Abstract
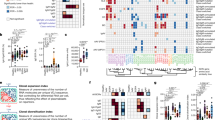
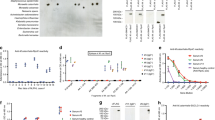
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) expressing stereotyped B-cell receptors (BCRs) endowed with rheumatoid factor (RF) activity and putatively recognizing the HCV E2 protein. To further untangle the shaping and function of these BCRs, we analyzed immunoglobulin gene rearrangements of monoclonal B cells from 13 patients with HCV-associated LPDs and correlated their features with the clinical outcomes of antiviral therapy. While only two patients shared a stereotyped heavy-chain complementarity determining region 3 (CDR3) sequence, two kappa chain CDR3 stereotyped sequences accounted for 77% of BCRs. Light chains were enriched in sequences homologous to anti-HCV E2 antibodies compared with heavy chains (7/13 vs. 0/13; p = 0.005). Anti-HCV E2 homology was uniquely associated (7/7 vs. 0/6; p = 0.0006) with a stereotyped CDR3 sequence encoded by IGKV3-20/3D-20 gene(s) accounting for 54% of BCRs. An IGKV3-15/IGKJ1-encoded stereotyped sequence homologous to WA RF accounted for 23% of BCRs. LPDs expressing KCDR3s homologous to anti-HCV E2 antibodies responded more frequently to the eradication of HCV by antiviral therapy (6/6 vs. 1/6; p = 0.015). These findings, although limited by the small sample size, suggest that a stereotyped KCDR3 may predominantly shape anti-HCV specificity of BCRs, possibly providing a signature that may help identifying bona fide HCV-dependent LPDs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Moreno C, Boudjograh M, Guida G, Smilevska T, et al. Over 20% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia carry stereotyped receptors: Pathogenetic implications and clinical correlations. Blood. 2007;109:259–70.
Zwick C, Fadle N, Regitz E, Kemele M, Stilgenbauer S, Bühler A, et al. Autoantigenic targets of B-cell receptors derived from chronic lymphocytic leukemias bind to and induce proliferation of leukemic cells. Blood. 2013;121:4708–17.
Hoogeboom R, Wormhoudt TA, Schipperus MR, Langerak AW, Dunn-Walters DK, Guikema JE, et al. A novel chronic lymphocytic leukemia subset expressing mutated IGHV3-7-encoded rheumatoid factor B-cell receptors that are functionally proficient. Leukemia. 2013;27:738–40.
Del Padre M, Todi L, Mitrevski M, Marrapodi R, Colantuono S, Fiorilli M, et al. Reversion of anergy signatures in clonal CD21low B cells of mixed cryoglobulinemia after clearance of HCV viremia. Blood. 2017;130:35–8.
De ReV, De Vita S, Marzotto A, Rupolo M, Gloghini A, Pivetta B, et al. Sequence analysis of the immunoglobulin antigen receptor of hepatitis C virus-associated non-Hodgkin lymphomas suggests that the malignant cells are derived from the rheumatoid factor-producing cells that occur mainly in type II cryoglobulinemia. Blood. 2000;96:3578–84.
Charles ED, Green RM, Marukian S, Talal AH, Lake-Bakaar GV, Jacobson IM, et al. Clonal expansion of immunoglobulin M+CD27+ B cells in HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood. 2008;111:1344–56.
Knight GB, Gao L, Gragnani L, Elfahal MM, De Rosa FG, Gordon FD, et al. Detection of WA B cells in hepatitis C virus infection: a potential prognostic marker for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and B cell malignancies. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2152–9.
Charles ED, Orloff MI, Nishiuchi E, Marukian S, Rice CM, Dustin LB. Somatic hypermutations confer rheumatoid factor activity in hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2430–40.
Ng PP, Kuo CC, Wang S, Einav S, Arcaini L, Paulli M, et al. B-cell receptors expressed by lymphomas of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected patients rarely react with the viral proteins. Blood. 2014;123:1512–5.
Gragnani L, Visentini M, Fognani E, Urraro T, De Santis A, Petraccia L, et al. Prospective study of guideline-tailored therapy with direct-acting antivirals for hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia. Hepatology. 2016;64:1473–82.
Frigeni M, Besson C, Visco C, Fontaine H, Goldaniga M, Visentini M, et al. Interferon-free compared to interferon-based antiviral regimens as first-line therapy for B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Leukemia. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-019-0687-2.
Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Hadzidimitriou A, Smilevska T, Kalagiakou E, Hatzi K, et al. Immunoglobulin light chain repertoire in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2005;106:3575–83.
Hadzidimitriou A, Darzentas N, Murray F, Smilevska T, Arvaniti E, Tresoldi C, et al. Evidence for the significant role of immunoglobulin light chains in antigen recognition and selection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2009;113:403–11.
Kostareli E, Gounari M, Janus A, Murray F, Brochet X, Giudicelli V, et al. Antigen receptor stereotypy across B-cell lymphoproliferations: the case of IGHV4-59/IGKV3-20 receptors with rheumatoid factor activity. Leukemia. 2012;26:1127–31.
Shiroishi M, Ito Y, Shimokawa K, Lee JM, Kusakabe T, Ueda T. Structure-function analyses of a stereotypic rheumatoid factor unravel the structural basis for germline-encoded antibody autoreactivity. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:7008–16.
Allander T, Drakenberg K, Beyene A, Rosa D, Abrignani S, Houghton M, et al. Recombinant human monoclonal antibodies against different conformational epitopes of the E2 envelope glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus that inhibit its interaction with CD81. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:2451–9.
Keck ZY, Pierce BG, Lau P, Lu J, Wang Y, Underwood A, et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies from an individual that naturally cleared multiple hepatitis C virus infections uncover molecular determinants for E2 targeting and vaccine design. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15:e1007772.
Kostareli E, Sutton LA, Hadzidimitriou A, Darzentas N, Kouvatsi A, Tsaftaris A, et al. Intraclonal diversification of immunoglobulin light chains in a subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia alludes to antigen-driven clonal evolution. Leukemia. 2010;24:1317–24.
Jiménez de Oya N, De Giovanni M, Fioravanti J, Übelhart R, Di Lucia P, Fiocchi A, et al. Pathogen-specific B-cell receptors drive chronic lymphocytic leukemia by light-chain-dependent cross-reaction with autoantigens. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9:1482–90.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Veronica Morea for critically revising the analysis of sequences.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Istituto Pasteur Italia-Fondazione Cenci Bolognetti (grant number 2017-76 to MV) and by the Intramural Research Program of Sapienza University of Rome (grant number RM11715C7D005D19 to MC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minafò, Y.A., Del Padre, M., Cristofoletti, C. et al. A stereotyped light chain may shape virus-specific B-cell receptors in HCV-dependent lymphoproliferative disorders. Genes Immun 21, 131–135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-020-0093-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-020-0093-9