Abstract
Drought stress is a major agricultural problem restricting the growth, development, and productivity of plants. Calcineurin B-like proteins (CBLs) and CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) significantly influence the plant response to different stresses. However, the molecular mechanisms of CBL–CIPK in the drought stress response of pepper are still unknown. Here, the function of CaCIPK3 in the regulation of drought stress in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) was explored. Transcriptomic data and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis revealed that CaCIPK3 participates in the response to multiple stresses. Knockdown of CaCIPK3 in pepper increased the sensitivity to mannitol and methyl jasmonate (MeJA). Transient overexpression of CaCIPK3 improved drought tolerance by enhancing the activities of the antioxidant system and positively regulating jasmonate (JA)-related genes. Ectopic expression of CaCIPK3 in tomato also improved drought and MeJA resistance. As the CaCIPK3-interacting partner, CaCBL2 positively influenced drought resistance. Additionally, CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41 directly bound the CaCIPK3 promoter to influence its expression. This study shows that CaCIPK3 acts as a positive regulator in drought stress resistance via the CBL–CIPK network to regulate MeJA signaling and the antioxidant defense system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is an economically important horticultural plant belonging to the Solanaceae family. Pepper fruits are rich in vitamins, pigments, and pungent compounds and are widely used in various cuisines and chemical industries1. The harvested area and production of pepper have increased significantly in recent years. The latest FAO data show that the annual production of pepper was 38.03 million tons worldwide in 20192.
Plants need to evolve complex mechanisms against diverse stresses under current global environmental deterioration3. In the northwest region of China, drought is a critical stress and significantly affects plant production. Exploring the molecular mechanisms of plants under drought stress can help enhance drought tolerance. Molecules such as calcium (Ca2+), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and abscisic acid (ABA) act as long-distance messengers in the regulation of drought stress4. Additionally, methyl jasmonate (MeJA) induces stomatal closure in response to drought stress5,6.
Ca2+ functions as an important second messenger and is related to various signaling pathways involved in drought stress7. The intracellular Ca2+ concentration is rapidly increased under abiotic and biotic stresses. The changes are captured by Ca2+ sensors, which transduce Ca2+ signals to downstream target proteins. As a special type of Ca2+ sensor, CBLs interact with their partner CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) to phosphorylate various substrates8. Recently, the functions of the CBL–CIPK network were extensively explored9. The typical CBL–CIPK network is a salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway related to salt stress and was first identified in Arabidopsis. SOS1 (plasma membrane-localized Na+/H+ exchanger 7), SOS3 (AtCBL4), and SOS2 (AtCIPK24) coregulate ion homeostasis to enhance salt tolerance by phosphorylation10,11,12. AtCIPK24 and the homologous member AtCIPK8 interact with AtCBL10 to activate Na+ extrusion13. In addition, the regulation of Na+, nitrate (NO3−), potassium (K+), and ABA signaling is influenced by the AtCBL1/AtCBL9-AtCIPK23 complex with different target proteins14,15,16,17. Compared with other well-known CBL–CIPK signaling pathways, studies related to drought and MeJA stress in Solanaceae vegetables are scarce.
Drought is currently the most severe environmental stress because of climate change and global warming18. Drought stress triggers ROS and ABA production, induces stomatal closure, and activates specific genes associated with signal transduction pathways19,20. In Arabidopsis, overexpression of AtCBL1 or AtCBL5 enhances drought tolerance21,22. In contrast, AtCIPK11 overexpression enhances sensitivity to drought stress23. The rice gene OsCIPK23 and wheat genes TaCIPK2 and TaCIPK27 positively regulate drought stress24,25,26. Transgenic apple-overexpressing MdCIPK22 was shown to exhibit higher sugar production and drought resistance based on MdSUT2.227. In grapevine, VaCIPK02 positively influenced drought stress via ABA signaling and ROS accumulation28.
MeJA is a common phytohormone that participates in defense responses, plant development, and secondary metabolite biosynthesis29. Coronatine-insensitive 1 (COI1), jasmonate ZIM-domain (JAZ), and myelocytomatosis (MYC) proteins are the core members of the JA signaling pathway30,31. Many transcription factors, such as MYC, NAC, MYB, and WRKY, participate in the JA signaling pathway30,32. Furthermore, JA induces the pheophorbide α oxygenase (PAO)/phyllobilin pathway during senescence. The accumulation of pheide α activates JA-responsive genes30,33. Previous studies show that some promoters of CIPKs, including AtCIPK6 and VaCIPK02, contain the TGACG motif (involved in MeJA responsiveness)28,34. Several BrrCBLs and BrrCIPKs are induced by MeJA treatment35. However, the functions of CBLs and CIPKs in response to drought and MeJA have not been revealed in pepper.
Our previous study revealed that CaCIPK3 is influenced by salt and osmotic stress36. In the present study, the role of CaCIPK3 in the regulation of drought and MeJA resistance was explored. Knocking down CaCIPK3 expression decreased drought and MeJA tolerance in pepper. In contrast, drought and MeJA resistance increased in CaCIPK3-overexpressing plants. Drought stress activated the antioxidant system to scavenge ROS in CaCIPK3-overexpressing plants. Moreover, the expression of JA-related genes was altered. CaCBL2, the interacting partner of CaCIPK3, resulted in a drought-sensitive phenotype in CaCBL2-silenced pepper. Furthermore, the activity of the CaCIPK3 promoter was regulated by CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41. Collectively, these findings show that CaCIPK3 potentially coregulates CaCBL2 and CaWRKYs via MeJA signaling and the antioxidant defense system to enhance drought tolerance in pepper.
Results
Sequence, subcellular localization, and evolutionary analyses of CaCIPK3
CIPKs are named based on their order on the chromosome36. CaCIPK3 is the third gene and located on chromosome 1. CaCIPK3 encodes a protein with 440 amino acid residues and a molecular weight of 49.81 kDa. CaCIPK3 belongs to an intron-poor clade that contains zero introns. MSA analysis showed that CaCIPK3 exhibits a typical structure of the CIPK family. The NAF motif is located between the protein kinase domain and the PPI motif. In addition, CaCIPK3 harbors transmembrane helices, suggesting that it may be localized at the membrane (Supplementary Fig. S1A). To explore the position and potential function of CaCIPK3, the gene was fused between the CaMV35S promoter and GFP (Supplementary Fig. S1B). The construct (pvbg2307:CaCIPK3-GFP) was transiently expressed in Nicotiana tabacum. Expression of the control (pvbg2307:GFP) was observed throughout the cell, whereas the CaCIPK3–GFP protein was only visible in the plasma membrane. A phylogenetic analysis was performed to analyze the evolutionary relationship of CIPKs in many species. According to the results, CaCIPK3 was most similar to tomato SlCIPK14 and tobacco NtCIPK14 (Supplementary Fig. S1C).
Expression analysis of CaCIPK3 in pepper and Arabidopsis
The expression patterns of CaCIPK3 under various stresses and hormones were integrated with published RNA-seq data (http://pepperhub.hzau.edu.cn/) to explore its potential functions37. CaCIPK3 responded to multiple stresses, including mannitol, NaCl, ABA, JA, cold, and heat (Supplementary Fig. S1D). Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to further verify the transcriptomic data of CaCIPK3 expression under NaCl, mannitol, MeJA, and ABA treatments at different time points (Fig. 1A–D). CaCIPK3 expression was slightly increased after NaCl and MeJA treatment, and the expression was the highest at 6 h posttreatment. ABA application decreased CaCIPK3 expression before 6 h but enhanced its expression at 12 h. Under mannitol treatment, CaCIPK3 expression peaked at the 6-h time point. Altogether, these results demonstrate that mannitol, MeJA, and ABA induce CaCIPK3 expression. Considering that CaCIPK3 is a member of the Ca2+ signaling pathway, we assessed whether Ca2+ influenced CaCIPK3 expression. The expression of CaCIPK3 was examined under different concentrations of CaCl2 at the 6-h time point. CaCIPK3 expression was induced by lower CaCl2 concentrations and downregulated by higher concentrations (>50 mM) (Fig. 1E), implying that CaCIPK3 may be vital in the Ca2+ signaling pathway.
A, B CaCIPK3 expression in pepper roots after treatment with NaCl and mannitol. C, D and E CaCIPK3 expression in pepper leaves after treatment with MeJA, ABA, and CaCl2. F Tissue-specific expression of CaCIPK3 in pepper. The values are the means ± SE (standard error) of three independent replicates. The letters (a–d) indicate significant differences according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05). G GUS staining of CaCIPK3pro:GUS transgenic plants in leaves (a), flowers (b), roots (c), seeds (d), and stems (e). GUS staining in seedlings of CaCIPK3pro:GUS transgenic plants in response to sterile water (f), 0.15 M NaCl (g), 0.3 M mannitol (h), 0.1 mM MeJA (i), and 2 µM ABA (j). (k) Quantification of GUS activity in response to different stresses (*, p < 0.05). Scale bars, 1 mm
CaCIPK3 transcript levels were assessed in different tissues of pepper to understand its spatial expression. The CaCIPK3 transcript levels were the highest in roots and leaves (Fig. 1F). Spatial expression was also affected by the promoter. A total of 1500 bp of the CaCIPK3 promoter was selected to analyze cis-acting elements. We found four MeJA-related cis-acting elements (Supplementary Table S1), implying that CaCIPK3 may participate in MeJA signaling. Notably, a W-box (TTGACC) element, which is potentially recognized by WRKY proteins, was identified in the promoter, indicating that WRKY proteins might regulate CaCIPK3. Arabidopsis was transformed with the pCAMBIA-CaCIPK3pro:GUS vector to detect whether the CaCIPK3 promoter influences GUS expression in different tissues. The GUS activity of CaCIPK3pro was higher in the leaves, flowers, and roots than in the seeds and stems of mature plants (Fig. 1G a–e). In two-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings, CaCIPK3 was expressed in all organs, especially in cotyledons. Notably, GUS activity in the fresh leaves of seedlings was induced by mannitol and MeJA but not salt or ABA (Fig. 1G f–k).
Silencing of CaCIPK3 decreases pepper resistance to drought and MeJA
Excess mannitol and MeJA activated CaCIPK3 expression, implying that CaCIPK3 potentially participates in drought and MeJA stress responses. A VIGS assay was performed to examine the effect of CaCIPK3 silencing in pepper under mannitol-induced dehydration stress38 and MeJA treatments. A specific 309-bp fragment of CaCIPK3 was selected to silence CaCIPK3 in pepper. Four weeks after injection, CaCIPK3 expression significantly decreased, confirming that CaCIPK3 was successfully silenced in the leaves (Fig. 2A). After four days of hydroponic cultivation, the plants were immersed in 300 mM mannitol to simulate drought stress. Compared with control plants, the CaCIPK3-silenced leaves significantly wilted at 6 h post treatment (Fig. 2B). The leaves of CaCIPK3-silenced plants accumulated more MDA, which reflected the degree of membrane damage (Fig. 2C). H2O2 accumulation in the control plants and CaCIPK3-silenced plants was determined using DAB staining and further quantified by detection kits (Solarbio, China). The CaCIPK3-silenced plants exhibited more H2O2 accumulation than the control plants (Fig. 2D–E). Furthermore, the members of the antioxidant system that scavenge excess ROS, including POD, SOD, and CAT, were measured. These enzymes were remarkably increased in the control plants under mannitol stress (Fig. 2F–H). Stomatal morphology was examined after 6 h of mannitol stress in the control and CaCIPK3-silenced plants. No significant difference in the stomatal apertures (width-to-length ratio) was observed between the control and CaCIPK3-silenced plants under normal conditions. However, the stomata shrank under mannitol treatment, but the stomatal apertures were decreased in the control plants (Fig. 2I, J). We also detected the expression of antioxidant-related genes (CaSOD, CaPOD, and CaCAT) in the control versus CaCIPK3-silenced plants. The expression levels of these genes were higher in the leaves of control plants than in the leaves of CaCIPK3-silenced plants (Fig. 2F). Dehydration-related genes (CaRD22 and CaRD29B) were rapidly induced in the leaves of both CaCIPK3-silenced and control plants under mannitol treatment. The expression of these genes was higher in the leaves of control plants (Fig. 2F). The expression of JA biosynthesis and signaling pathway genes (CaAOC, CaMYC, and CaJAZ) was altered in CaCIPK3-silenced and control plants. Compared with the leaves of CaCIPK3-silenced plants, the expression of CaAOC and CaMYC was higher in the control leaves, whereas the transcript level of CaJAZ was lower (Fig. 2F).
A The expression level of CaCIPK3 in CaCIPK3-silenced and control plants. B Appearance of pepper exposed to 300 mM mannitol. C MDA content. D H2O2 staining. E H2O2 content. F POD activity. G SOD activity. H CAT activity. I, J Stomatal aperture analysis. Scale bar, 10 µm. K The expression levels of CaSOD, CaPOD, CaCAT, CaRD22, CaRD29B, CaAOC, CaMYC, and CaJAZ in CaCIPK3-silenced and control plants under normal conditions and mannitol treatments. The values represent the means of three independent replicates ± SE (standard error). The letters (a–c) show significant differences according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)
Leaf disks from control and CaCIPK3-silenced leaves were immersed in 400 µM MeJA solutions or sterile water under normal conditions to explore the role of CaCIPK3 in MeJA. After seven days, the CaCIPK3-silenced leaf disks were more chlorotic and yellow than the controls (Supplementary Fig. S2A). The chlorophyll contents were significantly reduced in CaCIPK3-silenced plants compared with control plants (Supplementary Fig. S2A). Collectively, the results suggest that CaCIPK3 is critical for mannitol-induced drought stress and MeJA tolerance in pepper.
Transient overexpression of CaCIPK3 enhanced tolerance to drought and MeJA in pepper
The 35S:CaCIPK3-GFP vector was overexpressed in pepper leaves to investigate the effect of CaCIPK3 in response to drought and MeJA. The 35S:GFP empty vector served as a control. The expression level of CaCIPK3 was analyzed using qRT-PCR, and the GFP signals were visualized via Open FluorCam FC 800 at two days post inoculation (Fig. 3A). The plants were grown in dry soil at room temperature. Compared with the leaves transiently overexpressing CaCIPK3-GFP, the control leaves significantly wilted at 8 h (Fig. 3B). The leaves transiently overexpressing CaCIPK3 had lower MDA and H2O2 contents but enhanced activities of the main ROS-scavenging enzymes compared with the control leaves (Fig. 3C–H). In addition, transient overexpression of CaCIPK3 reduced stomatal opening in response to drought stress (Fig. 3I, J). We detected the expression of antioxidant-related genes, stress-related genes, and JA-related genes. The transcript levels of CaRD22 and CaAOC increased, whereas that of CaJAZ was reduced in the leaves transiently overexpressing CaCIPK3 under normal conditions (Fig. 3M). After drought stress, the expression of these genes, except CaJAZ, was significantly increased in CaCIPK3-overexpressing leaves.
A The expression of CaCIPK3 and GFP signals in CaCIPK3-overexpressing and control plants. B Appearance of pepper after drought treatment. C MDA content. D H2O2 staining. E H2O2 content. F POD activity. G SOD activity. H CAT activity. I, J Stomatal aperture analysis. Scale bar, 10 µm. K Expression of CaPOD, CaSOD, CaCAT, CaRD22, CaRD29B, CaAOC, CaMYC, and CaJAZ in overexpression and control plants. All the values represent the means of three independent replicates ± SE (standard error). Means with different letters are significantly different according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)
The function of CaCIPK3 in response to MeJA was also examined in leaves transiently overexpressing CaCIPK3. Leaf disks of the control leaves exhibited yellowing due to chlorophyll degradation, while those transiently overexpressing CaCIPK3 remained green after MeJA treatment (Supplementary Fig. S2B). Collectively, these results demonstrate that CaCIPK3 knockdown reduces the resistance of pepper to drought and MeJA. In contrast, CaCIPK3 overexpression improves the tolerance of pepper to these stresses, indicating that CaCIPK3 influences pepper resistance against drought and MeJA.
CaCIPK3 improves drought and MeJA tolerance in transgenic tomato
To further elucidate the function of CaCIPK3 in drought tolerance, CaCIPK3 was heterologously expressed in tomato plants. Germinated seeds of homozygous lines (OE-2, OE-6, and OE-9 overexpressing CaCIPK3) and the WT line were sown on MS medium supplemented with 0.15 M mannitol or 0.1 mM MeJA and cultured for seven days (Supplementary Fig. S3A, Fig. 4A). There was a significant increase in root length in mannitol-exposed CaCIPK3 transgenic seedlings compared to that of WT plants (Fig. 4B). The roots of the seedlings grew slowly under MeJA treatment, especially in the WT plants (Fig. 4C). Furthermore, water was withheld from four-week-old WT and OE plants for seven days to induce drought stress, while the control group was watered normally. After seven days, most leaves of the WT plants withered significantly, while those of the transgenic plants exhibited mild curling (Supplementary Fig. S3B). During drought stress, the WT plants showed a higher water loss rate than OE plants at the 6- and 7-day time points (Fig. 4D). Additionally, the levels of H2O2 and MDA were remarkably higher in the WT leaves than in the OE leaves (Fig. 4E–G). Although the contents of POD, SOD, and CAT increased in all the treatment groups, they were significantly higher in the transgenic plants (Fig. 4H–J). Moreover, the transgenic plants showed reduced leaf stomatal apertures compared with those of the WT plants (Fig. 4K, L). After drought stress, the genes related to stress, antioxidants, and JA were differentially expressed in the WT and OE plants (Fig. 4M). The expression patterns were consistent with those observed in pepper.
A Germinated seeds of WT and CaCIPK3-OE plants sown on MS medium containing 0.15 M mannitol and 0.1 mM MeJA. B, C Root length of WT and CaCIPK3-OE plants exposed to mannitol and MeJA. D Water loss. E H2O2 staining. F H2O2 content. G MDA content. H POD activity. I SOD activity. J CAT activity. K, L Stomatal aperture analysis. Scale bar, 5 µm. M Expression of SlDREB, SlDHN, SlRBOH1, SlCAT, SlAPX2, SlABI1, SlAOC, SlMYC2, and SlJAZ2. Data are the means ± SE (standard error) of three independent replicates. The letters (a–e) indicate significant differences based on Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)
Leaf disks of the WT and OE plants were immersed in sterile water with or without 400 µM MeJA and incubated at room temperature for seven days (Supplementary Fig. S3C). The chlorophyll levels of WT leaves were lower than those of OE plants (Supplementary Fig. S3D). Corresponding to the phenotype, the transcription of chlorophyll and leaf senescence-related genes (SlPAO and SlSGR) was remarkably upregulated in the WT plants (Supplementary Fig. S3E). Together, these results further indicate that CaCIPK3 overexpression improves tolerance to drought and MeJA. CaCIPK3 potentially regulates drought tolerance through the antioxidant-dependent pathway and MeJA signaling.
CaCIPK3 interacts with CaCBL2
Considering that CBLs activate CIPK enzyme activity, we examined the interactions between the CaCIPK3 protein and the nine pepper CBLs using yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) assays. Only CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2 grew on the QDOs with X-α-Gal and AbA screening medium (Fig. 5A). The interaction between CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2 was further examined using luciferase complementation imaging (LCI), which revealed that CaCIPK3 interacted with CaCBL2 (Fig. 5B). To determine whether the interaction of CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2 was based on Ca2+, we performed an LCI assay with CaCl2 and EGTA (chelated with Ca2+). The luminescence signal in the CaCl2 treatment was stronger than that in the control, whereas the luminescence signal in the EGTA treatment was almost undetectable, suggesting that the CaCBL2–CaCIPK3 interaction is facilitated by Ca2+ (Fig. 5C). Furthermore, bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis showed that the yellow fluorescence signals were distributed on the plasma membrane (Fig. 5D).
A Y2H assay of CaCIPK3 and CaCBLs. Different protein combinations were tested on the screening medium (DDO and QDO with 20 µg/mL X-α-Gal and 125 ng/mL AbA). B LUC assay of CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2. C Effects of CaCl2 and EGTA treatment on the interaction between CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2. D BiFC analysis of CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2. Scale bar = 50 µm
Knockdown of CaCBL2 reduces drought resistance in pepper
Given that CaCIPK3 interacts with CaCBL2, we hypothesized that CaCIPK3 might increase drought tolerance in a CaCBL2-dependent signal-transduction pathway. A specific 272 bp sequence of CaCBL2 was selected to successfully silence CaCBL2 using a VIGS assay (Supplementary Fig. S4A). In comparison with the control plants, CaCBL2-silenced plants were more sensitive to mannitol stress (Supplementary Fig. S4B). The contents of MDA and H2O2 increased rapidly in the CaCBL2-silenced plants (Supplementary Fig. S4C–E). Simultaneously, POD, SOD, and CAT activities were higher in the control plants (Supplementary Fig. S4F–H). Furthermore, the stomatal morphology in the CaCBL2-silenced plants and control plants was examined. The stomatal apertures were reduced in the control plants compared to those in CaCBL2-silenced plants (Supplementary Fig. S4I–J). In addition, the transcript levels of the genes related to antioxidant, stress, and JA signaling were significantly higher in the control plants than in CaCBL2-silenced plants (Supplementary Fig. S4K). These findings indicate that CaCBL2 weakens pepper resistance to drought by interacting with CaCIPK3.
The CaCIPK3 promoter is regulated by the CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41 proteins
According to the W box in CaCIPK3pro, we speculated that WRKYs mediate activation of the CaCIPK3 promoter. Three widely studied CaWRKYs (CaWRKY1, −41, −58) were selected to test their role in regulating the CaCIPK3 promoter. A Y1H assay was used to detect whether CaWRKYs directly target the CaCIPK3 promoter. The Y1H Gold yeast strain cotransformed with AD-CaWRKYs and pAbAi-CaCIPK3 grew better than the empty control on medium containing 500 ng/mL AbA (Fig. 6A). These results indicate that the three CaWRKYs associate with the CaCIPK3 promoter in vitro. To further examine the functions of CaWRKYs, the GUS transcript and enzymatic activity were analyzed in tobacco leaves. The reporter pCaCIPK3-Wbox-GUS combined with different effectors (35S:CaWRKYs) (Fig. 6B). The results suggest that CaWRKY1 suppresses the transcriptional activity of CaCIPK3, while CaWRKY41 induces CaCIPK3 activity (Fig. 6C, D). Notably, CaWRKY58 had no significant effect on CaCIPK3 activity. Collectively, these results suggest that CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41 directly bind to the CaCIPK3 promoter to regulate its activity.
A Y1H assay demonstrating that CaWRKYs bind directly to the CaCIPK3 promoter. pGADT7 served as a control. B Schematic representation of the reporter and effector. C Histochemical GUS staining in N. tabacum leaves. D GUS activity analysis. The data are the means of three independent replicates ± SE (standard error). Means with different letters are significantly different according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05)
Discussion
Calcium is the core molecule of the signal transduction pathway and participates in regulating various environmental stimuli in plants. Drought stress accelerates the concentration of cytosolic Ca2+, thereby activating the special Ca2+ sensor CBL and its interacting protein kinases to promote downstream protein activity and gene transcription. The CBL–CIPK modules have been functionally characterized under biotic and abiotic stimuli, especially under salt stress, ion homeostasis (K+ and NO3−), and ABA treatment. However, the functions of pepper CIPKs in drought and MeJA stress remain unclear.
Herein, we characterized a multiple stress-induced protein kinase CaCIPK3. CaCIPK3 is homologous to AtCIPK14 and TaCIPK2 in Arabidopsis and wheat, respectively. AtCIPK14 phosphorylates ARABIDOPSIS TO´ XICOS EN LEVADURA 31 (ATL31) to mediate carbon and nitrogen nutrients39. Additionally, AtCIPK14 phosphorylates WHIRLY1 (WHY1) to regulate the subcellular localization and distribution of plastids and the nucleus, which influence chloroplast protein metabolism in leaf senescence40,41. TaCIPK2 interacts with TaCBL1, and its overexpression improves drought tolerance in plants25. In this study, the interaction between CaCBL2 and CaCIPK3 was verified using Y2H, BiFC, and LCI. CaCBL2 is closely related to Arabidopsis AtCBL1/-9, wheat TaCBL1, and rice OsCBL1. AtCBL1 and AtCBL9 interact with different CIPKs to regulate NO3− homeostasis, K+ homeostasis, ABA signaling, and ROS signaling in the plasma membrane14,16,17,42. TaCBL1 interacts with TaCIPK23 and TaCIPK25 in the plasma membrane43,44. Plasma membrane-localized OsCBL1 modulates K+ and NO3− signaling and influences root development45,46. Similarly, we verified that CaCBL2 recruits CaCIPK3 to the plasma membrane in a Ca2+-dependent manner.
In this study, RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analysis showed that CaCIPK3 is regulated by abiotic stress and hormones. Salt, mannitol, and ABA induce the activity of AtCIPK6 promoter in Arabidopsis. Overexpression of AtCIPK6 improves salt resistance and influences ABA sensitivity34. Although some cis-acting elements related to ABA and MeJA were found in the CaCIPK3 promoter, GUS activity was only enhanced by mannitol and MeJA in pCaCIPK3pro:GUS-overexpression lines. We speculated that CaCIPK3 might play a vital function in response to drought and MeJA. The results of loss- and gain-of-function experiments showed opposite trends. Silencing of CaCIPK3 enhanced the vulnerability of pepper to stresses and influenced several physiological and gene expression changes. In contrast, CaCIPK3 overexpression enhanced drought resistance in pepper and tomato. Notably, CaCBL2-knockdown plants also exhibited decreased tolerance to drought stress. Drought induces excessive production of ROS in plants, which damages plant cellular structures and components47. ROS scavengers, including SOD, POD, and CAT, can convert excess and harmful ROS to harmless water in response to stress48,49. TaCIPK2-overexpressing lines showed greater ROS-scavenging abilities due to increased CAT and SOD activities in response to drought stress25. Drought stress causes stomatal closure facilitated by increased ABA production to relieve transpiration50. Similar to ABA, the phytohormone MeJA also induces stomatal closure5. In Arabidopsis, thioglucoside glucohydrolases TGG1 and TGG2 redundantly regulate guard cells via ROS production and Ca2+ elevation in ABA and MeJA signaling51. The grapevine CIPK member VaCIPK02 interacts with several CBLs and the ABA receptor PYL9. Overexpression of VaCIPK02 improves drought tolerance by regulating ABA content and stomatal closure28. In this study, the activities of SOD, CAT, and POD increased, while H2O2 and MDA contents decreased in CaCIPK3-overexpression plants under drought stress. Concurrently, the stomatal apertures in the CaCIPK3-overexpression plants were reduced to prevent evaporation. The expression of stress-related genes, JA signaling genes, and antioxidant-related genes increased significantly in the CaCIPK3-overexpression plants under drought stress. In particular, transient overexpression of CaCIPK3 induced the expression of CaRD22 and CaAOC but restrained the transcript levels of CaJAZ, suggesting that CaCIPK3 may facilitate plant drought tolerance by regulating the expression of these genes.
In this study, MeJA treatment significantly induced plant senescence and chlorophyll degradation. The biochemical pathway of chlorophyll degradation is regulated by chlorophyll catabolic genes (CCGs), including PAO, NYE (also called SGR1), and PPH. These genes coregulate chlorophyll degradation during leaf senescence30,33,52. The nye1–1, pph-1, and pao1 mutant lines showed stay-green phenotypes in comparison with the wild type. AtMYC2/-3/-4 proteins belonging to the JA-signaling pathway enhance the transcriptional activity of PAO, NYC1, and NYE1 by directly binding their promoters. These triple mutants of mycs showed the same phenotype as the pao1 mutant30. In this study, CaCIPK3-overexpression plants exhibited stay-green phenotypes, while CaCIPK3-knockdown plants turned yellow under MeJA treatment. Consistent with the chlorophyll content, overexpression of CaCIPK3 restrained the expression of CCGs to maintain a green phenotype.
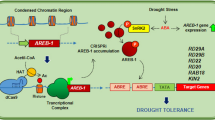
Many WRKY transcription factors have been identified to play significant roles in the response to drought stress in various plant species. AtWRKY1 negatively regulates stomatal movement in response to drought stress53. TaWRKY33 transgenic lines showed enhanced tolerance to drought54. Overexpression of CaWRKY1 improved drought resistance in potato55. WRKYs also play essential roles in leaf senescence56. AtWRKY53 interacts with the JA-inducible protein ESR to adjust leaf senescence by JA and salicylic acid (SA) equilibrium32. Considering that a W-box exists in the CaCIPK3 promoter, we examined the relationship between WRKYs and the CaCIPK3 promoter. The transcript level of CaWRKY58 was downregulated by exogenously applied MeJA57. CaWRKY41 is involved in H2O2 accumulation in pepper58. Thus, CaWRKY1, CaWRKY41, and CaWRKY58 proteins were selected to verify their interactions with the promoter region of CaCIPK3. The results suggest that CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41 regulate the activity of CaCIPK3. Few studies have focused on elucidating the connection between WRKY and CIPK. In wheat, TaWRKY9 binds to the TaCIPK25 promoter and downregulates TaCIPK25 expression44. In this study, CaCIPK3 interacted with CaCBL2 and was regulated by WRKYs, suggesting that CaCIPK3-mediated drought stress may involve positive or negative feedback regulation. In the working model (Fig. 7), when pepper suffers drought stress, the increase in cellular Ca2+ concentrations activates CaCBL2, which interacts with its partner CaCIPK3 and transduces the signal downstream. The expression levels of antioxidant-related genes and JA-related genes are influenced by CaCBL2 and CaCIPK3 under drought stress. However, the potential relationship of CaCBL2–CaCIPK3 and their downstream genes needs to be further studied. The activation of CaCIPK3 is possibly regulated by CaWRKY1 and CaWRKY41. Additionally, MeJA signals bind to the CGTCA motif in the CaCIPK3 promoter and induce stomatal closure during drought stress.
Under drought stress, Ca2+ is rapidly induced and actives CaCBL2 to recruit CaCIPK3. CaWRKYs directly bind to the W-box in CaCIPK3 promoter to regulate its expression. Overexpression of CaCIPK3 enhances antioxidase activity, regulates the expression of JA-related genes and promotes stomatal closure, which contribute to the improvement of drought tolerance. Solid arrows indicate the direction of control and regulation, while dotted arrows indicate the possible mechanism
In conclusion, these findings indicate that CaCIPK3 overexpression improves drought tolerance by regulating the antioxidant system and the expression of JA-related genes. Notably, CaCIPK3-regulated MeJA signaling potentially contributes to drought tolerance. These results provide physiological and molecular evidence to demonstrate the significance of CaCIPK3 in plant drought tolerance.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and treatments
Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) line P70, tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivar Micro-Tom, and transgenic seedlings were cultivated in growth chambers under a 16/8-h day/night photoperiod and 25/22 °C day/night temperature. The peppers were treated with different stresses (0.1 M NaCl, 0.3 M mannitol, 0.1 mM MeJA, and 0.57 μM ABA) at the 6–8 true leaf stage in growth chambers as previously described36. Plants of uniform size were selected and subjected to different treatments.
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was extracted from different tissues of the experimental plants using an RNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biotech, Xi’an, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA (1 µg per sample) was reverse transcribed to cDNA using a HiScript III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (+gDNA wiper) (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.). qRT-PCR was performed as previously described36. The reactions were performed in biological triplicates. Pepper CaUBI3 and tomato SlACTIN genes were used as the internal controls for normalization of gene expression. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method. The primers used are shown in Supplementary Table S2.
Isolation and analysis of CaCIPK3 and its promoter
The coding regions of CaCIPK3 were cloned from the cDNA template of P70 seedlings. Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) analysis and phylogenetic tree construction were performed as previously reported36. Homologous proteins were acquired from NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
The CaCIPK3 promoter was detected using PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)59. We cloned 1500 bp of the promoter from cDNA and inserted it into the pCAMBIA1381 vector. The pCAMBIA-CIPK3pro:GUS plasmid was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 using the freeze–thaw method60. The Agrobacterium culture was then used to transform wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana (Columbia-0) as described previously61. Transgenic Arabidopsis seeds were collected and screened on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 50 mg/L hygromycin. The T3 generations were used for subsequent experiments. A histochemical GUS assay was conducted to detect GUS activity as previously described62. Photographs showing GUS activity were taken using a microscope (SZX16, Olympus). GUS activities were quantified by ImageJ (National Institutes of Health) software.
Subcellular localization of CaCIPK3
The cDNA sequences of CaCIPK3 without stop codons were cloned from P70 leaves and inserted into the pVBG2307 vector harboring the green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter gene. The fusion construct was introduced into Agrobacterium strain GV3101 containing the p19-silencing plasmid and coinfiltrated into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) leaves. GFP fluorescence was visualized using a microscope (BX63, Olympus).
Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS)
Several fragments of the CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2 genes were amplified by PCR using specific primers acquired from the Sol Genomics Network (http://vigs.solgenomics.net/). The unique fragments were confirmed using BLAST analysis and then inserted into the pTRV2 vector as previously described36. Approximately four weeks later, the expression of target genes was determined in pTRV2:CaCIPK3/CaCBL2 and pTRV2 plants using qRT-PCR. Silencing and control plants were used to conduct mannitol (300 mM) and MeJA (400 µM) stress assays.
Overexpression of CaCIPK3 in pepper and tomato plants
A. tumefaciens GV3101 cultures containing 35S:CaCIPK3-GFP or 35S:GFP plasmid vectors were infiltrated into the leaves of pepper plants to transiently overexpress CaCIPK3 as previously reported63,64. GFP signals were captured using Open FluorCam (FC800, Photon System Instruments)65. Transgenic tomato (Micro-Tom) lines were generated using Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as described previously66. The putatively transformed tomato plants were screened on MS medium supplemented with 100 mg/L kanamycin. The lines that survived kanamycin selection were further screened using PCR to confirm the presence of the transgene. Seeds from wild-type (WT) plants and T3 generations of CaCIPK3 were used to conduct drought and MeJA assays.
Measurement of H2O2 and antioxidant enzyme activity
The content and activities of H2O2, superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) were determined at different wavelengths using detection kits (Solarbio, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. The production of H2O2 was detected using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining.
Physiological measurements and observations
The malondialdehyde (MDA) content was detected by thiobarbituric acid (TBA) using a modified protocol described previously67. The leaf chlorophyll (Chl) content was measured and calculated as described previously68. The water loss rate was calculated using the following formula: (FW–DW)/FW × 100% (FW: fresh weight; DW: dry weight).
Stomatal morphology was observed using a microscope (BX63, Olympus). Images were analyzed using ImageJ (National Institutes of Health) software.
Protein-interaction assays
For the Y2H assay, a MatchmakerTM Two-Hybrid System (Clontech, USA) was selected to identify the potential interacting proteins of CaCIPK3. The CDS of CaCIPK3 was cloned into pGBKT7, whereas nine CaCBLs were cloned into pGADT7. The Y2HGold yeast strain containing BD-CaCIPK3 and AD-CaCBLs was screened on SD/-Leu/-Trp (DDO) medium. The positive clones were dotted on SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade (QDO) medium supplemented with aureobasidin A (AbA) and X-α-Gal for selection and compared with the positive and negative controls. For the BiFC assay, CaCIPK3-pSPYNE, CaCBL2-pSPYCE, and p19 plasmids were infiltrated into Nicotiana tabacum as described by Xiao et al.69. Fluorescence was examined using a fluorescence microscope (BX63, Olympus) after 48 h of incubation. For the LCI assay, the CDSs of CaCIPK3 and CaCBL2 were cloned into pCAMBIA-nLUC and pCAMBIA-cLUC. The constructs were then introduced into A. tumefaciens GV3101 and coinfiltrated into the leaves of N. tabacum. After 48 h of incubation, luciferase activity was detected using a plant-imaging system (Lumazone Pylon 2048B, Princeton, USA) with an 8-min exposure. CaCl2 and EGTA treatments were performed as described in a previous study70.
Y1H assay
A Y1H assay was performed to identify the function of the W-box element. The assay was conducted using the MatchmakerTM One-Hybrid System (Clontech, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The unique sequence of the CaCIPK3 promoter containing the W-box elements was inserted into the pAbAi vector as bait. Three CaWRKY genes (CaWRKY1, -41, and -58) were ligated into pGADT7 as prey.
Evaluation of GUS activity
A unique sequence of the CaCIPK3 promoter containing the W-box elements was inserted into the pCAMBIA1381-GUS vector as the reporter plasmid (pCaCIPK3-Wbox-GUS). Three CaWRKY genes (CaWRKY1, -41, and -58) were cloned into the vector under the control of the CaMV35S promoter as effector plasmids. A. tumefaciens GV3101 harboring the reporter and effector plasmids was infiltrated into the leaves of N. tabacum. Histochemical GUS assays were performed as previously described62. Fluorescence was measured at 365 nm for excitation and 455 nm for emission using a Tecan Infinite M200 Pro Reader (Tecan, Switzerland). The specific GUS activity is expressed in pmol 4-MU µg−1 of protein min−1.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using SPSS 22.0 software. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to analyze the differences between various treatments. Significant differences were determined at p < 0.05 according to Tukey’s test. All data are presented as the means ± SE (standard error).
Data availability
The data that support the results are provided in this paper and its supplementary files.
References
Manivannan, A. et al. Next-generation sequencing approaches in genome-wide discovery of single nucleotide polymorphism markers associated with pungency and disease resistance in pepper. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 5646213 (2018).
FAO. FAOSTAT Statistics Database in 2019. http://www.fao.org/faostat/, Accessed 20 March 2021.
Zhu, J. K. Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167, 313–324 (2016).
Gong, Z. et al. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 63, 635–674 (2020).
Munemasa, S., Mori, I. C. & Murata, Y. Methyl jasmonate signaling and signal crosstalk between methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in guard cells. Plant Signal. Behav. 6, 21–23 (2011).
Kazan, K. Diverse roles of jasmonates and ethylene in abiotic stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 20, 219–229 (2015).
McAinsh, M. R. & Pittman, J. K. Shaping the calcium signature. New Phytol. 181, 275–294 (2009).
Kudla, J. et al. Advances and current challenges in calcium signaling. New Phytol. 218, 414–431 (2018).
Ma, X. et al. The CBL–CIPK pathway in plant response to stress signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1–27 (2020).
Liu, J. & Zhu, J.-K. A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280, 1943–1945 (1998).
Halfter, U. The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3735–3740 (2000).
Qiu, Q.-S., Guo, Y., Dietrich, M. A., Schumaker, K. S. & Zhu, J.-K. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 8436–8441 (2002).
Kim, B. G. et al. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 52, 473–484 (2007).
Ho, C. H., Lin, S. H., Hu, H. C. & Tsay, Y. F. CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell 138, 1184–1194 (2009).
Li, L., Kim, B.-G., Cheong, Y. H., Pandey, G. K. & Luan, S. A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12625–12630 (2006).
Ragel, P. et al. CIPK23 regulates HAK5-mediated high-affinity K+ uptake in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 169, 2863–2873 (2015).
Maierhofer, T. et al. Site-and kinase-specific phosphorylation-mediated activation of SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel stimulated by abscisic acid. Sci. Signal. 7, 1–12 (2014).
Barnabás, B., Jäger, K. & Fehér, A. The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell Environ. 31, 11–38 (2008).
Qi, J. et al. Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement in plant responses to drought stress and pathogen attack. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 60, 805–826 (2018).
Luan, S. Signalling drought in guard cells. Plant Cell Environ. 25, 229–237 (2002).
Cheong, Y. H. et al. CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15, 1833–1845 (2003).
Cheong, Y. H. et al. Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 29, 159–165 (2010).
Ma, Y. et al. The kinase CIPK11 functions as a negative regulator in drought stress response in arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. USA 20, 2422 (2019).
Yang, W. et al. Calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase OsCIPK23 functions in pollination and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. Genomics 35, 531–543 (2008).
Wang, Y. et al. A CBL-interacting protein kinase TaCIPK2 confers drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants through regulating the stomatal movement. PLoS ONE 11, 1–20 (2016).
Wang, Y. et al. A CBL-interacting protein kinase TaCIPK27 confers drought tolerance and exogenous ABA sensitivity in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 123, 103–113 (2018).
Ma, Q. J. et al. A CIPK protein kinase targets sucrose transporter MdSUT2.2 at Ser254 for phosphorylation to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 42, 1–13 (2018).
Xu, W. et al. Role of an Amur grape CBL-interacting protein kinase VaCIPK02 in drought tolerance by modulating ABA signaling and ROS production. Environ. Exp. Bot. 172, 103999 (2020).
Chen, Y. et al. Salt and methyl jasmonate aggravate growth inhibition and senescence in Arabidopsis seedlings via the JA signaling pathway. Plant Sci. 261, 1–9 (2017).
Zhu, X. et al. Jasmonic acid promotes degreening via MYC2/3/4- and ANAC019/055/072-mediated regulation of major chlorophyll catabolic genes. Plant J. 84, 597–610 (2015).
Sheard, L. B. et al. Jasmonate perception by inositol phosphate-potentiated COI1-JAZ co-receptor. Nature 468, 400–405 (2011).
Miao, Y. & Zentgraf, U. The antagonist function of Arabidopsis WRKY53 and ESR/ESP in leaf senescence is modulated by the jasmonic and salicylic acid equilibrium. Plant Cell 19, 819–830 (2007).
Aubry, S. et al. Pheophorbide A may regulate jasmonate signaling during Dark-induced senescence. Plant Physiol. 182, 776–791 (2020).
Chen, L. et al. Arabidopsis CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK6) is involved in plant response to salt/osmotic stress and ABA. Mol. Biol. Rep. 40, 4759–4767 (2013).
Yin, X. et al. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the calcineurin B-like protein and calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase gene families in Turnip (Brassica rapa var. rapa). Front. Plant Sci. USA 8, 1191 (2017).
Ma, X. et al. Identification of CBL and CIPK gene families and functional characterization of CaCIPK1 under Phytophthora capsici in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). BMC Genomics 20, 775 (2019).
Liu, F. et al. PepperHub, an informatics hub for the chili pepper research community. Mol. Plant 10, 1129–1132 (2017).
Lim, C. W., Baek, W. & Lee, S. C. Roles of pepper bZIP protein CaDILZ1 and its interacting partner RING-type E3 ligase CaDSR1 in modulation of drought tolerance. Plant J. 96, 452–467 (2018).
Yasuda, S., Aoyama, S., Hasegawa, Y., Sato, T. & Yamaguchi, J. Arabidopsis CBL-interacting protein kinases regulate carbon/nitrogen-nutrient response by phosphorylating ubiquitin ligase ATL31. Mol. Plant 10, 605–618 (2017).
Ren, Y., Li, Y., Jiang, Y., Wu, B. & Miao, Y. Phosphorylation of WHIRLY1 by CIPK14 shifts its localization and dual functions in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 10, 749–763 (2017).
Guan, Z., Wang, W., Yu, X., Lin, W. & Miao, Y. Comparative proteomic analysis of coregulation of CIPK14 and WHIRLY1/3 mediated pale yellowing of leaves in arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 2231 (2018).
Han, J. P. et al. Fine-tuning of RBOHF activity is achieved by differential phosphorylation and Ca2+ binding. New Phytol. 221, 1935–1949 (2018).
Cui, X. Y. et al. Wheat CBL-interacting protein kinase 23 positively regulates drought stress and ABA responses. BMC Plant Biol. 18, 1–13 (2018).
Jin, X. et al. Wheat CBL-interacting protein kinase 25 negatively regulates salt tolerance in transgenic wheat. Sci. Rep. 6, 28884 (2016).
Li, J. et al. The Os-AKT1 channel is critical for K+ uptake in rice roots and is modulated by the rice CBL1-CIPK23 complex. Plant Cell 26, 3387–3402 (2014).
Yang, J. et al. The calcium sensor OsCBL1 modulates nitrate signaling to regulate seedling growth in rice. PLoS ONE 14, 1–10 (2019).
Sewelam, N., Kazan, K. & Schenk, P. M. Global plant stress signaling: reactive oxygen species at the cross-road. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 1–21 (2016).
Noctor, G. & Foyer, C. H. Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 49, 249–279 (1998).
Xu, Y., Burgess, P., Zhang, X. & Huang, B. Enhancing cytokinin synthesis by overexpressing ipt alleviated drought inhibition of root growth through activating ROS-scavenging systems in Agrostis stolonifera. J. Exp. Bot. 67, 1979–1992 (2016).
Ashraf, M. Inducing drought tolerance in plants: recent advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 28, 169–183 (2010).
Islam, M. M. et al. Myrosinases, TGG1 and TGG2, redundantly function in ABA and MeJA signaling in arabidopsis guard cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 50, 1171–1175 (2009).
Schelbert, S. et al. Pheophytin pheophorbide hydrolase (pheophytinase) is involved in chlorophyll breakdown during Leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 767–785 (2009).
Qiao, Z., Li, C. L. & Zhang, W. WRKY1 regulates stomatal movement in drought-stressed Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol. Biol. 91, 53–65 (2016).
He, G. H. et al. Drought-responsive WRKY transcription factor genes TaWRKY1 and TaWRKY33 from wheat confer drought and/or heat resistance in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 16, 1–16 (2016).
Moon, S. J. et al. Ectopic expression of CaWRKY1, a pepper transcription factor, enhances drought tolerance in transgenic potato plants. J. Plant Biol. 57, 198–207 (2014).
Jiang, J. et al. WRKY transcription factors in plant responses to stresses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 59, 86–101 (2017).
Wang, Y. et al. CaWRKY58, encoding a group I WRKY transcription factor of Capsicum annuum, negatively regulates resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 14, 131–144 (2013).
Dang, F. et al. A feedback loop between CaWRKY41 and H2O2 coordinates the response to Ralstonia solanacearum and excess cadmium in pepper. J. Exp. Bot. 70, 1597–1611 (2019).
Lescot, M. et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327 (2002).
Wise, A. A., Liu, Z. & Binns, A. N. Three methods for the introduction of foreign DNA into Agrobacterium. Methods Mol. Biol. 343, 43–53 (2006).
Zhang, X., Henriques, R., Lin, S. S., Niu, Q. W. & Chua, N. H. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana using the floral dip method. Nat. Protoc. 1, 641–646 (2006).
Jefferson, R. A., Kavanagh, T. A. & Bevan, M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 6, 3901–3907 (1987).
Huang, J., Shen, L., Yang, S., Guan, D. & He, S. CaASR1 promotes salicylic acid- but represses jasmonic acid-dependent signaling to enhance the resistance of Capsicum annuum to bacterial wilt by modulating CabZIP63. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 6538–6554 (2020).
Liu, C. et al. Genome-wide analysis of NDR1/HIN1-like genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and functional characterization of CaNHL4 under biotic and abiotic stresses. Hortic. Res. 7, 93 (2020).
Bastet, A. et al. Mimicking natural polymorphism in eIF4E by CRISPR-Cas9 base editing is associated with resistance to potyviruses. Plant Biotechnol. J. 17, 1–15 (2019).
Sun, H. J., Uchii, S., Watanabe, S. & Ezura, H. A highly efficient transformation protocol for Micro-Tom, a model cultivar for tomato functional genomics. Plant Cell Physiol. 47, 426–431 (2006).
Yao, J. et al. Populus euphratica WRKY1 binds the promoter of H+-ATPase gene to enhance gene expression and salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 1527–1539 (2020).
Tian, Q., Zhang, X., Yang, A., Wang, T. & Zhang, W. H. CIPK23 is involved in iron acquisition of Arabidopsis by affecting ferric chelate reductase activity. Plant Sci. 246, 70–79 (2016).
Xiao, D. et al. SENESCENCE-SUPPRESSED PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE directly interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of SENESCENCE-ASSOCIATED RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE and negatively regulates leaf senescence in arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 169, 1275–1291 (2015).
Ding, L. et al. LlWRKY39 is involved in thermotolerance by activating LlMBF1c and interacting with LlCaM3 in lily (Lilium longiflorum). Hortic. Res. 8, 36 (2021).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31772309, No. U1603102, and No. 31860556).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XM and ZHG conceived the experiments. XM, YL, WXG, and CL performed the experiments. XM wrote the paper. XM and ZHG revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Li, Y., Gai, WX. et al. The CaCIPK3 gene positively regulates drought tolerance in pepper. Hortic Res 8, 216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-021-00651-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-021-00651-7
This article is cited by
-
RcMYB8 enhances salt and drought tolerance in rose (Rosa chinensis) by modulating RcPR5/1 and RcP5CS1
Molecular Horticulture (2024)
-
Exogenous strigolactone enhanced the drought tolerance of pepper (Capsicum chinense) by mitigating oxidative damage and altering the antioxidant mechanism
Plant Cell Reports (2024)
-
Salicylic acid-related ribosomal protein CaSLP improves drought and Pst.DC3000 tolerance in pepper
Molecular Horticulture (2023)
-
New insights on the regulatory network of drought-responsive key genes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Genetica (2023)
-
Insight into the CBL and CIPK gene families in pecan (Carya illinoinensis): identification, evolution and expression patterns in drought response
BMC Plant Biology (2022)