Abstract
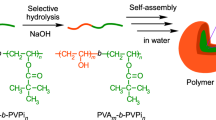
Cationic block copolymers containing a quaternized pyridinium salt and hydrophobic acrylates were prepared, and their fundamental properties as ink dispersants were evaluated. Block copolymers containing methyl acrylate (MA), ethyl acrylate (EA), or butyl acrylate (BA) as hydrophobic segments successfully dispersed dye particles in aqueous media; however, polymers containing octyl acrylate (OA), hexyl acrylate (HA), cyclohexyl acrylate (CyHA), or phenoxyethyl acrylate (PhEA) did not exhibit good dispersibility. Color dispersions containing block copolymers consisting of 4-vinylpyridine (4VP) and BA (poly(BA-b-4VP)) exhibited the lowest viscosity among all polymers examined and maintained a stable dye dispersion. The results of this study suggest that the hydrophobic/hydrophilic balance, flexibility of the polymer chain, and degree of molecular interaction between the dye and hydrophobic segment of the polymer chain should be carefully examined and optimized for better performance. This study demonstrates the application potential of quaternized pyridinium cations in the field of dispersants and surfactants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates CM, Bates FS. 50th anniversary perspective: Block polymers-pure potential. Macromolecules. 2017;50:3–22.
Fetsch C, Gaitzsch J, Messager L, Battaglia G, Luxenhofer R. Self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolypeptoids—micelles, worms and polymersomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33491.
Wu D, Huang Y, Xu F, Mai Y, Yan D. Recent advances in the solution self-assembly of amphiphilic “rod-coil” copolymers. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem. 2017;55:1459–77.
Nsib F, Ayed N, Chevalier Y. Selection of dispersants for the dispersion of C.I. pigment violet 23 in organic medium. Dye Pigment. 2007;74:133–40.
Costa JRC, Correia C, Góis JR, Silva SMC, Antunes FE, Moniz J, et al. Efficient dispersion of TiO2 using tailor made poly(acrylic acid)—based block copolymers, and its incorporation in water based paint formulation. Prog Org Coat. 2017;104:34–42.
Kim B, Jeong J, Mohanty AK, Lee T, Han S, Heo J, et al. Quaternized poly (poly(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate)-b-poly (2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) as block copolymers by sequential monomer addition: Dispersion of copper phthalocyanine. React Funct Polym. 2017;120:147–52.
Li J, Fan J, Cao R, Zhang Z, Du J, Peng X. Encapsulated dye/polymer nanoparticles prepared via miniemulsion polymerization for inkjet printing. ACS Omega. 2018;3:7380–7.
Singh M, Haverinen HM, Dhagat P, Jabbour GE. Inkjet printing-process and its applications. Adv Mater. 2010;22:673–85.
Man Y, Li X, Li S, Yang Z, Lee YI, Liu HG. Effects of hydrophobic/hydrophilic blocks ratio on PS-b-PAA self-assembly in solutions, in emulsions, and at the interfaces. Colloids Surf A. 2019;580:123684.
Iborra A, Díaz G, López D, Giussi JM, Azzaroni O. Copolymer based on lauryl methacrylate and poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate as amphiphilic macrosurfactant: Synthesis, characterization and their application as dispersing agent for carbon nanotubes. Eur Polym J. 2017;87:308–17.
Dange C, Phan TNT, André V, Rieger J, Persello J, Foissy A. Adsorption mechanism and dispersion efficiency of three anionic additives [poly(acrylic acid), poly(styrene sulfonate) and HEDP] on zinc oxide. J Coll Inter Sci. 2007;315:107–15.
Stankovich S, Piner RD, Chen X, Wu N, Nguyen ST, Ruoff RS. Stable aqueous dispersions of graphitic nanoplatelets via the reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide in the presence of poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate). J Mater Chem. 2006;16:155–8.
Shukla S, Bhattacharjee S, Weber AZ, Secanell M. Experimental and theoretical analysis of ink dispersion stability for polymer electrolyte fuel cell applications. J Electrochem Soc. 2017;164:F600–9.
Bhavsar RA, Nehete KM. Rheological approach to select most suitable associative thickener for water-based polymer dispersions and paints. J Coat Technol Res. 2019;16:1089–98.
Benchabane A, Bekkour K. Rheological properties of carboxymethyl cellulose (cmc) solutions. Colloid Polym Sci. 2008;286:1173–80.
Kennemur JG. Poly(vinylpyridine) segments in block copolymers: synthesis, self-assembly, and versatility. Macromolecules. 2019;52:1354–70.
Briones OX, Tapia RA, Campodónico PR, Urzúa M, Leiva Á, Contreras R, et al. Synthesis and characterization of poly (ionic liquid) derivatives of N-alkyl quaternized poly(4-vinylpyridine). React Funct Polym. 2018;124:64–71.
Samantaray PK, Madras G, Bose S. Antibacterial and antibiofouling polymeric membranes through immobilization of pyridine derivative leading to ROS generation and loss in bacterial membrane integrity. ChemistrySelect. 2017;2:7965–74.
Harjani JR, Singer RD, Garcia MT, Scammells PJ. Biodegradable pyridinium ionic liquids: design, synthesis and evaluation. Green Chem. 2009;11:83–90.
Jeong JW, Park WI, Kim MJ, Ross CA, Jung YS. Highly tunable self-assembled nanostructures from a poly(2-vinylpyridine- b -dimethylsiloxane) block copolymer. Nano Lett. 2011;11:4095–101.
Shahruzzaman M, Takafuji M, Ihara H. Tuning of separation mode using pyridinium salt-branched ionic polymer-grafted silica as stationary phase in HPLC. Chem Lett. 2015;45:13–5.
Wang Z, Liao S, Wang Y. Supramolecular polymer emulsifiers for one-step complex emulsions. Chin J Polym Sci. 2018;36:288–96.
Huang X, Yang Y, Shi J, Ngo HT, Shen C, Du W, et al. High-internal-phase emulsion tailoring polymer amphiphilicity towards an efficient NIR-sensitive bacteria filter. Small. 2015;11:4876–83.
Miao H, Wang Y, Dong H, Chen D. Complexation induced by weak interaction between DNA and PEO-b-P4VP below the cmc of the polymer. Chin J Polym Sci. 2017;35:46–53.
Badila M, Brochon C, Hébraud A, Hadziioannou G. Encapsulation of TiO2 in poly(4-vinyl pyridine)-based cationic microparticles for electrophoretic inks. Polymer. 2008;49:4529–33.
Křenek R, Cimrová V, Stamm M. Incorporation of dyes into polystyrene- block -poly(4-vinylpyridine) nanotemplates. Macromol Symp. 2008;268:86–90.
Duivenvoorde FL, Jansen K, Laven J, Linde R. Use of poly(2-vinylpyridine)-b-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) copolymers as pigment stabilizers in powder coatings. J Coat Technol. 2002;74:49–57.
Shi Z, Zhang X, Yu Z, Yang F, Liu H, Xue R, et al. Facile synthesis of imidazolium-based block copolypeptides with excellent antimicrobial activity. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22:2373–81.
Pirrung FOH, Quednau PH, Auschra C. Wetting and dispersing agents. Chimia. 2002;56:170–6.
Farrokhpay S, Morris GE, Fornasiero D, Self P. Influence of polymer functional group architecture on titania pigment dispersion. Colloids Surf A. 2005;253:183–91.
Spinelli HJ. Polymeric dispersants in ink jet technology. Adv Mater. 1998;10:1215–8.
Steiert N, Landfester K. Encapsulation of organic pigment particles via miniemulsion polymerization. Macromol Mater Eng. 2007;292:1111–25.
Fu SH, Fang KJ. Preparation of styrene-maleic acid copolymers and its application in encapsulated pigment red 122 dispersion. J Appl Polym Sci. 2007;105:317–21.
Nakamura M, Ikeda Y, Oguchi H, Yano T, Naito S Ink Set. U.S. Patent 9,718,978 B2 (August 1, 2017), assigned to Seiko Epson Corporation.
Danilovtseva EN, Zelinskiy SN, Pal’shin VA, Kandasamy G, Krishnan UM, Annenkov VV. Poly(1-vinylimidazole) prospects in gene delivery. Chin J Polym Sci. 2019;37:637–45.
Liu S, Sun YL, Chen CL, Xu H, Lei K, Lang MD. Preparation and properties of 4-vinylpyridine zwitterionic copolymer resin. J Funct Polym. 2018;31:553–60.
French RA, Jacobson AR, Kim B, Isley SL, Penn RL, Baveye PC. Influence of ionic strength, pH, and cation valence on aggregation kinetics of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43:1354–9.
Sharma R, Mahajan S, Mahajan RK. Surface adsorption and mixed micelle formation of surface active ionic liquid in cationic surfactants: conductivity, surface tension, fluorescence and NMR studies. Colloids Surf A. 2013;427:62–75.
Huibers PDT, Lobanov VS, Katritzky AR, Shah DO, Karelson M. Prediction of critical micelle concentration using a quantitative structure−property relationship approach. 1. Nonion Surfact Langmuir. 1996;12:1462–70.
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Kim HJ, Tilton RD, Lowry GV. Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J Nanopart Res. 2008;10:795–814.
Sehgal A, Lalatonne Y, Berret JF, Morvan M. Precipitation−redispersion of cerium oxide nanoparticles with poly(acrylic acid): toward stable dispersions. Langmuir 2005;21:9359–64.
Lu G, Duan YY, Wang XD. Surface tension, viscosity, and rheology of water-based nanofluids: a microscopic interpretation on the molecular level. J Nanopart Res. 2014;16:2564.
Yang Y, Cai Z, Huang Z, Tang X, Zhang X. Antimicrobial cationic polymers:from structural design to functional control. Polym J. 2018;50:33–44.
Lam SJ, Wong EHH, Boyer C, Qiao GG. Antimicrobial polymeric nanoparticles. Prog Polym Sci. 2018;76:40–64.
Acknowledgements
The author (TO) thanks Kana Ohira (Seiko Epson), and Chikako Fujita (Seiko Epson) for the GPC measurements and NMR measurements, respectively. The authors also thank Koichi Terao (Seiko Epson) and Hiroshi Kiguchi (Seiko Epson) for helpful discussions and encouragement, respectively. The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) and American Journal Experts (www.aje.com) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TO and HI designed and performed the experiments and analyzed the results. All the authors discussed the experimental results and commented on the manuscript. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtake, T., Ito, H. & Toyoda, N. Amphiphilic block copolymer surfactant-containing quaternized pyridinium salt segments for color dispersion. Polym J 54, 1203–1211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00673-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00673-5