Abstract
Background/objectives
This study was aimed to investigate the association of maternal serum and breast-milk levels of macronutrients, hormones, growth factors, and maternal body composition with infant’s body weight.
Subjects/methods
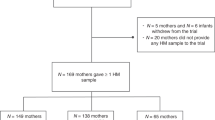
Eighty mother–infant pairs comprised 40 with overweight or obese infant and 40 with normal-weight infant were enrolled in this study. The level of ghrelin, Leptin, adiponectin, EGF, and IGF1 in plasma and breast milk were assessed. Daily breast milk intake and macronutrient concentration along with anthropometric indices of mother–infant pairs were also assessed.
Results
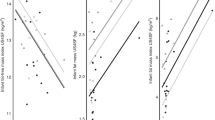
No significant differences were observed in concentrations of serum hormones between two groups (p > 0.05). However, hormones levels in maternal serum were higher than those in breast milk. A significant positive correlation was found between serum EGF and ghrelin (r = 0.57, p = 0 < 0001). Higher IGF1 in serum showed a significant association with its milk counterpart (r = 0.37). Current mother’s weight was associated with infant’s weight at the 2nd and 6th month (B = 0.023 p = 0.04, B = 0.055 p = 0.005). The breast-milk macronutrient content was not comparable between two groups. However, the average daily breast milk consumption in obese infants was higher than normals (p = 0.001). Milk EGF and leptin were related to a decrease of 59% and 46% the odds of obese infant development, respectively. There was a significant association of milk EGF and ghrelin with birth weight (B = −0.19, p = 0.04 and B = −0.2, p = 0.04, respectively), and also serum leptin with infant’s body weight at the 6th month.
Conclusions
Our findings provide a positive association of maternal weight, daily breast milk intake, EGF, and ghrelin with infant’s body weight.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Organization WH. Obesity and overweight: World Health Organization global strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Geneva: WHO; 2008.
Eilers E, Ziska T, Harder T, Plagemann A, Obladen M, Loui A. Leptin determination in colostrum and early human milk from mothers of preterm and term infants. Early Hum Dev. 2011;87(6):415–9.
Caballero B. The global epidemic of obesity: an overview. Epidemiol Rev. 2007;29(1):1–5.
Ravelli A, Van der Meulen J, Osmond C, Barker D, Bleker O. Infant feeding and adult glucose tolerance, lipid profile, blood pressure, and obesity. Arch Dis Child. 2000;82(3):248–52.
Victora CG, Adair L, Fall C, Hallal PC, Martorell R, Richter L, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: consequences for adult health and human capital. The lancet.. 2008;371(9609):340–57.
Lucas A. Long-term programming effects of early nutrition—implications for the preterm infant. Journal of Perinatology. 2005;25:S2–S6.
Hamosh M. Bioactive factors in human milk. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2001;48(1):69–86.
Andreas NJ, Hyde MJ, Gale C, Parkinson JR, Jeffries S, Holmes E, et al. Effect of maternal body mass index on hormones in breast milk: a systematic review. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(12):e115043.
Agostoni C. Ghrelin, leptin and the neurometabolic axis of breastfed and formula‐fed infants. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94(5):523–5.
Kobata R, Tsukahara H, Ohshima Y, Ohta N, Tokuriki S, Tamura S, et al. High levels of growth factors in human breast milk. Early Hum Dev. 2008;84(1):67–9.
Doneray H, Orbak Z, Yildiz L. The relationship between breast milk leptin and neonatal weight gain. Acta Paediatr. 2009;98(4):643–7.
Savino F, Liguori SA, Lupica MM. Adipokines in breast milk and preterm infants. Early Hum Dev. 2010;86(1):77–80.
Whitmore T, Trengove N, Graham D, Hartmann P. Analysis of insulin in human breast milk in mothers with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol. 2012;296368:1-9.
Donovan SM, Odle J. Growth factors in milk as mediators of infant development. Annu Rev Nutr. 1994;14(1):147–67.
Miralles O, Sánchez J, Palou A, Picó C. A physiological role of breast milk leptin in body weight control in developing infants. Obesity. 2006;14(8):1371–7.
Uysal F, Önal E, Aral Y, Adam B, Dilmen U, Ardicolu Y. Breast milk leptin: its relationship to maternal and infant adiposity. Clin Nutr. 2002;21(2):157–60.
Savino F, Lupica M, Benetti S, Petrucci E, Liguori S, Cordero Di Montezemolo L. Adiponectin in breast milk: relation to serum adiponectin concentration in lactating mothers and their infants. Acta Paediatr. 2012;101(10):1058–62.
Khodabakhshi A, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Rooki H, Vakili R, Hashemy S, Mirhafez S, et al. Comparative measurement of ghrelin, leptin, adiponectin, EGF and IGF-1 in breast milk of mothers with overweight/obese and normal-weight infants. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2015;69(5):614–8.
Shilina N, Gmoshinskaia M, Ivanushkina T. [Breast hormones—regulators of energy homeostasis: growth of infants]. Vopr Pitan. 2010;80(4):73–8.
Kierson JA, Dimatteo DM, Locke RG, MacKley AB, Spear ML. Ghrelin and cholecystokinin in term and preterm human breast milk. Acta Paediatr. 2006;95(8):991–5.
Wong W-M, Wright NA. Epidermal growth factor, epidermal growth factor receptors, intestinal growth, and adaptation. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 1999;23(5 suppl):S83–S8.
Burrin DG, Stoll B. Key nutrients and growth factors for the neonatal gastrointestinal tract. Clin Perinatol. 2002;29(1):65–96.
Pietrzkowski Z, Sell C, Lammers R, Ullrich A, Baserga R. Roles of insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and the IGF-1 receptor in epidermal growth factor-stimulated growth of 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12(9):3883–9.
Playford RJ, Macdonald CE, Johnson WS. Colostrum and milk-derived peptide growth factors for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(1):5–14.
Dimaraki EV, Jaffe CA. Role of endogenous ghrelin in growth hormone secretion, appetite regulation and metabolism. Rev Endocr Metab Dis. 2006;7(4):237–49.
Ong KK, Ahmed ML, Emmett PM, Preece MA, Dunger DB. Association between postnatal catch-up growth and obesity in childhood: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2000;320(7240):967–71.
Martin LJ, Woo JG, Geraghty SR, Altaye M, Davidson BS, Banach W, et al. Adiponectin is present in human milk and is associated with maternal factors. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83(5):1106–11.
Aydin S, Aydin S, Ozkan Y, Kumru S. Ghrelin is present in human colostrum, transitional and mature milk. Peptides. 2006;27(4):878–82.
Walczak M, Kędzia A. Active synthesis of epidermal growth factor in human mammary glands. Acta Sci Polon Technol Aliment. 2010;9(2):237–41.
Pan W, Kastin AJ. Diurnal variation of leptin entry from blood to brain involving partial saturation of the transport system. Life Sci. 2001;68(24):2705–14.
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, Morris DG, McGee P, Fairclough P, et al. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(6):2988.
Cesur G, Ozguner F, Yilmaz N, Dundar B. The relationship between ghrelin and adiponectin levels in breast milk and infant serum and growth of infants during early postnatal life. J Physiol Sci. 2012;62(3):185–90.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the mothers and their infants who took part in the study. This work was supported by Research Project No. 89962, as a MSc dissertation, financed by Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. None of the authors had a conflict of interest with respect to this article.
Author's contributions
The author’s contribution were as follows: AK and MS conceived and designed the research; AK performed the experiments; HMM, AK and FV analyzed the data, interpreted the results, prepared and drafted the manuscript; HMM and MS edited and revised the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodabakhshi, A., Mehrad-Majd, H., Vahid, F. et al. Association of maternal breast milk and serum levels of macronutrients, hormones, and maternal body composition with infant’s body weight. Eur J Clin Nutr 72, 394–400 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-017-0022-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-017-0022-9