Abstract
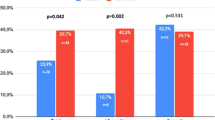
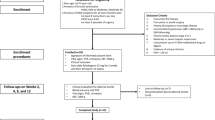
The aim was to compare the differences between daily 5 mg and on-demand 20 mg tadalafil use in diabetic patients with erectile dysfunction (ED), and the effects of two different tadalafil protocols on ejaculatory and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Of the 63 diabetic patients with ED, 31 were given 5 mg tadalafil once a day, and 32 were given 20 mg tadalafil on-demand four times a month over three months. Erectile function, erectile hardness, ejaculatory function, and LUTS were assessed at pretreatment, first- and third-month controls. Both tadalafil protocols increased International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) scores in all patients under 65 years, whereas patients older than 65 years did not benefit. Ejaculatory function, the quality of the hardness of an erection, and LUTS improved in both groups in the study. Tadalafil improved sexual function with acceptable side effects in diabetic men with ED. Both protocols equally improved LUTS and the quality of the erection. Daily use of 5 mg of tadalafil significantly improved the quality of ejaculation and LUTS more than the on-demand use of 20 mg of tadalafil. It may be beneficial to give 5 mg tadalafil daily to patients over 65 years old who do not benefit from treatment with 20 mg of tadalafil or in patients who have LUTS over 65 years old.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vickers MA Jr, Seiler M, Weidner N. Corpora cavernosa ultrastructure in vascular erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1990;143:1131–4.
Rew KT, Heidelbauch JJ. Erectile dysfunction. Am Pham Physician. 2016;94:820–7.
Global report on diabetes. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2016.
Giugliano F, Maiorino M, Bellastella G, Gicchino M, Giugliano D, Esposito K. Determinants of erectile dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Int J Impot Res. 2010;22:204–9.
Thorve VS, Kshirsagar AD, Vyawahare, Joshi VS, Ingane KG, Mohite RJ. Diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. J Diabetes Complicat. 2011;25:129–36.
Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Esposito K. Diabetes and sexual dysfunction: current perspectives. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2014;7:95–105.
Ciocca G, Carosa E, Stornelli M, Limoncin E, Gravina GL, Iannarelli R, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder, coping strategies and type 2 diabetes: psychometric assessment after L’Aquila earthquake. Acta Diabetol. 2015;52:513–21.
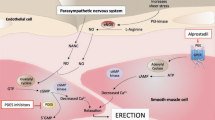
Cellek S. Let’s make NO mistake! Int J Impot Res. 2005;17:388–9.
Hurt KJ, Musicki B, Palese MA, Crone JK, Becker RE, Moriarity JL, et al. Akt-dependent phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase mediates penile erection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:4061–6.
Corona G, Rastrelli G, Burri A, Serra E, Gianfrilli D, Manucci E, et al. First-generation phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors dropout: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Andrology. 2016;4:1002–9.
Ritchie R, Sullivan M. Endothelins & erectile dysfunction. Pharmacol Res. 2011;63:496–501.
Porst H, Giuliano F, Glina S, Ralph D, Casabé AR, Elion-Mboussa A, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of once-a-day dosing of tadalafil 5 mg and 10 mg in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol. 2006;50:351–9.
Williams SB, Goldfine AB, Timimi FK, Ting HH, Roddy MA, Simonson DC, et al. Acute hyperglycemia attenuates endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans in vivo. Circulation. 1998;97:1695–701.
Kensinger C, Bian A, Fairchild M, Chen G, Lipworth L, Ikizler TA, et al. Long term evolution of endothelial function during kidney transplantation. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17:160.
Morelli A, Sarchielli E, Comeglio P, Filippi S, Mancina R, Gacci M, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 expression in human and rat lower urinary tract tissues and the effect of tadalafil on prostate gland oxygenization in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Sex Med. 2011;8:2746–60.
Park HJ, Won JE, Sorsaburu S, Rivera PD, Lee SW. Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) Secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and LUTS/BPH with erectile dysfunction in asian men: a systematic review focusing on tadalafil. World J Mens Health. 2013;31:193–207.
Turunç T, Deveci S, Güvel S, Peşkircioğlu L. The assessment of Turkish validation with 5 question version of International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5). Turk J Urol. 2007;33:45–49.
Francis SH, Corbin JD. PDE5 inhibitors: targeting erectile dysfunction in diabetics. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011;11:683–638.
Burns PR, Rosen RC, Dunn M, Baygani SK, Perelman MA. Treatment satisfaction of men and partners following switch from on-demand phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor therapy to tadalafil 5 mg once daily. J Sex Med. 2015;12:720–7.
Tang YX, Zhou HB, Peng SL, Jiang XZ, He LY, Li DJ. Effects of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction: on-demand versus once-daily dosing. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2012;18:472–4.
Limoncin E, Gravina GL, Corona G, Maggi M, Cioccia G, Lenzi A, et al. Erectile function recovery in men treated with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor administration after bilateral nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy: a systematic review of placebo-controlled randomized trials with trial sequential analysis. Andrology. 2017;5:863–72.
Carosa E, Martini P, Brandetti F, Di Stasi SM, Lombardo F, Lenzi A, et al. Type V phosphodiesterase inhibitor treatments for erectile dysfunction increase testosterone levels. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2004;61:382–6.
Jannini EA, Lenzi A. Ejaculatory disorders: epidemiology and current approaches to definition, classification and subtyping. World J Urol. 2005;23:68–75.
Karabakan M, Keskin E, Akdemir S, Bozkurt A. Effect of tadalafil 5mg daily treatment on the ejaculatory times, lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile function in patients with erectile dysfunction. Int Braz J Urol. 2017;43:317–24.
Paduch DA, Bolyakov A, Polzer PK, Watts SD. Effects of 12 weeks of tadalafil treatment on ejaculatory and orgasmic dysfunction and sexual satisfaction in patients with mild to severe erectile dysfunction: integrated analysis of 17 placebo-controlled studies. BJU Int. 2012;111:334–48.
Huang YP, Zheng FF, Yao FJ, Liu GH, Bian J, Gao Y, et al. Daily medication of low-dose tadalafil improves endothelial function and erectile hardness of ED patients. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2010;16:1052–5.
Yokoyama O, Igawa Y, Takeda M. Tadalafil lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a review of clinical data in Asian men and an update on the mechanism of action. Ther Adv Urol. 2015;7:249–64.
Morelli A, Sarchielli E, Comeglio P, Filippi S, Mancina R, Gacci M, et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 expression in human and rat lower urinary tract tissues and the effect of tadalafil on prostate gland oxygenation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Sex Med. 2011;8:2746–60.
Thieme M, Sivritas SH, Mergia, Potthoff SA, Yang G, Hering L, et al. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-dependent hypertension and renal vascular dysfunction. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2017;312:F474–F481.
Fukumoto K, Naga A, Hara R, Fujii T, Miyaji Y. Tadalafil for male lower urinary tract symptoms improves endothelial function. Int J Urol. 2016;11:1–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bolat, M.S., Cinar, O., Akdeniz, E. et al. Low dose daily versus on-demand high dose tadalafil in diabetic patients with erectile and ejaculatory dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 30, 102–107 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0019-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-018-0019-5
This article is cited by
-
Conservative Non-surgical Options for Erectile Dysfunction
Current Urology Reports (2023)
-
PDE-5-Hemmer auf Dauer kann sich lohnen
MMW - Fortschritte der Medizin (2019)