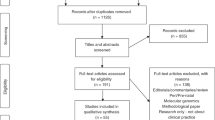
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate leadership in clinical genomics and identify likely implications of different leadership approaches for future implementation of clinical genomics.
Methods
We undertook 37 interviews in a cross-sectional qualitative study examining implementation of clinical genomics in Australia. Participants were either nongenetic medical specialists working with genomic initiatives (e.g., immunologists, nephrologists) or working at a service/organizational level (e.g., department heads, chief medical officers). We identified participants as genomic migrants (long-established practitioners) and genomic natives (those medical specialists coming into independent practice with genomic technology in situ). Data were analyzed deductively with reference to leadership approach.
Results
Leadership approaches were often blended or reported to iteratively support development of another. There was concern at both the absence or the excess of entrepreneurial leadership (i.e., risk-taking).
Conclusion
Entrepreneurial leadership is needed to promote innovativeness, risk-taking, and proactivity, essential in these early stages of clinical genomics. Shared decision-making is required from a wide range of clinicians, calling for both clinical and distributed leadership. Sharing leadership, and the potential loss of positional status from formal senior positions, may prove challenging to genomics “migrants,” who are essential for nurturing genomic “natives.” Clinicians will need support from their organizations and professional bodies to manage the transition.
Similar content being viewed by others
INTRODUCTION
Emerging complex medical technologies offer the promise of improved health outcomes, though they rarely integrate readily with pre-existing infrastructure and knowledge.1 The resultant whole of system changes envisaged for health care are likely to be disruptive to the extant health-care delivery environment.2 Genomic testing is an example of a new technology that holds the potential to provide faster, more reliable diagnosis and drive personalized treatment for many. However, providing results that are clinically meaningful requires not only substantial investment in the complex technology but also multiple professionals to engage throughout the system and across the sociotechnical divide. Engaging medical practitioners is essential to delivering sustained change.3 Yet, many medical practitioners feel underprepared for clinical genomics4,5 and carefully considered leadership approaches will be required to facilitate the adoption of this new complex technology. Despite being outdated, the traditional leadership model in medicine is hierarchical6 with those in senior roles utilizing “top down” approaches of leadership arising from their positional power and perceived expertise.7 Genomic medicine usurps this convention by providing opportunities for early career medical practitioners to lead different areas of clinical genomics delivery (e.g., in clinical genetics, nephrology, neurology, immunology). This raises interesting parallels with digital technologies: just as we talk about digital natives (i.e., those born in the digital era) and migrants (i.e., those who came to digital technologies later in their life)8 clinical genomics too has natives and migrants. Genomic natives are coming into independent medical practice with genomic technology already in situ. This is not to suggest they are experts or have assumed comfort in the field, but this phenomenon holds the potential to pose a challenge to migrants who see their status quo changing.8 These challenges relate to Prensky’s8 concepts of “legacy”, for example, traditional concepts around clinical practice and team management, and “future”, for example, imagining how medicine will be practised in the medium to longer term. Perhaps unsurprisingly, this shift can be challenging for more established practitioners/genomic migrants who are entrenched in historic cultures of leadership.
Leadership
The Australian health leadership framework describe leaders as those who “engage with others to influence health and well-being and the quality of care for birth, illness and the end of life”.9 Leadership is a controversial and complex concept and while there is no consensus definition of leadership there are common themes including vision,10 clarity of goals,11 and influencing others.12 Leadership theories are plentiful13 and have progressed from an early focus on the leaders’ personality (trait theory14) to the followers’ behavior (situational leadership15) to now recognizing that context and leadership are interwoven.16,17 Leadership approaches omnipresent in health care are senior leadership, clinical leadership, and distributed leadership (Fig. 1). Senior leadership, as outlined above, derives power from the position held in the organization, or through the medical hierarchy an assumption of an expert role.6,7 By contrast, clinical leadership calls for health-care professionals to draw on their clinical experience and knowledge to provide leadership focused on patient care. Edmonstone18 notes clinical leaders tend to (1) use persuasion, rather than hierarchical power; (2) prefer evidence-based and planned change in consultation with colleagues; and (3) use reflective practice rather than a technical–rational approach. Distributed leadership, where the responsibility for day-to-day decision-making and action is shared, has risen in prominence in health and social care as a means to promote formal and informal leaders working together to realize an organization's aspirations.19 Distributed (also known as shared or collective) leadership can be defined as “a collective social process emerging through the interactions of multiple actors”20 whereby leadership comes from all team members,19 where roles are fluid, and participants promote continual improvement.21 What these theoretical approaches do not take into consideration is leadership in the context of the uptake of new, and potentially challenging, complex technologies. We posit that entrepreneurial leadership can fill this void and complement senior, clinical, and distributed leadership as a means to deliver complex emerging clinical technologies such as genomics. Entrepreneurial leadership has been defined as “influencing and directing the performance of group members toward the achievement of organizational goals that involve recognizing and exploiting entrepreneurial opportunities”,22 and promotes innovativeness, risk-taking, and proactivity.23 This definition suggests open mindedness is needed to see emerging complex technologies implemented in health care.
Literature exploring leadership in genomics is sparse with limited original research studies evident. A large focus is placed on education,24 and the need to upskill the nongenetic workforce, highlighting the potential role many professions may play (e.g., social workers,25 physiotherapists26). Remarkably, medical practitioners are the focus of very few studies examining leadership in genomics. Using the Geisinger Health System and Kaiser Permanente as examples, Reinke27 identifies the need for leadership to encourage medical practitioners to make the move from genetics to genomics, noting that without this engagement, implementation will not succeed. Furthermore, Lieu et al.28 reported oncologists’ genomic practices were influenced by leadership, placing this variable even ahead of funding, and argued for the need to leverage this to facilitate implementation.
Aims
We sought to bridge theory and action by exploring the extent to which different leadership styles are employed in clinical genomics practice in Australia, a country progressing rapidly with genomics implementation. In particular, we address the following research questions: (1) Do medical practitioners implementing clinical genomics directly or indirectly engage with clinical, distributed, senior and/or entrepreneurial leadership? and (2) What are the implications of different leadership approaches for the implementation of clinical genomics in the future?
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Context
A large number of national genomic medicine initiatives have been funded worldwide to accelerate the implementation of genomics into clinical practice.29 In Australia, the Australian Genomics Health Alliance is a national collaborative research partnership that aims to pilot approaches and develop evidence to inform national integration of genomics into mainstream health care.30 In addition, several state-based programs have been funded, including the Melbourne Genomics Health Alliance, which is working to implement genomics in Victoria.2 Alongside the “top down” strategy, each of these health alliances promote a “bottom up” approach to clinical genomics with clinicians leading the delivery of the genomic medicine projects.
Research design
This study was part of a larger implementation research program investigating the barriers and enablers to the use of genomics in clinical practice and devising an implementation strategy for new adopters across Australia. An overview is provided here, and methodological detail, including interview schedule content, can be found elsewhere.31 To gather data on leadership, a deductive qualitative approach was adopted using secondary analysis of semistructured interviews.
Participants and recruitment
To examine perceptions of implementing clinical genomics, we purposively selected two participant groups via Australian Genomics and Melbourne Genomics: (1) service level decision makers, for an organizational level perspective, and (2) nongenetic medical specialists, for a frontline clinical view. An expert resource group, including clinicians and researchers each with relevant academic and/or contextual knowledge, proposed a total of 62 people who were then invited to interview by email (S.B.) with two follow-up reminder emails if required.
Data collection tools and procedure
We designed two theoretically informed interview schedules to examine the barriers and enablers to implementation of genomics in clinical practice. For the medical specialist interviews, we used the Theoretical Domains Framework32 to identify individual practitioner perceptions along the clinical patient pathway (ensuring appropriate patients are selected for genomic testing, requesting testing and interpreting the data, providing results to patients, and finally mainstreaming genomic testing). For the service level decision makers, we used Spoth et al.’s33 Translation Science to Population Impact framework to gather data along the adoption timeline (preadoption, adoption, implementation, and sustainability). We shared the study concept with the Melbourne Genomics Consumer Advisory Board (CAG) to gain their views on patient-relevant questions to ask at interview. The CAG was also asked for their views on the findings.
Ethical review was provided by Melbourne Health Human Research Ethics Committee (HREC/13/MH/326) and governance approval was provided by Austin Health; Australian Genomics Health Alliance; Monash Health; Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre; the Royal Childrens Hospital, Melbourne; and the Royal Melbourne Hospital. Following provision of participant information and an opportunity to ask questions, interviewees were asked to provide verbal consent for participation.
For consistency and reliability, one highly experienced qualitative researcher conducted all the interviews (S.B.). Interviews were conducted face-to-face where possible (n = 31) with the remaining interviews (n = 6) undertaken by videoconference. On average, interviews lasted 60 minutes. All were audio recorded with participant consent, fully transcribed, and managed using NVivo.34 Each transcript was de-identified, using a unique identifier (MP 1, 2… for clinicians and SL1, 2… for service level decision makers; GM for genomic migrants [i.e., long-established medical practitioners]; and GN for genomic natives [i.e., medical practitioners coming into independent practice with genomic technology in situ]). There are no established criteria for designating genomic migrants and natives and so two experienced coauthors (S.B. and Z.S.) independently assessed all the participants invited to interview to determine if they were genomic natives (i.e., had come to independent medical practice with genomic technology in situ for them) or were genomic migrants (i.e., longer-standing members of the medical community for whom genomics had been introduced after they had become an independent practitioner). There were no disagreements between assessors.
Data analysis
First, using broad leadership concepts of vision, clarity, influencing others, taking responsibility, and including any direct reference to leadership, we assessed the data for any mention of leadership. Typically, these data reflected participants' own experiences, perceptions, and expectations of leadership from others while implementing genomics in the clinical setting, but on occasion participants also discussed their own need and/or leadership style. Then, using a deductive approach we interrogated the interview data and identified the key components of leadership, in the context of clinical genomics, looking for evidence of (1) clinical leadership (i.e., the tendency to use persuasion, rather than hierarchical power; evidence-based change; and/or use of reflective practice); (2) distributed leadership (i.e., the propensity for responsibility to be diffused, and for formal and informal leaders to work together); (3) senior leadership (i.e., power through hierarchy); and (4) entrepreneurial leadership (i.e., the tendency to support innovativeness, risk-taking, and proactivity). See Supplementary file for further details. Transcripts were coded independently by two experienced qualitative researchers (S.B. and H.B.) and discrepancies in coding, for example where there was the potential for overlapping themes, were resolved through discussion to resolve uncertainty. Where needed, a third researcher (N.T.) assessed the transcripts as arbiter and gave a final decision.
RESULTS
First, we report on the demographics of the interviewees, then we present findings related to the leadership concepts stated above, including the merging of leadership approaches. Finally, we provide evidence where an absence or excess of entrepreneurial leadership was reported.
Demographics of interviewees
All who responded to the email invitation were interviewed (n = 37), representing 11 organizations. Participant demographics are presented in Table 1. The majority of service level decision makers were genomic migrants (n = 14/21) while the mainstay of the nongenetic medical specialists were genomic natives (n = 11/16). A large proportion of participants were based in Victoria possibly reflecting both the scale of support the Melbourne Genomics Health Alliance has received to date and Melbourne as the geographic base for Australian Genomics.
Specific leadership approaches
Examples of all four leadership approaches found in the interview data are presented here, including data where participants described combinations or a merging of approaches. There was no marked disparity in responses between nongenetic medical practitioners (MP) or service level decision makers (SL); however, there was a difference between MP genomic migrants and natives. MP genomic natives were more likely to discuss leadership with relatively few comments coming from MP genomic migrants. Only MP natives (and not MP migrants) referenced entrepreneurial leadership.
Table 2 provides exemplar quotes demonstrating the concepts for (1) clinical leadership, e.g., the use of nonhierarchical power or the importance of clinical champions; (2) distributed leadership, e.g., the need for collaboration ensuring formal and informal leaders work alongside each other; (3) senior leadership, e.g., engagement from people in senior management roles in the organization with the influence of senior leaders and the top down buy-in seen as essential to complement the activities of clinical leaders in implementing genomics; and (4) entrepreneurial leadership, e.g., proactivity and risk-taking.
There were cases where participants reported one leadership approach merging into another; for example, entrepreneurial with distributed leadership, with the initial proactivity leadership resulting in collaborative work:
“There was clearly very little or no implementation or translational research going on and so at that time we were talking a lot about how do we get something which is so clearly in the direction we’re going… then we had a few good people to lead it out and say actually, ‘You know, what we need is a partnership that just simply says we’ve just got to start.” SL2 GM
There were also examples of senior leadership blending with entrepreneurial leadership, with the senior figure exhibiting the risk-taking behavior of entrepreneurial leadership:
“…it was really the chief medical officer [who] really recognized that this is just a huge part of where medicine is going; it’s not just genetics… It’s going to touch all areas of medicine and that not being part of it when we were a genetics hub, for the state, would have been a bad error.” SL7 GM
In addition, the need for a range of leadership approaches at multiple levels was noted, here suggesting senior with clinical leadership:
“Responsibility [for implementation of genomics] lies at many different levels so you need high level leadership on this.… There needs to be a sustained effort in that regard and then it comes down to local leadership.” SL1 GN
Expanding and narrowing boundaries for entrepreneurial leadership
Concern was expressed when there was an absence of entrepreneurial leadership; for example, the lack of risk-taking associated with decisions not to invest funding now, given that benefits will not be realized for many years:
“It is a matter of somebody saying we’ll invest now and we’re expecting the outcome in 10, 20 years. Which is a brave... it is not the way cycles are done.” SL13 GM
Here, the interviewee is calling for risk-taking with funding to reap rewards longer term. Contrary to perceptions of a lack of entrepreneurial leadership, participants also identified concerns when entrepreneurial leadership goes too far:
“This is such a change of direction for clinical geneticists, and not everybody has the same evangelism that we do, and maybe the evangelism is a bit off-putting in a way. Maybe it’s a bit too gung-ho, I don’t know, or needed to appeal to their egos.” SL3 GM
This is a moment of clarity. Enthusiasm for the proactivity captured in entrepreneurial leadership, demonstrated in this quote, was seen to pose the risk of others being discouraged from engaging.
In summary, all four leadership approaches were found within the interview data. The leadership approaches were not always mobilized in isolation and could either be blended, or iteratively supported the development of other styles or roles. Participants noted there was a perceived lack of risk-taking at times suggesting an absence of entrepreneurial leadership. However, counter to this was concern of the impact of being “gung-ho” and overly proactive in furthering the genomics agenda.
DISCUSSION
Findings from this study indicate entrepreneurial leadership has a part to play alongside clinical and distributed leadership when implementing clinical genomics. Although clinical and distributed leadership have an essential role in day-to-day clinical practice, the openness to innovation, risk, and enthusiasm for activity or “just doing it” (SL4 GM) of those embracing entrepreneurial leadership can encourage participation with new complex technologies not envisaged by other leadership approaches.
Do medical practitioners implementing clinical genomics directly or indirectly engage with clinical, distributed, senior, and/or entrepreneurial leadership?
Clinical leadership is identified as essential: as autonomous practitioners, the implementation of any new clinical technology is destined to fail without securing engagement from clinicians.35 Senior leadership, to support clinicians, was also valued by genomic natives and migrants at both clinical and organizational levels. The need to be comfortable with taking risks, to be prepared to “put a toe in the water” (SL1 GN) and the significance of promoting a proactivity (and in some cases “militant” [MP16 GN]) agenda was highlighted demonstrating the presence of entrepreneurial leadership. Leadership styles were not always seen in isolation, suggesting no single approach will be effective, or even appropriate, on its own. Instead of generating a new theoretical approach, careful consideration to identify the best elements for use at the most appropriate times by the relevant people may be of value. Thus, contingency leadership—adopting the style and approach suited to the specific purpose and task at hand—looms as key to future progress with the implementation of genomic medicine.
What are the implications of different leadership approaches for the implementation of clinical genomics in the future?
The results highlighted that clinical leadership in isolation is unlikely to result in the sustainable implementation of clinical genomics and “responsibility lies at multiple levels” (SL1 GN). Although essential, the “bottom up” approach from clinicians without senior leadership may result in small pockets of excellence (or activity) leading to uneven adoption, patchy progress, and unsustainable service provision.36
Distributed leadership calls for an openness to contributions from the wider clinical team,20 including genomic natives, and leveling out of hierarchy,19 which is likely to lead to disruption of traditional medical structures and—in the context of genomics particularly, may subsequently begin to challenge the traditional “elite expert senior consultant” model of senior doctors. Sharing knowledge can result in a loss of “expert power”,37 which is challenging for the medical profession.38 If genomic natives arrive with new genomic skills gained and developed through sharing among the native cohorts there is a risk genomic migrants may feel slighted. Due to the enormity of data in clinical genomics, new approaches will be required for knowledge gathering, use, and integration (i.e., where to access knowledge rather than knowing all the answers). As genomic natives develop, they will need the support of more longstanding clinicians (i.e., genomic migrants) to help them navigate the health-care system infrastructure. There is potential here that the natives may eventually supersede the knowledge and skills of the migrants. This presents the challenge of not “eating our young”39 and ensuring genomic natives are nurtured.
Entrepreneurial leadership was not reported as a panacea for progress. Indeed, concern was expressed when it went unchecked, for example with genomic “evangelism” (SL3 GM). However, the absence of risk-taking, proactivity, and innovation is likely to hinder the implementation of clinical genomics and there is a need to promote a readiness to innovate and preparedness to learn from failure.40
As to limitations, this study was undertaken in one country with a specific health-care delivery infrastructure. Implementation strategies for genomics vary internationally so caution is warranted in interpreting these findings elsewhere. The interview schedule was designed to gather views about implementation of genomics into the clinical setting and as such could limit the findings on leadership. Nonetheless, the fact that leadership was not the focus of the interviews, but strongly emerged from the data is an important finding in and of itself demonstrating it is at the forefront of clinicians’ minds. Using this opportunity to analyze the data and start to bridge the knowledge/practice gap has highlighted a number of needs relating to the implementation of genomics, as well as new avenues for research. Our future research will look to specifically investigate leadership in clinical genomics across multiple health settings.
All in all, we have started to disentangle some of the early conversations in an emerging field to promote debate on identifying and adopting appropriate leadership approaches in clinical genomics. It raises many more questions and requires further study. We are now aware of some of the implications associated with these different leadership approaches. As such, new questions arise that will benefit from future research: how can we leverage the advantages of each approach? Are there more or less appropriate times or circumstances in which to apply any one style or role along the genomics implementation pipeline? Are different approaches required for natives versus migrants? Our aim was to bridge leadership literature and practice in clinical genomics. Our findings demonstrate clear recognition of all four leadership approaches and appreciate that, despite the autonomy of medical practitioners, there is a need for buy-in from senior leaders (migrants or natives). The “bottom up” approach of clinical leadership, prominent in Australia, in isolation, is unlikely to lead to sustainable implementation. The complexity of clinical genomics demands team decision-making and distributed leadership will be challenging for some. As a result of this shift in leadership approaches, support from professional bodies and medical opinion leaders will be required for genomic migrants to be comfortable in the fast moving era of genomics and also to ensure they can nurture the developing genomic natives.
References
Georgiou A, Ampt A, Creswick N, Westbrook JI, Braithwaite J. Computerized provider order entry—what are health professionals concerned about? A qualitative study in an Australian hospital. Int J Med Inform. 2009;78:60–70.
Gaff CL, Winship IM, Forrest SM, et al. Preparing for genomic medicine: a real world demonstration of health system change. npj Genomic Med. 2017;2:1–8.
Mintzberg H. The structuring of organisations. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall; 1979.
Crellin E, McClaren B, Nisselle A, Best S, Gaff C, Metcalfe S. Preparing medical specialists to practice genomic medicine: education an essential part of a broader strategy. Front Genet. 2019;10:1–7.
Stark Z, Nisselle A, McClaren B, et al. Attitudes of Australian health professionals towards rapid genomic testing in neonatal and paediatric intensive care. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019;27:1493–1501.
Dowton SB. Leadership in medicine: where are the leaders? Med J Aust. 2004;181:652–654.
Saxena A, Desanghere L, Stobart K, Walker K. Goleman’s leadership styles at different hierarchical levels in medical education. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17:1–9.
Prensky M. Digital natives, digital immigrants. Part 1 On the Horizon, MCB University Press. 2001;9:1–6.
Health LEADS Australia. Health LEADS Australia: the Australian health leadership framework. Health Workforce Australia. 2013. https://www.aims.org.au/documents/item/352.
Northouse PG. Leadership: theory and practice. 7th ed London: Sage; 2016.
Caillier JG. Linking transformational leadership to self-efficacy, extra-role behaviors, and turnover intentions in public agencies: the mediating role of goal clarity. Adm Soc. 2016;48:883–906.
Ford J, Harding NH, Gilmore S, Richardson S. Becoming the leader: leadership as material presence. Organ Stud. 2017;38:1553–1571.
Dinh JE, Lord RG, Gardner WL, Meuser JD, Liden RC, Hu J. Leadership theory and research in the new millennium: current theoretical trends and changing perspectives. Leadersh Q. 2014;25:36–62.
Carlyle T. On heroes, hero-worship, and the heroic in history. Boston: Houghton-Mifflin; 1849.
Hersey P, Blanchard K. Great ideas revisited: life-cycle theory of leadership. Train Dev. 1996;50:42.
Liden RC, Antonakis J. Considering context in psychological leadership research. Hum Relations. 2009;62:1587–1605.
Uhl-Bien M, Arena M. Complexity leadership: enabling people and organizations for adaptability. Organ Dyn. 2017;46:9–20.
Edmonstone J. Clinical leadership: the elephant in the room. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2009;290–305.
West M, Eckert R, Stewart K, Passmore B. Developing collective leadership for health care. 2014. http://www.kingsfund.org.uk/sites/files/kf/field/field_publication_file/developing-collective-leadership-kingsfund-may14.pdf.
Currie G, Lockett A. Distributing leadership in health and social care: concertive, conjoint or collective? Int J Manag Rev. 2011;13:286–300.
Bolden R. Distributed leadership in organizations: a review of theory and research. Int J Manag Rev. 2011;13:251–269.
Renko M, El Tarabishy A, Carsrud AL, Brännback M. Understanding and measuring entrepreneurial leadership style. J Small Bus Manag. 2015;53:54–74.
Currie G, Humphreys M, Ucbasaran D, Mcmanus S. Entrepreneurial leadership in the English public sector: paradox or possibility? Public Adm. 2008;86:987–1008.
Boyd AM, Alt-White AC, Anderson G, Schaa KL. Genomic competencies for nursing practice: implications for nursing leadership. J Nurs Adm. 2017;47:62–67.
Werner-Lin A, McCoyd JLM, Doyle MH, Gehlert SJ. Leadership, literacy, and translational expertise in genomics: challenges and opportunities for social work. Heal Soc Work. 2016;41:e52–e59.
Cornwall J, Osmotherly P. Genomic medicine and the future of physiotherapy. Australas Med J. 2014;7:361.
Reinke T. Leading health systems switch focus from genetics to genomics. Physician Leadersh J. 2015;2:28–30.
Lieu TA, Ray GT, Prausnitz SR, et al. Oncologist and organizational factors associated with variation in breast cancer multigene testing. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;163:167–176.
Stark Z, Dolman L, Manolio TA, et al. Integrating genomics into healthcare: a global responsibility. Am J Hum Genet. 2019;104:13–20.
Stark Z, Boughtwood T, Phillips P, et al. Australian genomics: a federated model for integrating genomics into healthcare. Am J Hum Genet. 2019;105:7–14.
Taylor N, Best S, Martyn M. A transformative translational change programme to introduce genomics into healthcare: a complexity and implementation science study protocol. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e024681.
Michie S, Richardson M, Johnston M, et al. The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Ann Behav Med. 2013;46:81–95.
Spoth R, Rohrbach LA, Greenberg M, et al. Addressing core challenges for the next generation of type 2 translation research and systems: the translation science to population impact (TSci Impact) framework. Prev Sci. 2013;14:319–351.
QSR International Pty Ltd. NVivo qualitative data analysis software Version 12. 2018.
Ingebrigtsen T, Georgiou A, Clay-Williams R, et al. The impact of clinical leadership on health information technology adoption: systematic review. Int J Med Inform. 2014;83:393–405.
Sarto F, Veronesi G. Clinical leadership and hospital performance: assessing the evidence base. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16(Suppl 2):169.
French JRP, Raven B. The bases of social power. In: Cartwright D, editor. Studies in social power. Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan. 1959. p. 150–67.
British Medical Association. Doctors’ perspectives on clinical leadership. Health policy economic research, British Medical Association London. 2012. https://www.bma.org.uk/-/media/files/pdfs/working%20for%20change/shaping%20healthcare/doctors%20on%20clinical%20leadership%20june%202012.pdf. Accessed 12 December 2019.
Gillespie GL, Grubb PL, Brown K, Boesch MC, Ulrich DL. “Nurses eat their young”: a novel bullying educational program for student nurses. J Nurs Educ Pract. 2017;7:11.
Edmondson AC. Leadership: strategies for learning from failure. Harv Bus Rev. 2011;89:48–55.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Targeted Call for Research grant (GNT1113531): “Preparing Australia for Genomic Medicine”. The research conducted at the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute was supported by the Victorian Government’s Operational Infrastructure Support Program. The funders played no part in the study design; data collection, analysis, and interpretation; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. If you remix, transform, or build upon this article or a part thereof, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Best, S., Stark, Z., Brown, H. et al. The leadership behaviors needed to implement clinical genomics at scale: a qualitative study. Genet Med 22, 1384–1390 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-020-0818-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41436-020-0818-1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Aligning intuition and theory: a novel approach to identifying the determinants of behaviours necessary to support implementation of evidence into practice
Implementation Science (2023)
-
Learning from scaling up ultra-rapid genomic testing for critically ill children to a national level
npj Genomic Medicine (2021)