Abstract
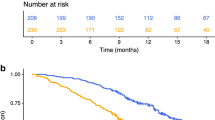
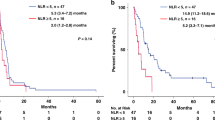
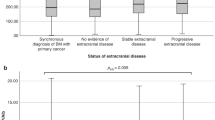
The prognostic value of the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) has been shown in various types of cancers. We aimed to evaluate the predictive values in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with status of EGFR mutations. We, retrospectively, examined 310 patients with brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with status of EGFR mutations. SII was calculated using P * N/L, where P, N, and L, respectively refer to peripheral blood lymphocyte, neutrophil, and platelet counts. The cut-off value of SII was assessed by area under the curve (AUC). The log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard model were used to confirm the impact of SII and other variables on survival. The SII value ≤ 1218.81 was associated with prolonged survival in patients with brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma in both variable and multivariable analysis In patients with EGFR mutations, the SII had statistical effect on OS only in invariable test. While, for patients with wild-type EGFR, SII achieved statistically significant differences both in variable and multivariable analyses. SII is an independent prognostic factor in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma. SII may have varying prognostic effects on patients with and without EGFR mutations and is a promising variable for the future prognostic systems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Sloan AE, Davis FG, Vigneau FD, Lai P, Sawaya RE. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973–2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:2865–72.
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors 316 in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:745–51.
Chao ST, De Salles A, Hayashi M, Levivier M, Ma L, Martinez R, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of limited (1–4) brain metasteses: systematic review and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society Practice Guideline. Neurosurgery. 2017;83:345–53.
Jamal-Hanjani M, Spicer J. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small cell lung cancer metastatic to the brain. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:938–44.
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, et al. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors 316 in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;37:745–51.
Sperduto PW, Berkey B, Gaspar LE, Mehta M, Curran W. A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: an analysis of 1960 patients in the RTOG database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:510–4.
Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK, et al. Diagnosis specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77:655–61.
Hu B, Yang XR, Xu Y, Sun YF, Sun C, Guo W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:6212–22.
Casadei Gardini A, Scarpi E, Faloppi L, Scartozzi M, Silvestris N, Santini D, et al. Immune inflammation indicators and implication for immune modulation strategies in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving sorafenib. Oncotarget. 2016;7:67142–9.
Fan L, Wang R, Chi C, Cai W, Zhang Y, Qian H, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the combined clinical outcome after sequential therapy with abiraterone and docetaxel for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Prostate. 2018;78:250–6.
Huang L, Liu S, Lei Y, Wang K, Xu M, Chen Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index, thymidine phosphorylase and survival of localized gastric cancer patients after curative resection. Oncotarget. 2016;7:44185–93.
Hong X, Cui B, Wang M, Yang Z, Wang L, Xu Q. Systemic immune-inflammation index, based on platelet counts and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio, is useful for predicting prognosis in small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2015;236:297–304.
Cools-Lartigue J, Spicer J, McDonald B, Gowing S, Chow S, Giannias B, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:3446–58.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Zhou Y, Wei Q, Fan J, Cheng S, Ding W, Hua Z. Prognostic role of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis containing 8252 patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;479:181–9.
Yang JJ, Hu ZG, Shi WX, Deng T, He SQ, Yuan SG. Prognostic significance of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:2807–15.
Feng F, Tian Y, Liu S, Zheng G, Liu Z, Xu G. et al. Combination of PLR, MLR, MWR, and tumor size could significantly increase the prognostic value for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Medicines. 2016;95:e3248
Yuan C, Li N, Mao X, Liu Z, Ou W, Wang SY. Elevated pretreatment neutrophil/white blood cell ratio and monocyte/lymphocyte ratio predict poor survival in patients with curatively resected non-small cell lung cancer: results from a large cohort. Thorac Cancer. 2017;8:350–8.
Sakurai K, Tamura T, Toyokawa T, Amano R, Kubo N, Tanaka H, et al. Low preoperative prognostic nutritional index predicts poor survival post-gastrectomy in elderly patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:3669–76.
Yu J, Li SM, Kong Y, Si L, Sheng X, Chi Z, et al. Association of immune-inflammation index with outcome of high-risk acral melanoma patients treated with adjuvant highdose interferon. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34
Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Massager N, et al. Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases: estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;60:218–24.
Golden DW, Lamborn KR, McDermott MW, Kunwar S, Wara WM, Nakamura JL, et al. Prognostic factors and grading systems for overall survival in patients treated with radiosurgery for brain metastases: variation by primary site. J Neurosurg. 2008;109:77–86.
deSouza NM, Liu Y, Chiti A, Oprea-Lager D, Gebhart G, Van Beers BE, et al. Strategies and technical challenges for imaging oligometastatic disease: recommendations from the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer imaging group. Eur J Cancer. 2018;91:153–63.
Fink KR, Fink JR. Imaging of brain metastases. Surg Neurol Int. 2013;4(Suppl 4):S209–S19.
Ando M, Ando Y, Hasegawa Y, Shimokata K, Minami H, Wakai K, et al. Prognostic value of performance status assessed by patients themselves, nurses, and oncologists in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:1634–9.
Wang K, Diao F, Ye Z, Zhang X, Zhai E, Ren H, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer. 2017;36:75.
Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:425–30.
Ngabire D, Kim GD. Autophagy and inflammatory response in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18:2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
These authors contributed equally: Hongwei Li, Guochao Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wang, G., Zhang, H. et al. Prognostic role of the systemic immune-inflammation index in brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma with different EGFR mutations. Genes Immun 20, 455–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-018-0050-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41435-018-0050-z
This article is cited by
-
Dynamic changes in the systemic immune-inflammation index predict the prognosis of EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving brain metastasis radiotherapy
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2022)
-
Worldwide Prevalence of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Molecular Diagnosis & Therapy (2022)