Abstract
The homeobox gene family encodes transcription factors that are essential for cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation, and its dysfunction is linked to tumor initiation and progression. Sine oculis homeobox (SIX) belongs to the homeobox gene family, with SIX3 being a core member. Recent studies indicate that SXI3 functions as a cancer suppressor or promoter, which is mainly dependent on SIX3’s influence on the signal pathways that promote or inhibit cancer in cells. The low expression of SIX3 in most malignant tumors was confirmed by detailed studies, which could promote the cell cycle, proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis. The recovery or upregulation of SIX3 expression to suppress cancer is closely related to the direct or indirect inhibition of the Wnt pathway. However, in some malignancies, such as esophageal cancer and gastric cancer, SIX3 is a tumor-promoting factor, and repressing SIX3 improves patients’ prognosis. This review introduces the research progress of SIX3 in tumors and gives a comprehensive analysis, intending to explain why SIX3 plays different roles in different cancers and provide new cancer therapy strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar JP. The sine oculis homeobox (SIX) family of transcription factors as regulators of development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:565–83.
Seo HC, Curtiss J, Mlodzik M, Fjose A. Six class homeobox genes in drosophila belong to three distinct families and are involved in head development. Mech Dev. 1999;83:127–39.
Kawakami K, Sato S, Ozaki H, Ikeda K. Six family genes—structure and function as transcription factors and their roles in development. Bioessays. 2000;22:616–26.
Turcu DC, Lillehaug JR, Seo HC. SIX3 and SIX6 interact with GEMININ via C-terminal regions. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2019;20:100695.
Kobayashi M, Nishikawa K, Suzuki T, Yamamoto M. The homeobox protein Six3 interacts with the Groucho corepressor and acts as a transcriptional repressor in eye and forebrain formation. Dev Biol. 2001;232:315–26.
Cheng Q, Ning D, Chen J, Li X, Chen XP, Jiang L. SIX1 and DACH1 influence the proliferation and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating p53. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19:381–90.
Abate-Shen C. Deregulated homeobox gene expression in cancer: cause or consequence? Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:777–85.
Li L, Liang Y, Kang L, Liu Y, Gao S, Chen S, et al. Transcriptional regulation of the Warburg effect in cancer by SIX1. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:368–385. e7
Zhou H, Blevins MA, Hsu JY, Kong D, Galbraith MD, Goodspeed A, et al. Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor that disrupts the SIX1/EYA2 complex, EMT, and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020;80:2689–702.
Oliphant MUJ, Vincent MY, Galbraith MD, Pandey A, Zaberezhnyy V, Rudra P, et al. SIX2 mediates late-stage metastasis via direct regulation of SOX2 and induction of a cancer stem cell program. Cancer Res. 2019;79:720–34.
Hou H, Yu X, Cong P, Zhou Y, Xu Y, Jiang Y. Six2 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell stemness via transcriptionally and epigenetically regulating E-cadherin. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12617.
Sun X, Hu F, Hou Z, Chen Q, Lan J, Luo X, et al. SIX4 activates Akt and promotes tumor angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383:111495.
Zhang B, Shen C, Ge F, Ma T, Zhang Z. Epigenetically controlled Six3 expression regulates glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasion alongside modulating the activation levels of WNT pathway members. J Neurooncol. 2017;133:509–18.
Mo ML, Okamoto J, Chen Z, Hirata T, Mikami I, Bosco-Clément G, et al. Down-regulation of SIX3 is associated with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e71816.
Sun Y, Zheng Y, Wang C, Liu Y. Glutathione depletion induces ferroptosis, autophagy, and premature cell senescence in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:753.
Yu Z, Feng J, Wang W, Deng Z, Zhang Y, Xiao L, et al. The EGFR-ZNF263 signaling axis silences SIX3 in glioblastoma epigenetically. Oncogene. 2020;39:3163–78.
Chen B. A novel long noncoding RNA lncWDR26 suppresses the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through interaction with SIX3. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:688–98.
Yu Z, Sun Y, She X, Wang Z, Chen S, Deng Z, et al. SIX3, a tumor suppressor, inhibits astrocytoma tumorigenesis by transcriptional repression of AURKA/B. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:115.
Du J. Upregulation of sine oculis homeobox homolog 3 is associated with proliferation, invasion, migration, as well as poor prognosis of esophageal cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2019;30:596–603.
Zaimy MA, Saffarzadeh N, Mohammadi A, Pourghadamyari H, Izadi P, Sarli A, et al. New methods in the diagnosis of cancer and gene therapy of cancer based on nanoparticles. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017;24:233–43.
Tsimberidou AM, Fountzilas E, Nikanjam M, Kurzrock R. Review of precision cancer medicine: evolution of the treatment paradigm. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020;86:102019.
Gotwals P, Cameron S, Cipolletta D, Cremasco V, Crystal A, Hewes B, et al. Prospects for combining targeted and conventional cancer therapy with immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:286–301.
Oliver G, Mailhos A, Wehr R, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Gruss P. Six3, a murine homologue of the sine oculis gene, demarcates the most anterior border of the developing neural plate and is expressed during eye development. Development. 1995;121:4045–55.
Granadino B, Gallardo ME, López-Ríos J, Sanz R, Ramos C, Ayuso C, et al. Genomic cloning, structure, expression pattern, and chromosomal location of the human SIX3 gene. Genomics. 1999;55:100–5.
Cheyette BN, Green PJ, Martin K, Garren H, Hartenstein V, Zipursky SL. The Drosophila sine oculis locus encodes a homeodomain-containing protein required for the development of the entire visual system. Neuron. 1994;12:977–96.
Leppert GS, Yang JM, Sundin OH. Sequence and location of SIX3, a homeobox gene expressed in the human eye. Ophthalmic Genet. 1999;20:7–21.
Yang C, Guo Z, Zhao Z, Wei Y, Wang X, Song Y. miR-4306 suppresses proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell by targeting SIX3. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021.
Zhan T, Rindtorff N, Boutros M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36:1461–73.
Reya T, Clevers H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature. 2005;434:843–50.
Tang Q, Chen J, Di Z, Yuan W, Zhou Z, Liu Z, et al. TM4SF1 promotes EMT and cancer stemness via the Wnt/β-catenin/SOX2 pathway in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:232.
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149:1192–205.
Yu F, Yu C, Li F, Zuo Y, Wang Y, Yao L, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:307.
Silva-García O, Valdez-Alarcón JJ, Baizabal-Aguirre VM. Wnt/β-catenin signaling as a molecular target by pathogenic bacteria. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2135.
Wang J, Cai H, Liu Q, Xia Y, Xing L, Zuo Q, et al. Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48:703–18.
Yang S, Liu Y, Li MY, Ng CSH, Yang SL, Wang S, et al. FOXP3 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:124.
Lagutin OV, Zhu CC, Kobayashi D, Topczewski J, Shimamura K, Puelles L, et al. Six3 repression of Wnt signaling in the anterior neuroectoderm is essential for vertebrate forebrain development. Genes Dev. 2003;17:368–79.
Jacobsen A, Bosch LJW, Martens-de Kemp SR, Carvalho B, Sillars-Hardebol AH, Dobson RJ, et al. Aurora kinase A (AURKA) interaction with Wnt and Ras-MAPK signalling pathways in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8:7522.
Kumar R, Balasenthil S, Manavathi B, Rayala SK, Pakala SB. Metastasis-associated protein 1 and its short form variant stimulates Wnt1 transcription through promoting its derepression from Six3 corepressor. Cancer Res. 2010;70:6649–58.
Mazieres J, He B, You L, Xu Z, Jablons DM. Wnt signaling in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2005;222:1–10.
Teng Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Ma D. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;392:373–9.
Laflamme C, Filion C, Bridge JA, Ladanyi M, Goldring MB, Labelle Y. The homeotic protein Six3 is a coactivator of the nuclear receptor NOR-1 and a corepressor of the fusion protein EWS/NOR-1 in human extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas. Cancer Res. 2003;63:449–54.
Hisaoka M, Okamoto S, Yokoyama K, Hashimoto H. Coexpression of NOR1 and SIX3 proteins in extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcomas without detectable NR4A3 fusion genes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004;152:101–7.
Oser MG, Niederst MJ, Sequist LV, Engelman JA. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:e165–72.
Liu S, Tian Y, Zheng Y, Cheng Y, Zhang D, Jiang J, et al. TRIM27 acts as an oncogene and regulates cell proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer through SIX3-β-catenin signaling. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12:25564–80.
Wang T, Du G, Wang D. The S100 protein family in lung cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;520:67–70.
Tan BS, Yang MC, Singh S, Chou YC, Chen HY, Wang MY, et al. LncRNA NORAD is repressed by the YAP pathway and suppresses lung and breast cancer metastasis by sequestering S100P. Oncogene. 2019;38:5612–26.
Kikuchi K, McNamara KM, Miki Y, Iwabuchi E, Kanai A, Miyashita M, et al. S100P and Ezrin promote trans-endothelial migration of triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 2019;42:67–80.
Zimmer DB, Wright Sadosky P, Weber DJ. Molecular mechanisms of S100-target protein interactions. Microsc Res Tech. 2003;60:552–9.
Guo L, Chen S, Jiang H, Huang J, Jin W, Yao S. The expression of S100P increases and promotes cellular proliferation by increasing nuclear translocation of β-catenin in endometrial cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:2102–12.
Shu J, Wang L, Han F, Chen Y, Wang S, Luo F. BTBD7 downregulates E-cadherin and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:5937635.
Manshouri R, Coyaud E, Kundu ST, Peng DH, Stratton SA, Alton K, et al. ZEB1/NuRD complex suppresses TBC1D2b to stimulate E-cadherin internalization and promote metastasis in lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2019;10:5125.
Chae YK, Chang S, Ko T, Anker J, Agte S, Iams W, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signature is inversely associated with T-cell infiltration in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Sci Rep. 2018;8:2918.
Astudillo P. Extracellular matrix stiffness and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in physiology and disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020;48:1187–98.
Liang T, Ye X, Liu Y, Qiu X, Li Z, Tian B, et al. FAM46B inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in prostate cancer through ubiquitination of β-catenin. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50:1–12.
Yin Z, Xu W, Xu H, Zheng J, Gu Y. Overexpression of HDAC6 suppresses tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by inhibition of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:7082–90.
Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;62:50–60.
Xing L, Tang X, Wu K, Huang X, Yi Y, Huan J. TRIM27 functions as a novel oncogene in non-triple-negative breast cancer by blocking cellular senescence through p21 ubiquitination. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:910–23.
Zhang HX, Xu ZS, Lin H, Li M, Xia T, Cui K, et al. TRIM27 mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3441.
Jiang J, Xie C, Liu Y, Shi Q, Chen Y. Up-regulation of miR-383-5p suppresses proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer cells by targeting TRIM27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:595–601.
Makki J. Diversity of breast carcinoma: histological subtypes and clinical relevance. Clin Med Insights Pathol. 2015;8:23–31.
Stewart DJ. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106:djt356.
Cicchini M, Chakrabarti R, Kongara S, Price S, Nahar R, Lozy F, et al. Autophagy regulator BECN1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis driven by WNT1 activation and following parity. Autophagy. 2014;10:2036–52.
Dong B, Yi M, Luo S, Li A, Wu K. RDGN-based predictive model for the prognosis of breast cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9:1–12.
Li DQ, Kumar R. Unravelling the complexity and functions of MTA coregulators in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2015;127:1–47.
Sen N, Gui B, Kumar R. Role of MTA1 in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014;33:879–89.
Fujita N, Jaye DL, Kajita M, Geigerman C, Moreno CS, Wade PA. MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell. 2003;113:207–19.
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Vats P, Su F, Lonigro RJ, Cao X, et al. Activating ESR1 mutations in hormone-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2013;45:1446–51.
Kumar R. Another tie that binds the MTA family to breast cancer. Cell. 2003;113:142–3.
Si W, Huang W, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Liu X, Shan L, et al. Dysfunction of the reciprocal feedback loop between GATA3- and ZEB2-nucleated repression programs contributes to breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2015;27:822–36.
Wang H, Liu Y, Wang J, Xiong B, Hou X. Electrochemical impedance biosensor array based on DNAzyme-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes using Gaussian process regression for Cu(II) and Hg(II) determination. Mikrochim Acta. 2020;187:207.
Hu X, Xiang D, Xie Y, Tao L, Zhang Y, Jin Y, et al. LSD1 suppresses invasion, migration and metastasis of luminal breast cancer cells via activation of GATA3 and repression of TRIM37 expression. Oncogene. 2019;38:7017–34.
Xu HX, Wu KJ, Tian YJ, Liu Q, Han N, He XL, et al. Expression profile of SIX family members correlates with clinic-pathological features and prognosis of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2016;95:e4085.
Liu H, Song Y, Qiu H, Liu Y, Luo K, Yi Y, et al. Downregulation of FOXO3a by DNMT1 promotes breast cancer stem cell properties and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:966–83.
Zhou Z, Li HQ, Liu F. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and their therapeutic potential. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18:2448–57.
Pan Y, Liu G, Zhou F, Su B, Li Y. DNA methylation profiles in cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18:1–14.
Zhang Z, Tang H, Wang Z, Zhang B, Liu W, Lu H, et al. MiR-185 targets the DNA methyltransferases 1 and regulates global DNA methylation in human glioma. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:124.
Pitts TM, Davis SL, Eckhardt SG, Bradshaw-Pierce EL. Targeting nuclear kinases in cancer: development of cell cycle kinase inhibitors. Pharm Ther. 2014;142:258–69.
Pérez-Fidalgo JA, Gambardella V, Pineda B, Burgues O, Piñero O, Cervantes A. Aurora kinases in ovarian cancer. ESMO Open. 2020;5:e000718.
Alafate W, Wang M, Zuo J, Wu W, Sun L, Liu C, et al. Targeting Aurora kinase B attenuates chemoresistance in glioblastoma via a synergistic manner with temozolomide. Pathol-Res Pract. 2019;215:152617.
Gully CP, Velazquez-Torres G, Shin JH, Fuentes-Mattei E, Wang E, Carlock C, et al. Aurora B kinase phosphorylates and instigates degradation of p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:E1513–22.
Lee D-F, Su J, Ang Y-S, Carvajal-Vergara X, Mulero-Navarro S, Pereira CF, et al. Regulation of embryonic and induced pluripotency by aurora kinase-p53 signaling. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11:179–94.
Stupp R, Brada M, van den Bent MJ, Tonn JC, Pentheroudakis G. High-grade glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25:iii93–101.
Carlin D, Sepich D, Grover VK, Cooper MK, Solnica-Krezel L, Inbal A. Six3 cooperates with Hedgehog signaling to specify ventral telencephalon by promoting early expression of Foxg1a and repressing Wnt signaling. Development. 2012;139:2614–24.
He Q, Lin Z, Wang Z, Huang W, Tian D, Liu M, et al. SIX4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating YAP1 and c-MET. Oncogene. 2020;39:7279–95.
Liu X, Xie S, Zhang J, Kang Y. Long noncoding RNA XIST contributes to cervical cancer development through targeting miR-889-3p/SIX1 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020;35:640–9.
Cai B, Li Z, Ma M, Wang Z, Han P, Abdalla BA, et al. LncRNA-Six1 encodes a micropeptide to activate Six1 in Cis and is involved in cell proliferation and muscle growth. Front Physiol. 2017;8:230.
Zhu Y, Wang Y, Xia C, Li D, Li Y, Zeng W, et al. WDR26: a novel Gbeta-like protein, suppresses MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2004;93:579–87.
Goto T, Matsuzawa J, Iemura S, Natsume T, Shibuya H. WDR26 is a new partner of Axin1 in the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2016;590:1291–303.
Smyth EC, Lagergren J, Fitzgerald RC, Lordick F, Shah MA, Lagergren P, et al. Oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017;3:17048.
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY, Yang SL. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37:12061–70.
Zhang L, Tong Z, Sun Z, Zhu G, Shen E, Huang Y. MiR-25-3p targets PTEN to regulate the migration, invasion, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;40:BSR20201901.
Wang T, Wang J, Ren W, Liu ZL, Cheng YF, Zhang XM. Combination treatment with artemisinin and oxaliplatin inhibits tumorigenesis in esophageal cancer EC109 cell through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer. 2020;11:2316–24.
Zhang LN, Zhao L, Yan XL, Huang YH. Loss of G3BP1 suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:20469–84.
Shorning BY, Dass MS, Smalley MJ, Pearson HB. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and prostate cancer: at the crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:4507–53.
Hemmatzadeh M, Mohammadi H, Karimi M, Musavishenas MH, Baradaran B. Differential role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of Esophageal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;82:509–19.
Zhang B, Wu J, Cai Y, Luo M, Wang B, Gu Y. TCF7L1 indicates prognosis and promotes proliferation through activation of Keap1/NRF2 in gastric cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 2019;51:375–85.
Lu J, Xu Y, Xie W, Tang Y, Zhang H, Wang B, et al. Long noncoding RNA DLGAP1-AS2 facilitates Wnt1 transcription through physically interacting with Six3 and drives the malignancy of gastric cancer. Cell Death Disco. 2021;7:255.
Ren P, Hu M. A three long non-coding RNA signature to improve survival prediction in patients with Wilms’ tumor. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:6164–70.
De Carvalho DD, Sharma S, You JS, Su SF, Taberlay PC, Kelly TK, et al. DNA methylation screening identifies driver epigenetic events of cancer cell survival. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:655–67.
Helin K, Dhanak D. Chromatin proteins and modifications as drug targets. Nature. 2013;502:480–8.
Acknowledgements
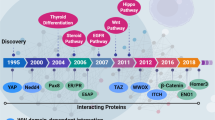
We thank Yi-he Hu and Jie Xie for the critical reading of the manuscript. Figure 2 was created by Figdraw (WWW.Figdraw.com), for which we are grateful. We apologize to those authors whose primary work we did not directly reference due to space restrictions.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81974339) and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Hunan Province (Grant No. 2019JJ40499).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T-LM and PZ wrote the original draft. T-LM, PZ and J-XC participated in writing and editing the review. PZ and J-XC prepared the figures. Y-HH and JX edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, TL., Zhu, P., Chen, JX. et al. SIX3 function in cancer: progression and comprehensive analysis. Cancer Gene Ther 29, 1542–1549 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00488-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-022-00488-9