Abstract
Ferroptosis is a recently defined form of regulated cell death, which is biochemically and morphologically distinct from traditional forms of programmed cell death such as apoptosis or necrosis. It is driven by iron, reactive oxygen species, and phospholipids that are oxidatively damaged, ultimately resulting in mitochondrial damage and breakdown of membrane integrity. Numerous cellular signaling pathways and molecules are involved in the regulation of ferroptosis, including enzymes that control the cellular redox status. Alterations in the ferroptosis-regulating network can contribute to the development of various diseases, including cancer. Evidence suggests that ferroptosis is commonly suppressed in cancer cells, allowing them to survive and progress. However, cancer cells which are resistant to common chemotherapeutic drugs seem to be highly susceptible to ferroptosis inducers, highlighting the great potential of pharmacologic modulation of ferroptosis for cancer treatment. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are considered master regulators of various cellular processes, particularly in cancer where they have been implicated in all hallmarks of cancer. Recent work also demonstrated their involvement in the molecular control of ferroptosis. Hence, ncRNA-based therapeutics represent an exciting alternative to modulate ferroptosis for cancer therapy. This review summarizes the ncRNAs implicated in the regulation of ferroptosis in cancer and highlights their underlying molecular mechanisms in the light of potential therapeutic applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Facts
-
Ferroptosis is a unique, iron-dependent, oxidative form of regulated cell death.
-
Ferroptosis is frequently suppressed in cancer supporting its growth and progression.
-
Ferroptotic rich regulatory network is essentially modulated by ncRNAs.
-
NcRNA-based therapeutics targeting ferroptosis is a promising novel anti-cancer therapy.
Open questions
-
What is the relationship between ncRNAs, ferroptosis and other forms of regulated cell death in cancer?
-
Are individual ncRNAs potential molecular markers of ferroptosis that could be used in living cells and tissues?
-
What are the optimal delivery systems of novel ncRNAs-therapeutics, particularly for efficient intracellular uptake and controlled release?
-
Would potential combination of available drugs with novel ncRNA-therapeutics modulating ferroptosis result in an improved cancer treatment?
Introduction
Non-coding RNAs: master regulators of cellular processes
Non-coding RNAs (NcRNAs) are a miscellaneous group of non-coding transcripts with limited protein-coding potential that perform important cellular functions through different molecular mechanisms [1]. Initially, it was thought that they are functionally irrelevant. However, as a myriad of functional ncRNAs were identified and characterized, the central dogma of proteins being the functional end product of gene expression has drastically changed [2].
Broadly spoken, they can either be subdivided into short and long ncRNAs (a general cut off value is 200 nucleotides in length), or subdivided due to their biological roles [3]. Three major classes of functional ncRNAs are short microRNAs (miRNAs), long ncRNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs). Depending on their intrinsic features, they may show tissue- and/or disease-specificity and may be detected in all body fluids making them interesting for their potential utilization as biomarkers [4]. In addition, ncRNAs are frequently deregulated in various diseases, including cancer [5]. In many instances their involvement in drug resistance in cancers has been reported [6,7,8,9]. Thus, targeting of ncRNAs might be a promising therapeutic option to modulate drug resistance-promoting pathways in cancer cells and improve the outcome of patients [10].
Ferroptosis: the molecular mechanisms of a recently identified form of cell death
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, oxidative form of cell death that is biochemically and morphologically different from other types of regulated cell death [11,12,13]. Ferroptosis is caused by excessive oxidative destruction (peroxidation) of lipids in the cellular membranes. The process relies on iron, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) [14,15,16].
Lipid peroxidation occurs when a bisallylic hydrogen atom, located between two carbon–carbon double bonds, is removed from the PUFAs in the membrane phospholipids. The result is formation of a carbon-centered phospholipid radical, phospholipid peroxyl radical, and phospholipid peroxides, a form of lipid ROS. Phospholipid peroxides can react with iron to generate free alkoxyl and peroxyl radicals [17]. The requirement of iron in this form of cell death inspired the term ferroptosis [12]. If not converted to its corresponding alcohol, phospholipid peroxides, together with phospholipid free radicals, promote further phospholipid peroxide formation via the processes of hydrogen removal and reaction with oxygen. It is the unrestrained lipid peroxidation that is considered to be the hallmark of ferroptosis [18].
Some first hints of ferroptosis-like death have been observed in the middle of 20-th century in studies investigating metabolism and neuronal cell death. The earliest reports attributed ferroptosis either to other forms of regulated cell death, or it was not recognized as being biologically significant. It was not interpreted as sufficient evidence for a distinct cell death until early 2000s when the Stockwell lab conducted screening of lethal compounds in RAS-transformed cancer cells. They identified erastin and RAS synthetic lethal 3 (RSL3) as inducers of non-apoptotic, iron-dependent cell death preventable by iron chelators and lipophilic antioxidants [19, 20]. The following findings, including the mechanism of action of erastin and RSL3, lead to the idea of a unique regulated cell death form. The term ferroptosis was introduced in 2012, and, thus, the field of ferroptosis research is rather officially young [12]. Despite being frequently cited as a new type of cell death, ferroptosis may actually be considered the oldest and evolutionary most conserved form of regulated cell death owing to its simple molecular requirements of iron and oxygen. In fact, ferroptosis-like death has been observed in less-complex species including protozoa, prokaryotes, fungi and plants [21,22,23,24].
Ferroptosis initiation and regulation
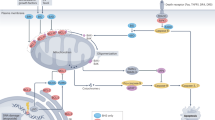
Lipid peroxidation can be initiated by non-enzymatic and enzymatic processes [25]. The non-enzymatic process is triggered by Fenton reaction, where iron and hydrogen peroxide react toward free radical formation and propagation of lipid peroxidation [15]. Numerous enzymes were implicated in the regulation of ferroptosis and are outlined in Fig. 1. Some of the key enzymes are described below.
Ferroptosis can be initiated by non-enzymatic and enzymatic processes. The non-enzymatic process includes Fenton reaction, where iron and hydrogen peroxide react and form free radicals. Various enzymes and proteins drive ferroptosis via increasing iron availability and enhancing free radical formation (CYP450, HO-1, HIFs), and performing important roles in biosynthesis and oxidation of PUFAs (ACSL4, LPCAT3, ALOX). In contrast, ferroptosis is suppressed by several enzymes and cofactors with antioxidant functions (GPX4, GSH, FSP1, CoQ10, BH4) and system xc- cystine/glutamate antiporter (SLC7A11 and SLC3A2) that import cystine which is necessary for the biosynthesis of antioxidant enzymes. Consequences of ferroptosis are various harmful breakdown products (e.g., MDA and 4-HNE), modified and oxidized proteins (e.g., reparatory ESCRT-III), damaged mitochondria and eventual disruption of membrane integrity. MDA, malondialdehyde; 4-HNE, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; TfR1, transferrin receptor 1; PUFAs-OOH, polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxides; ROS, reactive oxygen species; PROM2, prominin 2; system xc-, cystine/glutamate antiporter; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC3A2, solute carrier family 3 member 2; ESCRT-III, endosomal sorting complexes required for transport-III; Fe, ferrum (iron); ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; ALOX, lipoxygenase; CYP450, cytochrome P450; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; FTH1, ferritin heavy chain 1; FTL, ferritin light chain; NRF2, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; IREB2, iron-responsive element binding protein 2; HIFs, hypoxia-inducible factors; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1. Created with BioRender.
Ferroptosis antagonists
Glutathione peroxidases (GPXs) protect cells from oxidative stress, and hence ferroptosis [14,15,16]. In fact, GPX4 is the main enzyme catalyzing the reduction of phospholipid peroxides to its corresponding phospholipid alcohol. This selenoprotein is regulated by a number of ncRNAs including miR-101-3p, miR-324-3p, lncPVT1, circCDK14, circKDM4C, and circDTL [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. In addition, cofactor of GPX4 is glutathione, an antioxidant that uses cysteine for its synthesis [14,15,16]. In addition to the intracellular synthesis from methionine and glucose, and the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through intermediate cystathionine (transsulfuration pathway), cysteine can be imported from the environment [15]. The oxidized form (cystine) is imported by the system xc- cystine/glutamate antiporter (see also Fig. 1). Subunits of this transmembrane protein complex are solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) and solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2) [33]. Numerous ncRNAs regulate the expression of SLC7A11, including miR-375, miR-214-3p, miR-5096, LINC00618, P53RRA, OIP5-AS1, circPVT1, circEPSTI1 [34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41].
Cyst(e)ine-GSH-GPX4-system xc- is considered as the main antagonist of ferroptosis. Ferroptotic death via inhibition of system xc- and GPX4 can be induced by the compounds erastin and RSL3 [19, 20]. While RSL3 impairs GPX4 activity directly, erastin inhibits cystine import into the cell and thereby indirectly affects GPX4 activity. Erastin additionally targets voltage-dependent ion channels inducing mitochondrial dysfunction [19, 20]. RSL3 and erastin are frequently used in experimental approaches to induce ferroptosis.
Several other opposing mechanisms of ferroptosis have been described. Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) reduces lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis by reducing the oxidized form of coenzyme Q10, ubiquinone, to yield ubiquinol, which then reduces lipid radicals and prevents propagation of lipid peroxidation [42]. Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) protects phospholipids from oxidative degradation by acting as an antioxidant and aids ubiquinone synthesis [43]. In addition, FSP1 may also indirectly reduce lipid peroxidation via regeneration of vitamin E, another strong antioxidant of lipids [44]. There is evidence that vitamin E (and possibly selenium) supplementation may promote cancer development [45]. FSP1 is indirectly upregulated by miR-4443, and several transcription factors including nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NRF2) [46, 47]. NRF2 is an important transcription activator that regulates various genes involved in metabolism, inflammation, mitochondrial respiratory, proliferative and transport processes [48]. In particular, NRF2 is crucial for cell survival during the oxidative stress. In addition to FSP1, it promotes the expression of several other negative regulators of ferroptosis, such as ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1), SLC7A11, and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) (Fig. 1) [49,50,51]. Radical-trapping antioxidants ferrostatin 1 and liproxstatin 1 are useful in experimental studies to suppress ferroptosis [52].
Ferroptosis agonists
Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) and lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) are essential drivers of ferroptosis (Fig. 1) [53]. ACSL4 is the important enzyme in lipogenesis. It catalyzes the reaction between long-chain PUFAs with coenzyme A to produce long-chain fatty acyl-CoA esters. These products are re-esterified into phospholipids by LPCAT3 enzyme, thus enhancing the incorporation of long-chain PUFAs into lipids and membranes [53]. MiR-23a-3p, miR-424-5p, and NEAT1 post-transcriptionally suppress, while circKDM4C upregulates expression of ACSL4 [32, 54,55,56]. Furthermore, reports suggest that certain arachidonate lipoxygenases (ALOXs) may contribute to ferroptosis via stereotactic insertion of oxygen in PUFAs [15], while lipoxygenase inhibitors act as radical-trapping antioxidants (Fig. 1) [15, 57, 58]. MiR-7-5p and miR-522 are known repressors of ALOX12 and ALOX15, respectively [59, 60]. Interestingly, Pseudomonas aeruginosa secretes lipoxygenases that can induce oxidation of membrane lipids of human red blood cells and induce ferroptosis in bronchial epithelial cells, a finding particularly important for cystic fibrosis patients who are susceptible to this bacterium [21, 22].
In addition, cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase may initiate lipid peroxidation by reducing ferric iron (Fe3+) to ferrous iron (Fe2+), a reaction that is crucial for the Fenton reaction and lipid peroxidation (Fig. 1) [61]. Although phospholipid peroxides may interact with both forms of iron, ferrous iron is likely to be more important since ferric iron has poor solubility and bioavailability in cells [14].
Consequences of ferroptosis
Some of the main end products of this process are two omega-6 fatty acids, toxic 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) and mutagenic malondialdehyde (MDA) (Fig. 1) [62]. Consequences of ferroptosis include formation of various secondary lipid peroxide breakdown products, modification and oxidation of proteins, and eventual breakdown of membrane integrity. Morphologically, ferroptotic cells have small mitochondria with increased mitochondrial membrane densities, reduced or vanishing mitochondrial cristae, and rupture of the outer mitochondrial membrane [52]. In addition, ferroptotic death may induce cell membrane rupture, release of intracellular content such as damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), inducing sterile inflammation and can therefore be classified as a form of regulated necrosis [15]. Membrane repair is dependent on endosomal sorting complexes required for transport-III (ESCRT)-III (Fig. 1). This protein complex, consisting of 12 subunits, assembles into the spiral filament and mediates membrane remodeling [63].
Ferroptosis, metabolic and cellular signaling pathways
The regulation of ferroptosis is strongly connected to various essential cellular processes, including metabolic pathways (iron, lipids, amino acids, and glucose metabolism), mitochondrial activity, maintenance of redox status, or response to radiation exposure. Furthermore, several key mediators of cell signaling pathways have been implicated in the regulation of ferroptosis, including multiple oncogenic and tumor-suppressive proteins (e.g., p53) [14, 16].
Iron metabolism plays a central role in ferroptosis. For example, transferrin and its receptor import iron into the cells and promote ferroptosis [64]. In contrast, mechanisms that export cellular iron have been shown to reduce ferroptosis [65, 66]. Autophagic degradation of major iron-storage protein ferritin promotes ferroptosis due to increased iron availability (Fig. 1). This process is named ferritinophagy [67]. Other types of autophagy, such as lipophagy, clockophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy may also contribute to induction of ferroptosis via degradation of negative regulators of ferroptosis [68,69,70]. Indeed, there is growing evidence asserting the interaction between ferroptotic and autophagic machinery [71]. For example, lipid peroxidation products (i.e., 4-HNE) may induce autophagosome formation [72]. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), a source of intracellular iron, is found to promote macroautophagy [73]. Erastin also promotes chaperone-mediated autophagy via upregulation of lysosome-associated membrane protein 2a (LAMP-2A), that may also degrade GPX4 [74]. In contrast, overexpression of GPX4 has been shown to inhibit ROS-mediated autophagy [75].
The activity of several metabolic pathways can affect the generation of ROS and are therefore strongly associated with the induction of ferroptosis. For example, glutamine can replenish tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle through the generation of α-ketoglutarate [64]. High glutamine uptake and metabolism can result in increased TCA cycle activity and increased rate of mitochondrial respiration, leading to ROS formation and loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential. High extracellular concentration of glutamate impedes system xc- function due to inhibition of cystine uptake, and eventual intracellular glutathione synthesis, therefore leading to the ferroptosis induction [12]. Hypoxia promotes ferroptosis by increasing ROS production which can directly contribute to lipid peroxidation and activation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) [14]. HIFs have been shown to drive ferroptosis in clear cell renal carcinoma [76]. Even though glucose starvation increases ROS generation, it actually suppresses ferroptosis through the activation of energy sensor AMP activated kinase (AMPK). Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase which blocks the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA and thus synthesis of PUFAs [77, 78]. In contrast, the core regulator of autophagosome formation Beclin-1 (BECN1) promotes ferroptosis by inhibiting system xc- activity in energy-sufficient AMPK-mediated manner [79].
Tumor suppressor proteins may sensitize cells to ferroptosis. P53, an important regulator of apoptosis and autophagy, enhances ferroptosis and prevents tumor development via suppressing the transcription of system xc- component SLC7A11 [80]. In addition, BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) also promotes ferroptosis by SLC7A11 downregulation [81]. Involvement of oncogenes in ferroptosis is best illustrated through the initial discovery of stronger lethality of erastin and RSL3 in RAS-mutated cancer cells, suggesting determining role of RAS-RAF-MEK pathway in ferroptosis [82].
Furthermore, ionizing radiation has been shown to upregulate ACSL4 expression in cancer leading to increased lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis [83]. Clearly, many more regulators of ferroptosis are yet to be discovered and characterized. As mentioned, and exemplified earlier in text, ncRNAs as versatile master regulators of cellular processes have also recently been linked to the regulation of ferroptosis (Fig. 2). The following sections will systematically summarize the current knowledge on the involvement ncRNAs in regulation of ferroptosis and their role in cancer.
NcRNAs regulate ferroptosis via modulation of its key players at mRNA and protein levels. Ferroptosis agonists (ASCL4, LPCAT3, ALOX, CYP450) and ferroptosis antagonists (GPX4, SLC7A11, SLC3A2, FSP1) can be sponged and inhibited by overexpressed lncRNAs (pathways 1 and 2), circRNAs (pathways 3 and 4), and miRNAs (pathway 5) thus regulating the ferroptosis activity. Created with BioRender.
The role of miRNAs in the regulation of ferroptosis in cancer
MiRNAs are a class of small evolutionarily conserved ncRNAs with a length of approximately 22 nucleotides. Their main function is post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression through binding to complementary target mRNA sequences, leading to translational inhibition or mRNA degradation. The final result is halted protein synthesis [84, 85]. In addition, it has been reported that miRNAs may also induce gene expression by binding to target sequence and act as translational activator [86]. While they were completely unknown less than three decades ago, nowadays it has been estimated that miRNAs control the expression of over 60% of all protein-coding genes [87]. Given their substantial regulatory capacity, it seems obvious that deregulation of this tightly controlled miRNA network is frequently linked to cardiovascular, autoimmune, infectious, and neurodegenerative diseases [84]. In fact, they are increasingly recognized as major mediators of disease. The first link between miRNA and human cancer was reported in 2002 by Calin and colleagues [88]. Since then, thousands of miRNAs have been discovered, their deregulation in virtually every type of cancer has been confirmed, and their involvement in all hallmarks of cancer has been revealed [89]. Their regulatory roles in ferroptosis in cancer are not well understood yet, but there is strong evidence that miRNAs are also involved in this crucial process in cancer cells (Fig. 2). Some prominent examples are outlined below and a broader overview is provided in Table 1.
Ferroptosis-stimulating miRNAs
MiR-214-3p promotes ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by downregulating the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) [35]. ATF4 is induced by stress signals and prevents ferroptosis through the induction of SLC7A11 [90]. In addition, ATF4 regulates the expression of genes involved in differentiation, metastasis and angiogenesis [91]. In gliomas, ATF4 promotes tumor angiogenesis which can be diminished in vitro with ferroptosis inducers [92].
In lung cancer, miR-101-3p is found to be downregulated [26]. When available, this miRNA targets oncogenic transducin beta-like 1X-linked (TBLR1) protein. Low expression of miR-101-3p and high expression of TBLR1 result in enhanced activity of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), which regulates ferroptosis through GPX4 and prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2). Interestingly, appealing results on tumor growth reduction were observed in in vivo experiments when miR-101-3p was delivered in the form of nanoparticles [26].
Moreover, miR-324-3p is significantly downregulated in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cell lines when compared to healthy cells. When overexpressed, miR-324-3p induces ferroptosis by targeting GPX4, and enhances cisplatin sensitivity [27]. This miRNA is additionally upregulated by metformin in breast cancer cell lines, and in vivo experiments lead to GPX4 downregulation and ferroptosis induction [28].
Ferroptosis-inhibitory miRNAs
It has been shown in melanoma cells that miR-137 inhibits lipid peroxidation and iron accumulation in vitro and in vivo by directly targeting solute carrier family 1 member 5 (SLC1A5) [93]. SLC1A5, a non-member of system xc-, is a neutral amino acid transporter of alanine, serine, cysteine, and glutamine [94]. As a consequence, reduced levels of this important glutamine transporter lead to decreased glutamine uptake, glutaminolysis, and MDA accumulation [93]. Under physiological conditions, glutamine uptake and its metabolism induce lipid ROS generation and ferroptotic cell death [64]. In addition, miR-137 is associated with TNM stage, metastasis and drug resistance in various cancers through different pathways [95,96,97,98].
In addition, miR-7-5p is highly expressed in radioresistant cell lines of ovarian, oral squamous cell and HCC. miR-7-5p downregulates mitoferrin, a protein responsible for transporting iron into mitochondria. Ferroptosis is diminished as a result of reduced iron levels [99]. This miRNA is also upregulated in radioresistant cervical cancer [59]. The observed radio-resistance in cervical and oral squamous carcinoma cell lines is, at least partly, due to miR-7-5p effect on ferroptosis. Knockdown of miR-7-5p is shown to increase ROS levels, mitochondrial membrane potential, intracellular Fe2+ content, as well as downregulation of the iron storage protein ferritin, and upregulation ALOX12 expression [59].
MiR-4443 is upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) where it contributes to cisplatin resistance [46]. In addition, this miRNA may be transferred to the sensitive cells via exosomes and make them resistant. Mechanistically, miR-4443 inhibits ferroptosis via regulation of FSP1 expression in an N6-methyladenosine (m6A) manner by directly targeting its gene METLL3 [46].
MiRNAs have extremely diverse regulatory roles. In addition to direct regulation of ferroptotic key players, as outlined in the above section, miRNAs may indirectly regulate this cell death process via interaction with other ncRNAs, as illustrated in the following sections.
The role of lncRNAs in the regulation of ferroptosis in cancer
LncRNAs are a class of heterogeneous ncRNAs that are more than 200 nucleotides in length. They share many features with mRNA regarding transcriptional and post-transcriptional processing [100]. Despite being classified as ncRNA, the relevance of the protein-coding potential of lncRNA is growing [101]. Nevertheless, current evidence infers that lncRNAs mainly regulate cellular processes through the interaction with various other molecules, such as DNA, RNA, and proteins [102, 103]. Having a much broader interactome than miRNAs, lncRNAs can also control chromatin structure, methylation status, sequestration of miRNAs, assembly or disruption of protein complexes, and post-translational modifications [100, 103]. Another feature of lncRNAs is their tissue- and condition-specific (e.g., cancer-specific) expression pattern [100]. The first lncRNAs, H19 and Xist, were discovered in 1980s and 1990s, but they remained exceptions until the early 2000s when characterization of ncRNAs started to outpace protein-coding genes [104]. Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in all hallmarks of cancers, including sustained angiogenesis and deregulated cellular metabolism [105, 106]. In addition, mounting evidence suggest their importance in ferroptosis regulation, as outlined below (Fig. 2).
Ferroptosis-stimulating lncRNAs
Tumor suppressive lncRNA P53RRA, also known as LINC00472, is downregulated in various cancers including lung, liver, colon, renal and breast cancers [107,108,109,110,111]. In lung cancer, it interacts with Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 (G3BP1) in the cytosol [38]. This cytosolic P53RRA–G3BP1 interaction displaces p53 from the G3BP1 complex. In turn, p53 is retained in the nucleus, leading to cell-cycle arrest, apoptosis, and ferroptosis. P53RRA promotes ferroptosis and apoptosis by affecting transcription of several metabolic genes, including the downregulation of SCL7A11. Additionally, P53RRA increases erastin-induced ferroptosis, lipid ROS and iron concentrations [38].
Furthermore, lncRNA GA binding protein transcription factor beta subunit 1 antisense RNA 1 (GABPB1-AS1) is upregulated by erastin in HCC cells. It inhibits the translation of GA binding protein transcription factor subunit beta 1 (GABPB1) protein, which acts as an activation subunit of transcription activator nuclear respiration factor 2, also called GA-binding protein (GABP). Downregulated GABPB1 protein leads to the downregulation of peroxiredoxin-5 peroxidase (PRDX5). The resulting suppression of the cellular antioxidant capacity causes accumulation of ROS and MDA, and reduction in cell viability [112].
Metallothionein 1D pseudogene (MT1DP) is a lncRNA that regulates erastin-induced ferroptosis through NRF2 [113]. Ectopic MT1DP expression in NSCLC upregulates ROS and MDA levels, increases intracellular ferrous iron concentration, and reduces glutathione levels in cancer cells exposed to erastin. These effects are achieved through downregulation of NRF2, indirectly via stabilization of miR-365a-3p that normally targets NRF2 mRNA. Interestingly, Gai and colleagues designed folate-modified liposome nanoparticles to enhance the bioavailability and the efficiency of the targeted delivery of both erastin and MT1DP. In vivo mice studies have shown promising results for erastin-induced ferroptosis through this particular pathway in NSCLC [113].
Ferroptosis-inhibitory lncRNAs
LINC00336 is a nuclear lncRNA with oncogenic functions in lung cancer, including the regulation of ferroptosis [114]. It interacts with RNA-binding protein ELAV-like RNA-binding protein 1 (ELAVL1), which stabilizes the LINC00336 via binding adenylate and uridylate (AU)-rich elements (AREs), the signal regions that determine RNA stability. In addition, it is indirectly upregulated through the p53 signaling pathway since LSH increases ELAVL1 expression. When upregulated, LINC00336 acts as an endogenous sponge of miR-6852, thus preventing miRNA-induced downregulation of CBS. The result is inhibited ferroptosis in lung cancer cells, leading to enhanced cell proliferation, colony formation, and tumor formation. LINC00336 has been shown to decrease iron concentration, lipid ROS, and mitochondrial superoxide, and increases mitochondrial membrane potential [114].
Zhang et al. investigated the effects of chronic cadmium exposure - one of the causative factors of prostate cancer - on cellular growth and ferroptosis resistance in vitro and in vivo. After the cadmium exposure, the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins (particularly GPX4, FTH1 and SLC7A11) was increased, suggesting that cadmium exposure confers ferroptosis resistance. These effects were preceded by upregulation of lncRNA OIP5-AS1 expression. OIP5-AS1 acts as an endogenous sponge of miR-128-3p to regulate the expression of SLC7A11 [39].
Nuclear enriched transcript 1 (NEAT1) is a well-known oncogenic perinuclear lncRNA that has significant roles in non-cancerous diseases as well [115, 116]. It is associated with several hallmarks of cancers including proliferation, cell cycle, invasion, migration and apoptosis [117]. Wu et al. found that NEAT1 is capable of binding to ACSL4 mRNA, thus reducing the expression level of this pro-ferroptotic enzyme in NSCLC [56]. While NEAT1 contributes to apoptosis, its role in ferroptosis in NSCLC seems to be independent from it. Also, its contribution to ferroptosis is mediated exclusively via ACSL4 as erastin induction does not significantly affect other ferroptotic players, such as SLC7A11, GPX4, and TfR1 levels [56].
Table 2 provides additional lncRNAs involved in ferroptosis regulation in cancer.
Ferroptosis-related lncRNAs in the prediction of therapy responses and outcomes
In addition to the above-mentioned lncRNAs with confirmed regulatory mechanisms, RNAseq investigations associated many other lncRNAs with ferroptosis. For example, signatures consisting of eight to twelve differentially expressed lncRNAs were shown to be independent prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) in breast cancer [118, 119]. In the study from Zhang et al., patients with high-risk score had worse prognosis when treated with endocrine therapy, anthracycline, cyclophosphamide or paclitaxel, but not anti-HER2 therapy. In general, their tumors were immunologically cold due to inactivation of immune-related pathways and reduced tumor’s immune cells infiltration [119]. Similarly, Yao et al. correlated seven ferroptosis-related lncRNAs with clinical prediction of prognosis and immunotherapeutic responses in LUAD [120]. In the same fashion, Jian et al. developed ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature for glioma consisting of 15 lncRNAs. They also showed that patients in high-risk group had lower tumor purity, higher infiltration of immunosuppressive cells, and higher expression of immune checkpoints. In addition, those patients had no survival benefits of radiotherapy, compared to the low-risk group [121].
In the first study investigating the roles of ferroptosis-associated lncRNAs in the prognosis of head and neck cancer (HNSCC), a total of 25 differently expressed lncRNAs were found to be independent prognosis factors for OS [122]. It was revealed that those novel ferroptosis-related lncRNAs in HNSCC may regulate immune and tumor-related pathways, particularly the expression of PD-1, CTLA4, LAG3, and BTLA [122]. Hence, combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with ferroptosis inducers may synergistically reduce cancer growth [123]. There is limited ongoing research that explores the relationship between immune checkpoints, radiotherapy and ferroptosis. Therefore, lncRNAs implicated in these processes should be investigated further. Nevertheless, all above-mentioned signature profiles need further validation using different cohorts and complete molecular characterization before having a potential of being used as biomarkers or targets for novel medications.
The role of circRNAs in the regulation of ferroptosis in cancer
CircRNAs are single-stranded, covalently closed ncRNA molecules with distinct characteristics from other ncRNAs [124]. Their existence was first reported several decades ago. Initially, it was believed that they are merely splicing-associated noise that arises from irregular splicing and represents procedural errors. Therefore, their biological relevance was initially underappreciated [125].
Generally being classified as non-coding molecules, it has been found that some circRNAs have AUG sites and may be abundantly associated with polysomes [125, 126]. Similar to lncRNAs, circRNAs seem to be highly conserved and exhibit tissue-specific expression [127, 128]. Fairly contrary to the linear miRNAs and lncRNAs, circRNAs are exceptionally stable thanks to their circular nature, leaving them without free ends to be degraded by exonucleases. Due to their increased stability, circRNAs can be found in exosomes and extracellular fluids, such as saliva and plasma. Therefore, they have great biomarker potential [129].
While some circRNAs (e.g., intron-containing circRNAs) are found only in the nucleus where they might play a role in transcription regulation, most circRNAs are located in the cytoplasm [125]. There they usually function as miRNA sponges. Individual circRNAs can bind to multiple miRNAs that regulate different pathways [124, 125]. This feature is of particular importance for the potential therapeutic purposes. Importantly, miRNA-circRNA interactions might not always result in miRNA suppression, but also vice versa. Therefore, circRNAs may also function as miRNAs transportation or reservoir agents [124, 130]. However, growing caution stands for the alteration of miRNAs’ activity via sequestration by other ncRNAs (e.g., circRNAs and lncRNAs), the phenomenon called competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) hypothesis [131]. Recent findings alert that physiological and even pathological changes in individual ceRNA expression are usually insufficient in significant miRNA activity suppression [132,133,134]. This limitation is based on the fact that individual ceRNA constitute only a small fraction of miRNAs’ large target pool. Moreover, mathematical models assert that optimal ceRNA inhibition occurs when miRNA and targets are at near equimolar concentrations [135,136,137]. Many previously published studies have used supraphysiologic concentrations of transfected oligonucleotides or expression vectors that frequently exceed total cellular concentrations of their natural counterparts. This clearly suggests an overestimation of ceRNA activity and demand for better molecular models. Lastly, ceRNA as the appealing and straightforward approach in ncRNA studying may potentially hinder researchers’ consideration of other confirmed ncRNAs’ mechanisms of action. Nevertheless, circRNAs are important regulators of numerous normal and pathological cellular processes and diseases, including cancer [138]. So far, circRNAs have been associated with several hallmarks of cancers, including sustained proliferative signaling, evasion of growth suppressors, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis, and evading cell death and senescence [124, 138]. Growing evidence associate them with ferroptosis (Fig. 2).
Ferroptosis-stimulating circRNAs
Three circRNAs capable of ferroptosis induction are cIARS, circKDM4C and circ_0000190. cIARS is derived from the IARS gene, and it is found to be highly expressed in HCC after sorafenib treatment. Liu et al. found that it promotes ferroptosis after sorafenib treatment through, at least partially, activation of autophagy and ferritinophagy. This circRNA physically interacts with RNA binding protein AlkB Homolog 5 (ALKBH5) [139]. ALKBH5 is known for the improvement of Bcl-2 mRNA stability by catalyzing m6A demethylation, thus enhancing Bcl-2/BECN1 interactions. It is also known as autophagy inhibitor in cancer [140]. Sorafenib administration increases cIARS–ALKBH5 interaction, which is probably due to sorafenib-induced expression of cIARS as this kinase inhibitor has no influence on the ALKBH5 protein levels. Consequently, cIARS represses negative role of ALKBH5 in autophagy leading to enhanced autophagy, ferritinophagy and ferroptosis [139]. Up to date, cIARS is the only circRNA that regulates ferroptosis via interaction with a formed protein.
Further, circKDM4C is downregulated in AML. Normally, it sponges miRNA let-7b-5p which targets p53. In addition to indirect upregulation of p53, circKDM4C, when not retrieved from the circRNA pool, is capable of ferroptosis induction via increasing cellular iron content, upregulation of ACSL4 and PTGS2, and downregulation of GPX4 and FTH1 [32].
Ferroptosis-inhibitory circRNAs
Xian et al. found that circular ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 10 (circABCB10) is upregulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) where it acts as a sponge to miR-326. Consequently, its target C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) is overexpressed and contributes to carcinogenic effects, including inhibition of apoptosis and ferroptosis [141]. CCL5 has already been associated with CRC development and progression [142]. However, its exact mechanism in ferroptosis is still not reported.
Furthermore, circEPSTI1 is upregulated in cervical cancer contributing to enhanced cellular proliferation. Mechanistically, circEPSTI1 is capable of sponging three miRNAs, namely miR-375, miR-409-3p and miR-515-5p. All three of those miRNAs normally target SLC7A11, that acts as a ferroptosis inhibitor [41]. Other circRNAs that upregulate SLC7A11 are circ0097009 (sponges miR-1261 in HCC) [143], circ_0067934 (sponges miR-545-3p in thyroid cancer) [144], circCDK14 (sponges miR-3938 in glioma) [30], and circPVT1 (sponges miR-30a-5p in esophageal cancer) [40].
Moreover, GPX4 is, as mentioned above, considered to be pivotal regulator of ferroptosis, analogous to bcl-2 in apoptosis [145]. CircKIF4A, upregulated in papillary thyroid cancer, acts as a sponge of miR-1231, leading to GPX4 overexpression [146].
Table 3 provides an overview of additional circRNAs involved in ferroptosis regulation in cancer.
Ferroptosis and ncRNAs interplay: therapeutic potential in cancer
Remarkably, this form of cell death has been associated with numerous pathologic processes including neurodegeneration, liver and lung fibrosis, ischemia-reperfusion injuries in brain, heart, kidneys and organ transplantation [14, 16]. Nevertheless, there is major evidence of its particular relevance in cancer. It has been shown that mesenchymal and dedifferentiated cancer cells, which are resistant to cancer therapeutics and apoptosis, are highly susceptible to ferroptosis inducers [147, 148]. Hence, inducing ferroptotic cell death (e.g., by pharmacologic manipulation) may help to overcome resistance of malignant cells to chemotherapy and therefore has great potential for cancer treatment. Several strategies to specifically induce ferroptosis are already being tested. One option is to target key enzymes involved in ferroptosis in cancer cells. For example, pharmacologic and genetic inhibition of system xc- by blocking SLC3A2 and SLC7A11 have shown promising results in mouse models with low toxicity [149,150,151,152]. Similarly, targeting FSP1 is a promising approach due to its irrelevance in normal mice development indicating a potential broad therapeutic window [42, 153].
While GPX4 is expressed in most cancer cell lines, it is essential for various organs, including kidneys and neurons [145, 154, 155]. Therefore, GPX4 inhibitors (e.g., RSL3) should be delivered specifically to the cancer cells to prevent side effects. Indirect ferroptosis inducers such as erastin may have low solubility and labile metabolism in the complex human body [156]. Incorporation of ferroptotic inducer compounds into protective delivery systems, such as nanoparticles, may overcome this problem. In addition, nanoparticles delivering iron, peroxides, and ncRNAs targeting key inhibitors of ferroptosis into cancer cells are already actively being tested in vitro and in vivo studies. NcRNAs are notably emerging as they ultimately carry several advantages. They are naturally occurring molecules in cells meaning their therapeutic counterparts may utilize existing cellular metabolic pathways. Additionally, ncRNAs frequently target multiple genes within one and/or more pathways causing a broader yet specific anti-cancer response, such as the case with miR-15 and miR-16 cluster that regulates various anti-apoptotic and cell cycle players, including bcl-2, mcl1 and c-JUN [157]. Lastly, ncRNA therapeutics can be fairly easy chemically synthesized shaping them as cost-effective medications of the future.
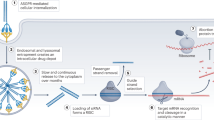
Indeed, several ncRNA-based therapies are currently developed, including antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNAs, short hairpin RNAs, miRNA mimics, miRNA sponges, anti-microRNAs (antimiRs), and therapeutic circular RNAs (Fig. 3) [158, 159]. Some of them are targeting up-regulated oncogenic molecules, while others replenish downregulated tumor suppressors. Although majority are still being tested in clinical studies, eleven ncRNA-based therapeutics have already been approved for several other disease entities [159]. Major current limitations of ncRNA-based therapeutics are specificity, delivery, and tolerability. Issues with specificity and off-target effects occur due to uptake by the untargeted cells. The unstable nature of ncRNAs leads to their inefficient intracellular delivery, and adverse immune responses occur if ncRNAs are recognized as foreign viral nucleic acids [158,159,160]. Nevertheless, newer generations of RNA therapeutics are being designed to overcome those limitations and increase their chances of eventual clinical utilization. For example, it has been shown that circularization of small RNAs mediates more efficient and longer inhibiting effects on their targets, and overcome major current limitations of ncRNA-based therapeutics [161,162,163]. Particular advances have been made with chemical modifications and optimization of delivery methods that include lipid nanoparticles, polymers, antibodies, bacteriophages, and exosomes (Fig. 3) [159]. Furthermore, immune checkpoint inhibitors, radiotherapy and several medications including sorafenib, sulfasalazine, metformin, artesunate, temozolomide, cisplatin, may all induce ferroptosis and/or sensitize cells to ferroptosis (Fig. 4) [83, 164,165,166,167,168,169]. These findings propose the potential drug repositioning and synergistic combinatorial therapeutic regimens in the future. Figure 4 highlights the compounds, including available therapeutics, with their suggested roles in ferroptosis.
Several ncRNA-based therapeutics exist, including antisense oligonucleotides, siRNAs, shRNAs, miRNA mimics, anti-miRNAs, miRNA sponges, and therapeutic circRNAs (box 1). Their major limitations and side effects can expectedly be overcome by usage of unique delivery systems that include lipid and polymer nanoparticles, antibodies, bacteriophages, exosomes and viral vectors (box 2). Newer generation of ncRNA therapeutics with convenient clinical administration (box 3) are awaited candidates due to their numerous advantages, including utilization of existing cellular processing mechanisms, capability of multiple signaling pathway targeting and promising cost-effective production (box 4). siRNA, small interfering RNA; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; antimiRs, anti-microRNAs; circRNAs, circular RNAs. Created with BioRender.
Some of these compounds are clinically available therapeutics that may additionally induce ferroptosis and/or sensitize cells to ferroptosis (cisplatin, metformin, sulfasalazine, sorafenib, immune checkpoint inhibitors HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, ionizing radiation, artesunate, haloperidol, lapatinib, ibuprofen, acetaminophen, temozolomide), while others may prevent ferroptosis (selenium, idebenone, CoQ10, zileuton, rosiglitazone, vitamin E, DFO, CPX, resveratrol). In addition, several compounds currently limited to experimental studies carry potential for optimization toward clinical utilization in ferroptosis induction (erastin, RSL3, FIN56, BSO, ML-210, IKE, apocynin, DPI, dioscin) and ferroptosis blockade (baicalein, triascin C, ferrostatin 1, liproxstatin 1, BHT, BH4). RSL3, RAS synthetic lethal 3; BSO, buthionine sulfoximine; IKE, imidazole ketone erastin; DPI, diphenyleneiodonium chloride; BHT, butylated hydroxytoluene; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; DFO, deferoxamine; CPX, ciclopirox olamine. Created with BioRender.
Conclusion
Recently characterized as unique form of regulated cell death, ferroptosis has already been associated with numerous diseases – above all with cancer. However, our knowledge about ferroptosis is still fairly limited and many open questions remain. We still do not know the complete relationship between ferroptosis and other forms of regulated cell death that share some common upstream mechanisms, such as p53. In addition, redox-independent roles of iron as well as the roles of other metals (e.g., copper) are not completely ruled out in ferroptosis induction. In addition, the exact molecular events responsible for the execution of cell death via ferroptosis are not fully understood. This is particularly pronounced in our ignorance of molecular events that occur downstream of lipid peroxidation including crucial moment(s) when activated ferroptosis cannot longer be suppressed. Finally, specific markers of ferroptosis suitable for application in live cells and intact tissues are still lacking. Furthermore, ncRNAs are a heterogenous group of non-coding transcripts with exceptional regulatory and biomarker capacities. Only a fraction of annotated ncRNAs have been investigated in the context of ferroptosis and cancer. Nevertheless, current evidence suggests that ferroptosis is frequently inhibited in cancer through the deregulation of usually tightly controlled ncRNA networks, thereby aiding cancer cell survival and progression. Hence, artificial induction of ferroptosis carries a great therapeutic potential. Albeit in their infancies, emerging innovative discoveries in both fields are paving the exciting path toward the successful utilization of novel ferroptosis-modulating ncRNA-therapeutics in cancer.
Data availability
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Martin Pichler.
References
Qu Z, Adelson DL. Evolutionary conservation and functional roles of ncRNA. Front Genet. 2012;3:205.
Cech TR, Steitz JA. The noncoding RNA revolution—trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 2014;157:77–94.
Ling H, Vincent K, Pichler M, Fodde R, Berindan-Neagoe I, Slack FJ, et al. Junk DNA and the long non-coding RNA twist in cancer genetics. Oncogene. 2015;34:5003–11.
Kim T, Reitmair A. Non-Coding RNAs: functional aspects and diagnostic utility in oncology. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:4934–68.
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:861–74.
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z, Kong D, Ali S. Implication of microRNAs in drug resistance for designing novel cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2010;13:57–66.
Jiang W, Xia J, Xie S, Zou R, Pan S, Wang ZW, et al. Long non-coding RNAs as a determinant of cancer drug resistance: Towards the overcoming of chemoresistance via modulation of lncRNAs. Drug Resist Updat. 2020;50:100683.
Hua X, Sun Y, Chen J, Wu Y, Sha J, Han S, et al. Circular RNAs in drug resistant tumors. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109233.
Posch F, Prinz F, Balihodzic A, Mayr C, Kiesslich T, Klec C, et al. MiR-200c-3p modulates cisplatin resistance in biliary tract cancer by ZEB1-independent mechanisms. Cancers. 2021;13:3996.
Matsui M, Corey DR. Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2017;16:167–79.
Bedoui S, Herold MJ, Strasser A. Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its physiological implications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:678–95.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Agostinis P, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541.
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22:266–82.
Kuang F, Liu J, Tang D, Kang R. Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:586578.
Li J, Cao F, Yin H, Huang Z, Lin Z, Mao N, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:88.
Collin F. Chemical basis of reactive oxygen species reactivity and involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:2407.
Rishi G, Huang G, Subramaniam VN. Cancer:the role of iron and ferroptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;141:106094.
Yang WS, Stockwell BR. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem Biol. 2008;15:234–45.
Yagoda N, von Rechenberg M, Zaganjor E, Bauer AJ, Yang WS, Fridman DJ, et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature. 2007;447:864–8.
Aldrovandi M, Banthiya S, Meckelmann S, Zhou Y, Heydeck D, O’Donnell VB, et al. Specific oxygenation of plasma membrane phospholipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipoxygenase induces structural and functional alterations in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2018;1863:152–64.
Dar HH, Tyurina YY, Mikulska-Ruminska K, Shrivastava I, Ting HC, Tyurin VA, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa utilizes host polyunsaturated phosphatidylethanolamines to trigger theft-ferroptosis in bronchial epithelium. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:4639–53.
Bogacz M, Krauth-Siegel RL. Tryparedoxin peroxidase-deficiency commits trypanosomes to ferroptosis-type cell death. Elife. 2018;7:e37503.
Distefano AM, Martin MV, Cordoba JP, Bellido AM, D’Ippolito S, Colman SL, et al. Heat stress induces ferroptosis-like cell death in plants. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:463–76.
Zheng J, Conrad M. The metabolic underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020;32:920–37.
Luo Y, Niu G, Yi H, Li Q, Wu Z, Wang J, et al. Nanomedicine promotes ferroptosis to inhibit tumour proliferation in vivo. Redox Biol. 2021;42:101908.
Deng SH, Wu DM, Li L, Liu T, Zhang T, Li J, et al. miR-324-3p reverses cisplatin resistance by inducing GPX4-mediated ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;549:54–60.
Hou Y, Cai S, Yu S, Lin H. Metformin induces ferroptosis by targeting miR-324-3p/GPX4 axis in breast cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2021;53:333–41.
He GN, Bao NR, Wang S, Xi M, Zhang TH, Chen FS. Ketamine induces ferroptosis of liver cancer cells by targeting lncRNA PVT1/miR-214-3p/GPX4. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021;15:3965–78.
Chen S, Zhang Z, Zhang B, Huang Q, Liu Y, Qiu Y, et al. CircCDK14 promotes tumor progression and resists ferroptosis in glioma by regulating PDGFRA. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18:841–57.
Shanshan W, Hongying M, Jingjing F, Yiming Y, Yu R, Rui Y. CircDTL functions as an oncogene and regulates both apoptosis and ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Front Genet. 2021;12:743505.
Dong LH, Huang JJ, Zu P, Liu J, Gao X, Du JW, et al. CircKDM4C upregulates P53 by sponging hsa-let-7b-5p to induce ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36:1288–302.
Liu M, Zhu W, Pei D. System Xc−: a key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer. Investig N. Drugs. 2021;39:1123–31.
Ni H, Qin H, Sun C, Liu Y, Ruan G, Guo Q, et al. MiR-375 reduces the stemness of gastric cancer cells through triggering ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:325.
Bai T, Liang R, Zhu R, Wang W, Zhou L, Sun Y. MicroRNA-214-3p enhances erastin-induced ferroptosis by targeting ATF4 in hepatoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235:5637–48.
Yadav P, Sharma P, Sundaram S, Venkatraman G, Bera AK, Karunagaran D. SLC7A11/ xCT is a target of miR-5096 and its restoration partially rescues miR-5096-mediated ferroptosis and anti-tumor effects in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021;522:211–24.
Wang Z, Chen X, Liu N, Shi Y, Liu Y, Ouyang L, et al. A nuclear long non-coding RNA LINC00618 accelerates ferroptosis in a manner dependent upon apoptosis. Mol Ther. 2021;29:263–74.
Mao C, Wang X, Liu Y, Wang M, Yan B, Jiang Y, et al. A G3BP1-Interacting lncRNA promotes ferroptosis and apoptosis in cancer via nuclear sequestration of p53. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3484–96.
Zhang Y, Guo S, Wang S, Li X, Hou D, Li H, et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 inhibits ferroptosis in prostate cancer with long-term cadmium exposure through miR-128-3p/SLC7A11 signaling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;220:112376.
Yao W, Wang J, Meng F, Zhu Z, Jia X, Xu L, et al. Circular RNA CircPVT1 inhibits 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity by regulating ferroptosis through MiR-30a-5p/FZD3 axis in esophageal cancer cells. Front Oncol. 2021;11:780938.
Wu P, Li C, Ye Dmei, Yu K, Li Y, Tang H, et al. Circular RNA circEPSTI1 accelerates cervical cancer progression via miR-375/409-3P/515-5p-SLC7A11 axis. Aging. 2021;13:4663–73.
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R, Aldrovandi M, da Silva MC, Ingold I, et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature. 2019;575:693–8.
Kraft VAN, Bezjian CT, Pfeiffer S, Ringelstetter L, Muller C, Zandkarimi F, et al. GTP cyclohydrolase 1/tetrahydrobiopterin counteract ferroptosis through lipid remodeling. ACS Cent Sci. 2020;6:41–53.
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang PH, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575:688–92.
Klein EA, Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Crowley JJ, Lucia MS, Goodman PJ, et al. Vitamin E and the risk of prostate cancer: the Selenium and Vitamin E Cancer Prevention Trial (SELECT). JAMA. 2011;306:1549–56.
Song Z, Jia G, Ma P, Cang S. Exosomal miR-4443 promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma by regulating FSP1 m6A modification-mediated ferroptosis. Life Sci. 2021;276:119399.
Chorley BN, Campbell MR, Wang X, Karaca M, Sambandan D, Bangura F, et al. Identification of novel NRF2-regulated genes by ChIP-Seq: influence on retinoid X receptor alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:7416–29.
Wu S, Lu H, Bai Y. Nrf2 in cancers: A double-edged sword. Cancer Med. 2019;8:2252–67.
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R, et al. Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 2016;63:173–84.
Chen D, Tavana O, Chu B, Erber L, Chen Y, Baer R, et al. NRF2 is a major target of ARF in p53-independent tumor suppression. Mol Cell. 2017;68:224–32.
Liu N, Lin X, Huang C. Activation of the reverse transsulfuration pathway through NRF2/CBS confers erastin-induced ferroptosis resistance. Br J Cancer. 2020;122:279–92.
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, et al. Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016;23:369–79.
Dixon SJ, Winter GE, Musavi LS, Lee ED, Snijder B, Rebsamen M, et al. Human haploid cell genetics reveals roles for lipid metabolism genes in nonapoptotic cell death. ACS Chem Biol. 2015;10:1604–9.
Lu Y, Chan Y-T, Tan H-Y, Zhang C, Guo W, Xu Y, et al. Epigenetic regulation of ferroptosis via ETS1/miR-23a-3p/ACSL4 axis mediates sorafenib resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:3.
Ma LL, Liang L, Zhou D, Wang SW. Tumor suppressor miR-424-5p abrogates ferroptosis in ovarian cancer through targeting ACSL4. Neoplasma. 2021;68:165–73.
Wu H, Liu A. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates ferroptosis sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Int Med Res. 2021;49:300060521996183.
Jin G, Arai K, Murata Y, Wang S, Stins MF, Lo EH, et al. Protecting against cerebrovascular injury: contributions of 12/15-lipoxygenase to edema formation after transient focal ischemia. Stroke.2008;39:2538–43.
Song L, Yang H, Wang HX, Tian C, Liu Y, Zeng XJ, et al. Inhibition of 12/15 lipoxygenase by baicalein reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulation of multiple signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 2014;19:567–80.
Tomita K, Nagasawa T, Kuwahara Y, Torii S, Igarashi K, Roudkenar MH, et al. MiR-7-5p is involved in ferroptosis signaling and radioresistance Thru the generation of ROS in Radioresistant HeLa and SAS Cell Lines. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:8300.
Zhang Z, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H, Liu D, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:43.
Zou Y, Li H, Graham ET, Deik AA, Eaton JK, Wang W, et al. Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase contributes to phospholipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2020;16:302–9.
Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:360438.
Liu J, Kang R, Tang D. ESCRT-III-mediated membrane repair in cell death and tumor resistance. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020;28:1–4.
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R, Jiang X. Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2015;59:298–308.
Tuo QZ, Lei P, Jackman KA, Li XL, Xiong H, Li XL, et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22:1520–30.
Brown CW, Amante JJ, Chhoy P, Elaimy AL, Liu H, Zhu LJ, et al. Prominin2 drives ferroptosis resistance by stimulating iron export. Dev Cell. 2019;51:575–86.
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT III, Zeh HJ, et al. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy. 2016;12:1425–8.
Bai Y, Meng L, Han L, Jia Y, Zhao Y, Gao H, et al. Lipid storage and lipophagy regulates ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508:997–1003.
Yang M, Chen P, Liu J, Zhu S, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, et al. Clockophagy is a novel selective autophagy process favoring ferroptosis. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaaw2238.
Wu Z, Geng Y, Lu X, Shi Y, Wu G, Zhang M, et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is involved in the execution of ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:2996–3005.
Zhou Y, Shen Y, Chen C, Sui X, Yang J, Wang L, et al. The crosstalk between autophagy and ferroptosis: what can we learn to target drug resistance in cancer? Cancer Biol Med. 2019;16:630.
Haberzettl P, Hill BG. Oxidized lipids activate autophagy in a JNK-dependent manner by stimulating the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Redox Biol. 2013;1:56–64.
Zukor H, Song W, Liberman A, Mui J, Vali H, Fillebeen C, et al. HO-1-mediated macroautophagy: a mechanism for unregulated iron deposition in aging and degenerating neural tissues. J Neurochem. 2009;109:776–91.
Wu Z, Geng Y, Lu X, Shi Y, Wu G, Zhang M, et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is involved in the execution of ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:2996–3005.
Garg AD, Dudek AM, Ferreira GB, Verfaillie T, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, et al. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy. 2013;9:1292–307.
Zou Y, Palte MJ, Deik AA, Li H, Eaton JK, Wang W, et al. A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1617.
Lee H, Zandkarimi F, Zhang Y, Meena JK, Kim J, Zhuang L, et al. Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:225–34.
Lee H, Zhuang L, Gan B. Energy stress inhibits ferroptosis via AMPK. Mol Cell Oncol. 2020;7:1761242.
Song X, Zhu S, Chen P, Hou W, Wen Q, Liu J, et al. AMPK-Mediated BECN1 phosphorylation promotes ferroptosis by directly blocking system Xc– activity. Curr Biol. 2018;28:2388–99.
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T, Hibshoosh H, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520:57–62.
Zhang Y, Shi J, Liu X, Feng L, Gong Z, Koppula P, et al. BAP1 links metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:1181–92.
Hirschhorn T, Stockwell BR. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:130–43.
Lei G, Zhang Y, Koppula P, Liu X, Zhang J, Lin SH, et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res. 2020;30:146–62.
Almeida MI, Reis RM, Calin GA. MicroRNA history: discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat Res Mol Mech Mutagen. 2011;717:1–8.
O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:402.
Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA. Switching from repression to activation: MicroRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science. 2007;318:1931–4.
Zhang F, Wang D. The pattern of microRNA binding site distribution. Genes. 2017;8:296.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–9.
Peng Y, Croce CM. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004.
Lewerenz J, Maher P. Basal levels of eIF2α phosphorylation determine cellular antioxidant status by regulating ATF4 and xCT expression. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:1106.
Ameri K, Harris AL. Activating transcription factor 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40:14–21.
Chen D, Fan Z, Rauh M, Buchfelder M, Eyupoglu IY, Savaskan N. ATF4 promotes angiogenesis and neuronal cell death and confers ferroptosis in a xCT-dependent manner. Oncogene. 2017;36:5593–608.
Lou M, Wu L, Zhang K, Wang H, Zhang T, Gutierrez L, et al. miR-137 regulates ferroptosis by targeting glutamine transporter SLC1A5 in melanoma. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:1457–72.
Scalise M, Pochini L, Console L, Losso MA, Indiveri C. The Human SLC1A5 (ASCT2) Amino Acid Transporter: from function to structure and role in cell biology. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:96.
Yin F, Zhang Q, Dong Z, Hu J, Ma Z. LncRNA HOTTIP participates in cisplatin resistance of tumor cells by regulating miR-137 expression in pancreatic cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:2689.
Li D-M, Chen Q-D, Wei G-N, Wei J, Yin J-X, He J-H, et al. Hypoxia-Induced miR-137 inhibition increased glioblastoma multiforme growth and chemoresistance through LRP6. Front Oncol. 2020;10:611699.
Liang J, Tian X-F, Yang W. Effects of long non-coding RNA Opa-interacting protein 5 antisense RNA 1 on colon cancer cell resistance to oxaliplatin and its regulation of microRNA-137. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26:1474.
Su T-J, Ku W-H, Chen H-Y, Hsu Y-C, Hong Q-S, Chang G-C, et al. Oncogenic miR-137 contributes to cisplatin resistance via repressing CASP3 in lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2016;6:1317.
Tomita K, Fukumoto M, Itoh K, Kuwahara Y, Igarashi K, Nagasawa T, et al. MiR-7-5p is a key factor that controls radioresistance via intracellular Fe 2+ content in clinically relevant radioresistant cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;518:712–8.
Statello L, Guo C-J, Chen L-L, Huarte M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;22:96–118.
Xing J, Liu H, Jiang W, Wang L. LncRNA-encoded peptide: functions and predicting methods. Front Oncol. 2020;10:622294.
Jonas K, Calin GA, Pichler M. RNA-binding proteins as important regulators of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:2969.
Bartonicek N, Maag JLV, Dinger ME. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer: mechanisms of action and technological advancements. Mol Cancer. 2016;15:1–10.
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Disco. 2011;1:391–407.
Teppan J, Barth DA, Prinz F, Jonas K, Pichler M, Klec C. Involvement of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumor angiogenesis. Non-Coding RNA. 2020;6:42.
Balihodzic A, Barth DA, Prinz F, Pichler M. Involvement of long non-coding RNAs in glucose metabolism in cancer. Cancers. 2021;13:977.
Deng X, Xiong W, Jiang X, Zhang S, Li Z, Zhou Y, et al. LncRNA LINC00472 regulates cell stiffness and inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by binding to YBX1. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:945.
Chen C, Zheng Q, Kang W, Yu C. Long non-coding RNA LINC00472 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion through miR-93-5p/PDCD4 pathway. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019;43:436–45.
Ye Y, Yang S, Han Y, Sun J, Xv L, Wu L, et al. Linc00472 suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis through elevating PDCD4 expression by sponging miR-196a in colorectal cancer. Aging. 2018;10:1523–33.
Gao S, Wang Z. Comprehensive analysis of regulatory network for LINC00472 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Health Eng. 2021;2021:1–20.
Shen Y, Katsaros D, Loo LWM, Hernandez BY, Chong C, Canuto EM, et al. Prognostic and predictive values of long non-coding RNA LINC00472 in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:8579–92.
Qi W, Li Z, Xia L, Dai J, Zhang Q, Wu C, et al. LncRNA GABPB1-AS1 and GABPB1 regulate oxidative stress during erastin-induced ferroptosis in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16185.
Gai C, Liu C, Wu X, Yu M, Zheng J, Zhang W, et al. MT1DP loaded by folate-modified liposomes sensitizes erastin-induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-365a-3p/NRF2 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:751.
Wang M, Mao C, Ouyang L, Liu Y, Lai W, Liu N, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00336 inhibits ferroptosis in lung cancer by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:2329.
Yu X, Li Z, Zheng H, Chan MTV, Wu WKK. NEAT1: A novel cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Cell Prolif. 2017;50:e12329.
Prinz F, Kapeller A, Pichler M, Klec C. The Implications of the long non-coding RNA NEAT1 in non-cancerous diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:627.
Klec C, Prinz F, Pichler M. Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis. Mol Oncol. 2019;13:46–60.
Wu ZH, Tang Y, Yu H, Li HD. The role of ferroptosis in breast cancer patients: a comprehensive analysis. Cell Death Disco. 2021;7:93.
Zhang K, Ping L, Du T, Liang G, Huang Y, Li Z, et al. A ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature predicts prognosis and immune microenvironment for breast cancer. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:678877.
Yao J, Chen X, Liu X, Li R, Zhou X, Qu Y. Characterization of a ferroptosis and iron-metabolism related lncRNA signature in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:340.
Zheng J, Zhou Z, Qiu Y, Wang M, Yu H, Wu Z, et al. A prognostic ferroptosis-related lncRNAs signature associated with immune landscape and radiotherapy response in Glioma. Front cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:675555.
Tang Y, Li C, Zhang YJ, Wu ZH. Ferroptosis-Related Long Non-Coding RNA signature predicts the prognosis of Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17:702–11.
Tang R, Xu J, Zhang B, Liu J, Liang C, Hua J, et al. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in anticancer immunity. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:110.
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT, Kjems J. Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene. 2018;37:555–65.
Guria A, Sharma P, Natesan S, Pandi G. Circular RNAs—the road less traveled. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;6:146.
Miao Q, Ni B, Tang J. Coding potential of circRNAs: new discoveries and challenges. PeerJ. 2021;9:e10718.
Lu M. Circular RNA: functions, applications and prospects. ExRNA. 2020;2:1–7.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–57.
Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J. Circular RNAs: promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine. 2018;34:267–74.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Thomson DW, Dinger ME. Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:272–83.
Bosson AD, Zamudio JR, Sharp PA. Endogenous miRNA and target concentrations determine susceptibility to potential ceRNA competition. Mol Cell. 2014;56:347–59.
Jens M, Rajewsky N. Competition between target sites of regulators shapes post-transcriptional gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;16:113–26.
Denzler R, Agarwal V, Stefano J, Bartel DP, Stoffel M. Assessing the ceRNA hypothesis with quantitative measurements of miRNA and target abundance. Mol Cell. 2014;54:766–76.
Ala U, Karreth FA, Bosia C, Pagnani A, Taulli R, Leópold V, et al. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:7154–9.
Bosia C, Pagnani A, Zecchina R. Modelling competing endogenous RNA networks. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e66609.
Figliuzzi M, Marinari E, De Martino A. MicroRNAs as a selective channel of communication between competing RNAs: a steady-state theory. Biophys J. 2013;104:1203–13.
Verduci L, Tarcitano E, Strano S, Yarden Y, Blandino G. CircRNAs: role in human diseases and potential use as biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:468.
Liu Z, Wang Q, Wang X, Xu Z, Wei X, Li J. Circular RNA cIARS regulates ferroptosis in HCC cells through interacting with RNA binding protein ALKBH5. Cell Death Disco. 2020;6:72.
Zhu H, Gan X, Jiang X, Diao S, Wu H, Hu J. ALKBH5 inhibited autophagy of epithelial ovarian cancer through miR-7 and BCL-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:163.
Xian ZY, Hu B, Wang T, Cai JL, Zeng JY, Zou Q, et al. CircABCB10 silencing inhibits the cell ferroptosis and apoptosis by regulating the miR-326/CCL5 axis in rectal cancer. Neoplasma. 2020;67:1063–73.
Suarez-Carmona M, Chaorentong P, Kather JN, Rothenheber R, Ahmed A, Berthel A, et al. CCR5 status and metastatic progression in colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2019;8:e1626193.
Lyu N, Zeng Y, Kong Y, Chen Q, Deng H, Ou S, et al. Ferroptosis is involved in the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through the circ0097009/miR-1261/SLC7A11 axis. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9:675.
Wang H-H, Ma J-N, Zhan X-R. Circular RNA Circ_0067934 attenuates ferroptosis of thyroid cancer cells by miR-545-3p/SLC7A11 signaling. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:670031.
Yang WS, Sriramaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Chen W, Fu J, Chen Y, Li Y, Ning L, Huang D, et al. Circular RNA circKIF4A facilitates the malignant progression and suppresses ferroptosis by sponging miR-1231 and upregulating GPX4 in papillary thyroid cancer. Aging. 2021;13:16500–12.
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S, Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 2017;547:453–7.
Hangauer MJ, Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Bole D, Eaton JK, Matov A, et al. Drug-tolerant persister cancer cells are vulnerable to GPX4 inhibition. Nature. 2017;551:247–50.
Zhang Y, Tan H, Daniels JD, Zandkarimi F, Liu H, Brown LM, et al. Imidazole Ketone Erastin Induces Ferroptosis and Slows Tumor Growth in a Mouse Lymphoma Model. Cell Chem Biol. 2019;26:623–33. e9
Savaskan NE, Heckel A, Hahnen E, Engelhorn T, Doerfler A, Ganslandt O, et al. Small interfering RNA–mediated xCT silencing in gliomas inhibits neurodegeneration and alleviates brain edema. Nat Med. 2008;14:629–32.
Badgley MA, Kremer DM, Maurer HC, DelGiorno KE, Lee HJ, Purohit V, et al. Cysteine depletion induces pancreatic tumor ferroptosis in mice. Science. 2020;368:85–9.
Sato M, Onuma K, Domon M, Hasegawa S, Suzuki A, Kusumi R, et al. Loss of the cystine/glutamate antiporter in melanoma abrogates tumor metastasis and markedly increases survival rates of mice. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:3224–35.
Mei J, Webb S, Zhang B, Shu H-B. The p53-inducible apoptotic protein AMID is not required for normal development and tumor suppression. Oncogene. 2006;25:849–56.
Yoo SE, Chen L, Na R, Liu Y, Rios C, Van Remmen H, et al. Gpx4 ablation in adult mice results in a lethal phenotype accompanied by neuronal loss in brain. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;52:1820–7.
Conrad M, Pratt DA. The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15:1137–47.
Larraufie M-H, Yang WS, Jiang E, Thomas AG, Slusher BS, Stockwell BR. Incorporation of metabolically stable ketones into a small molecule probe to increase potency and water solubility. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25:4787.
Calin GA, Cimmino A, Fabbri M, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Shimizu M, et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:5166–71.
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2017;16:203–22.
Winkle M, El-Daly SM, Fabbri M, Calin GA. Noncoding RNA therapeutics — challenges and potential solutions. Nat Rev Drug Disco. 2021;20:629–51.
Slaby O, Laga R, Sedlacek O. Therapeutic targeting of non-coding RNAs in cancer. Biochem J. 2017;474:4219–51.
Zhang L, Liang D, Chen C, Wang Y, Amu G, Yang J, et al. Circular siRNAs for reducing off-target effects and enhancing long-term gene silencing in cells and mice. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;10:237–44.
Hagiwara K, Honma M, Harumoto T, Harada K, Sawada T, Yamamoto J, et al. Development of prodrug type circular siRNA for in vivo knockdown by systemic administration. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020;30:346–64.
Gnanamony M, Demirkhanyan L, Ge L, Sojitra P, Bapana S, Norton JA, et al. Circular dumbbell miR-34a-3p and -5p suppresses pancreatic tumor cell-induced angiogenesis and activates macrophages. Oncol Lett. 2021;21:75.
Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijon M, Kennedy PD, Johnson JK, et al. CD8 + T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;569:270–4.
Li ZJ, Dai HQ, Huang XW, Feng J, Deng JH, Wang ZX, et al. Artesunate synergizes with sorafenib to induce ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharm Sin. 2021;42:301–10.
Yang J, Zhou Y, Xie S, Wang J, Li Z, Chen L, et al. Metformin induces Ferroptosis by inhibiting UFMylation of SLC7A11 in breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:1–19.
Lin X, Ping J, Wen Y, Wu Y. The mechanism of ferroptosis and applications in tumor treatment. Front Pharm. 2020;11:1061.
Sehm T, Rauh M, Wiendieck K, Buchfelder M, Eyupoglu IY, Savaskan NE. Temozolomide toxicity operates in a xCT/SLC7a11 dependent manner and is fostered by ferroptosis. Oncotarget. 2016;7:74630–47.
Guo J, Xu B, Han Q, Zhou H, Xia Y, Gong C, et al. Ferroptosis: a novel anti-tumor action for cisplatin. Cancer Res Treat. 2018;50:445–60.
Gomaa A, Peng D, Chen Z, Soutto M, Abouelezz K, Corvalan A, et al. Epigenetic regulation of AURKA by miR-4715-3p in upper gastrointestinal cancers. Sci Rep. 2019;9:16970.
Xu Z, Chen L, Wang C, Zhang L, Xu W. MicroRNA-1287-5p promotes ferroptosis of osteosarcoma cells through inhibiting GPX4. Free Radic Res. 2022;55:1119–29.
Zhang K, Wu L, Zhang P, Lou M, Du J, Gao T, et al. miR-9 regulates ferroptosis by targeting glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase GOT1 in melanoma. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57:1566–76.
Liao Y, Jia X, Ren Y, Deji Z, Gesang Y, Ning N, et al. Suppressive role of microRNA-130b-3p in ferroptosis in melanoma cells correlates with DKK1 inhibition and Nrf2-HO-1 pathway activation. Hum Cell. 2021;34:1532–44.
Niu Y, Zhang J, Tong Y, Li J, Liu B. Physcion 8-O-β-glucopyranoside induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-103a-3p/GLS2 axis in gastric cancer. Life Sci. 2019;237:116893.
Chen J, Qin C, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Mao M, Yang J. Metformin may induce ferroptosis by inhibiting autophagy via lncRNA H19 in breast cancer. FEBS Open Bio. 2022;12:146–53.
Luo W, Wang J, Xu W, Ma C, Wan F, Huang Y, et al. LncRNA RP11-89 facilitates tumorigenesis and ferroptosis resistance through PROM2-activated iron export by sponging miR-129-5p in bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:1043.
Ma Q, Dai X, Lu W, Qu X, Liu N, Zhu C. Silencing long non-coding RNA MEG8 inhibits the proliferation and induces the ferroptosis of hemangioma endothelial cells by regulating miR-497-5p/NOTCH2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;556:72–8.
Jiang M, Mo R, Liu C, Wu H. Circ_0000190 sponges miR-382-5p to suppress cell proliferation and motility and promote cell death by targeting ZNRF3 in gastric cancer. J Biochem. 2022;mvac003. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvac003.
Zhang HY, Zhang BW, Zhang ZB, Deng QJ. Circular RNA TTBK2 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and ferroptosis via miR-761/ITGB8 axis in glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci. 2020;24:2585–600.
Zhang H, Ge Z, Wang Z, Gao Y, Wang Y, Qu X. Circular RNA RHOT1 promotes progression and inhibits ferroptosis via mir-106a-5p/STAT3 axis in breast cancer. Aging. 2021;13:8115–26.
Bazhabayi M, Qiu X, Li X, Yang A, Wen W, Zhang X, et al. CircGFRA1 facilitates the malignant progression of HER‐2‐positive breast cancer via acting as a sponge of miR‐1228 and enhancing AIFM2 expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:10248.
Xu Q, Zhou L, Yang G, Meng F, Wan Y, Wang L, et al. CircIL4R facilitates the tumorigenesis and inhibits ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the miR-541-3p/GPX4 axis. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44:2344–56.
Wang Y, Chen H, Wei X. Circ_0007142 downregulates miR-874-3p-mediated GDPD5 on colorectal cancer cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2021;51:e13541.
Funding
This work was supported by BioTechMed-Graz (Lab Rotation Program 2020, to AB). The research of MP was supported by the Austrian Science Fund FWF (DK-MCD, W 1226).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AB, FP, MD, GAC, PJ and MP wrote the manuscript, and all authors approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by G. Melino
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Balihodzic, A., Prinz, F., Dengler, M.A. et al. Non-coding RNAs and ferroptosis: potential implications for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ 29, 1094–1106 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-022-00998-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-022-00998-x
This article is cited by
-
The roles and molecular mechanisms of non-coding RNA in cancer metabolic reprogramming
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
HMGA1 drives chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing ferroptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
Exploring the Role of Ferroptosis-Related Circular RNAs in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Molecular Biotechnology (2024)
-
Oxytosis/Ferroptosis in Neurodegeneration: the Underlying Role of Master Regulator Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4)
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Epigenetically silenced lncRNA SNAI3-AS1 promotes ferroptosis in glioma via perturbing the m6A-dependent recognition of Nrf2 mRNA mediated by SND1
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)