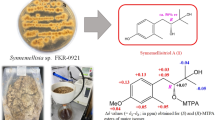
Abstract
Two new berkeley meroterpenoids (1 and 2), along with seven known compounds (3‒9) were isolated from a fungus, Penicillium sp. SSW03M2 GY derived from a sediment at Seosan bay, South Korea. Chemical structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated on the basis of 1D, 2D NMR, HRESIMS, and optical rotation. All the isolated compounds, 1 showed anti-virulence activity by significantly inhibiting α-toxin (Hla) secreted by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus without its growth inhibition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geris R, Simpson TJ. Meroterpenoids produced by fungi. Nat Prod Rep. 2009;26:1063–94.
Zhao M, Tang Y, Xie J, Zhao Z, Cui H. Meroterpenoids produced by fungi: Occurrence, structural diversity, biological activities, and their molecular targets. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;209:112860.
Stierle DB, Stierle AA, Patacini B, McIntyre K, Girtsman T, Bolstad E. Berkeleyones and related meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste fungus that inhibit the production of interleukin 1-β from induced inflammasomes. J Nat Prod. 2011;74:2273–7.
Huang ZH, Liang X, Li CJ, Gu Q, Ma X, Qi SH. Talaromynoids A–I, highly oxygenated meroterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus SCSIO 41517 and their lipid accumulation inhibitory activities. J Nat Prod. 2021;84:2727–37.
Long Y, Cui H, Liu X, Xiao Z, Wen S, She Z, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory meroterpenoid from a mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. 16-5c. Molecules. 2017;22:727.
Sun J, Zhu ZX, Song YL, Dong D, Zheng J, Liu T, et al. Nitric oxide inhibitory meroterpenoids from the fungus Penicillium purpurogenum MHZ 111. J Nat Prod. 2016;79:1415–22.
Santos RM, Rodrigues-Filho E. Structures of meroterpenes produced by Penicillium sp, an endophytic fungus found associated with Melia azedarach. J Braz Chem Soc. 2003;14:722–7.
de Silva ED, Williams DE, Jayanetti DR, Centko RM, Patrick BO, Wijesundera RL, et al. Dhilirolides A−D, meroterpenoids produced in culture by the fruit-infecting fungus Penicillium purpurogenum collected in Sri Lanka. Org Lett. 2011;13:1174–7.
Arunpanichlert J, Rukachaisirikul V, Phongpaichit S, Supaphon O, Sakayaroj J. Meroterpenoid, isocoumarin, and phenol derivatives from the seagrass-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. PSU-ES194. Tetrahedron. 2015;71:882–8.
Fleitas Martínez O, Cardoso MH, Ribeiro SM, Franco OL. Recent advances in anti-virulence therapeutic strategies with a focus on dismantling bacterial membrane microdomains, toxin neutralization, quorum-sensing interference and biofilm inhibition. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019;9:74.
Johnson BK, Abramovitch RB. Small molecules that sabotage bacterial virulence. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38:339–62.
Ford CA, Hurford IM, Cassat JE. Antivirulence strategies for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections: a mini review. Front Microbiol. 2021;11:632706.
Berube BJ, Bubeck Wardenburg J. Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin: nearly a century of intrigue. Toxins. 2013;5:1140–66.
Li J, Yang X, Lin Y, Yuan J, Lu Y, Zhu X, et al. Meroterpenes and azaphilones from marine mangrove endophytic fungus Penicillium 303. Fitoterapia. 2014;97:241–6.
Stierle DB, Stierle AA, Hobbs JD, Stokken J, Clardy J. Berkeleydione and berkeleytrione, new bioactive metabolites from an acid mine organism. Org Lett. 2004;6:1049–52.
Iida M, Ooi T, Kito K, Yoshida S, Kanoh K, Shizuri Y, et al. Three new polyketide–terpenoid hybrids from Penicillium sp. Org Lett. 2008;10:845–8.
Gu BB, Wu W, Liu LY, Tang J, Zeng YJ, Wang SP, et al. 3, 5‐Dimethylorsellinic acid derived meroterpenoids from Eupenicillium sp. 6A‐9, a fungus isolated from the marine sponge Plakortis simplex. Eur J Org Chem. 2018;2018:48–59.
Stierle DB, Stierle AA, Patacini B. The berkeleyacetals, three meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste Penicillium. J Nat Prod. 2007;70:1820–3.
Qi B, Liu X, Mo T, Zhu Z, Li J, Wang J, et al. 3, 5-Dimethylorsellinic acid derived meroterpenoids from Penicillium chrysogenum MT-12, an endophytic fungus isolated from Huperzia serrata. J Nat Prod. 2017;80:2699–707.
Fill TP, Pereira GK, dos Santos RM, Rodrigues-Fo E. Four additional meroterpenes produced by Penicillium sp. found in association with Melia azedarach. Possible biosynthetic intermediates to austin. Z Naturforsch B. 2007;62:1035–44.
Stephens PJ, Harada N. ECD cotton effect approximated by the Gaussian curve and other methods. Chirality. 2010;22:229–33.
Bonesso MF, Yeh AJ, Villaruz AE, Joo HS, McCausland J, Fortaleza CM, Cavalcante RS, Sobrinho MT, Ronchi CF, Cheung GY, Cunha ML, Otto M. Key role of α-toxin in fatal pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 398. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193:217–20.
Matsuda Y, Abe I. Biosynthesis of fungal meroterpenoids. Nat Prod Rep. 2016;33:26–53.
Zhang T, Wan J, Zhan Z, Bai J, Liu B, Hu Y. Activation of an unconventional meroterpenoid gene cluster in Neosartorya glabra leads to the production of new berkeleyacetals. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018;8:478–87.
Kim DR, Lee Y, Kim HK, Kim W, Kim YG, Yang YH, et al. Phenol-Soluble Modulin-Mediated Aggregation of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid. Cells. 2020;9:788.
Joo HS, Otto M. The isolation and analysis of phenol-soluble modulins of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1106:93–100.
Piewngam P, Zheng Y, Nguyen TH, Dickey SW, Joo HS, Villaruz AE, et al. Pathogen elimination by probiotic Bacillus via signalling interference. Nature. 2018;562:532–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (NRF-2021R1A2C1004958 and NRF-2022R1A4A3022401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ku, H., Lee, Y., Lee, S. et al. New meroterpenoids from a soil-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SSW03M2 GY and their anti-virulence activity. J Antibiot 76, 57–64 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00587-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00587-7