Abstract
We report previously undocumented evidence of genetic discrimination by Australian insurance companies, obtained through direct consumer reports. We surveyed 174 consumers with cancer-predisposing variants, recruited by cancer organisations Lynch Syndrome Australia and Pink Hope. Questions related to experiences accessing risk-rated insurance after genetic testing. Results indicate that both legal (permitted under current regulation) and illegal discrimination is occurring. Although some respondents had not applied for risk-rated insurance, or had insurance in place before genetic testing (n = 100), those seeking new policies (n = 74) commonly experienced difficulties obtaining insurance (86%, 64/74). Of those experiencing difficulties, 50% (32/64) had no prior history or symptoms of cancer, and had undertaken risk reduction through surveillance and/or preventative surgery. Seventy-seven percent (49/64) reported difficulties related to life insurance. Follow-up telephone interviews with four respondents further described cases of apparent illegal breaches. All reports of discrimination identified were, to our knowledge, previously unreported in the literature. The number of cases suggests a systemic problem with the Australian life insurance industry. We support calls for government oversight of the inherently conflicted model of industry self-regulation in Australia, and an immediate ban on the use of genetic test results in insurance underwriting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In Australia, discrimination on the basis of genetic status is prohibited by the Disability Discrimination Act 1992(Cth), but an exception allows insurance discrimination on actuarial grounds. Insurers can use genetic test results, even in the absence of disease symptoms, to deny coverage or impose increased premiums on products such as life, income protection, permanent disability and travel insurance. However, genetic discrimination must be actuarially or reasonably justified. Insurers must consider risk-reducing measures, including surveillance and surgery. This requirement creates a distinction between legal genetic discrimination, where an insurer’s actions are within current legal regulation (but ethically contentious [1]), and illegal genetic discrimination—where an insurer’s behaviour is in breach of a clear regulatory requirement. Private health insurance, which is community rated in Australia (no individual risk assessment), is not affected.
Predictive genetic testing can identify modifiable disease risk, especially for cancer, where life-saving intervention is possible. Conditions commonly benefiting from predictive testing include Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer syndrome (BRCA1/2 genes) and Lynch syndrome, which increases risk for colon, endometrial and other cancers. Risk-reduction programs and preventive surgeries are available and highly effective for both of these conditions. Preventative surgery in BRCA1/2 carriers (mastectomy/salpingo-oophorectomy) can reduce risk of breast and/or ovarian cancer to below population average [2]. Intensive breast surveillance also reduces risk, with 10-year survival >95% with magnetic resonance imaging screening [3]. For Lynch syndrome, surveillance through colonoscopy and chemoprevention significantly reduces colorectal cancer incidence and mortality [4], and preventative gynaecological surgery significantly reduces risk of gynaecological cancer [5].
Previous studies have shown that life insurance companies in Australia do not always consider risk reduction in underwriting [6,7,8]. In addition, several consumers have recently come forward to the media, reporting difficulties accessing life insurance, even after undergoing risk-reducing surgery and/or surveillance. In one well-documented case, involving an application to the Australian Human Rights Commission, multiple life insurers failed to consider risk reduction for Lynch syndrome when underwriting [7].
Further evidence indicates consumer fears regarding insurance deter the uptake of genetic testing and participation in medical research in Australia [9,10,11,12]. In one study, individuals informed of possible insurance implications of genetic testing were more than twice as likely to decline testing as those not informed [10]. This is an acknowledged barrier to progress in genomic medicine, compromising Australian medical research [13]. Further, the current model of industry self-regulation has resulted in inadequate transparency and limited accountability for policy breaches [14].
In March 2018, a Parliamentary Joint Committee (PJC) inquiry into the Australian life insurance industry released its official report [13], recommending an urgent ban on the use of predictive genetic test results. The PJC recommended a ban similar to the UK moratorium, and informed by bans in other countries [14, 15]. To date, no ban has been implemented in Australia. The Financial Services Council (FSC) recently announced an industry-regulated moratorium to commence mid-2019, which falls short of the PJC’s recommendations—it has significant financial limits and no government involvement. At the time of writing, the FSC has commenced consultation on the proposed terms.
Historically, it has been difficult to quantify the scale of genetic discrimination in Australian insurance, and identify new cases. Accessing records of underwriting decisions by life insurers has been difficult, and controlled by the peak insurer body, the FSC. Data on underwriting has been periodically made available to researchers for analysis and resulting publication [8, 16]. However, published datasets have typically lacked completeness, with limited numbers of insurers contributing data, and have been significantly out-of-date by publication.
This study aimed to identify previously unreported cases of genetic discrimination in Australian insurance, through direct consumer reports.
Materials and methods
We partnered with education and advocacy bodies for individuals with inherited cancer-predisposing variants: Lynch Syndrome Australia (LSA) and Pink Hope (PH). These organisations have broad networks of consumers undertaking genetic testing. As there is no national register of variant carriers in Australia, these support organisations provided the most efficient and direct access to a convenience sample of consumers who may have experienced difficulties accessing insurance products after genetic testing.
Our sequential mixed-methods study was descriptive and exploratory. It comprised an online survey designed to identify experiences of discrimination on the basis of genetic test results by insurance companies, followed by targeted telephone interviews to describe selected consumer experiences in greater detail. Products offered by life insurance companies (including life, income protection and disability insurance, collectively referred to hereafter as “life insurance products”) were of primary interest in this study. However, we also included reports of discrimination in other risk-rated insurance, including mortgage protection and travel insurance. Health insurance, which is community rated, was excluded.
The first survey draft was developed collaboratively with LSA, and then adapted for PH members. While covering the same topics, the surveys were modified slightly between the groups to better capture relevant information. Questions included demographics, relevant medical details, variant detected, prior cancer diagnoses, relatives affected, risk-reducing surveillance/surgery, and insurance experiences (Supplementary Materials). At the end of the survey, respondents were asked whether they would be willing to be re-contacted by researchers to discuss experiences further. Follow-up telephone interviews (semi-structured) were conducted with a limited number of respondents, and were designed to gather more in-depth data on consumer reports of genetic discrimination, particularly related to suspected breaches of current policy.
Surveys were distributed by email and social media to LSA and PH group members, to reach a convenience sample of consumers likely to have experienced insurance discrimination after genetic testing. LSA sent one email and promoted on social media once. PH promoted the survey on social media twice. Semi-structured follow-up telephone interviews were designed to collect more detail from a small subset of the respondents who consented to re-contact. Follow-up respondents were selected on the basis of the type of discrimination reported in the survey. We prioritised respondents who reported what appeared to be illegal discrimination, characterised by a failure of insurance companies to consider risk-reducing surgery. Our aim was not to reach saturation but to gather more data on specific cases of illegal discrimination.
Data analysis involved descriptive statistics of survey responses. Follow-up interviews were recorded and analysed to describe the key features of respondents’ experiences. The project was approved by the Alfred Human Research Ethics Committee, number 332/18.
Results
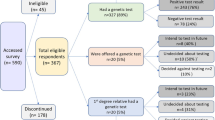
LSA emailed its survey to 550 members, then promoted via social media with an estimated reach of 700–800 people, based on metrics reports (September–October 2017). PH promoted its survey via social media in March and April 2018 (estimated reach of 2540). Due to the online recruitment method, overall survey response rates could not be calculated.
We received completed surveys from 214 respondents. Respondents without cancer-predisposing variants and those from outside Australia were excluded. The resulting 174 respondents comprised the final data set (summary results Table 1). The majority were female (91%), and aged 40–60 years (55%). The most common variant was BRCA1 (23%).
Many respondents who obtained insurance did so before genetic testing (55%, 61/110). Another 22% (39/110) reported no attempt to obtain insurance. Of the remainder (n = 74), 86% (64/74) experienced difficulty obtaining risk-rated insurance after having genetic testing (Table 1). This included denials of cover (n = 45) or premiums increased above standard rates (n = 16), with three participants not disclosing the type of difficulty. Of these, 77% (49/64) experienced difficulty obtaining life insurance products.
Of those who reported difficulties, 50% (32/64) had no personal cancer history and reported risk reduction (regular surveillance and/or preventative surgery). These represented possible cases of illegal discrimination (for details see Supplementary Table S1). Only 9% (6/64) of respondents who had difficulty reported appealing the insurer’s decision. LSA participants were asked specific questions about reasons for not appealing, and of those who did not appeal the insurer’s decision, 50% (21/42) said they did not know that this was an option (Table S1).
Of the PH respondents without preventative surgery (n = 17), all but one were in high-risk breast surveillance. All LSA respondents without bowel cancer (n = 57) had regular colonoscopy. Of those who obtained life insurance products after testing (n = 10), none had a prior history of cancer, and all had some preventative surgery and/or regular surveillance.
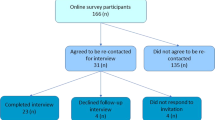
Seventy-one respondents agreed to re-contact for follow-up, 29 of whom had reported difficulty accessing life insurance products. Resource limitations precluded interviewing all 29 respondents. Four respondents were chosen for interviews, whose reported circumstances indicated that risk-reducing measures had not been considered by life insurance companies in underwriting. All four case studies demonstrated aspects of failure by insurers to consider risk reduction. Due to space constraints, and the overlap in issues raised in the four case studies, three were selected to present the experiences of this group (Table 2). We sought pro-bono legal advice regarding Case 1 and Case 3, as they took place in 2018 and were considered the most suitable for legal challenge. We received an initial indication that they could both have grounds for legal challenge on the basis that the insurer was reported to have failed to consider risk reduction in making an adverse decision.
Discussion
Of 64 individuals reporting genetic discrimination by insurers, we identified 32 individuals reporting experiences of arguably illegal genetic discrimination. Based on initial consideration, legal remedies could be pursued in several of these cases.
Difficulties accessing insurance after genetic testing were common in the surveyed population. Strikingly, half of all respondents reporting difficulties accessing insurance had no personal cancer history and were following recommended guidelines for cancer prevention, often reducing risk below population average [2,3,4], yet they still had policies denied and premiums loaded, without actuarial justification. The limited knowledge of the appeals process reinforces earlier research regarding barriers to uptake of legal remedies [17].
Although some respondents did not report difficulty obtaining insurance, very few actually obtained life insurance products at standard rates after receiving a positive genetic test result. Many reported having some insurance in place before having testing, consistent with common pre-test genetic counselling discussions in Australia, regarding considering life insurance before having genetic testing [18].
Discriminating on genetic test results penalises individuals who are proactive about health. By contrast, those who remain uninformed of their risk are not penalised in the same way. Almost all respondents in this cohort took significant steps to reduce their risks of cancer after receiving positive genetic test results. This suggests at-risk consumers who are members of organisations like PH and LSA are motivated to reduce risk, rather than prioritise seeking higher levels of life insurance, although participants were not directly asked this question. This is consistent with a US study showing women with BRCA1/2 variants did not purchase more life insurance than untested women [19]. This would need to be tested in a larger sample to confirm whether this holds at the population level.
In many cases, individuals bear the costs of proactive risk mitigation, but can still be financially disadvantaged by discriminatory insurance underwriting. Although insurers are legally obliged to consider risk reduction, this study indicates that in many cases, they do not. This means that not only are individuals choosing not to have predictive testing, but further, their subsequent lack of access to preventative measures has potential negative effects on their health and life expectancy. If insurers were to accept a ban as recommended, it would encourage at-risk individuals to take steps to mitigate their risk, making claims less likely [1].
Legal and illegal discrimination
These and other social policy reasons support an argument that even the legal genetic discrimination identified should not be allowed [1]. A ban on the use of genetic test results by insurers, as applied in many other countries and recommended by the Australian PJC [13], would protect consumers from all genetic discrimination in life insurance and allow individuals to pursue genetic testing and participate in research without insurance fears. It is important to note that the recommended ban would not apply to family history information, only genetic test results. Further, the recommended ban would allow the use of genetic test results to counter a negative family history (i.e. to show that an individual does not have a genetic variant that runs in the family and contributes to a family history of disease).
In at least 50% of the cases of discrimination reported, insurers failed to consider risk-reducing measures, consistent with illegal genetic discrimination. If substantiated, these cases would indicate insurer disregard for existing regulations, and minimal accountability for breaches of current regulatory requirements. Government oversight and stricter penalties are required to ensure compliance within a self-regulated industry. Legal remedies for insurance discrimination flow from federal and state anti-discrimination legislation [17]. However, the appeal pathway is unclear and the cost of legal advice can be prohibitive, meaning available legal remedies are often not pursued by affected consumers [7, 17]. In our study, only 9% of affected consumers appealed adverse decisions.
Limitations
Our survey relied on consumer self-reports, and investigators did not have access to primary insurance documentation to verify reports of discrimination. Differences between the LSA/PH surveys resulted in some differences in data collected, and the total reach of the survey could not be calculated accurately due to online advertising methods. We provided our best estimate, based on reported social media statistics. Recruitment through support networks may have resulted in participant bias towards proactive individuals. While this bias is acknowledged and may limit the generalisability of some results, the number of discrimination cases identified remains pertinent. We accept that the sample is likely more educated, computer savvy and resourceful than the general population, and more likely to be aware of and report genetic discrimination. In our view, the extent of discrimination experienced by those without those characteristics (who are not even aware that discrimination is occurring) is underestimated by this study.
This study provides an up-to-date description of reported cases of genetic discrimination in Australian risk-rated insurance, with a particular focus on life insurance. We reached only a fraction of possibly affected consumers, likely underestimating the scale of the problem and future research could survey a broader range of consumers. Our findings highlight the material impact on consumers experiencing both legal and illegal discrimination by Australian insurers. In light of the documented adverse impact of insurance concerns on uptake of clinical testing and research participation, the findings support calls for an immediate ban on the use of genetic test results in underwriting in Australia, and greater government oversight.
Change history
29 July 2019
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0475-5
References
Rothstein MA. Time to end the use of genetic test results in life insurance underwriting. J Law Med Ethics. 2018;46:794–801.
Domchek SM, Friebel TM, Singer CF, Evans DG, Lynch HT, Isaacs C, et al. Association of risk-reducing surgery in BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation carriers with cancer risk and mortality. JAMA. 2010;304:967–75.
Gareth ED, Nisha K, Yit L, Soujanye G, Emma H, Massat NJ, et al. MRI breast screening in high-risk women: cancer detection and survival analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;145:663–72.
Burn J, Gerdes A-M, Macrae F, Mecklin J-P, Moeslein G, Olschwang S, et al. Long-term effect of aspirin on cancer risk in carriers of hereditary colorectal cancer: an analysis from the CAPP2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:2081–7.
Schmeler KM, Lynch HT, Chen L-m, Munsell MF, Soliman PT, Clark MB, et al. Prophylactic surgery to reduce the risk of gynecologic cancers in the Lynch syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:261–9.
Barlow-Stewart K, Taylor SD, Treloar SA, Stranger M, Otlowski M. Verification of consumers’ experiences and perceptions of genetic discrimination and its impact on utilization of genetic testing. Genet Med. 2009;11:193.
Keogh LA, Otlowski M. Life insurance and genetic test results: a mutation carrier’s fight to achieve full cover. Med J Aust. 2013;199:363–6.
Otlowski M, Barlow-Stewart K, Taylor S, Stranger M, Treloar S. Investigating genetic discrimination in the Australian life insurance sector: the use of genetic test results in underwriting, 1999–2003. J Law Med. 2007;14:367–96.
Keogh LA, Niven H, Rutstein A, Flander L, Gaff C, Jenkins M. Choosing not to undergo predictive genetic testing for hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes: expanding our understanding of decliners and declining. J Behav Med. 2017;40:583–94.
Keogh LA, van Vliet CM, Studdert DM, Maskiell JA, Macrae FA, St John DJ, et al. Is uptake of genetic testing for colorectal cancer influenced by knowledge of insurance implications? Med J Aust. 2009;191:255.
Tiller J, Otlowski M, Lacaze P. Should Australia ban the use of genetic test results in life insurance? Front Public Health. 2017;5:330.
Smit AK, Espinoza D, Newson AJ, Morton RL, Fenton G, Freeman L, et al. A pilot randomised controlled trial of the feasibility, acceptability and impact of giving information on personalised genomic risk of melanoma to the public. Cancer Epidemiol Prev Biomarkers. 2016;cebp.0395.2016.
Commonwealth of Australia. Life insurance industry. In: Committee PJ, Services oCaF, editors. Canberra 2018. https://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Joint/Corporations_and_Financial_Services/LifeInsurance/Report.
Newson AJ, Tiller J, Keogh LA, Otlowski M, Lacaze P. Genetics and insurance in Australia: concerns around a self-regulated industry. Public Health Genom. 2017;20:247–56.
Otlowski M, Taylor S, Bombard Y. Genetic discrimination: international perspectives. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 2012;13:433–54.
Barlow-Stewart K, Liepins M, Doble A, Otlowski M. How are genetic test results being used by Australian life insurers? Eur J Hum Genet 2018;26;1248–56.
Otlowski M, Taylor S, Barlowstewart K, Stranger M, Treloar S. The use of legal remedies in Australia for pursuing allegations of genetic discrimination: findings of an empirical study. Int J Discrim Law. 2007;9:3–35.
Tiller J, Keogh L, Wake S, Delatycki M, Otlowski MFA, Lacaze P. Genetics, insurance and professional practice: survey of the Australasian clinical genetics workforce. Front Public Health. 2018;6:333.
Zick CD, Smith KR, Mayer RN, Botkin JR. Genetic testing, adverse selection, and the demand for life insurance. Am J Med Genet. 2000;93:29–39.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Australian Genetic Non-Discrimination Working Group, the Human Genetics Society of Australasia, Australian Genomics, Genetic Support Network Victoria, Rare Cancers Australia, Rare Voices Australia and many others for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Tiller, J., Morris, S., Rice, T. et al. Genetic discrimination by Australian insurance companies: a survey of consumer experiences. Eur J Hum Genet 28, 108–113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0426-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-019-0426-1
This article is cited by
-
Direct notification by health professionals of relatives at-risk of genetic conditions (with patient consent): views of the Australian public
European Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Community concerns about genetic discrimination in life insurance persist in Australia: A survey of consumers offered genetic testing
European Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
Future implications of polygenic risk scores for life insurance underwriting
npj Genomic Medicine (2024)
-
Addressing the ethical and societal challenges posed by genome-wide association studies of behavioral and brain-related traits
Nature Neuroscience (2023)
-
Health professionals’ views and experiences of the Australian moratorium on genetic testing and life insurance: A qualitative study
European Journal of Human Genetics (2022)