Abstract
Background/Objectives
Whether to conduct early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics (EEN/probiotics) in stroke patients remains controversial. This study was aimed to systematically explore the efficacy and safety of EEN/probiotics in stroke patients.
Subject/Methods
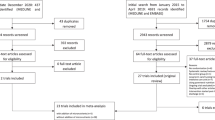
We performed searches in EMBASE, PubMed, Medline, Cochrane Library, Chinese Biomedicine Literature Database (SinoMed), Chinese Scientific Journal Database (VIP), Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Wanfang database.
Results
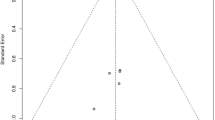
A total of 26 randomized controlled trials (2216 patients) were included. Meta-analysis showed a significantly lower incidence of gastrointestinal complications (%) (OR, 0.29; 95% CI,0.24–0.36; P < 0.00001), a lower incidence of infection (%) (OR, 0.27; 95% CI, 0.21–0.36; P < 0.00001), a shorter length of hospital stay (d) (MD, −8.70; 95% CI, −13.24 to −4.16; P = 0.003), and a lower dysbacteriosis rate (%) (OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.07–0.41; P < 0.0001) in the EEN/probiotics group than EEN group. Compared with EEN group, EEN/probiotics group had lower levels of diamine oxidase (U/L) (MD, −0.78; 95% CI, −0.93 to −0.63; P < 0.00001), D-lactic acid (mmol/L) (MD, −0.06; 95% CI, −0.07 to −0.05; P < 0.00001) and higher levels of albumin (g/L) (MD, 3.38; 95% CI, 2.74–4.02; P < 0.00001), prealbumin (mg/L) (MD, 32.20; 95% CI, 24.42–39.98; P < 0.00001), total protein (g/L) (MD, 4.91; 95% CI, 3.20–6.62; P < 0.00001), hemoglobin (g/L) (MD, 9.62; 95% CI, 7.92–11.32; P < 0.00001), immunoglobulin A (g/L) (MD, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.12–0.34; P < 0.0001) and immunoglobulin G (g/L) (MD, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.21–0.45; P < 0.00001).
Conclusion
Early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics may effectively improve the nutritional status of stroke patients, regulate the intestinal flora and intestinal mucosal barrier function, improve the immune function, reduce the incidence of infectious complications and gastrointestinal motility disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register: a preliminary report. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;54:541–53.
Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:182–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70031-5.
Kim BR, Lee J, Sohn MK, Kim DY, Lee SG, Shin YI, et al. Risk factors and functional impact of medical complications in stroke. Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41:753–60. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.5.753.
Xu CY, Ye HW, Chen B, Wu YF, Cao Z, Ding Z, et al. Analysis of risk factors and prognosis of post-stroke pulmonary infection in integrated ICU. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2021;25:856–65. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202101_24654.
Li X, Wang L, Zhao B, Mei D, Jiang J. Enteral nutrition bibliometry from 2010 to 2019. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2020;29:681–9. https://doi.org/10.6133/apjcn.202012_29(4).0002.
Sheng L, Yin L, Peng D, Zhao L. From best evidence to best practice: enteral nutrition from continuous nasal feeding in stroke patients. Int J Gen Med. 2020;13:927–36. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S269393.
Yuan MZ, Li F, Fang Q, Wang W, Peng JJ, Qin DY, et al. Research on the cause of death for severe stroke patients. J Clin Nurs. 2018;27:450–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.13954.
Mi H, Li S, Li H, Hu W. The effects of infection on severe stroke patients in the neurological intensive care unit in China. Int J Neurosci. 2018;128:715–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2017.1412966.
Lieber AC, Hong E, Putrino D, Nistal DA, Pan JS, Kellner CP. Nutrition, energy expenditure, dysphagia, and self-efficacy in stroke rehabilitation: a review of the literature. Brain Sci. 2018;8:218. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8120218.
Zhao D, Qin HL, Li N. [Integrated strategy based on microecological therapy in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;23:38–44. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn.441530-20200414-00205.
Cunningham M, Azcarate-Peril MA, Barnard A, Benoit V, Grimaldi R, Guyonnet D, et al. Shaping the future of probiotics and prebiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2021;S0966-842X:00005–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2021.01.003.
Du T, Jing X, Song S, Lu S, Xu L, Tong X, et al. Therapeutic effect of enteral nutrition supplemented with probiotics in the treatment of severe craniocerebral. Injury: A Syst Rev Meta-Anal World Neurosurg. 2020;139:e553–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.04.083.
Yi LJ, Tian X, Shi B, Pi YP, Chen WQ. Early enteral nutrition supplemented with probiotics improved the clinical outcomes in severe head injury: some promising findings from Chinese patients. Medicine. 2019;98:e15426. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000015426.
Gu WJ, Deng T, Gong YZ, Jing R, Liu JC. The effects of probiotics in early enteral nutrition on the outcomes of trauma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JPEN J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2013;37:310–7. https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607112463245.
Page MJ, Moher D. Evaluations of the uptake and impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) Statement and extensions: a scoping review. Syst Rev. 2017;6:263. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-017-0663-8.
Wang XD. Diagnosis points of various cerebrovascular diseases[J]. Chin J Neurol. 1996;029:379–80.
Higgins J. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1. The Cochrane Collaboration[J]. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie, 2008;5:S38.
Veroniki AA, Jackson D, Viechtbauer W, Bender R, Bowden J, Knapp G, et al. Methods to estimate the between-study variance and its uncertainty in meta-analysis. Res Synth. Methods. 2016;7:55–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1164.
Wang J, Ru R, Sun J, Mi XC, Dong ZH, Liu YF, et al. Effects of Enteral Nutrition Combined with Probiotics on Nutritional Status in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke After Neural Intervention Therapy[J]. J Chengdu Med Coll. 2021;16:29–32. CNKI:SUN:CDYU.0.2021-01-007.
Dong GH. Clinical effect of probiotics combined with enteral nutrition in the treatment of patients with severe stroke[J]. Chin Remedies Clin. 2020;20:1687–8. CNKI:SUN:YWLC.0.2020-10-052.
He XH, Li L, Ma XW. Effect of bifidobacterium combined with enteral nutrition on nutrition, immunity and intestinal flora in patients with severe stroke[J]. China Health Care Nutr. 2020;30:75.
Xie YM. Effect of early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics on nutritional status and gastrointestinal function of stroke patients with nasal feeding[J]. J North Pharm. 2020;17:44–45+52. CNKI:SUN:BFYX.0.2020-09-015.
Zhang L. Effect of early enteral nutrition combined with microecological preparation on patients with dysphagia after stroke and its effect on nutrition indexes[J]. Chin Foreign Med Res. 2020;18:170–2. https://doi.org/10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.14.070
Ban BX, Sun ZG, Jin J. Influence of Probiotics combined with Enteral Nutrition on Nutritional Status and Complications in Acute Stroke Pa-tients with Type 2 Diabetes[J]. J Med Theory Pract. 2019;32:3588–90. https://doi.org/10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2019.22.003.
Chen JQ. Effect of Bifidobacterium Tetravaccine tablets combined with enteral nutrition on gastrointestinal complications and intestinal mucosal barrier function in patients with severe stroke[J]. Med Forum. 2019;23:2397–8. https://doi.org/10.19435/j.1672-1721.2019.17.018.
Chen JY, Luo YY, Zhu ZP, Zhu BH, Fu P. Effects of early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics on intestinal flora and immune function in patients with severe ischemic stroke[J]. Chin J Integr Traditional West Med Intensive Crit Care. 2019;26:329–33. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2019.03.019.
Chen K. Application effect analysis of probiotics combined with early indwelling gastric tube nasogastric feeding enteral nutrition support in elderly patients with severe stroke[J]. Yiyao Qianyan. 2019;9:155–6. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1752.2019.02.122.
Huang J, Jiang ZL. Early enteral nutrition reconstructs intestinal microecology to promote the rehabilitation of ischemic stroke[J]. Mod Digestion Intervent. 2019;24:398–401. CNKI:SUN:XDXH.0.2019-04-018.
Jin X, Shi Y, Yuan B, Wang HL, Liu HY, Chen YJ, et al. The effect of early enteral nutrition supplemented with probiotics on ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with severe stroke[J]. Chin J Microecol. 2019;31:174–8. https://doi.org/10.13381/j.cnki.cjm.201902012.
Li JH, Li JY. Effect of Bifidobacterium Tetravaccine tablets combined with enteral nutrition on gastrointestinal complications and intestinal mucosal barrier function in patients with severe stroke[J]. J China Prescr Drug. 2019;17:125–6. CNKI:SUN:ZGCF.0.2019-09-075.
Zhang HB, Lu L, Tian YN, Li Y, Zheng Q. Effect of enteral nutrition support on acute cardiogenic stroke patients with swallowing dysfunction[J]. Chin J Microecol. 2019;31:90–93. https://doi.org/10.13381/j.cnki.cjm.201901020.
Gao SJ. Effect of early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics in patients with acute severe stroke[J]. China Med Eng. 2018;26:34–37. https://doi.org/10.19338/j.issn.1672-2019.2018.06.010.
Gao YX. The effect of early enteral nutrition combined with Clostridium caseinate Enterococcus triunion on improving intestinal flora and nutritional index in elderly stroke patients[J]. Chin J Geriatr Care. 2018;16:65–67. CNKI:SUN:LNBJ.0.2018-02-025.
Liao P. Effect of early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics on nutritional status and gastrointestinal function of stroke patients with nasal feeding[J]. Yiyao Qianyan. 2018;8:186–7. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1752.2018.28.165.
Sun HC, Zhang XG, Liu Z, Wang X, Zheng YL, Jin Y, et al. Effect of Bifidobacterium Tetravaccine Tablets on intestinal function in patients with severe stroke[J]. Chin J Microecol. 2018;30:1292–6. https://doi.org/10.13381/j.cnki.cjm.201811013.
Zhou Q. Effect of Bifid Triple Viable capsules combined with early enteral nutrition on nutritional status and complications in patients with severe stroke[J]. Diet Health. 2018;5:66–67. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-8439.2018.01.078.
Dong GH. Clinical effect of probiotics combined with enteral nutrition in the treatment of patients with severe stroke[J]. Jiankang Qianyan. 2017;26:123. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.9128-6509.2017.10.116.
Chen CC. Clinical effect of enteral nutrition with probiotics on stroke patients[J].Journal of BingTuan. Medicine. 2016;48:15–16. CNKI:SUN:BTYU.0.2016-02-006.
Chen DY, Chen J. Effect of Bifid Triple Viable capsules combined with early enteral nutrition on nutritional status and complications in patients with severe stroke[J]. J Brain Nerv Dis. 2016;24:79–81. CNKI:SUN:LYSJ.0.2016-02-004.
Hou JH. Influence of BifidobacteriumT etravaccine Tablets Combined with Enteral Nutrition on Complications of Digestive Canal and Intestinal Mucous Membrane Barrier Function of Patients with Severe Stroke[J]. Chin J Pharmacoepidemiol. 2016;25:11–13+42. CNKI:SUN:YWLX.0.2016-01-004.
Wang Y, Shi J, Gong LY. Effect of probiotics combined with early enteral nutrition on the incidence of pulmonary infection in patients with acute severe stroke[J]. China Health Industry Development Working Committee, China Medical Education Association. 2016:415–6. https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/conference/ChZDb25mZXJlbmNlTmV3UzIwMjEwNTIxEgc4Nzk0OTE5GghncmppMXk0OQ%3D%3D.
Wu LJ, Li JP, Guo BW. Additional bifidobacteria in severe stroke patients receiving enteral nutrition[J]. Parenter Enter Nutr. 2016;23:220–2. https://doi.org/10.16151/j.1007-810x.2016.04.007.
Hou JH, Zhuo JM, Zhong WG, Guan XB, Xia B. Effect of Bifidobacterium Tetravaccine tablets on nutritional status and immune indexes in patients with severe stroke[J]. Chin J Rural Med Pharm. 2016;23:6–7. https://doi.org/10.19542/j.cnki.1006-5180.2016.07.003.
Bai GY. Clinical research of probiotics enteral nutrition for the treatment of critically ill patients with cerebral apoplexy[D]. Xinjiang:Xinjiang Medical University, 2014. https://doi.org/10.7666/d.D601665.
Gomes F, Emery PW, Weekes CE. Risk of malnutrition is an independent predictor of mortality, length of hospital stay, and hospitalization costs in stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.2016;25:799–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.
Setyopranoto I, Lestari LA, Wijayanti PM, Rochmah MA. The effects of local food-based enteral nutrition to improve nutritional status of post-stroke patients. J Neurosci Rural Pract.2021;12:204–9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1721202.
English C, MacDonald-Wicks L, Patterson A, Attia J, Hankey GJ. The role of diet in secondary stroke prevention. Lancet Neurol.2021;20:150–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30433-6.
Bonsack B, Jiang RH, Borlongan CV. A gut feeling about stroke reveals gut-brain axis’ active role in homeostasis and dysbiosis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020;40:1132–4. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X19900037.
Sharifi-Rad J, Rodrigues CF, Stojanović-Radić Z, Dimitrijević M, Aleksić A, Neffe-Skocińska K, et al. Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health. Med (Kaunas). 2020;56:433. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina56090433.
Jiang J, Chu C, Wu C, Wang C, Zhang C, Li T, et al. Efficacy of probiotics in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review of preclinical trials and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0fo03203d.
Zhang XF, Guan XX, Tang YJ, Sun JF, Wang XK, Wang WD, et al. Clinical effects and gut microbiota changes of using probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-021-02503-5.
Biswasroy P, Pradhan D, Sahu DK, Sahu A, Ghosh G, Rath G. Recent advances in clinical utility of probiotics in gastrointestinal tract disorders. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 29 Oct 2020. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201021666201029154239. Epub ahead of print.
Patejdl R, Kästner M, Kolbaske S, Wittstock M. Clinical nutrition and gastrointestinal dysfunction in critically ill stroke patients. Neurol Res. 2017;39:959–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1367545.
Prame Kumar K, Wong CH. Imbalance in the force: the dark side of the microbiota on stroke risk and progression. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020;62:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.
Battaglini D, Pimentel-Coelho PM, Robba C, Dos Santos CC, Cruz FF, Pelosi P, et al. Gut microbiota in acute ischemic stroke: from pathophysiology to therapeutic implications. Front Neurol.2020;11:598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.00598.
Stanley D, Mason LJ, Mackin KE, Srikhanta YN, Lyras D, Prakash MD, et al. Translocation and dissemination of commensal bacteria in post-stroke infection. Nat Med.2016;22:1277–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4194.
Metin M, Altun A, Köylüoğlu G. The effect of probiotics on ıntestinal motility in an experimental short bowel model. Acta Cir Bras. 2020;35:e202000804. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-865020200080000004.
Xu H, Ma C, Zhao F, Chen P, Liu Y, Sun Z, et al. Adjunctive treatment with probiotics partially alleviates symptoms and reduces inflammation in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Nutr. 2021;60:2553–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-020-02437-4. Epub 22 Nov 2020.
Kambale RM, Nancy FI, Ngaboyeka GA, Kasengi JB, Bindels LB, Van der Linden D. Effects of probiotics and synbiotics on diarrhea in undernourished children: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2020;S0261-5614:30701–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.12.026.
Lehtoranta L, Latvala S, Lehtinen MJ. Role of probiotics in stimulating the immune system in viral respiratory tract infections: a narrative review. Nutrients. 2020;12:3163. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103163.
Tan AH, Lim SY, Chong KK, Manap A, Hor JW, Lim JL. Probiotics for constipation in Parkinson disease: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Neurology. 2021;96:e772–82. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000010998.
Zhao Y, Zeng Y, Zeng D, Wang H, Zhou M, Sun N, et al. Probiotics and MicroRNA: their roles in the host-microbe interactions. Front Microbiol. 2021;11:604462. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.604462.
Funding
This research was supported by a program of Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (No. 2021YFS0022). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: XC, YH. Data curation: XC, JY. Formal analysis: XC, XY. Project administration: KL. Resources: KL. Software: XC, YH. Supervision: KL, JY. Writing—original draft: XC, YH, XY. Writing—review and editing: KL, JY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics statement
The need for ethics approval was waived because this was a meta-analysis and involved no people or animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Hu, Y., Yuan, X. et al. Effect of early enteral nutrition combined with probiotics in patients with stroke: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 76, 592–603 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-021-00986-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-021-00986-3