Abstract
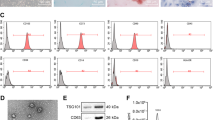
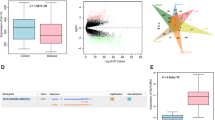
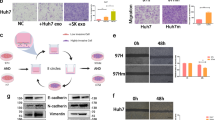
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a lethal malignancy with few effective options for therapeutic treatment in its advanced stages. While exosomal LINC00161 has been identified as a potential biomarker for HCC, its regulatory function and clinical values remain largely unknown. LINC00161 expressions in serum-derived exosomes from HCC patients and HCC cells were determined by qRT-PCR. The ability of proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in HUVECs was assessed by MTT, Transwell, and tube formation. Luciferase reporter assay and AGO2-RIP assay were conducted to explore the interactions among LINC00161, miR-590-3p, and ROCK2. The level of ROCK signal-related proteins was examined by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay. Subcutaneous tumor growth was observed in nude mice, in which in vivo metastasis was observed following tail vein injection of HCC cells. High levels of LINC00161 were detected in both serum-derived exosomes from HCC patients and the supernatants of HCC cell lines and were significantly associated with poor survival. Functional study demonstrated that exosomal LINC00161 derived from HCC-cells were significantly associated with enhanced proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in HUVECs in vitro, all of which were effectively inhibited when LINC00161 was sliced with shRNA in HCC-cells. In vivo experiment showed that LINC00161 loss inhibited tumorigenesis and metastasis of HCC. Mechanistic study revealed that exosome-carried LINC00161 directly targeted miR-590-3p and induced its downstream target ROCK2, finally activating growth/metastasis-related signals in HCC. Exosome-carried LINC00161 promotes HCC tumorigenesis through inhibiting miR-590-3p to activate the ROCK2 signaling pathway, suggesting that LINC00161 may be used as potential targets to improve HCC treatment efficiency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-021-00338-0
References
Balogh J, Victor D III, Asham EH, Burroughs SG, Boktour M, Saharia A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2016;3:41–53.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32.
Dhir M, Melin AA, Douaiher J, Lin C, Zhen WK, Hussain SM, et al. A review and update of treatment options and controversies in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2016;263:1112–25.
Yu S, Cao H, Shen B, Feng J. Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer progression and treatment failure. Oncotarget. 2015;6:37151–68.
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer metastasis Rev. 2013;32:623–42.
Abudoureyimu M, Zhou H, Zhi Y, Wang T, Feng B, Wang R, et al. Recent progress in the emerging role of exosome in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019;52:e12541.
Suchorska WM, Lach MS. The role of exosomes in tumor progression and metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:1237–44.
Zhang H, Chen Z, Wang X, Huang Z, He Z, Chen Y. Long non-coding RNA: a new player in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2013;6:37.
Gutschner T, Diederichs S. The hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol. 2012;9:703–19.
Zhang C, Yang X, Qi Q, Gao Y, Wei Q, Han S. lncRNA-HEIH in serum and exosomes as a potential biomarker in the HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer biomarkers: Sect A Dis markers. 2018;21:651–9.
Li X, Lei Y, Wu M, Li N. Regulation of macrophage activation and polarization by HCC-derived exosomal lncRNA TUC339. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:2958.
Xu H, Chen Y, Dong X, Wang X. Serum exosomal long noncoding RNAs ENSG00000258332.1 and LINC00635 for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2018;27:710–6.
Li B, Mao R, Liu C, Zhang W, Tang Y, Guo Z. LncRNA FAL1 promotes cell proliferation and migration by acting as a CeRNA of miR-1236 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 2018;197:122–9.
Xu LC, Chen QN, Liu XQ, Wang XM, Chang QM, Pan Q, et al. Up-regulation of LINC00161 correlates with tumor migration and invasion and poor prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:56168–73.
Sun L, Su Y, Liu X, Xu M, Chen X, Zhu Y, et al. Serum and exosome long non coding RNAs as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2018;9:2631–9.
He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31.
Bracken CP, Scott HS, Goodall GJ. A network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:719–32.
Yao H, Liu N, Lin MC, Zheng J. Positive feedback loop between cancer stem cells and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016;379:213–9.
Xu X, Tao Y, Shan L, Chen R, Jiang H, Qian Z, et al. The role of microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2018;9:3557–69.
Salem M, O’Brien JA, Bernaudo S, Shawer H, Ye G, Brkic J, et al. miR-590-3p promotes ovarian cancer growth and metastasis via a novel FOXA2-versican pathway. Cancer Res. 2018;78:4175–90.
Di Agostino S, Valenti F, Sacconi A, Fontemaggi G, Pallocca M, Pulito C, et al. Long non-coding MIR205HG depletes Hsa-miR-590-3p leading to unrestrained proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 2018;8:1850–68.
Zhang J, Jin M, Chen X, Zhang R, Huang Y, Liu H, et al. Loss of PPM1F expression predicts tumour recurrence and is negatively regulated by miR-590-3p in gastric cancer. Cell Prolif. 2018;51:e12444.
He B, Lu P, Guan L, Li T, Zhang L, Zhu QG, et al. Identifying key regulating miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinomas by an omics’ method. Oncotarget. 2017;8:103919–30.
Li TM, Liu SC, Huang YH, Huang CC, Hsu CJ, Tsai CH, et al. YKL-40-Induced inhibition of miR-590-3p promotes interleukin-18 expression and angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells. int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017;18:920.
Bao MH, Li GY, Huang XS, Tang L, Dong LP, Li JM. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00657 Acting as a miR-590-3p Sponge to Facilitate Low Concentration Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Angiogenesis. Mol Pharm. 2018;93:368–75.
Zhang JG, Zhang DD, Liu Y, Hu JN, Zhang X, Li L, et al. RhoC/ROCK2 promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation primarily through ERK/MMPs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865:1113–25.
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Man K, Ng IO. Rho-kinase 2 is frequently overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and involved in tumor invasion. Hepatology. 2009;49:1583–94.
Liu J, Wada Y, Katsura M, Tozawa H, Erwin N, Kapron CM, et al. Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) in molecular regulation of angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018;8:6053–69.
Castellano JJ, Navarro A, Vinolas N, Marrades RM, Moises J, Cordeiro A, et al. LincRNA-p21 impacts prognosis in resected non-small cell lung cancer patients through angiogenesis regulation. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:2173–82.
Zhao X, Liu Y, Li Z, Zheng S, Wang Z, Li W, et al. Linc00511 acts as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate VEGFA expression through sponging hsa-miR-29b-3p in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:655–67.
Muller S, Raulefs S, Bruns P, Afonso-Grunz F, Plotner A, Thermann R, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals novel differentially regulated mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, sdRNAs and a piRNA in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:94.
Tsai MC, Spitale RC, Chang HY. Long intergenic noncoding RNAs: new links in cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3–7.
Bryan BA, Dennstedt E, Mitchell DC, Walshe TE, Noma K, Loureiro R, et al. RhoA/ROCK signaling is essential for multiple aspects of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2010;24:3186–95.
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, Au SL, Lee JM, Poon RT, et al. The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:322–31.
Xiang Q, Chen W, Ren M, Wang J, Zhang H, Deng DY, et al. Cabozantinib suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by a dual blockade of VEGFR2 and MET. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:2959–70.
Gramantieri L, Baglioni M, Fornari F, Laginestra MA, Ferracin M, Indio V, et al. LncRNAs as novel players in hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Oncotarget. 2018;9:35085–99.
Wang Y, Zhang L, Zheng X, Zhong W, Tian X, Yin B, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00161 sensitises osteosarcoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by regulating the miR-645-IFIT2 axis. Cancer Lett. 2016;382:137–46.
Xu M, Zhou K, Wu Y, Wang L, Lu S. Linc00161 regulated the drug resistance of ovarian cancer by sponging microRNA-128 and modulating MAPK1. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58:577–87.
Conigliaro A, Costa V, Lo Dico A, Saieva L, Buccheri S, Dieli F, et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:155.
Li R, Wang Y, Zhang X, Feng M, Ma J, Li J, et al. Exosome-mediated secretion of LOXL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:18.
He M, Qin H, Poon TC, Sze SC, Ding X, Co NN, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomes promote motility of immortalized hepatocyte through transfer of oncogenic proteins and RNAs. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36:1008–18.
Shan Y, Ma J, Pan Y, Hu J, Liu B, Jia L. LncRNA SNHG7 sponges miR-216b to promote proliferation and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer through upregulating GALNT1. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:722.
Miao L, Liu HY, Zhou C, He X. LINC00612 enhances the proliferation and invasion ability of bladder cancer cells as ceRNA by sponging miR-590 to elevate expression of PHF14. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:143.
Ueno K, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Chen Y, Zaman MS, Singh K, et al. Tumour suppressor microRNA-584 directly targets oncogene Rock-1 and decreases invasion ability in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2011;104:308–15.
Hoang MV, Whelan MC, Senger DR. Rho activity critically and selectively regulates endothelial cell organization during angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:1874–9.
Lin C, Song L, Liu A, Gong H, Lin X, Wu J, et al. Overexpression of AKIP1 promotes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2015;34:384–93.
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010;141:52–67.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Research and Innovation Fund of Xinjiang Medical University (NO.XJC2013118).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: Wu-Hui Huang; study concepts: Wu-Hui Huang, Qin-Wen Tai; study design: Wu-Hui Huang, Li-Na You, Lin Xu, Yi Hao; definition of intellectual content: Lin Xu; literature research: Li-Na You; clinical studies: Wen-JiaGuo; experimental studies: Wu-Hui Huang, Wen-JiaGuo; data acquisition: Qiao Zhang; data analysis: Wu-Hui Huang, Qing Tong; statistical analysis: Qiao Zhan, Li-Na You; manuscript preparation: Wu-Hui Huang, Heng Zhang; manuscript editing: Qing Tong; manuscript review: Heng Zhang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The study protocol was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Hospital of Southern Medical University and all patients provided written informed consent. All experimentations involving animals were carried out in full accordance with the institutional animal welfare guideline and approved by Shenzhen Hospital of Southern Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, LN., Tai, QW., Xu, L. et al. Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis via regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 719–736 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00269-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00269-2
This article is cited by
-
Cancer-derived exosomes as novel biomarkers in metastatic gastrointestinal cancer
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Research progress of exosomes in the angiogenesis of digestive system tumour
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
Key therapeutic targets implicated at the early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma identified through machine-learning approaches
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Unveiling the functional paradigm of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in cancer: based on a narrative review and systematic review
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in prostate cancer therapy
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)