Abstract
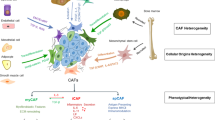
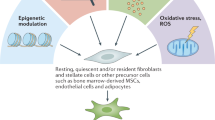
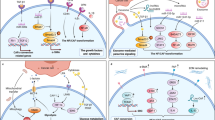
Tumors are one of the main causes of death in humans. The development of safe and effective methods for early diagnosis and treatment of tumors is a difficult problem that needs to be solved urgently. It is well established that the occurrence of tumors involves complex biological mechanisms, and the tumor microenvironment (TME) plays an important role in regulating the biological behavior of tumors. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are a group of activated fibroblasts with significant heterogeneity and plasticity in the tumor microenvironment. They secrete a variety of active factors to regulate tumor occurrence, development, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Although most studies suggest that CAFs have significant tumor-promoting functions, some evidence indicates that they may have certain tumor-suppressive functions in the early stage of tumors. Current research on CAFs continues to face many challenges, and the heterogeneity of their origin, phenotype, and function is a major difficulty and hot spot. To provide new perspectives for the research on CAFs and tumor diagnosis and treatment, this review summarizes the definition, origin, biomarkers, generation mechanism, functions, heterogeneity, plasticity, subpopulations, pre-metastasis niches (PMN), immune microenvironment, and targeted therapy of CAFs, describes the research progress and challenges, and proposes possible future research directions based on existing reports.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
28 June 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00343-3
References
Feng R-M, Zong Y-N, Cao S-M, Xu R-H. Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun. 2019;39:22.
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G. Cancer statistics: a comparison between World Health Organization (WHO) and Global Burden of Disease (GBD). Eur J Public Health. 2020;30:1026–7.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Rupaimoole R, Calin GA, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK. miRNA deregulation in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:235–46.
Eckert MA, Coscia F, Chryplewicz A, Chang JW, Hernandez KM, Pan S, et al. Proteomics reveals NNMT as a master metabolic regulator of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nature. 2019;569:723–8.
Kwa MQ, Herum KM, Brakebusch C. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: how do they contribute to metastasis? Clin Exp Metastasis. 2019;36:71–86.
Chen S, Giannakou A, Wyman S, Gruzas J, Golas J, Zhong W, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts suppress SOX2-induced dysplasia in a lung squamous cancer coculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E11671–E11680.
Borriello L, Nakata R, Sheard MA, Fernandez GE, Sposto R, Malvar J, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts share characteristics and protumorigenic activity with mesenchymal stromal cells. Cancer Res. 2017;77:5142–57.
Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Macrophages and metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019;30:36–50.
Meurette O, Mehlen P. Notch signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:536–48.
Vuong L, Kotecha RR, Voss MH, Hakimi AA. Tumor microenvironment dynamics in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:1349–57.
Zhou Z, Lu ZR. Molecular imaging of the tumor microenvironment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;113:24–48.
Osman A, Afify SM, Hassan G, Fu X, Seno A, Seno M. Revisiting cancer stem cells as the origin of cancer-associated cells in the tumor microenvironment: a hypothetical view from the potential of iPSCs. Cancers. 2020;12:879.
Roswall P, Bocci M, Bartoschek M, Li H, Kristiansen G, Jansson S, et al. Microenvironmental control of breast cancer subtype elicited through paracrine platelet-derived growth factor-CC signaling. Nat Med. 2018;24:463–73.
Su S, Chen J, Yao H, Liu J, Yu S, Lao L, et al. CD10(+)GPR77(+) cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer formation and chemoresistance by sustaining cancer stemness. Cell. 2018;172:841–56 e816.
Chen X, Song E. Turning foes to friends: targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18:99–115.
Fiori ME, Di Franco S, Villanova L, Bianca P, Stassi G, De Maria R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as abettors of tumor progression at the crossroads of EMT and therapy resistance. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:70.
Kobayashi H, Enomoto A, Woods SL, Burt AD, Takahashi M, Worthley DL. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:282–95.
Álvarez-Teijeiro S, García-Inclán C, Villaronga M, Casado P, Hermida-Prado F, Granda-Díaz R, et al. Factors secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts that sustain cancer stem properties in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells as potential therapeutic targets. Cancers. 2018;10:334.
Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M, Evans RM, et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:174–86.
Ao Z, Shah SH, Machlin LM, Parajuli R, Miller PC, Rawal S, et al. Identification of cancer-associated fibroblasts in circulating blood from patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4681–7.
Mishra R, Haldar S, Suchanti S, Bhowmick NA. Epigenetic changes in fibroblasts drive cancer metabolism and differentiation. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019;26:R673–R688.
Bu L, Baba H, Yoshida N, Miyake K, Yasuda T, Uchihara T, et al. Biological heterogeneity and versatility of cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2019;38:4887–901.
Du H, Che G. Genetic alterations and epigenetic alterations of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncol Lett. 2017;13:3–12.
LeBleu VS, Kalluri R. A peek into cancer-associated fibroblasts: origins, functions and translational impact. Dis Model Mech. 2018;11:dmm029447.
Ringuette Goulet C, Bernard G, Tremblay S, Chabaud S, Bolduc S, Pouliot F. Exosomes induce fibroblast differentiation into cancer-associated fibroblasts through TGFbeta signaling. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16:1196–204.
Yeon JH, Jeong HE, Seo H, Cho S, Kim K, Na D, et al. Cancer-derived exosomes trigger endothelial to mesenchymal transition followed by the induction of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Acta Biomater. 2018;76:146–53.
Krzysiek-Maczka G, Targosz A, Szczyrk U, Strzalka M, Brzozowski T, Ptak-Belowska A. Involvement of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors in the mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-induced fibroblasts activation. J Physiol Pharm. 2019;70:727–36.
Sun Q, Zhang B, Hu Q, Qin Y, Xu W, Liu W, et al. The impact of cancer-associated fibroblasts on major hallmarks of pancreatic cancer. Theranostics. 2018;8:5072–87.
Tan HX, Cao ZB, He TT, Huang T, Xiang CL, Liu Y. TGFbeta1 is essential for MSCs-CAFs differentiation and promotes HCT116 cells migration and invasion via JAK/STAT3 signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:5323–34.
Raz Y, Cohen N, Shani O, Bell RE, Novitskiy SV, Abramovitz L, et al. Bone marrow-derived fibroblasts are a functionally distinct stromal cell population in breast cancer. J Exp Med. 2018;215:3075–93.
Abangan RS Jr., Williams CR, Mehrotra M, Duncan JD, Larue AC. MCP1 directs trafficking of hematopoietic stem cell-derived fibroblast precursors in solid tumor. Am J Pathol. 2010;176:1914–26.
McDonald LT, Russell DL, Kelly RR, Xiong Y, Motamarry A, Patel RK, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell-derived cancer-associated fibroblasts are novel contributors to the pro-tumorigenic microenvironment. Neoplasia. 2015;17:434–48.
Nair N, Calle AS, Zahra MH, Prieto-Vila M, Oo AKK, Hurley L, et al. A cancer stem cell model as the point of origin of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6838.
Sasaki R, Devhare P, Ray RB, Ray R. Hepatitis C virus-induced tumor-initiating cancer stem-like cells activate stromal fibroblasts in a xenograft tumor model. Hepatology. 2017;66:1766–78.
Jia B, Gao Y, Li M, Shi J, Peng Y, Du X, et al. GPR30 promotes prostate stromal cell activation via suppression of ERα expression and its downstream signaling pathway. Endocrinology. 2016;157:3023–35.
Bochet L, Lehuédé C, Dauvillier S, Wang YY, Dirat B, Laurent V, et al. Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5657–68.
Ning X, Zhang H, Wang C, Song X. Exosomes released by gastric cancer cells induce transition of pericytes into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:2350–9.
Tan HX, Gong WZ, Zhou K, Xiao ZG, Hou FT, Huang T, et al. CXCR4/TGF-β1 mediated hepatic stellate cells differentiation into carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and promoted liver metastasis of colon cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21:258–68.
Liao Z, Tan ZW, Zhu P, Tan NS. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment—accomplices in tumor malignancy. Cell Immunol. 2019;343:103729.
Liu CJ, Wang YK, Kuo FC, Hsu WH, Yu FJ, Hsieh S, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection-induced hepatoma-derived growth factor regulates the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells to myofibroblast-like cells. Cancers. 2018;10:479.
Nurmik M, Ullmann P, Rodriguez F, Haan S, Letellier E. In search of definitions: cancer-associated fibroblasts and their markers. Int J Cancer. 2020;146:895–905.
Naito Y, Yamamoto Y, Sakamoto N, Shimomura I, Kogure A, Kumazaki M, et al. Cancer extracellular vesicles contribute to stromal heterogeneity by inducing chemokines in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2019;38:5566–79.
Wong PF, Wei W, Gupta S, Smithy JW, Zelterman D, Kluger HM, et al. Multiplex quantitative analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts and immunotherapy outcome in metastatic melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:194.
Cremasco V, Astarita JL, Grauel AL, Keerthivasan S, MacIsaac K, Woodruff MC, et al. FAP delineates heterogeneous and functionally divergent stromal cells in immune-excluded breast tumors. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018;6:1472–85.
Kuzet SE, Gaggioli C. Fibroblast activation in cancer: when seed fertilizes soil. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365:607–19.
Shimoda M, Principe S, Jackson HW, Luga V, Fang H, Molyneux SD, et al. Loss of the Timp gene family is sufficient for the acquisition of the CAF-like cell state. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16:889–901.
Ferrari N, Calvo F. Tumor microenvironment: unleashing metalloproteinases to induce a CAF phenotype. Curr Biol. 2014;24:R1009–1011.
Fang T, Lv H, Lv G, Li T, Wang C, Han Q, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9:191.
Rai A, Greening DW, Chen M, Xu R, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes derived from human primary and metastatic colorectal cancer cells contribute to functional heterogeneity of activated fibroblasts by reprogramming their proteome. Proteomics. 2019;19:e1800148.
Zhang D, Li L, Jiang H, Li Q, Wang-Gillam A, Yu J, et al. Tumor-stroma IL1beta-IRAK4 feedforward circuitry drives tumor fibrosis, chemoresistance, and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1700–12.
Yoshida GJ. Regulation of heterogeneous cancer-associated fibroblasts: the molecular pathology of activated signaling pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:112.
Ham IH, Oh HJ, Jin H, Bae CA, Jeon SM, Choi KS, et al. Targeting interleukin-6 as a strategy to overcome stroma-induced resistance to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:68.
Tommelein J, De Vlieghere E, Verset L, Melsens E, Leenders J, Descamps B, et al. Radiotherapy-activated cancer-associated fibroblasts promote tumor progression through paracrine IGF1R activation. Cancer Res. 2018;78:659–70.
Chan TS, Hsu CC, Pai VC, Liao WY, Huang SS, Tan KT, et al. Metronomic chemotherapy prevents therapy-induced stromal activation and induction of tumor-initiating cells. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2967–88.
Dart A. Less is more. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:3–3.
Park D, Sahai E, Rullan A. SnapShot: cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell. 2020;181:486–486.e481.
Goulet CR, Champagne A, Bernard G, Vandal D, Chabaud S, Pouliot F, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells through paracrine IL-6 signalling. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:137.
Wang L, Zhang F, Cui JY, Chen L, Chen YT, Liu BW. CAFs enhance paclitaxel resistance by inducing EMT through the IL6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Oncol Rep. 2018;39:2081–90.
Ren Y, Jia HH, Xu YQ, Zhou X, Zhao XH, Wang YF, et al. Paracrine and epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: the role of HOTAIR stimulated by TGF-ss1 secretion. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:5.
Tang X, Tu G, Yang G, Wang X, Kang L, Yang L, et al. Autocrine TGF-beta1/miR-200s/miR-221/DNMT3B regulatory loop maintains CAF status to fuel breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 2019;452:79–89.
Bayer SV, Grither WR, Brenot A, Hwang PY, Barcus CE, Ernst M, et al. DDR2 controls breast tumor stiffness and metastasis by regulating integrin mediated mechanotransduction in CAFs. eLife. 2019;8:e45508.
von Ahrens D, Bhagat TD, Nagrath D, Maitra A, Verma A. The role of stromal cancer-associated fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:76.
Yang Z, Peng YC, Gopalan A, Gao D, Chen Y, Joyner AL. Stromal hedgehog signaling maintains smooth muscle and hampers micro-invasive prostate cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2017;10:39–52.
Ozdemir BC, Pentcheva-Hoang T, Carstens JL, Zheng X, Wu CC, Simpson TR, et al. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:719–34.
Miyai Y, Esaki N, Takahashi M, Enomoto A. Cancer-associated fibroblasts that restrain cancer progression: hypotheses and perspectives. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:1047–57.
Mizutani Y, Kobayashi H, Iida T, Asai N, Masamune A, Hara A, et al. Meflin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibit pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2019;79:5367–81.
Tang YA, Chen YF, Bao Y, Mahara S, Yatim S, Oguz G, et al. Hypoxic tumor microenvironment activates GLI2 via HIF-1alpha and TGF-beta2 to promote chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E5990–E5999.
Garvey CM, Lau R, Sanchez A, Sun RX, Fong EJ, Doche ME, et al. Anti-EGFR therapy induces EGF secretion by cancer-associated fibroblasts to confer colorectal cancer chemoresistance. Cancers. 2020;12:1393.
Kunita A, Morita S, Irisa TU, Goto A, Niki T, Takai D, et al. MicroRNA-21 in cancer-associated fibroblasts supports lung adenocarcinoma progression. Sci Rep. 2018;8:8838.
Zhang L, Yao J, Li W, Zhang C. Micro-RNA-21 regulates cancer-associated fibroblast-mediated drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Res. 2018;26:827–35.
Broekgaarden M, Anbil S, Bulin AL, Obaid G, Mai Z, Baglo Y, et al. Modulation of redox metabolism negates cancer-associated fibroblasts-induced treatment resistance in a heterotypic 3D culture platform of pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials. 2019;222:119421.
Bordignon P, Bottoni G, Xu X, Popescu AS, Truan Z, Guenova E, et al. Dualism of FGF and TGF-beta signaling in heterogeneous cancer-associated fibroblast activation with ETV1 as a critical determinant. Cell Rep. 2019;28:2358–72 e2356.
Pereira BA, Vennin C, Papanicolaou M, Chambers CR, Herrmann D, Morton JP, et al. CAF subpopulations: a new reservoir of stromal targets in pancreatic cancer. Trends Cancer. 2019;5:724–41.
Costa A, Kieffer Y, Scholer-Dahirel A, Pelon F, Bourachot B, Cardon M, et al. Fibroblast heterogeneity and immunosuppressive environment in human breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:463–79 e410.
Elwakeel E, Bruggemann M, Fink AF, Schulz MH, Schmid T, Savai R, et al. Phenotypic plasticity of fibroblasts during mammary carcinoma development. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:4438.
Feldmann K, Maurer C, Peschke K, Teller S, Schuck K, Steiger K, et al. Mesenchymal plasticity regulated by Prrx1 drives aggressive pancreatic cancer biology. Gastroenterology. 2020;S0016-5085:35147–7.
Farhood B, Najafi M, Mortezaee K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: secretions, interactions, and therapy. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:2791–2800.
Oya Y, Hayakawa Y, Koike K. Tumor microenvironment in gastric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:2696–707.
Vennin C, Melenec P, Rouet R, Nobis M, Cazet AS, Murphy KJ, et al. CAF hierarchy driven by pancreatic cancer cell p53-status creates a pro-metastatic and chemoresistant environment via perlecan. Nat Commun. 2019;10:3637.
Ligorio M, Sil S, Malagon-Lopez J, Nieman LT, Misale S, Di Pilato M, et al. Stromal microenvironment shapes the intratumoral architecture of pancreatic. Cancer Cell. 2019;178:160–.e127.
Bartoschek M, Oskolkov N, Bocci M, Lovrot J, Larsson C, Sommarin M, et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5150.
Biffi G, Oni TE, Spielman B, Hao Y, Elyada E, Park Y, et al. IL1-induced JAK/STAT signaling is antagonized by TGFbeta to shape CAF heterogeneity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:282–301.
Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G, Elyada E, Almeida AS, Ponz-Sarvise M, et al. Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med. 2017;214:579–96.
Brechbuhl HM, Barrett AS, Kopin E, Hagen JC, Han AL, Gillen AE, et al. Fibroblast subtypes define a metastatic matrisome in breast cancer. JCI Insight. 2020;5:e130751.
Kieffer Y, Hocine HR, Gentric G, Pelon F, Bernard C, Bourachot B, et al. Single-cell analysis reveals fibroblast clusters linked to immunotherapy resistance in cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:1330–51.
Ishibashi M, Neri S, Hashimoto H, Miyashita T, Yoshida T, Nakamura Y, et al. CD200-positive cancer associated fibroblasts augment the sensitivity of epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive lung adenocarcinomas to EGFR Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46662.
Umakoshi M, Takahashi S, Itoh G, Kuriyama S, Sasaki Y, Yanagihara K, et al. Macrophage-mediated transfer of cancer-derived components to stromal cells contributes to establishment of a pro-tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2019;38:2162–76.
Kong J, Tian H, Zhang F, Zhang Z, Li J, Liu X, et al. Extracellular vesicles of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts creates a pre-metastatic niche in the lung through activating fibroblasts. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:175.
An Y, Liu F, Chen Y, Yang Q. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24:13–24.
Qian L, Tang Z, Yin S, Mo F, Yang X, Hou X, et al. Fusion of dendritic cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts for activation of anti-tumor cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2018;14:1826–35.
Zhang R, Qi F, Zhao F, Li G, Shao S, Zhang X, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance tumor-associated macrophages enrichment and suppress NK cells function in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:273.
Cheng Y, Li H, Deng Y, Tai Y, Zeng K, Zhang Y, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce PDL1+ neutrophils through the IL6-STAT3 pathway that foster immune suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:422.
Hanley CJ, Mellone M, Ford K, Thirdborough SM, Mellows T, Frampton SJ, et al. Targeting the myofibroblastic cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype through inhibition of NOX4. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018;110:109–20.
Liu T, Han C, Wang S, Fang P, Ma Z, Xu L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: an emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:86.
Moren A, Bellomo C, Tsubakihara Y, Kardassis D, Mikulits W, Heldin CH, et al. LXRalpha limits TGFbeta-dependent hepatocellular carcinoma associated fibroblast differentiation. Oncogenesis. 2019;8:36.
Lang J, Zhao X, Qi Y, Zhang Y, Han X, Ding Y, et al. Reshaping prostate tumor microenvironment to suppress metastasis via cancer-associated fibroblast inactivation with peptide-assembly-based nanosystem. ACS Nano. 2019;13:12357–71.
Freedman JD, Duffy MR, Lei-Rossmann J, Muntzer A, Scott EM, Hagel J, et al. An oncolytic virus expressing a T-cell engager simultaneously targets cancer and immunosuppressive stromal cells. Cancer Res. 2018;78:6852–65.
Qin X, Yan M, Wang X, Xu Q, Wang X, Zhu X, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived IL-6 promotes head and neck cancer progression via the osteopontin-NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Theranostics. 2018;8:921–40.
Heichler C, Scheibe K, Schmied A, Geppert CI, Schmid B, Wirtz S, et al. STAT3 activation through IL-6/IL-11 in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes colorectal tumour development and correlates with poor prognosis. Gut. 2020;69:1269–82.
Wen S, Hou Y, Fu L, Xi L, Yang D, Zhao M, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-derived IL32 promotes breast cancer cell invasion and metastasis via integrin beta3-p38 MAPK signalling. Cancer Lett. 2019;442:320–32.
Wei L, Ye H, Li G, Lu Y, Zhou Q, Zheng S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote progression and gemcitabine resistance via the SDF-1/SATB-1 pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1065.
Sjoberg E, Meyrath M, Milde L, Herrera M, Lovrot J, Hagerstrand D, et al. A novel ACKR2-dependent role of fibroblast-derived CXCL14 in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:3702–17.
Catalano S, Panza S, Augimeri G, Giordano C, Malivindi R, Gelsomino L, et al. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) Is highly expressed in cancer-associated fibroblasts and enhances breast tumor progression. Cancers. 2019;11:1740.
Kock A, Larsson K, Bergqvist F, Eissler N, Elfman LHM, Raouf J, et al. Inhibition of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 in cancer-associated fibroblasts suppresses neuroblastoma tumor growth. EBioMedicine. 2018;32:84–92.
Cioni B, Nevedomskaya E, Melis MHM, van Burgsteden J, Stelloo S, Hodel E, et al. Loss of androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) promotes CCL2- and CXCL8-mediated cancer cell migration. Mol Oncol. 2018;12:1308–23.
An YZ, Cho E, Ling J, Zhang X. The Axin2-snail axis promotes bone invasion by activating cancer-associated fibroblasts in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:987.
Zhai Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Lu W, Liu S, Yu Y, et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 contributes to cancer-associated fibroblasts-mediated chemo-protection of AML cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:147.
Cho H, Seo Y, Loke KM, Kim SW, Oh SM, Kim JH, et al. Cancer-stimulated CAFs enhance monocyte differentiation and protumoral TAM activation via IL6 and GM-CSF secretion. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:5407–21.
Liu C, Liu L, Chen X, Cheng J, Zhang H, Zhang C, et al. LSD1 stimulates cancer-associated fibroblasts to drive Notch3-dependent self-renewal of liver cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 2018;78:938–49.
Cadamuro M, Brivio S, Mertens J, Vismara M, Moncsek A, Milani C, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-D enables liver myofibroblasts to promote tumor lymphangiogenesis in cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2019;70:700–9.
Kumar D, New J, Vishwakarma V, Joshi R, Enders J, Lin F, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts drive glycolysis in a targetable signaling loop implicated in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3769–82.
Santolla MF, Vivacqua A, Lappano R, Rigiracciolo DC, Cirillo F, Galli GR, et al. GPER mediates a feedforward FGF2/FGFR1 paracrine activation coupling CAFs to cancer cells toward breast tumor progression. Cells 2019;8:223.
Hegab AE, Ozaki M, Kameyama N, Gao J, Kagawa S, Yasuda H, et al. Effect of FGF/FGFR pathway blocking on lung adenocarcinoma and its cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Pathol. 2019;249:193–205.
Yang Z, Zhang C, Qi W, Cui C, Cui Y, Xuan Y. Tenascin-C as a prognostic determinant of colorectal cancer through induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and proliferation. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018;105:216–22.
Lai SL, Tan ML, Hollows RJ, Robinson M, Ibrahim M, Margielewska S, et al. Collagen induces a more proliferative, migratory and chemoresistant phenotype in head and neck cancer via DDR1. Cancers. 2019;11:1766.
Nissen NI, Karsdal M, Willumsen N. Collagens and Cancer associated fibroblasts in the reactive stroma and its relation to cancer biology. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:115.
Hughes RM, Simons BW, Khan H, Miller R, Kugler V, Torquato S, et al. Asporin restricts mesenchymal stromal cell differentiation, alters the tumor microenvironment, and drives metastatic progression. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3636–50.
Yu B, Wu K, Wang X, Zhang J, Wang L, Jiang Y, et al. Periostin secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes cancer stemness in head and neck cancer by activating protein tyrosine kinase 7. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1082.
Miyazaki K, Togo S, Okamoto R, Idiris A, Kumagai H, Miyagi Y. Collective cancer cell invasion in contact with fibroblasts through integrin-alpha5beta1/fibronectin interaction in collagen matrix. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:4381–92.
Erdogan B, Ao M, White LM, Means AL, Brewer BM, Yang L, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote directional cancer cell migration by aligning fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:3799–816.
Saini H, Rahmani Eliato K, Veldhuizen J, Zare A, Allam M, Silva C, et al. The role of tumor-stroma interactions on desmoplasia and tumorigenicity within a microengineered 3D platform. Biomaterials. 2020;247:119975.
Zeltz C, Pasko E, Cox TR, Navab R, Tsao MS. LOXL1 is regulated by integrin alpha11 and promotes non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenicity. Cancers. 2019;11:705.
Ben Baruch B, Mantsur E, Franco-Barraza J, Blacher E, Cukierman E, Stein R. CD38 in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes pro-tumoral activity. Lab Invest. 2020;100:1517–31.
Boyle ST, Poltavets V, Kular J, Pyne NT, Sandow JJ, Lewis AC, et al. ROCK-mediated selective activation of PERK signalling causes fibroblast reprogramming and tumour progression through a CRELD2-dependent mechanism. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:882–95.
Primac I, Maquoi E, Blacher S, Heljasvaara R, Van Deun J, Smeland HY, et al. Stromal integrin alpha11 regulates PDGFR-beta signaling and promotes breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:4609–28.
Sung JS, Kang CW, Kang S, Jang Y, Chae YC, Kim BG, et al. ITGB4-mediated metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2020;39:664–76.
Zhou Z, Zhou Q, Wu X, Xu S, Hu X, Tao X, et al. VCAM-1 secreted from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances the growth and invasion of lung cancer cells through AKT and MAPK signaling. Cancer Lett. 2020;473:62–73.
Yoshida T, Ishii G, Goto K, Neri S, Hashimoto H, Yoh K, et al. Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment induce primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:642–51.
Errarte P, Larrinaga G, Lopez JI. The role of cancer-associated fibroblasts in renal cell carcinoma. An example of tumor modulation through tumor/non-tumor cell interactions. J Adv Res. 2020;21:103–8.
Goetz JG, Minguet S, Navarro-Lerida I, Lazcano JJ, Samaniego R, Calvo E, et al. Biomechanical remodeling of the microenvironment by stromal caveolin-1 favors tumor invasion and metastasis. Cell. 2011;146:148–63.
Yamao T, Yamashita YI, Yamamura K, Nakao Y, Tsukamoto M, Nakagawa S, et al. Cellular senescence, represented by expression of caveolin-1, in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes tumor invasion in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26:1552–9.
Richardson AM, Havel LS, Koyen AE, Konen JM, Shupe J, Wiles WGt, et al. Vimentin is required for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via heterotypic tumor cell-cancer-associated fibroblast interactions during collective invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:420–32..
Dorsam B, Bosl T, Reiners KS, Barnert S, Schubert R, Shatnyeva O, et al. Hodgkin lymphoma-derived extracellular vesicles change the secretome of fibroblasts toward a CAF phenotype. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1358.
Strutz F, Okada H, Lo CW, Danoff T, Carone RL, Tomaszewski JE, et al. Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J Cell Biol. 1995;130:393–405.
Anfuso CD, Longo A, Distefano A, Amorini AM, Salmeri M, Zanghi G, et al. Uveal melanoma cells elicit retinal pericyte phenotypical and biochemical changes in an in vitro model of coculture. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:5557.
Sung PJ, Rama N, Imbach J, Fiore S, Ducarouge B, Neves D, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts produce netrin-1 to control cancer cell plasticity. Cancer Res. 2019;79:3651–61.
Zhang W, Bouchard G, Yu A, Shafiq M, Jamali M, Shrager JB, et al. GFPT2-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts mediate metabolic reprogramming in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3445–57.
Leca J, Martinez S, Lac S, Nigri J, Secq V, Rubis M, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived annexin A6+ extracellular vesicles support pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:4140–56.
Lambies G, Miceli M, Martinez-Guillamon C, Olivera-Salguero R, Pena R, Frias CP, et al. TGFbeta-activated USP27X deubiquitinase regulates cell migration and chemoresistance via stabilization of snail1. Cancer Res. 2019;79:33–46.
Yang Z, Yang X, Xu S, Jin P, Li X, Wei X, et al. Reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts by SNAI2 contributes to tumor desmoplasia and ovarian cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:163.
Li YY, Tao YW, Gao S, Li P, Zheng JM, Zhang SE, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. EBioMedicine. 2018;36:209–20.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Xin Cheng for her assistance in illustrating the schematic figure.
Funding
This review was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Funds of China (grant no. 82060536); Open Project from the Tumor Immunization and Prevention Key Experiment Laboratory of Yunnan Provincial (grant no. 2017DG004-04); Scientific Research Fund from the Education Department of Yunnan Provincial (grant no. 2020J0218); and the Health Science and Technology Talent Training Project of Kunming city (grant no. 2020-SW-12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ping, Q., Yan, R., Cheng, X. et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: overview, progress, challenges, and directions. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 984–999 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00318-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00318-4
This article is cited by
-
Cellular and micro-environmental responses influencing the antitumor activity of all-trans retinoic acid in breast cancer
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
vissE: a versatile tool to identify and visualise higher-order molecular phenotypes from functional enrichment analysis
BMC Bioinformatics (2024)
-
Cancer associated fibroblasts-derived SULF1 promotes gastric cancer metastasis and CDDP resistance through the TGFBR3-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
The nerve cells in gastrointestinal cancers: from molecular mechanisms to clinical intervention
Oncogene (2024)
-
Exosomal cargos-mediated metabolic reprogramming in tumor microenvironment
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)