of the Kiruna district 2, Stockholm, 278 pp (1910).
Hitzman, M. W., Oreskes, N. & Einaudi, M. T. Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of proterozoic iron-oxide (Cu-U-Au-Ree) deposits. Precambrian Res. 58, 241–287 (1992).
Nyström, J. O., Billström, K., Henríquez, F., Fallick, A. E. & Naslund, H. R. Oxygen isotope composition of magnetite in iron ores of the Kiruna type in Chile and Sweden. GFF 130, 177–188 (2008).
Weihed, P. et al. Precambrian geodynamics and ore formation: The Fennoscandian Shield. Ore Geol. Rev. 27, 273–322 (2005).
Oyarzún, J. & Frutos, J. Tectonic and petrological frame of the Cretaceous iron deposits of north Chile. Min. Geol. 34, 21–31 (1984).
Lyons, J. I. Volcanogenic iron oxide deposits, Cerro de Mercado and vicinity, Durango, Mexico. Econ. Geol. 83, 1886–1906 (1988).
Naslund, H. R., Henríquez, F., Nyström, J. O., Vivallo, W. & Dobbs, F. M. Magmatic iron ores and associated mineralisation: Examples from the Chilean High Andes and Coastal Cordillerain. In Hydrothermal Iron Oxide Copper-Gold and Related Deposits : A Global Perspective (ed. Porter, T. M.) 207–226 (2002).
Helvaci, C. Apatite-rich iron deposits of the Avnik (Bingol) region, southeastern Turkey. Econ. Geol. 79, 354–371 (1984).
Mücke, A. & Younessi, R. Magnetite-apatite deposits (Kiruna-type) along the Sanandaj-Sirjan zone and in the Bafq area, Iran, associated with ultramafic and calcalkaline rocks and carbonatites. Mineral. Petrol. 50, 219–244 (1994).
Zhang, Z. et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and tectonic settings of the major iron deposits in China: an overview. Ore Geol. Rev. 57, 247–263 (2014).
Seo, J., Choi, S. G., Kim, D. W., Park, J. W. & Oh, C. W. A new genetic model for the Triassic Yangyang iron-oxide-apatite deposit, South Korea: constraints from in situ U-Pb and trace element analyses of accessory minerals. Ore Geol. Rev. 70, 110–135 (2015).
Bilenker, L. D. et al. Fe-O stable isotope pairs elucidate a high-temperature origin of Chilean iron oxide-apatite deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 177, 94–104 (2016).
Hofstra, A. H. et al. Mineral thermometry and fluid inclusion studies of the pea ridge iron oxide-apatite-rare earth element deposit, Mesoproterozoic St. Francois Mountains Terrane, Southeast Missouri, USA. Econ. Geol. 111, 1985–2016 (2016).
Montreuil, J. F., Corriveau, L., Potter, E. G. & De Toni, A. F. On the relationship between alteration facies and metal endowment of iron oxide-alkali-altered systems, Southern Great Bear Magmatic Zone (Canada). Econ. Geol. 111, 2139–2168 (2016).
Tornos, F., Velasco, F. & Hanchar, J. M. Iron-rich melts, magmatic magnetite, and superheated hydrothermal systems: the El Laco deposit, Chile. Geology 44, 427–430 (2016).
Tornos, F., Velasco, F. & Hanchar, J. M. The magmatic to magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of the El Laco Deposit (Chile) and its implications for the genesis of magnetite-apatite deposits. Econ. Geol. 112, 1595–1628 (2017).
Westhues, A., Hanchar, J. M., Whitehouse, M. J. & Martinsson, O. New constraints on the timing of host-rock emplacement, hydrothermal alteration, and iron oxide-apatite mineralization in the Kiruna District, Norrbotten, Sweden. Econ. Geol. 111, 1595–1618 (2016).
Westhues, A. et al. Tracing the fluid evolution of the Kiruna iron oxide apatite deposits using zircon, monazite, and whole rock trace elements and isotopic studies. Chem. Geol. 466, 303–322 (2017).
Westhues, A., Hanchar, J. M., LeMessurier, M. J. & Whitehouse, M. J. Evidence for hydrothermal alteration and source regions for the Kiruna iron oxide-apatite ore (northern Sweden) from zircon Hf and O isotopes. Geology 45, 571–574 (2017).
Broughm, S. G., Hanchar, J. M., Tornos, F., Westhues, A. & Attersley, S. Mineral chemistry of magnetite from magnetite-apatite mineralization and their host rocks: examples from Kiruna, Sweden, and El Laco, Chile. Miner. Depos. 52, 1223–1244 (2017).
He, X. F., Santosh, M., Tsunogae, T. & Malaviarachchi, S. P. K. Magnetite-apatite deposit from Sri Lanka: implications on Kiruna-type mineralization associated with ultramafic intrusion and mantle metasomatism. Am. Mineral. 103, 26–38 (2018).
Frietsch, R. On the magmatic origin of iron ores of the Kiruna type. Econ. Geol. 73, 478–485 (1978).
Parak, T. Kiruna iron ores are not intrusive-magmatic ores of the kiruna type. Econ. Geol. 70, 1242–1258 (1975).
Nyström, J. O., Henriquez, F. Magmatic features of iron ores of the Kiruna type in Chile and Sweden: ore textures and magnetite geochemistry. Econ. Geol. 89, 820–839 (1994).
Sillitoe, R. H. & Burrows, D. R. New field evidence bearing on the origin of the El Laco magnetite deposit, Northern Chile. Econ. Geol. 97, 1101–1109 (2002).
Smith, M. P., Storey, C. D., Jeffries, T. E. & Ryan, C. In situ U-Pb and trace element analysis of accessory minerals in the Kiruna District, Norrbotten, Sweden: New constraints on the timing and origin of mineralization. J. Petrol. 50, 2063–2094 (2009).
Smith, M. P., Gleeson, S. A. & Yardley, B. W. D. Hydrothermal fluid evolution and metal transport in the Kiruna District, Sweden: contrasting metal behaviour in aqueous and aqueous-carbonic brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 102, 89–112 (2013).
Dare, S. A. S., Barnes, S. J. & Beaudoin, G. Did the massive magnetite “lava flows” of El Laco (Chile) form by magmatic or hydrothermal processes? New constraints from magnetite composition by LA-ICP-MS. Miner. Depos. 50, 607–617 (2014).
Knipping, J. L. et al. Giant Kiruna-type deposits form by efficient flotation of magmatic magnetite suspensions. Geology 43, 591–594 (2015).
Rhodes, A. L. & Oreskes, N. Oxygen isotope composition of magnetite depositsat El Laco, Chile: Evidence of formation from isotopically heavy fluids. In: Geology and Ore Deposits of the Central Andes, Brian J. Skinner, ed., Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication 7, 333–351 (1999).
Naslund, H. R. The effect of oxygen fugacity on liquid immiscibility in iron- bearing silicate melts. Am. J. Sci. 283, 1034–1059 (1983).
Lledo, H. I. & Jenkins, D. M. Experimental investigation of the upper thermal stability of Mg-rich actinolite; implications for kiruna-type iron deposits. J. Petrol. 49, 225–238 (2008).
Lester, G. W., Clark, A. H., Kyser, T. K. & Naslund, H. R. Experiments on liquid immiscibility in silicate melts with H2O, P, S, F and Cl: implications for natural magmas. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 166, 329–349 (2013).
Mungall, J. E. Immiscible silicate and Fe-P oxide melts preserved in unconsolidated tephra at El Laco volcano, Chile. Geology 46, 255–258 (2018).
Hou, T. et al. Experimental study of liquid immiscibility in the Kiruna-type Vergenoeg iron–fluorine deposit, South Africa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 203, 303–322 (2017).
Hou, T. et al. Immiscible hydrous Fe-Ca-P melt and the origin of iron oxide-apatite ore deposits. Nat. Commun. 9, 1–8 (2018).
Heimann, A., Beard, B. L. & Johnson, C. M. The role of volatile exsolution and sub-solidus fluid/rock interactions in producing high 56Fe/54Fe ratios in siliceous igneous rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 72, 4379–4396 (2008).
Allen, R. L., Lundström, I., Ripa, M., Simeonov, A. & Christofferson, H. Facies analysis of a 1.9 Ga, continental margin, back-arc, felsic caldera province with diverse Zn-Pb-Ag-(Cu-Au) sulfide and Fe oxide deposits, Bergslagen Region, Sweden. Econ. Geol. 91, 979–1006 (1996).
Jonsson, E., Harlov, D. E., Majka, J., Högdahl, K. & Persson-Nilsson, K. Fluorapatite-monazite-allanite relations in the Grängesberg apatite-iron oxide ore district, Bergslagen, Sweden. Am. Mineral. 101, 1769–1782 (2016).
Mokhtari, M. A. A., Zadeh, G. H. & Emami, M. H. Genesis of iron-apatite ores in Posht-e-Badam Block (Central Iran) using REE geochemistry. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 122, 795–807 (2013).
Ramezani, J. & Tucker, R. D. The Saghand Region, Central Iran: U-Pb geochronology, petrogenesis and implications for Gondwana tectonics. Am. J. Sci. 303, 622–665 (2003).
Barnes, J. D., Paulick, H., Sharp, Z. D., Bach, W. & Beaudoin, G. Stable isotope (δ18O, δD, δ37Cl) evidence for multiple fluid histories in mid-Atlantic abyssal peridotites (ODP Leg 209). Lithos 110, 83–94 (2009).
Wang, Y. et al. Iron isotope fractionation during skarn-type metallogeny: a case study of Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au deposit in the Middle-Lower Yangtze valley. Ore Geol. Rev. 43, 194–202 (2011).
Sossi, P. A., Foden, J. D. & Halverson, G. P. Redox-controlled iron isotope fractionation during magmatic differentiation: An example from the Red Hill intrusion, S. Tasmania. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 164, 757–772 (2012).
Dziony, W. et al. In-situ Fe isotope ratio determination in Fe-Ti oxides and sulfides from drilled gabbros and basalt from the IODP Hole 1256D in the eastern equatorial Pacific. Chem. Geol. 363, 101–113 (2014).
Childress, T. M., Simon, A. C., Day, W. C., Lundstrom, C. C. & Bindeman, I. N. Iron and oxygen isotope signatures of the Pea Ridge and Pilot Knob magnetite-apatite deposits, Southeast Missouri, USA. Econ. Geol. 111, 2033–2044 (2016).
Valley, P. M., Hanchar, J. M. & Whitehouse, M. J. New insights on the evolution of the Lyon Mountain Granite and associated Kiruna-type magnetite-apatite deposits, Adirondack Mountains, New York State. Geosphere 7, 357–389 (2011).
H. P. Taylor. in Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits (ed. Barnes, H. L.) 109–142 (Holt, Rinehart and Winston Inc., New York, 1967).
Bilenker, L. D., Van Tongeren, J. A., Lundstrom, C. C. & Simon, A. C. Iron isotopic evolution during fractional crystallization of the uppermost Bushveld Complex layered mafic intrusion. Geochem. Geophys. 18, 956–972 (2017).
Aupers K. Gangue mineralogy and deportment of deleterious elements in the iron ore of the Kiirunavaara deposit, Sweden, M.Sc. thesis, TU Bergakademie Freiberg, 167 p (2014).
Gray, W. Genesis of the Kiirunavaara nodular porphyry and Kiruna-type iron deposits: clues from titanite geothermometry and magnetite trace element compositions. Bachelor thesis, University of St. Andrews, 54 p (2016).
Dauphas, N. et al. Magma redox and structural controls on iron isotope variations in Earth’s mantle and crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 398, 127–140 (2014).
Telus, M. et al. Iron, zinc, magnesium and uranium isotopic fractionation during continental crust differentiation: The tale from migmatites, granitoids, and pegmatites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 97, 247–265 (2012).
Kyser, T. K., Lesher, C. E. & Walker, D. The effects of liquid immiscibility and thermal diffusion on oxygen isotopes in silicate liquids. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 133, 373–381 (1998).
Taylor, H. P. The oxygen isotope geochemistry of igneous rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 19, 1–71 (1968).
Bindeman, I. Oxygen isotopes in mantle and crustal magmas as revealed by single crystal analysis. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 69, 445–478 (2008).
Huberty, J. M. et al. Crystal orientation effects in δ18O for magnetite and hematite by SIMS. Chem. Geol. 276, 269–283 (2010).
Donoghue, E. et al. Low-temperature hydrothermal alteration of intra-caldera tuffs, Miocene Tejeda caldera, Gran Canaria, Canary Islands. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 176, 551–564 (2008).
Donoghue, E., Troll, V. R. & Harris, C. Fluid-rock interaction in the miocene, post-caldera, Tejeda Intrusive Complex, Gran Canaria (Canary Islands): insights from mineralogy, and O- and H-isotope geochemistry. J. Petrol. 51, 2149–2176 (2010).
Henriquez, F. & Nyström, J. O. Magnetite bombs at El Laco volcano, Chile. GFF 120, 269–271 (1998).
O’Driscoll, B., Stevenson, C. T. E. & Troll, V. R. Mineral lamination development in layered gabbros of the british palaeogene igneous province: a combined anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility, quantitative textural and mineral chemistry study. J. Petrol. 49, 1187–1221 (2008).
Millet, M. A., Baker, J. A. & Payne, C. E. Ultra-precise stable Fe isotope measurements by high resolution multiple-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with a Fe-57-Fe-58 double spike. Chem. Geol. 304, 18–25 (2012).
Ingri, J. et al. Iron isotope fractionation in river colloidal matter. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 245, 792–798 (2006).
Borrok, D. et al. Separation of copper, iron, and zinc from complex aqueous solutions for isotopic measurement. Chem. Geol. 242, 400–414 (2007).
Harris, C. & Vogeli, J. Oxygen isotope composition of garnet in the Peninsula Granite, Cape Granite Suite, South Africa: constraints on melting and emplacement mechanisms. S. Afr. J. Geol. 113, 401–412 (2010).
Harris, C., Smith, S. H. & le Roex, A. P. Oxygen isotope composition of phenocrysts from Tristan da Cunha and Gough Island lavas: variation with fractional crystallization and evidence for assimilation. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 138, 164–175 (2000).
Anbar, A. D. Iron stable isotopes: beyond biosignatures. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 217, 223–236 (2004).
Severmann, S. & Anbar, A. D. Reconstructing paleoredox conditions through a multitracer approach: the key to the past is the present. Elements 5, 359–364 (2009).
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. N. Arndt (Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble), Prof. J. Gamble (Victoria University, Wellington), Dr. J. O. Nyström (Swedish Museum of Natural History, Stockholm), Gunnar Rauséus (Dannemora Mineral AB), and Prof. C. J. Stillman (Trinity College Dublin) for donating samples for this study. We further thank Dr. J. Omrani, Dr. A. Houshmandzadeh, Dr. M. Kargarrazi, and the Geological Survey of Iran for their help and support during field work and data interpretation, as well as the staff at the Geological Survey of Sweden (SGU) Mineral Office in Malå, for helpful assistance during drill core sampling. We thank Joel Baker for his help during isotope analyses at the Victoria University in Wellington and Harri Geiger, and Weian Sun for help during the microprobe sessions. Generous funding from the SGU, the Swedish Research Council (VR) and Uppsala University (UU) is gratefully acknowledged. This is Vegacenter contribution #012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
V.R.T., E.J., and K.H. conceived the study. Field work was carried out by E.J., K.H., K.P.N., S.A.M., U.B.A., and V.R.T. Sample preparation was carried out by F.W. and S.S. Isotope analyses were performed by C.H., E.K., F.W., and M.A.M. Modeling was performed by F.W., V.R.T., and C.H., and illustrations were prepared by F.W. and V.R.T. The manuscript was written by V.R.T. and F.W. with contributions from all co-authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Journal peer review information: Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Troll, V.R., Weis, F.A., Jonsson, E. et al. Global Fe–O isotope correlation reveals magmatic origin of Kiruna-type apatite-iron-oxide ores. Nat Commun 10, 1712 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09244-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09244-4
This article is cited by
-
Formation of magnetite-(apatite) systems by crystallizing ultrabasic iron-rich melts and slag separation
Mineralium Deposita (2024)
-
Formation of giant iron oxide-copper-gold deposits by superimposed episodic hydrothermal pulses
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The Montecristo mining district, northern Chile: the relationship between vein-like magnetite-(apatite) and iron oxide-copper–gold deposits
Mineralium Deposita (2023)
-
In-situ trace elements and Fe isotope compositions of magnetite in Gwanin Fe-Ti oxide deposit, South Korea
Geosciences Journal (2023)
-
Petrogenetic characterization of the host rocks of the Sanaga iron ore prospect, southern Cameroon
Acta Geochimica (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.