Abstract
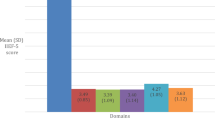
The aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction (ED) in a sample of Chinese type 2 diabetic men. Between October 2016 and April 2017, male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated in our diabetes outpatient clinic were recruited in this study. The participants were asked to complete a short version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5), which was a validated and self-administered questionnaire for the diagnosis and grading of ED severity. All patients screened for erectile function also underwent detailed physical examination, and interviewed for demographic and medical history. A total of 550 men were recruited in this study, of whom 20 patients were excluded and 35 did not complete all scheduled study procedures, leaving 495 patients in the final analysis. As determined by IIEF-5 score, 318 (64.2%) patients had ED. Among the 318 patients with ED, mild, mild-to-moderate, moderate, and severe were 37 (11.6%), 65 (20.4%), 95 (29.9%), and 121 (38.1%), respectively. The prevalence of ED in patients with high education, secondary education, and less than secondary education were 83.3%, 60.2%, and 35.4%, respectively (P < 0.0001). The prevalence of ED was 64.2% in Chinese type 2 diabetic men. Increased age, longer duration of diabetes mellitus, and worse glycemic control may promote the progression of ED among Chinese type 2 diabetic men. We also found that the higher education levels may increase the risk of ED in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994;151:54–61.
Fisher WA, Eardley I, McCabe M, Sand M. Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a shared sexual concern of couples I: couple conceptions of ED. J Sex Med. 2009;6:2746–60.
Salonia A, Castagna G, Sacca A, Ferrari M, Capitanio U, Castiglione F, et al. Is erectile dysfunction a reliable proxy of general male health status? The case for the International Index of Erectile Function-Erectile Function domain. J Sex Med. 2012;9:2708–15.
Melman A, Gingell JC. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1999;161:5–11.
Zhang X, Yang B, Li N, Li H. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Chinese adult males. J Sex Med. 2017;14:1201–8.
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D, Deng Q, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013. JAMA. 2017;317:2515–23.
Malavige LS, Jayaratne SD, Kathriarachchi ST, Sivayogan S, Fernando DJ, Levy JC. Erectile dysfunction among men with diabetes is strongly associated with premature ejaculation and reduced libido. J Sex Med. 2008;5:2125–34.
Giuliano FA, Leriche A, Jaudinot EO, de Gendre AS. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction among 7689 patients with diabetes or hypertension, or both. Urology. 2004;64:1196–201.
De Berardis G, Franciosi M, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S, Kaplan SH, et al. Erectile dysfunction and quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: a serious problem too often overlooked. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:284–91.
Esposito K, Giugliano D. Obesity, the metabolic syndrome, and sexual dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17:391–8.
Fonseca V, Seftel A, Denne J, Fredlund P. Impact of diabetes mellitus on the severity of erectile dysfunction and response to treatment: analysis of data from tadalafil clinical trials. Diabetologia. 2004;47:1914–23.
Penson DF, Latini DM, Lubeck DP, Wallace KL, Henning JM, Lue TF. Do impotent men with diabetes have more severe erectile dysfunction and worse quality of life than the general population of impotent patients? Results from the Exploratory Comprehensive Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction (ExCEED) database. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:1093–9.
Siu SC, Lo SK, Wong KW, Ip KM, Wong YS. Prevalence of and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Hong Kong diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 2001;18:732–8.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2012; 35 (Suppl 1): S64–71.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Peñ BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26.
De Berardis G, Pellegrini F, Franciosi M, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S, et al. Clinical and psychological predictors of incidence of self-reported erectile dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Urol. 2007;177:252–7.
Azadzoi KM, Saenz de Tejada I. Diabetes mellitus impairs neurogenic and endothelium-dependent relaxation of rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. J Urol. 1992;148:1587–91.
Castela A, Gomes P, Silvestre R, Guardao L, Leite L, Chilro R, et al. Vasculogenesis and diabetic erectile dysfunction: how relevant is glycemic control? J Cell Biochem. 2017;118:82–91.
Solomon H, Man JW, Jackson G. Erectile dysfunction and the cardiovascular patient: endothelial dysfunction is the common denominator. Heart. 2003;89:251–3.
Wen Y, Skidmore JC, Porter-Turner MM, Rea CA, Khokher MA, Singh BM. Relationship of glycation, antioxidant status and oxidative stress to vascular endothelial damage in diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2002;4:305–8.
El-Sakka AI, Lin CS, Chui RM, Dahiya R, Lue TF. Effects of diabetes on nitric oxide synthase and growth factor genes and protein expression in an animal model. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:123–32.
Cellek S, Rodrigo J, Lobos E, Fernandez P, Serrano J, Moncada S. Selective nitrergic neurodegeneration in diabetes mellitus - a nitric oxide-dependent phenomenon. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;128:1804–12.
Angulo J, Gonzalez-Corrochano R, Cuevas P, Fernandez A, La Fuente JM, Rolo F, et al. Diabetes exacerbates the functional deficiency of NO/cGMP pathway associated with erectile dysfunction in human corpus cavernosum and penile arteries. J Sex Med. 2010;7(2 Pt 1):758–68.
Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF, Cellek S, Chitaley K, Webb RC, et al. RhoA/Rho-kinase suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the penis: a mechanism for diabetes-associated erectile dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:9121–6.
Bleustein CB, Arezzo JC, Eckholdt H, Melman A. The neuropathy of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2002;14:433–9.
Yagihashi S, Yamagishi S, Wada R. Pathology and pathogenetic mechanisms of diabetic neuropathy: correlation with clinical signs and symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77(Suppl 1):S184–189.
Lau JT, Kim JH, Tsui HY. Prevalence of male and female sexual problems, perceptions related to sex and association with quality of life in a Chinese population: a population-based study. Int J Impot Res. 2005;17:494–505.
Nicolosi A, Moreira ED Jr, Shirai M, Bin Mohd Tambi MI, Glasser DB. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction in four countries: cross-national study of the prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 2003;61:201–6.
Ponholzer A, Temml C, Mock K, Marszalek M, Obermayr R, Madersbacher S. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in 2869 men using a validated questionnaire. Eur Urol. 2005;47:80–85. discussion 85–86
Derby CA, Mohr BA, Goldstein I, Feldman HA, Johannes CB, McKinlay JB. Modifiable risk factors and erectile dysfunction: can lifestyle changes modify risk? Urology. 2000;56:302–6.
Cho NH, Ahn CW, Park JY, Ahn TY, Lee HW, Park TS, et al. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Korean men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2006;23:198–203.
Wing RR, Rosen RC, Fava JL, Bahnson J, Brancati F, Gendrano Iii IN, et al. Effects of weight loss intervention on erectile function in older men with type 2 diabetes in the Look AHEAD trial. J Sex Med. 2010;7(1 Pt 1):156–65.
Binmoammar TA, Hassounah S, Alsaad S, Rawaf S, Majeed A. The impact of poor glycaemic control on the prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. JRSM Open. 2016;7:2054270415622602.
El-Sakka AI, Tayeb KA. Erectile dysfunction risk factors in noninsulin dependent diabetic Saudi patients. J Urol. 2003;169:1043–7.
Kupelian V, Hall SA, McKinlay JB. Common prescription medication use and erectile dysfunction: results from the Boston Area Community Health (BACH) survey. BJU Int. 2013;112:1178–87.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Tianjin Medical University Metabolic Disease Hospital (China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, Y. et al. Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction in type 2 diabetic men: a population-based cross-sectional study in Chinese men. Int J Impot Res 31, 9–14 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0060-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0060-4
This article is cited by
-
Magnitude of erectile dysfunction and associated factors among adult diabetic men on follow-up at Goba and Robe hospitals, Bale Zone, South East Ethiopia: hospital-based cross-sectional study
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2023)
-
Evaluation of the frequency of metabolic syndrome and assessment of cardiometabolic index among men with erectile dysfunction: a prospective cross-sectional study
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2023)
-
Leech-Centipede Granules Suppress EndMT to Improve Erectile Dysfunction in Rats with Diabetes Mellitus via TGF-β/Smad Pathway
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2023)