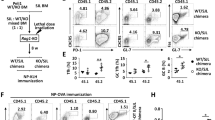
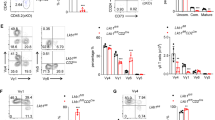
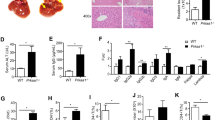
Abstract
The specification of the αβ/γδ lineage and the maturation of medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) coordinate central tolerance to self-antigens. However, the mechanisms underlying this biological process remain poorly clarified. Here, we report that dual-stage loss of TOX in thymocytes hierarchically impaired mTEC maturation, promoted thymic IL-17A-producing γδ T-cell (Tγδ17) lineage commitment, and led to the development of fatal autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) via different mechanisms. Transfer of γδ T cells from TOX-deficient mice reproduced AIH. TOX interacted with and stabilized the TCF1 protein to maintain the balance of γδ T-cell development in thymic progenitors, and overexpression of TCF1 normalized αβ/γδ lineage specification and activation. In addition, TOX expression was downregulated in γδ T cells from AIH patients and was inversely correlated with the AIH diagnostic score. Our findings suggest multifaceted roles of TOX in autoimmune control involving mTEC and Tγδ17 development and provide a potential diagnostic marker for AIH.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, Czaja AJ, Manns MP, Krawitt EL, Vierling JM, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2018;4:18017.
Chascsa DM, Ferre EMN, Hadjiyannis Y, Alao H, Natarajan M, Quinones M, et al. APECED-associated hepatitis: clinical, biochemical, histological and treatment data from a large, predominantly American cohort. Hepatology. 2021;73:1088–104.
Takahama Y, Ohigashi I, Baik S, Anderson G. Generation of diversity in thymic epithelial cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17:295–305.
Paolino M, Koglgruber R, Cronin SJF, Uribesalgo I, Rauscher E, Harreiter J, et al. RANK links thymic regulatory T cells to fetal loss and gestational diabetes in pregnancy. Nature. 2021;589:442–7.
Fujikado N, Mann AO, Bansal K, Romito KR, Ferre EMN, Rosenzweig SD, et al. Aire inhibits the generation of a perinatal population of interleukin-17A-producing gammadelta T cells to promote immunologic tolerance. Immunity. 2016;45:999–1012.
Khan O, Giles JR, McDonald S, Manne S, Ngiow SF, Patel KP, et al. TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Nature. 2019;571:211–8.
Wang X, He Q, Shen H, Xia A, Tian W, Yu W, et al. TOX promotes the exhaustion of antitumor CD8(+) T cells by preventing PD1 degradation in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2019;71:731–41.
Aliahmad P, Kaye J. Development of all CD4 T lineages requires nuclear factor TOX. J Exp Med. 2008;205:245–56.
Page N, Klimek B, De Roo M, Steinbach K, Soldati H, Lemeille S, et al. Expression of the DNA-binding factor TOX promotes the encephalitogenic potential of microbe-induced autoreactive CD8(+) T cells. Immunity. 2018;48:937–50.e8.
Papotto PH, Ribot JC, Silva-Santos B. IL-17(+) gammadelta T cells as kick-starters of inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:604–11.
McGinley AM, Sutton CE, Edwards SC, Leane CM, DeCourcey J, Teijeiro A, et al. Interleukin-17A serves a priming role in autoimmunity by recruiting IL-1beta-producing myeloid cells that promote pathogenic T cells. Immunity. 2020;52:342–56.e6.
Agerholm R, Bekiaris V. Evolved to protect, designed to destroy: IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells in infection, inflammation, and cancer. Eur J Immunol. 2021;51:2164–77.
Papotto PH, Reinhardt A, Prinz I, Silva-Santos B. Innately versatile: gammadelta17 T cells in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 2018;87:26–37.
Colpitts SL, Puddington L, Lefrancois L. IL-15 receptor alpha signaling constrains the development of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2015;112:9692–7.
Munoz-Ruiz M, Ribot JC, Grosso AR, Goncalves-Sousa N, Pamplona A, Pennington DJ, et al. TCR signal strength controls thymic differentiation of discrete proinflammatory gammadelta T cell subsets. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:721–7.
Kadekar D, Agerholm R, Rizk J, Neubauer HA, Suske T, Maurer B, et al. The neonatal microenvironment programs innate gammadelta T cells through the transcription factor STAT5. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:2496–508.
Zuberbuehler MK, Parker ME, Wheaton JD, Espinosa JR, Salzler HR, Park E, et al. The transcription factor c-Maf is essential for the commitment of IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:73–85.
Malhotra N, Narayan K, Cho OH, Sylvia KE, Yin C, Melichar H, et al. A network of high-mobility group box transcription factors programs innate interleukin-17 production. Immunity. 2013;38:681–93.
Spidale NA, Sylvia K, Narayan K, Miu B, Frascoli M, Melichar HJ, et al. Interleukin-17-producing gammadelta T cells originate from SOX13(+) progenitors that are independent of gammadeltaTCR signaling. Immunity. 2018;49:857–72.e5.
Hu Y, Fang K, Wang Y, Lu N, Sun H, Zhang C. Single-cell analysis reveals the origins and intrahepatic development of liver-resident IFN-gamma-producing gammadelta T cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:954–68.
Li F, Hao X, Chen Y, Bai L, Gao X, Lian Z, et al. The microbiota maintain homeostasis of liver-resident gammadeltaT-17 cells in a lipid antigen/CD1d-dependent manner. Nat Commun. 2017;7:13839.
Wang X, Tian Z. gammadelta T cells in liver diseases. Front Med. 2018;12:262–8.
Nishio K, Miyagi T, Tatsumi T, Mukai K, Yokoyama Y, Yoshioka T, et al. Invariant natural killer T cell deficiency leads to the development of spontaneous liver inflammation dependent on gammadeltaT cells in mice. J Gastroenterol. 2015;50:1124–33.
Seo W, Eun HS, Kim SY, Yi HS, Lee YS, Park SH, et al. Exosome-mediated activation of toll-like receptor 3 in stellate cells stimulates interleukin-17 production by gammadelta T cells in liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2016;64:616–31.
Ma S, Cheng Q, Cai Y, Gong H, Wu Y, Yu X, et al. IL-17A produced by gammadelta T cells promotes tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014;74:1969–82.
Zheng M, Li D, Zhao Z, Shytikov D, Xu Q, Jin X, et al. Protein phosphatase 2A has an essential role in promoting thymocyte survival during selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2019;116:12422–7.
Zhang W, Zhangyuan G, Wang F, Jin K, Shen H, Zhang L, et al. The zinc finger protein Miz1 suppresses liver tumorigenesis by restricting hepatocyte-driven macrophage activation and inflammation. Immunity. 2021;54:1168–85.e8.
Danzl NM, Donlin LT, Alexandropoulos K. Regulation of medullary thymic epithelial cell differentiation and function by the signaling protein Sin. J Exp Med. 2010;207:999–1013.
Morimoto J, Nishikawa Y, Kakimoto T, Furutani K, Kihara N, Matsumoto M, et al. Aire controls in trans the production of medullary thymic epithelial cells expressing Ly-6C/Ly-6G. J Immunol. 2018;201:3244–57.
Chen Y, Kwon SW, Kim SC, Zhao Y. Integrated approach for manual evaluation of peptides identified by searching protein sequence databases with tandem mass spectra. J Proteome Res. 2005;4:998–1005.
Kernfeld EM, Genga RMJ, Neherin K, Magaletta ME, Xu P, Maehr R. A single-cell transcriptomic atlas of thymus organogenesis resolves cell types and developmental maturation. Immunity. 2018;48:1258–70.e6.
Carow B, Gao Y, Coquet J, Reilly M, Rottenberg ME. lck-driven Cre expression alters T cell development in the thymus and the frequencies and functions of peripheral T cell subsets. J Immunol. 2016;197:2261–8.
Fiala GJ, Schaffer AM, Merches K, Morath A, Swann J, Herr LA, et al. Proximal Lck promoter-driven Cre function is limited in neonatal and ineffective in adult gammadelta T cell development. J Immunol. 2019;203:569–79.
Lai JC, Wlodarska M, Liu DJ, Abraham N, Johnson P. CD45 regulates migration, proliferation, and progression of double negative 1 thymocytes. J Immunol. 2010;185:2059–70.
Kadekar D, Agerholm R, Vinals MT, Rizk J, Bekiaris V. The immune checkpoint receptor associated phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2 are not required for gammadeltaT17 cell development, activation, or skin inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2020;50:873–9.
Heilig JS, Tonegawa S. Diversity of murine gamma genes and expression in fetal and adult T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986;322:836–40.
Irla M, Hugues S, Gill J, Nitta T, Hikosaka Y, Williams IR, et al. Autoantigen-specific interactions with CD4+ thymocytes control mature medullary thymic epithelial cell cellularity. Immunity. 2008;29:451–63.
Shi J, Hou S, Fang Q, Liu X, Liu X, Qi H. PD-1 controls follicular T helper cell positioning and function. Immunity. 2018;49:264–74.e4.
Karnell JL, Rieder SA, Ettinger R, Kolbeck R. Targeting the CD40-CD40L pathway in autoimmune diseases: humoral immunity and beyond. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;141:92–103.
Horner AA, Jabara H, Ramesh N, Geha RS. gamma/delta T lymphocytes express CD40 ligand and induce isotype switching in B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1995;181:1239–44.
Steinke FC, Yu S, Zhou X, He B, Yang W, Zhou B, et al. TCF-1 and LEF-1 act upstream of Th-POK to promote the CD4(+) T cell fate and interact with Runx3 to silence Cd4 in CD8(+) T cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:646–56.
Renand A, Cervera-Marzal I, Gil L, Dong C, Garcia A, Kervagoret E, et al. Integrative molecular profiling of autoreactive CD4 T cells in autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 2020;73:1379–90.
Rozman P, Svajger U. The tolerogenic role of IFN-gamma. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;41:40–53.
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1123–32.
Markle JG, Mortin-Toth S, Wong AS, Geng L, Hayday A, Danska JS. gammadelta T cells are essential effectors of type 1 diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse model. J Immunol. 2013;190:5392–401.
Ujiie H, Shevach EM. gammadelta T cells protect the liver and lungs of mice from autoimmunity induced by scurfy lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2016;196:1517–28.
Martins EB, Graham AK, Chapman RW, Fleming KA. Elevation of gamma delta T lymphocytes in peripheral blood and livers of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and other autoimmune liver diseases. Hepatology. 1996;23:988–93.
Hammerich L, Bangen JM, Govaere O, Zimmermann HW, Gassler N, Huss S, et al. Chemokine receptor CCR6-dependent accumulation of gammadelta T cells in injured liver restricts hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology. 2014;59:630–42.
Kim E, Um H, Park J, Jung JW, Kim JE, Lee H, et al. TM4SF5-dependent crosstalk between hepatocytes and macrophages to reprogram the inflammatory environment. Cell Rep. 2021;37:110018.
Rezende RM, Lanser AJ, Rubino S, Kuhn C, Skillin N, Moreira TG, et al. gammadelta T cells control humoral immune response by inducing T follicular helper cell differentiation. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3151.
Aliahmad P, Kadavallore A, de la Torre B, Kappes D, Kaye J. TOX is required for development of the CD4 T cell lineage gene program. J Immunol. 2011;187:5931–40.
Scott AC, Dundar F, Zumbo P, Chandran SS, Klebanoff CA, Shakiba M, et al. TOX is a critical regulator of tumour-specific T cell differentiation. Nature. 2019;571:270–4.
Rossi SW, Kim MY, Leibbrandt A, Parnell SM, Jenkinson WE, Glanville SH, et al. RANK signals from CD4(+)3(−) inducer cells regulate development of Aire-expressing epithelial cells in the thymic medulla. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1267–72.
Roberts NA, White AJ, Jenkinson WE, Turchinovich G, Nakamura K, Withers DR, et al. Rank signaling links the development of invariant gammadelta T cell progenitors and Aire(+) medullary epithelium. Immunity. 2012;36:427–37.
Melichar HJ, Narayan K, Der SD, Hiraoka Y, Gardiol N, Jeannet G, et al. Regulation of gammadelta versus alphabeta T lymphocyte differentiation by the transcription factor SOX13. Science. 2007;315:230–3.
Mielke LA, Liao Y, Clemens EB, Firth MA, Duckworth B, Huang Q, et al. TCF-1 limits the formation of Tc17 cells via repression of the MAF-RORgammat axis. J Exp Med. 2019;216:1682–99.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the State Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation (81930086 and 82120108012 to BS, 82073157 and 81600487 to WT), the Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province (BE2018603 to BS), and the Postgraduate Innovative Research Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX20_0047 to QH). BS is a Yangtze River scholars Distinguished Professor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QH, YLu, WT, RJ, and BS designed the experiments. QH, YLu, WT, RJ, WY, YLiu, MS, FW, HZ, and NW performed the experiments, provided reagents, and/or analyzed the data. QH, YLu, WT, and ZD discussed and interpreted the data. QH and BS wrote and revised the paper. BS conceived, supervised, and revised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., Lu, Y., Tian, W. et al. TOX deficiency facilitates the differentiation of IL-17A-producing γδ T cells to drive autoimmune hepatitis. Cell Mol Immunol 19, 1102–1116 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-022-00912-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-022-00912-y
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lkb1 orchestrates γδ T-cell metabolic and functional fitness to control IL-17-mediated autoimmune hepatitis
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2024)