Abstract
Chemokines are important regulators of the immune system, inducing specific cellular responses by binding to receptors on immune cells. In SLE patients, decreased expression of CCL2 on mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) prevents inhibition of B-cell proliferation, causing the characteristic autoimmune phenotype. Nevertheless, the intrinsic role of CCL2 on B-cell autoimmunity is unknown. In this study using Ccl2 KO mice, we found that CCL2 deficiency enhanced BCR signaling by upregulating the phosphorylation of the MST1-mTORC1-STAT1 axis, which led to reduced marginal zone (MZ) B cells and increased germinal center (GC) B cells. The abnormal differentiation of MZ and GC B cells were rescued by in vivo inhibition of mTORC1. Additionally, the inhibition of MST1-mTORC1-STAT1 with specific inhibitors in vitro also rescued the BCR signaling upon antigenic stimulation. The deficiency of CCL2 also enhanced the early activation of B cells including B-cell spreading, clustering and signalosome recruitment by upregulating the DOCK8-WASP-actin axis. Our study has revealed the intrinsic role and underlying molecular mechanism of CCL2 in BCR signaling, B-cell differentiation, and humoral response.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), also known as monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), is a small cytokine that recruits monocytes, memory T cells, and dendritic cells to sites of injured and infected tissue [1, 2]. The CCL2 precursor has a signal peptide of 23 amino acids and a mature peptide of 76 amino acids [3, 4]. CCL2 binds to the cell surface receptors C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) and CCR4 [5]. CCL2 is critical in controlling autoimmune diseases, such as SLE. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) from healthy humans inhibit the normal B-cell proliferation, differentiation, and antibody secretion in vitro. However, the expression of CCL2 is reduced in the MSC of SLE patients, decreasing their suppressive function over B-cell proliferation and differentiation [6]. Whether the reduction of CCL2 expression in B cells contributes to SLE intrinsically is unknown.
Spontaneous germinal centers (Spt-GCs) harbor autoreactive B cells that promote autoimmunity. B-cell-intrinsic IFN-γ receptor (IFN-γR) and STAT1 signaling mediate Spt-GC and follicular T-helper cell (Tfh cell) development by driving B-cell IFN-γ production and T-bet expression. Additionally, STAT-1 signaling regulates oncostatin M (OSM)-stimulated CCL2 expression in human osteoblastic cells and LPS stimulated CCL2 expression in macrophages [7, 8]. However, it is unknown whether CCL2 regulates STAT1 activation to control autoimmunity in B cells.
Recently, extensive research has been done on the role of immune cell metabolism in autoimmunity. It is well recognized that an overactive immune system correlates with metabolically abnormal immune cells. In the lupus mouse model, disease is decreased with activation of AMPK and inhibition of mTOR, which restricts B-cell differentiation into GC B cells and plasma cells (PCs) [9]. In SLE patients, CD19+ B cells have increased mTOR activation in plasmablast cells (PBCs) [10]. These studies suggest that mTOR plays a central role in controlling autoimmunity. The correlation between CCL2 and mTOR is only beginning to be understood. CCL2 activates the estrogen receptor α by phosphorylating Ser167 via the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 signaling pathway in cells [11]. However, little is known whether CCL2 activates mTOR signaling in B cells to check peripheral tolerance.
MST1 has been demonstrated to control autoimmunity negatively and positively. The expression of MST1 in Treg cells is required for preventing autoimmunity [12]. Yet, the absence of MST1 reduces the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and protects against collagen-induced arthritis development. Also, deletion of MST1 in CD4+ T cells is sufficient to alleviate CNS inflammation during EAE [13]. Furthermore, Mst−/− B cells show decreased stimulation to B-cell mitogens in vitro, deficient Ag-specific Ig production in vivo, BCR signaling and BCR clustering [13, 14]. Thus, it is not known whether MST1 promotes or inhibits autoimmunity. Although a correlation between MST1 and CCL2 has not been reported, interaction between mTOR and STAT1 was recently identified in human cells [15]. MST1 was also found to bind to AKT in glioma cells and negatively regulate AKT and mTOR activity [16]. But we do not know whether the CCL2-MST1-mTOR-STAT1 axis exists to regulate B-cell autoimmunity.
In this study using Ccl2 KO mice, we found that the proximal BCR signaling was enhanced, including activation of CD19, BTK, and SHIP-1, which caused a reduction in marginal zone (MZ) B cells and an increase in Spt-GCs. The increased BCR signaling correlated with increased activation of the metabolic signaling axis-PI3K-mTOR-AKT, actin reorganization pathway- MST1-DOCK8-WASP-F-actin and transcriptional factors- STAT1, STAT5, and NF-κB. Reduction of mTORC1 signaling by rapamycin treatment restored BCR signaling and differentiation of MZ and GC B cells in Ccl2 KO B cells. Additionally, BCR signaling in Ccl2 KO B cells were also restored with treatment of MST1 inhibitor and STAT1 inhibitors. Overall, we have shown the underlying molecular mechanism of CCL2 in BCR signaling, B-cell differentiation, and humoral response.
Materials and methods
Mice
Ccl2 KO mice on a C57BL/6J background were purchased from Jackson laboratory. C57BL/6J (CD45.2+ and CD45.1+) mice were from Charles River (Beijing, China). All mice were maintained in pathogen-free conditions. Mouse experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Ethics Committee of Animal Experimentation of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan, China).
Cell isolation
Mouse bone marrow cells were isolated and purified by Red Cell Lysis Buffer (RT122-02, TIANGEN). Mouse splenic lymphocytes were isolated using a Ficoll (17-1440-02, GE healthcare) density gradient centrifugation and the splenic B cells were purified as described previously [17]. Briefly, anti-CD90.2 mAb (105310, BioLegend) and guinea pig complement (C300-0500, Rockland) were used to deplete T cells, and then cells were incubated in cell culture flasks for 1 h to remove monocyte cells from suspension.
Flow cytometry and antibodies
For analysis of cell surface markers, bone marrow (BM) cells were stained in PBS containing 2% fetal bovine serum (1767839, Gibco) using the following antibodies: anti-mouse CD16/CD32, with anti-CD43 (143208), anti-BP-1 (108307, Biolegend), anti-B220 (103234, Biolegend), anti-CD24 (101822, Biolegend), and anti-IgM (406518, Biolegend). Splenic lymphocytes were stained with anti-CD19 (101506, Biolegend), anti-CD23 (101608, Biolegend), anti-IgD (405710, Biolegend), anti-CD21 (123412, Biolegend), anti-B220 (103247, Biolegend), anti-IgM, anti-CD19 (101506, Biolegend), anti-GL7 (144606, Biolegend), anti-CD95 (152606, Biolegend), anti-B220 (103206, Biolegend), anti-Annexin V (640906, Biolegend), anti-CD5 (100622, Biolegend), anti-CD11b (101226, Biolegend), anti-CD138 (142521, Biolegend), anti-NP (N-5070-1, Biosearch), anti-CD45.1 (110716, Biolegend), and anti-CD45.2 (109838, Biolegend). Annexin V staining was performed using Annexin V Binding Buffer (422201, Biolegend). For Breg analysis, splenic lymphocytes were stimulated with LPS (10 μg/ml, L2880, Sigma), PMA (50 ng/ml; P1585-1MG, Sigma-Aldrich), ionomycin (1 μM; 9995 S, CST), and GolgiStop (1:1000; 554724BD, Biosciences) at 37 °C for 5 h. Then, cells were stained with surface marker CD19, and then intracellular IL-10 (554467, Biolegend) staining was performed. To detect the level of phosphorylated WASP and F-actin in primary B cells, splenic B cells were first stained with anti-B220, followed by biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig (M + G) (115-066-068, Jackson ImmunoResearch) for 30 min on ice, next streptavidin was added and cells were incubated at 37 °C for varying times. Then cells were immediately fixed and permeabilized with Phosflow Lyse/Fix buffer and Phosflow Perm buffer III (BD Biosciences) and stained with anti-Phospho WASP antibody (A300-205A, Bethyl) and F-actin (R37110, Thermo fisher), followed by goat-anti-rabbit IgG AF405 antibody (A-31556, Thermo Fisher). To detect the level of T-bet, splenic B cells were activated with 10 μg/ml F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgM (115-156-020, Jackson ImmunoResearch) for different time points, then cells were fixed and permeabilized with Phosflow Lyse/Fix buffer and Phosflow Perm buffer III (BD Biosciences), and stained with anti-B220 and anti-T-bet (644809, Biolegend).
For T-cell analysis, lymphocytes from thymus, lymph node (LN), and spleen were stained with anti-CD4 (100531, BioLegend), anti-CD8a (100751, BioLegend), anti-TCRβ (109220, BioLegend), and 7-AAD (559925, BD Pharmingen. For intracellular staining, cells were fixed and permeabilized with Fixation/Permeabilization Kit (00-5123, 00-5223, eBioscience), and then cells were stained with anti-FOXP3 (53-5773-82, Thermo Fisher Scientific) in permeabilization buffer. To assess the levels of cytokines, lymphocyte from thymus, spleen, and LN were stimulated with PMA (50 ng/ml; P1585-1MG, Sigma-Aldrich), ionomycin (1 μM; 9995S, CST) and GolgiStop (1:1000; 554724, BD Biosciences) at 37 °C for 5 h. Then, cells were stained with surface marker: anti-CD4 (100408, BioLegend), anti-CD8a, anti-CD44 and anti-TCR-β. And then cells were fixed and permeabilized with Fixation/Permeabilization Kit, and then stained with anti-IL-4 (504106, BioLegend), anti-IFN-γ (505826, BioLegend), anti-IL-17A (506925, BioLegend) and anti-IL-2 (503806, BioLegend) in permeabilization buffer.
To measure the expression of CCL2 or CCR2 on B cells, lymphocytes from BM were stained with the surface marker anti-CD43, anti-BP-1, anti-B220, anti-CD24, anti-IgM and splenic lymphocytes were stained with anti-CD23, anti-CD21, anti-IgM, anti-IgD and anti-B220, and then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with anti-MCP-1 (2029S, Cell Signaling Technology) or anti-CCR2 (ab203128, abcam).
Flow cytometry data were measured on a LSRII (BD Biosciences CA, USA) or Attune NxT (Thermo Fisher) and analyzed with FlowJo 10 software.
Immunofluorescence analysis of tissue samples
For Immunofluorescence analyses, spleens, and kidneys were freshly frozen in OCT embedding medium, and cut into 10 μm thick cryosections, followed by fixation with cold acetone for 5 min and then washed with PBS for 15 min. Next, the slides were incubated with 5% bovine serum albumin (4240GR100, BiFroxx) containing 1% anti-CD16/CD32 mAb (101319, BioLegend) to block nonspecific binding prior to staining with the following primary antibodies diluted in blocking buffer overnight at 4 °C: PE-CD4 (100407, BioLegend), FITA-GL-7 (562080, BD Biosciences), IgD (13-5993-85, Thermo Fisher), Alexa Fluor 488 IgG (715-545-151, Jackson ImmunoResearch), or complement C3 (1:400, NB200-540, NOVUS). Slides were rinsed for 15 min in PBS and incubated with Dylight 650 (84547, Thermo Fisher), or Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti rat IgG (A11006, Thermo Fisher). Fluorescent images were captured using a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope or a Nikon confocal microscope.
Serum antibodies
Serum anti-dsDNA antibody and immunoglobulin were quantified by ELISA as described previously [18].
Confocal and TIRFm analysis of B cells
For confocal analysis, highly purified splenic B cells were stimulated with Alexa Fluor 594 F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgM+IgG (H+L) (115-586-068, Jackson ImmunoResearch) at 37 °C for different time points, as previously described [19]. Then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with pCD19 (ab203615, abcam), pY (05-321, merck-millipore), pBTK (ab52192, abcam), pSHIP-1 (3941S, Cell Signaling Technology), pFOXO1 (9641S, Cell Signaling Technology), pWASP, F-actin, pSTAT1 (9167S, Cell Signaling Technology), pNF-κB (3033S, Cell Signaling Technology), and pSTAT5 (4322S, Cell Signaling Technology) antibodies, followed by Alexa Fluor 488 goat anti-rabbit IgG (A-11008, Thermo Fisher), Alexa Fluor 405 goat anti-mouse IgG (A-31553, Thermo Fisher) or Alexa Fluor 405 goat anti-rabbit IgG. Images were taken using a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope or a Nikon Eclipse Ti-PFS (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). Colocalization using the correlation coefficient was determined by NIS-elements AR 5.01 software.
For TIRFm analysis, purified splenic B cells were activated with an Ag-tethered lipid bilayer at 37 °C for varying lengths of time, as previously described [19]. Then, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with pY, pBTK, pCD19, pSHIP-1, pWASP, F-actin and DOCK8 (11622-1-AP, Proteintech). TIRFm images were acquired using a Nikon TIRFm and interference reflection microscopy (IRM). The area of B-cell spreading using IRM and the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in the contact zone were analyzed using NIS-elements AR 5.01. Each set of data was performed from three independent experiments.
Real-time PCR
The total RNA of purified splenic B cells was extracted using AxyPrep Multisource RNA Kit (AP-MN-MS-RNA-50, Axygen), and reverse transcribed with PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (RR047A, Takara). Then the synthetic cDNA was assessed for the expression of transcription levels of different genes with SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM (RR420A, Takara) on a StepOne Real-Time PCR System (Alllied Biosystems). The Ct value (cycle threshold) was used to assess the gene expression by the 2−ΔΔct method. Fold amplification was normalized by GAPDH and the appropriate primer sequences for the target genes are as follows:
cd19 5′ primer: ggacagtgaacgtggaggat and 3′ primer: gggcacatacaggctttgtt
gapdh 5′ primer: ggtgaaggtcggtgtgaacg and 3′ primer: ctcgctcctggaagatggtg
Immunoblot analysis
For immunoblot analysis, purified B cells were activated with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig (M + G) at 10 μg/ml plus streptavidin (sAg) at 20 μg/ml at 37 °C for varying times. For CCL2-CCR2 binding analysis, purified B cells were incubated with anti-CCR2 antibody at 1 μg/2 × 106 cell with or without F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig (M + G) at 10 μg/ml for 30 min on ice, and then added goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) (A-11008, Thermo Fisher) at 5 μg/2 × 106 cell with or without streptavidin at 20 μg/ml on ice for 10 min, and then activated at 37 °C for 5 min. Then cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (P0013B, Beyotime) containing protease inhibitor cocktail (G2006, Servicebio), NaF (1 M, G2007-1, Servicebio), and Na3VO3 (100Mm, G2007-1, Servicebio). The cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by western blotting and probed for anti-pCD19, anti-pY, anti-pBTK, anti-BTK (8547S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pSHIP-1, anti-SHIP-1 (2728S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pFOXO1 (9461S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-FOXO1 (2880S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pPI3K (4228S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-PI3K (4292S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pAKT (4060 L, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-AKT (9272S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pS6 (4856S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-S6 (2217S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pmTOR (5536S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-mTOR (2983S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pEzrin (3726S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-DOCK8, anti-pWASP, anti-WASP (sc-13139, Santacruz), anti-pMST1 (3681S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-MST1 (PA5-22015), anti-pSTAT1, anti-STAT1 (14994S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pSTAT5, anti-STAT5 (ab194898, abcam), anti-pIKKB (2697S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-IKKB (8943S, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-pNF-κB, anti- NF-κB (4764S, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-pPKC-β (ab194749, abcam). Loading was normalized by using anti-β-actin (60008-1-IG-10, proteintech). Immunoreactive bands were captured with the ChemiDoc™XRS + imaging systems (Bio-Rad).
Treatment with rapamycin, XMU-MP-1, fluradine or bindarit inhibitor in vivo or in vitro
WT and Ccl2 KO mice were injected intraperitoneally with vehicle (0.25% PEG, 0.25% Tween-80) or 2 mg/kg of rapamycin (HY-10219, MedChem Express) every other day for 28 days. Splenic B cells were pretreated with 20 nM rapamycin, 3 μM XMU-MP-1 (T4212, TargetMol) or 5 μg/ml fluradine (T1038, TargetMol) at 37 °C for 2 h, or 100 μM Bindarit (HY-B0498, MedChem Express) at 37 °C for 3 h before incubating with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig (G + M).
Seahorse analysis
For oxygen consumption rates and extracellular acidification rates, purified splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were pre-stimulated with 10 μg/ml LPS (L2880, Sigma) for 1 h and detected in XF medium under basal conditions and in response to oligomycin at 1.5 μM (abs42024304, Absin), fluoro-carbonylcyanide phenylhydrazone (FCCP) at 1 μM (C2920, Sigma) and rotenone at 500 nM (R8875, Sigma) plus antimycin A at 1 μM (abs42013402, Absin) using an XF-24.
Calcium flux
For calcium flux analysis, purified splenic B cells were washed with calcium free D-Hank’s solution (PYG0079, BOSTER), and incubated with 0.5 μM Fluo-4 AM (S1060, Beyotime) in D-Hank’s solution at 37 °C for 25 min. After loading, cells were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min to ensure complete conversion of Fluo-4 AM to Fluo-4, while incubating the anti-B220 as well. After washing, a baseline of fluorescence was measured for 30 s, then cells were stimulated with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig(M + G) and fluorescence intensity were monitored for 300 s using a LSRII flow cytometer. Data were analyzed with FlowJo 7.6 software.
Cell differentiation and proliferation
For PC differentiation assay in vitro, purified B cells were cultured in 96-well plates for 96 h in 1640 medium (Gibco, C11875500BT) containing 10% FBS (Gibco, 10091-148), 10 μM HEPES (Gibco, 1804629) and 50 μM β-mercaptoethanol (M2650, Sigma), and stimulated with 10 μg/ml of LPS. For B-cell proliferation analysis, purified B cells were pre-labeled with 5 μM Cell Trace Violet (C34557, Thermo Fisher) and then cultured in 5 μg/ml LPS with or without 100 μM Bindarit for 72 h.
Bone marrow chimeras
For chimera analysis, BM cells (5 × 106) from WT or Ccl2 KO (CD45.2+) mice were mixed with that of C57BL/6J (CD45.1+) mice at a proportion of 1:1 and then transferred intravenously into 6 weeks old female irradiated (7 Gy) C57BL/6J (CD45.1+) recipients randomly. Eight weeks after the transfer, recipients were euthanized, and B cells analyzed by flow cytometry.
Statistical analysis
Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was carried out when comparing between two groups. Multiple t test was carried out when comparing between more than two groups. Statistical significance was performed by t tests or multiple t tests using Prism 7.0 (GraphPad) software. Significance was defined as *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
Results
CCL2 is important for the development of peripheral B cells, but not bone marrow B cells
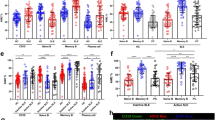
First, we examined the expression of CCL2 in BM and splenic B cells, and found that CCL2 expression has subtle difference in each subpopulation of WT BM and splenic B cells (Fig. S1A, B). To study the effects of CCL2 deficiency on BM and peripheral B-cell development, we examined the BM subpopulations firstly, and found that the majority of the subsets were normal except for the increased percentage and number of late-pre B cells (Fig. 1A–C), suggesting only a mild effect of CCL2 on the development of BM B cells. And then we found that the percentage and number of FO, T1, and T2 B cells in splenic B cells were not altered in Ccl2 KO mice (Fig. 1D–G). The percentage and number of MZ B cells was decreased in KO mice (Fig. 1H, I), but that of GC B cells was increased in Ccl2 KO mice (Fig. 1J, K), which was shown to be immune cell intrinsic by using CD45.1 and CD45.2 BM mixed chimera mice (Fig. S1C, D). Furthermore, the percentage of B1a cells was decreased, yet the number of B1a cells was increased (Fig. 1L, M). However, the percentage and number of B1b cells was increased (Fig. 1L, N). Furthermore, the increased GC B cells indicated development of Spt-GCs and autoimmune phenotype [20]. Indeed, as expected for systemic autoimmunity, we found that the glomeruli of the Ccl2 KO mouse kidney contained prominent IgG and complement deposits and that there was an increase in anti-dsDNA antibody levels in the KO mice (Fig. 1O–Q, S1E). Next, we examined the expression of T-bet, which is essential for the formation of Spt-GCs by B cells upon stimulation with IgM. T-bet expression was enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells upon soluble antigen (sAg) stimulation, which was in accordance with the increase of Spt-GCs (Fig. S1F). In addition, we examined whether CCL2 deficiency affects the development and differentiation of T cells. We found that there was no significant difference in the percentage of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in thymus and LN of WT and Ccl2 KO mice, but the percentage of CD8+ T cells in spleen was slightly increased in KO mice (Fig. S2A, C, D). The percentage of CD4+ Foxp3+ Tregs and the levels of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A, and IL-2 produced by CD4+T cells were not alerted in thymus, spleen, and LN in KO mice (Figs. S2B, E, S3A–H). Finally, we examined whether the CCL2 deficiency affects the regulatory B cells in KO mice, and there was no significant difference between WT and KO mice (Fig. S3I, J). All of these results suggest that CCL2 is essential for maintaining the homeostasis of peripheral B cells and controlling the peripheral autoimmunity.
A–C Flow cytometry analysis of pre-pro (A), pro (B), early-pre (C), late-pre (D), immature (E), and recirculating mature (F) B-cell subsets of BM cells obtained from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 7). Shown are representative dot plots and statistics of the average percentages (±SD) and total cell number of the subpopulations of BM cells. D–K Flow cytometry analysis of follicular (FO), transitional 1 (T1), transitional 2 (T2), marginal zone (MZ), and germinal center (GC) B cells in splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 7). Shown are representative dot plots and average percentages (±SD) and numbers of subpopulations in spleens. L–N Flow cytometry analysis of B1a and B1b cell subsets of peritoneal B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 5). Shown are representative dot plots and average percentages (±SD) and numbers of subpopulations in peritoneal B cells. O Immunofluorescent analysis of IgG deposits in kidney sections. Shown are representative glomeruli using a ×60 objective. Scale bar, 10 μm. P Hematoxylin and eosin staining of kidney from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 6). Shown are representative images using a ×60 objective. Scale bar, 25 μm. Q Quantification by ELISA of the level of anti-dsDNA antibody in the serum of WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 13). Dots represent individual mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
CCL2 negatively regulates the proximal BCR signaling
Increased development of Spt-GC B cells indicates there may be enhanced antigenic BCR signaling. Thus, we investigated whether the deficiency of CCL2 affects BCR signaling by examining the upstream BCR signaling molecule, CD19. We found that the colocalization between activated CD19 (pCD19) and the BCR following sAg stimulation was significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells at 5 and 10 min (Fig. 2A, B). The levels of pCD19 were increased in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 2C). The increased pCD19 was not due to increased expression of CD19, as mRNA and protein levels in the Ccl2 KO B cells were comparable to that of WT (Fig. 2D, E). This suggests that the loss of CCL2 affects the spatiotemporal organization and activation levels of CD19. We then examined total levels of BCR signaling, phosphotyrosine proteins (pY). Additionally, activated BTK (pBTK), the immediate downstream signaling molecule of CD19, as well as the activation of SHIP-1, a proximal negative regulator of BCR signaling, were examined. The colocalization of pY, pBTK, or pSHIP-1 with the BCR was significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 2F–J). Furthermore, the levels of pY, pBTK, and pSHIP-1 were significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells upon antigenic stimulation (Fig. 2K, L). To further determine whether the effect of CCL2 deficiency on BCR signaling is immune cell intrinsic, we isolated CCL2 deficient B cells mature in WT recipient and examined the BCR downstream signaling. We found that the levels of pBTK were increased in CD45.2+ B220+ Ccl2 KO B cells upon antigenic stimulation (Fig. S4A). As such significant changes in B cells of Ccl2 KO mice, whether similar results can be achieved using CCL2 inhibitor in vitro experiments. To explore this, we examined the activation of BTK of WT B cells in presence of CCL2 inhibitor-Bindarit, following sAg stimulation. We found that the levels of pBTK were increased in WT B cells treated with Bindarit (Fig. S4B), indicating that the CCL2 negatively regulates the BCR signaling. Finally, we examined the calcium flux as a functional readout for BCR signaling and found that the calcium level was increased in Ccl2 KO B cells upon sAg stimulation (Fig. 2M). Similarly, the activation of PKC-β, which requires cytosolic calcium (Ca2+) for their activity, was slightly increased in KO B cells (Fig. 2N). Taken together, these results suggest that CCL2 negatively regulates proximal BCR signaling.
A, B Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were stimulated with AF594 F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgG + IgM (10 μg/ml), then fixed, permeabilized, and stained for pCD19. The colocalization between pCD19 and the BCR was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. C Immunoblot of pCD19 levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig(M + G) plus streptavidin (sAg) for 0, 5,10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. D RT-PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of Cd19 in purified B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 3). E Flow cytometry analysis of the MFI of CD19 in B220+ B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 12). F–J Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were stimulated with AF594 F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgG + IgM (10 μg/ml), then fixed, permeabilized, and stained for pY, pBTK, or pSHIP-1. The colocalization of pY, pBTK, or pSHIP-1 with the BCR was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Images were captured using a Zeiss confocal fluorescence microscope and analyzed using the NIS-elements AR 5.01. Scale bars, 2.5 μm. K, L Immunoblot of pY, pBTK, BTK, pSHIP-1, and SHIP-1 levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig(M + G) plus streptavidin (sAg) for 0, 5, 10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. M Ca2+ flux in splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with 10 μg/ml biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig(M + G). Data are representative of three independent experiments. N Immunoblot of pPKC-β levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with biotin-conjugated F(ab′)2 anti-mouse Ig(M + G) plus streptavidin (sAg) for 0, 5, 10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
CCL2 deficiency regulates the peripheral B-cell differentiation by enhancing the PI3K-AKT-mTORC1 mediated metabolic signaling pathway
SHIP reduces PI3K activity by hydrolyzing PIP3 into PIP2 while PI3K initiates the AKT-mTORC1 pathway [21, 22]. Thus, we examined mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling pathways mediated by PI3K. Surprisingly, the activation of PI3K was increased in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 3A). Next, the activation of mTORC1 and mTORC2 signaling, pAKT, pS6 and pmTOR, were increased in Ccl2 KO B cells upon stimulation (Fig. 3A). Meanwhile, the levels of pPI3K, pAKT and pS6 were increased in WT B cells treated with Bindarit (Fig. S5A). We then examined the downstream transcription factor of mTORC2 signaling, FOXO-1. Interestingly, the colocalization between pFOXO-1 and the BCR was significantly reduced in Ccl2 KO B cells at all time points examined. However, the levels of pFOXO-1 were enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells upon stimulation (Fig. 3B–D). In order to examine whether CCL2 regulates the peripheral B-cell differentiation via mTORC1 activity, Ccl2 KO mice were fed rapamycin for 28 days. To guarantee the effect of rapamycin treatment in vivo, we examined the activity of S6 in B cells of Ccl2 KO mice treated with rapamycin. Interestingly, we found that the phosphorylation of S6 was abolished (Fig. 3E), and the percentage of MZ and GC B cells in Ccl2 KO mice treated with rapamycin was restored to the degree of WT mice (Fig. 3F–I). Mechanistically, rapamycin treatment of Ccl2 KO B cells in vitro restored the activation of BCR signaling molecules- BTK, SHIP-1, PI3K, S6, AKT, and mTOR to the degree of WT B cells (Fig. 3J). Indeed, the levels of pS6 were also decreased in WT B cells treated with rapamycin upon antigenic stimulation (Fig. S5B). These results suggest that CCL2 regulates the peripheral B-cell differentiation via mTORC1 activity. We then examined cell metabolism, which is highly correlated with mTORC activity. We found that both basal and maximal rates of respiration were higher in Ccl2 KO B cells compared to WT B cells, which is consistent with the increased mTORC activity in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 3K). Furthermore, in order to assess whether the increased metabolic activity has the biological significance, we examined the proliferation of Ccl2 KO B cells stimulated with LPS. We found that Ccl2 KO B cells proliferated more extensively than WT B cells (Fig. 3L). Similarly, the WT B cells treated with CCL2 inhibitor also proliferated more extensively in the presence of LPS stimulation than that of WT B cells (Fig. S5C). These results imply that CCL2 inhibits the differentiation of MZ and GC B cells via downregulating the PI3K-AKT-mTORC1 mediated metabolic signaling pathway.
A, B Western blot of pPI3K (p85), PI3K, pAKT, AKT, pS6, S6, pmTOR, mTOR, pFOXO1, and FOXO1 levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with sAg for 0, 5, 10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. C, D Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were stimulated with 10 μg/ml F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgG + IgM, then fixed, permeabilized and stained for pFOXO1. The colocalization between pFOXO1 and the BCR was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Images were captured using a Zeiss confocal fluorescence microscope. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. E Splenic B cells from 8-week-old WT and Ccl2 KO mice were treated with vehicle or rapamycin for 28 days and stimulated with sAg. The levels of pS6 were detected by western blotting. F–I Splenic lymphocytes from WT and Ccl2 KO mice (n = 4) were treated with vehicle or rapamycin for 28 days, and then analyzed for MZ and GC B cells by flow cytometry. Shown are representative dot plots and the average percentages (±SD). J Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were pretreated with 20 nM rapamycin for 2 h, stimulated with sAg, and then pBTK, pSHIP-1, pPI3K, pS6, and pmTOR levels were detected by western blotting. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments (K) OCR measurements from splenic B cells of WT and Ccl2 KO mice responding to the inhibitors: oligomycin, FCCP and rotenone plus antimycin. L Proliferation of purified splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice at day 3 after stimulation with LPS (10 μg/ml). Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
Loss of CCL2 enhances the accumulation of F-actin mediated by the MST1-mTORC1-DOCK8-WASP axis
Previous research has shown that the inhibition of cortactin phosphorylation attenuates CCL2-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell G-actin polymerization, F-actin stress fiber formation, and migration [23]. To study the correlation between CCL2 and actin in B cells, WT and Ccl2 KO B cells were examined for activated WASP cellular location and F-actin reorganization. Interestingly, we found that the colocalization between pWASP and BCR was not altered, but that between F-actin and BCR was significantly increased at 10 and 30 min (Fig. 4A–C). Additionally, we found that pWASP levels were enhanced (Fig. 4D, E), which correlated with increased actin accumulation (Fig. 4F). And WT B cells treated with CCL2 inhibitor showed increased pWASP levels (Fig. S6A). However, we did not observe obvious differences for the levels of pEzrin between WT and Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 4D). The MST1-DOCK8-WASP axis is involved in actin reorganization [24, 25]. Thus, we found that the levels of pMST1 and DOCK8 were enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells upon antigenic stimulation (Fig. 4D). To further pursue the underlying mechanism of whether CCL2 regulates BCR signaling through the MST1-DOCK8-WASP axis, we treated Ccl2 KO B cells in vitro with MST1 inhibitor, XMU-MP-1, and found the levels of pBTK, pSHIP-1, pPI3K, pFOXO-1, pmTOR, DOCK8, and pWASP in Ccl2 KO B cells treated with XMU-MP-1 were all restored to the degree of WT B cells (Fig. 4G). Thus, we examined whether the XMU-MP-1 treatment has the same effect on WT B cells. We found that the levels of pAKT, pS6, and pFOXO1 were decreased in WT B cells treated with XMU-MP-1 (Fig. S6B). mTORC1 is downstream of MST1, so we examined whether the inhibition of mTORC1 in Ccl2 KO B cells also rescues the DOCK8-WASP axis. Interestingly, we found that the levels of DOCK8 and pWASP in Ccl2 KO B cells treated with rapamycin were rescued to the degree of WT B cells (Fig. 4H). Meanwhile, the levels of pWASP in WT B cells treated with rapamycin were also decreased (Fig. S6C). These results suggest that CCL2 regulates BCR signaling and DOCK8-WASP mediated actin reorganization via MST1-mTORC1. Next, we examined whether loss of CCL2 can affect CCR2 expression in B cells and result in the changes of MST1/mTORC1 and MST1-DOCK8-WASP signaling pathways. We found that the level of CCR2 was not different between WT and KO B cells (Fig. S6D), suggesting loss of CCL2 did not affect the expression of CCR2 in B cells and result in the changes of MST1/mTORC1 and MST1-DOCK8-WASP signaling pathways. To further investigate whether the intrinsic CCL2 signaling is involved in PI3K-AKT-mTOR, we used CCR2 antibody to mimic the CCL2 binding to CCR2 and stimulate B cells together with sAg. Interestingly, we found the levels of pS6, pAKT and pSTAT5 were decreased in CCR2 and BCR activation group compared to BCR activation only (Fig. 4I, J), suggesting that CCL2 signaling is involved in downregulating the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. The expression levels of CCL2 were not altered after 12 h of sAg stimulation in WT B cells, which excludes the effect of CCL2 expression on the BCR signaling upon antigenic stimulation (Fig. S6E).
A–C Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were stimulated with 10 μg/ml AF594 F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgG + IgM, fixed, permeabilized, and stained with pWASP and F-actin. The colocalization between pWASP or F-actin and the BCR was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Images were captured using a Zeiss confocal fluorescence microscope. Scale bars, 2.5 μm. D Western blots of pWASP, WASP, pEzrin, pMST1, MST1, and DOCK8 levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated with sAg for 0, 5, 10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments (E, F) Splenic B cells were pre-incubated with B220, followed by stimulation with sAg for 0, 5, 10, and 30 min. After fixation and permeabilization, cells were stained with pWASP and F-actin and analyzed by flow cytometry. The MFI of pWASP and F-actin in B220+ B cells was quantified by FlowJo 10 software. G, H Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were pretreated with 3 μM XMU-MP-1 or 20 nM rapamycin for 2 h, then stimulated with sAg, and the pBTK, pSHIP-1, pPI3K, pFOXO1, pmTOR, DOCK8, and pWASP levels were detected by Western blotting. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments (I) Immunoblot of pS6 in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated by sAg with or without anti-CCR2 for 0, 5, and 30 min. J Immunoblot of pAKT and pSTAT5 levels in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice stimulated by sAg with or without anti-CCR2 for 5 min. Data are representative of three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001.
The enhanced actin in Ccl2 KO B cells correlates with the increased BCR clustering and positive signalosome recruitment
To investigate the loss of CCL2 on the early activation of B cells, including BCR clustering and signalosome accumulation, we used total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFm) to observe B cells stimulated with membrane-tethered antigens (mAg). We found that B-cell spreading and BCR clustering in the B-cell contact zone was significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 5F, G). Additionally, the recruitment of pY, pCD19, pBTK, and pSHIP-1 in signalosomes of the B-cell contact zone was significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 5A, C, D, H–K). Consistent with the established model for B-cell actin remodeling during BCR activation, the recruitment of pWASP, DOCK8, and F-actin was also significantly increased in the contact zone of Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 5B, E, L–N). Altogether, these results indicate that the deficiency of CCL2 increases the recruitment of F-actin mediated by WASP at the plasma membrane, which correlates with the increased BCR clustering and the enhanced BCR signaling.
A–E Splenic B cells from WT and KO mice were incubated with AF546–mB-Fab–anti-Ig tethered to lipid bilayers for 1, 3, 5, and 7 min, then fixed, permeabilized, and stained for pY/pBTK, pWASP/F-actin, pCD19, pSHIP-1, and DOCK8. Shown are representative images captured using Nikon TIRFm from three independent experiments. Scale bars, 2.5 μm. F–N The B-cell area in the contact zone, the MFI of BCR, and the MFI of pY, pBTK, pWASP, F-actin, pCD19, pSHIP-1, and DOCK8 in the contact zone were quantified using NIS-Elements AR 5.0.1 software. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
CCL2 negatively regulates the activation of STAT1, which in turn offers feedback to the BCR signaling
To determine the downstream transcriptional effectors that are affected by the loss of CCL2, we examined the activation of STAT1, STAT5, and NF-κB, and found that the colocalization between BCR and pSTAT1 or pSTAT5 was significantly increased at 5 and 10 min in Ccl2 KO B cells upon sAg stimulation (Figs. 6A, B, S7A, B). Concurrently, the levels of pSTAT1 and pSTAT5 were also significantly enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 6E). Interestingly, we found that the colocalization between BCR and pNF-κB was significantly increased in Ccl2 KO B cells upon sAg stimulation (Fig. 6C, D). The levels of pIKKB and pNF-κB were also significantly enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. 6E). To identify which transcriptional factor is essential for the regulation of BCR signaling, we used different inhibitors for the transcriptional factors. We found that the treatment of Ccl2 KO B cells with STAT1 inhibitor restored the degree of BCR signaling to that of WT, including the levels of pBTK, pSHIP-1, pPI3K, pAKT, pS6, pmTOR, pFOXO-1, pMST1, DOCK8, pWASP, pSTAT5, and pNF-kB (Fig. 6F). As with the WT B cells, the pPI3K and pS6 signals in WT B cells treated with STAT1 inhibitor were also reduced (Fig. S7C). To further confirm that MST1-mTORC1-STAT1 regulates BCR signaling, the Ccl2 KO B cells treated with MST1 or mTORC1 inhibitor upon sAg stimulation were detected. We found that the levels of pSTAT1, pSTAT5, and pNF-kB were rescued to the degree of WT B cells after XMU-MP-1 or rapamycin treatment (Fig. 6G, H). Similarly, the signal of pNF-κB in WT B cells treated with MST1 inhibitor was also reduced (Fig. S7D). These results suggest that CCL2 couples with MST1-mTORC1-STAT1 to regulate BCR signaling.
A–D Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were stimulated with 10 μg/ml AF594 F(ab′)2 goat anti-mouse IgG + IgM, fixed, permeabilized, and stained for pSTAT1 or pNF-κB. The colocalization between pSTAT1/pNF-κB and the BCR was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Images were captured using a Nikon confocal fluorescence microscope. Scale bars, 2.5 μm. E Immunoblot showing the levels of pSTAT1, STAT1, pSTAT5, STAT5, pIKKB, IKKB, pNF-κB, and NF-κB in B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice that were stimulated with sAg for 5, 10, and 30 min. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. F–H Splenic B cells from WT and Ccl2 KO mice were pretreated with 3 μM XMU-MP-1, 5 μg/ml Fluradine, or 20 nM rapamycin for 2 h, stimulated with sAg, and then levels of the indicated proteins were detected by western blotting. Shown are representative blots from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
CCL2 deficiency leads to decreased plasma cell and antibody production in the T-dependent immune response
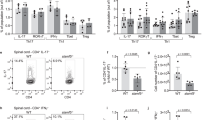
To determine the effect of CCL2 deficiency on the humoral immune response, mice were immunized with NP-KLH to examine the T-cell-dependent immune response. After immunization, the percentages of FO B cells in Ccl2 KO mice were significantly decreased compared to WT mice (Fig. 7A, B), the percentage of T1 B cells was increased in Ccl2 KO mice compared to WT mice (Fig. 7A, C), and the percentage and number of T2 B cells was increased in Ccl2 KO mice compared to WT mice (Fig. 7A, D). But the numbers of FO and T1 B cells were increased both for WT and Ccl2 KO mice after immunization compared to before immunization (Fig. 7B, C). The percentage of MZ and GC B cells was decreased after immunization in Ccl2 KO mice compared to WT mice (Fig. 7E–H). The number of MZ B cells was increased in WT and Ccl2 KO mice after immunization compared to before immunization (Fig. 7F). The percentage of PC, PBC, and memory B-cell (MBC) were decreased in Ccl2 KO mice compared to WT mice (Fig. 7I–M). Furthermore, we examined the splenic architecture in WT and Ccl2 KO mice after immunization by HE staining and immunofluorescence staining, and found that the size of the follicular area and GCs in Ccl2 KO mice were smaller than that of WT mice (Fig. 7N, O). Finally, we found that the levels of NP-specific IgM and IgG1 were both decreased in Ccl2 KO mice (Fig. 7P). Because the Ccl2 KO B cells tended to have reduced PC formation, a PC differentiation assay was performed in vitro, whereby naïve B cells were stimulated with LPS. We found decreased percentages of PC and PBC for Ccl2 KO B cells (Fig. S8A–C). Altogether, these results suggest that CCL2 is important for eliciting the humoral immune response after NP-KLH immunization.
Eight weeks old male WT and Ccl2 KO mice were immunized by intraperitoneal injection with 50 μg of NP-KLH precipitated in adjuvant, and then sacrificed 2 weeks later. A–M Flow cytometry analysis of B-cell subsets FO, T1, T2 MZ, GC, PC, PBC, and MBC B cells from mouse spleen. Shown are representative dot plots from three independent experiments and the statistics of the average percentages (±SD) and total cell number of the subpopulations of splenic B cells. Non nonimmunized, IM immunized. (n = 4). N Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin-stained spleens from immunized WT and Ccl2 KO mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. O Immunofluorescence staining of splenic sections from immunized WT and Ccl2 KO mice. Shown are representative GC B cells using CD4 (red), IgD (blue), and GL-7 (green). Scale bar, 10 μm. P ELISA was used to quantify NP-specific NP-IgM and NP-IgG1 from NP-KLH immunized mice (n = 4). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.
Discussion
As a chemokine, the role of CCL2 in T-lymphocyte function has been studied extensively. However, its role in B-cell functions has not been addressed, likely because of the lower expression in B cells. This is the first report investigating the role of CCL2 in BCR signaling and B-cell differentiation. Interestingly, we found that BCR signaling was enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells upon antigenic stimulation, which contributes to the reduction of MZ B cells and the increase of GC B cells and formation of Spt-GCs. Moreover, we found that the metabolism signaling axis-PI3K-mTOR-AKT and actin reorganization axis-MST1-DOCK8-WASP were also enhanced in Ccl2 KO B cells, as well as the transcriptional factors-STAT1, STAT5 and NF-kB. Excitingly, the inhibition of mTORC1, MST1 and STAT1 all restored the BCR signaling to normal levels. Given that MST1 is upstream of mTOR, we concluded that CCL2 regulates the BCR signaling and B-cell differentiation via the MST1-mTOR-STAT1 axis.
In SLE patients, the reduction of CCL2 in MSC fails to inhibit the differentiation, proliferation, and antibody secretion of B cells. This explains the underlying molecular mechanism of the development of autoimmune disease in SLE patients. But whether the intrinsically impaired B-cell function also accounts for the autoimmune disease is unknown. We have shown that CCL2 is a negative regulator of BCR signaling. The Ccl2 KO mice have increased spontaneous formation of GCs and increased T-bet expression. These also contribute to the autoimmune phenotype in SLE patients. The Ccl2 KO in mice is a germline deletion and it is highly possible that multiple factors contribute to the autoimmune phenotype. Our research has established the intrinsic role of Ccl2 KO B cells in causing the autoimmune activity.
The role of MST1 in autoimmunity has been established, whereby deficiency of MST1 in CD4+ T cells or Tregs prevents immune cell inhibition and induces autoimmunity. Surprisingly, MST1 deficiency in B cells causes a reduced response including decreased BCR signaling, B-cell clustering and antibody secretion. However, the deficiency of CCL2 in B cells enhances the activation of MST1, which may cause the autoimmune phenotype seen in B cells. Additionally, the regulation of MST1 by CCL2 has not been investigated before, although the correlation between CCL2 and actin reorganization has been previously reported. Therefore, our study has identified an upstream factor of CCL2 to regulate the DOCK8-WASP-actin reorganization pathway. We found the loss of CCL2 induces higher activation of mTOR in B cells, which also contributes to the autoimmunity in B cells and reduction of MZ B-cell differentiation. Lastly, we have identified an increase in transcriptional factors such as STAT1, STAT5, NF-kB in CCL2 deficient B cells. The enhanced activation of STAT1 causes increased expression of T-bet, which induces autoimmunity. Therefore, our study has established that CCL2 affects multiple factors to regulate autoimmunity. In summary, the signaling aixs- CCL2-MST1-mTOR-STAT1 controls B-cell autoimmunity.
CCL2 deficiency caused upregulation of BCR signaling. However, the humoral immune response was reduced in Ccl2 KO mice following immunization with NP-KLH, including reduction of PC, PBC, and MBC, as well as NP-specific IgM and IgG1 antibody production. Our previous research showed that the optimal BCR signaling is required for the humoral immune response [26, 27]. Higher or lower BCR signaling may induce a reduced humoral immune response. Additionally, some proportion of the IgG antibodies are autoimmune antibodies, which further reduces the effective antibodies in Ccl2 KO mice. To exclude the effects of other immune cells, such as T-cell lineages, it would be ideal to use CCL2 flox mice crossed with CD19cre or Mb1cre mice to obtain B-cell specific Ccl2 KO mice. This would be more precise in evaluating the effect of CCL2 on the humoral immune response. Another alternative is to adoptively transfer a mixture of BM B cells from Ccl2 KO mice with WT mice into μMT mice.
Overall, our study has dissected the intrinsic role of CCL2 in B cells and autoimmunity. Additionally, we have established the signaling axis- CCL2-MST1-mTOR-STAT1 as a regulatory pathway for B-cell autoimmunity and peripheral B-cell differentiation. The multiple layers of control over autoimmunity by CCL2 can provide more targets for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, such as SLE.
References
Carr MW, Roth SJ, Luther E, Rose SS, Springer TA. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:3652–6.
Xu LL, Warren MK, Rose WL, Gong W, Wang JM. Human recombinant monocyte chemotactic protein and other C-C chemokines bind and induce directional migration of dendritic cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1996;60:365–71.
Yoshimura T, Yuhki N, Moore SK, Appella E, Lerman MI, Leonard EJ. Human monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). Full-length cDNA cloning, expression in mitogen-stimulated blood mononuclear leukocytes, and sequence similarity to mouse competence gene JE. FEBS Lett. 1989;244:487–93.
Furutani Y, Nomura H, Notake M, Oyamada Y, Fukui T, Yamada M, et al. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for human monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;159:249–55.
Craig MJ, Loberg RD. CCL2 (Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1) in cancer bone metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:611–9.
Che N, Li X, Zhang L, Liu R, Chen H, Gao X, et al. Impaired B cell inhibition by lupus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells is caused by reduced CCL2 expression. J Immunol. 2014;193:5306–14.
Kok SH, Hong CY, Kuo MY, Wang CC, Hou KL, Lin YT, et al. Oncostatin M-induced CCL2 transcription in osteoblastic cells is mediated by multiple levels of STAT-1 and STAT-3 signaling: an implication for the pathogenesis of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1451–62.
Park CY, Heo JN, Suk K, Lee WH. Sodium azide suppresses LPS-induced expression MCP-1 through regulating IkappaBzeta and STAT1 activities in macrophages. Cell Immunol. 2017;315:64–70.
Lee SY, Moon SJ, Kim EK, Seo HB, Yang EJ, Son HJ, et al. Metformin suppresses systemic autoimmunity in roquin(san/san) mice through inhibiting B cell differentiation into plasma cells via regulation of AMPK/mTOR/STAT3. J Immunol. 2017;198:2661–70.
Torigoe M, Iwata S, Nakayamada S, Sakata K, Zhang M, Hajime M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming commits differentiation of human CD27(+)IgD(+) B cells to plasmablasts or CD27(−)IgD(−) cells. J Immunol. 2017;199:425–34.
Riverso M, Kortenkamp A, Silva E. Non-tumorigenic epithelial cells secrete MCP-1 and other cytokines that promote cell division in breast cancer cells by activating ERalpha via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;53:281–94.
Shi H, Liu C, Tan H, Li Y, Nguyen TM, Dhungana Y, et al. Hippo kinases Mst1 and Mst2 sense and amplify IL-2R-STAT5 signaling in regulatory T cells to establish stable regulatory activity. Immunity. 2018;49:899–914.e6.
Salojin KV, Hamman BD, Chang WC, Jhaver KG, Al-Shami A, Crisostomo J, et al. Genetic deletion of Mst1 alters T cell function and protects against autoimmunity. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e98151.
Bai X, Huang L, Niu L, Zhang Y, Wang J, Sun X, et al. Mst1 positively regulates B-cell receptor signaling via CD19 transcriptional levels. Blood Adv. 2016;1:219–30.
Fielhaber JA, Han YS, Tan J, Xing S, Biggs CM, Joung KB, et al. Inactivation of mammalian target of rapamycin increases STAT1 nuclear content and transcriptional activity in alpha4- and protein phosphatase 2A-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:24341–53.
Chao Y, Wang Y, Liu X, Ma P, Shi Y, Gao J, et al. Mst1 regulates glioma cell proliferation via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Neurooncol. 2015;121:279–88.
Sharma S, Orlowski G, Song W. Btk regulates B cell receptor-mediated antigen processing and presentation by controlling actin cytoskeleton dynamics in B cells. J Immunol. 2009;182:329–39.
Jing Y, Kang D, Liu L, Huang H, Chen A, Yang L, et al. Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 2 couples with lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 to regulate expression of CD21 and B-cell differentiation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2019;144:1377–90.e4.
Huang L, Zhang Y, Xu C, Gu X, Niu L, Wang J, et al. Rictor positively regulates B cell receptor signaling by modulating actin reorganization via ezrin. PLoS Biol. 2017;15:e2001750.
Domeier PP, Chodisetti SB, Soni C, Schell SL, Elias MJ, Wong EB, et al. IFN-gamma receptor and STAT1 signaling in B cells are central to spontaneous germinal center formation and autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2016;213:715–32.
Marat AL, Wallroth A, Lo WT, Muller R, Norata GD, Falasca M, et al. mTORC1 activity repression by late endosomal phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate. Science. 2017;356:968–72.
Backers K, Blero D, Paternotte N, Zhang J, Erneux C. The termination of PI3K signalling by SHIP1 and SHIP2 inositol 5-phosphatases. Adv Enzym Regul. 2003;43:15–28.
Janjanam J, Chandaka GK, Kotla S, Rao GN. PLCbeta3 mediates cortactin interaction with WAVE2 in MCP1-induced actin polymerization and cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26:4589–606.
Sun X, Wang J, Qin T, Zhang Y, Huang L, Niu L, et al. Dock8 regulates BCR signaling and activation of memory B cells via WASP and CD19. Blood Adv. 2018;2:401–13.
Geng J, Sun X, Wang P, Zhang S, Wang X, Wu H, et al. Kinases Mst1 and Mst2 positively regulate phagocytic induction of reactive oxygen species and bactericidal activity. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:1142–52.
Yang L, Jing YK, Wang WJ, Ying WJ, Lin L, Chang J, et al. DOCK2 couples with LEF-1 to regulate B cell metabolism and memory response. Biochem Bioph Res Commun. 2020;529:296–302.
Li N, Jiang P, Chen A, Luo X, Jing Y, Yang L, et al. CX3CR1 positively regulates BCR signaling coupled with cell metabolism via negatively controlling actin remodeling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77:4379–95.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (1316203 to HM), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682419), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82001656, 31970839, and 31900654), and HUST Academic Frontier Youth Team (2018QYTD10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LY draft the paper. CL designed the study, reviewed, and revised the initial paper. LY, DY, and AC performed the TRIFm experiments. LY, PJ, JL, and XD performed the confocal experiments. LY, NL, YJ, DK, QC, and YH carried out the western blotting. LY, NL, JT, JC, LL, HG, ZL, and QC carried out the flow cytometry assay. LY analyzed the date and generated figures. HM, YC, and LQ, HM, YH, and QG assisted with the paper. All authors approved the final paper as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by J.P. Medema
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Li, N., Yang, D. et al. CCL2 regulation of MST1-mTOR-STAT1 signaling axis controls BCR signaling and B-cell differentiation. Cell Death Differ 28, 2616–2633 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00775-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00775-2
This article is cited by
-
Expression of USP25 associates with fibrosis, inflammation and metabolism changes in IgG4-related disease
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
The mTORC1 pathway participate in hyper-function of B cells in immune thrombocytopenia
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Radix Scrophulariae Extracts Exert Effect on Hyperthyroidism via MST1/Hippo Signaling Pathway
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine (2023)