Abstract
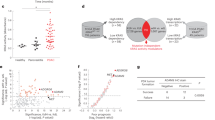
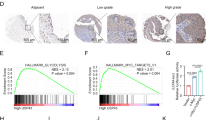
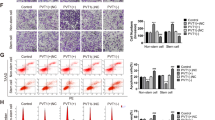
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is an essential member of the STAT family. STAT3 regulates diverse genes that mediate inflammatory reactions, cell survival, proliferation, and angiogenesis, and it is aberrantly upregulated and activated in various types of malignancies. Furthermore, STAT3 signalling is involved in multiple feedback loops and pathways. In this study, we demonstrate that miR-93-3p plays an oncogenic role in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) by enhancing RCC cell proliferation and suppressing apoptosis. In addition, STAT3 can regulate the transcription of miR-93 by directly binding its promoter region. miR-93 can inhibit death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) at the protein level. Moreover, STAT3 can block DAPK1 expression at the RNA level. Importantly, we verified that DAPK1 overexpression in turn suppresses the entry of activated STAT3 into the cell nucleus. Thus, this study reveals a potential continuously activated signalling transduction pathway, STAT3-miR93-DAPK1, and may provide a novel clinical therapeutic approach for RCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373:1119–32.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32.
Capitanio U, Montorsi F. Renal cancer. Lancet. 2016;387:894–906.
Beitzinger M, Meister G. Preview. MicroRNAs: from decay to decoy. Cell. 2010;140:612–4.
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:287–314.
Hammond SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;87:3–14.
Medina PP, Slack FJ. microRNAs and cancer: an overview. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2485–92.
Mohr AM, Mott JL. Overview of microRNA biology. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35:3–11.
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wen J, Liu L, Zhai X, Liu J, et al. A genetic variant in the promoter region of miR-106b-25 cluster and risk of HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e32230.
Lo Sardo F, Forcato M, Sacconi A, Capaci V, Zanconato F, Di Agostino S, et al. MCM7 and its hosted miR-25, 93 and 106b cluster elicit YAP/TAZ oncogenic activity in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2017;38:64–75.
Cioffi M, Vallespinos-Serrano M, Trabulo SM, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Firment AN, Vazquez BN, et al. MiR-93 controls adiposity via inhibition of Sirt7 and Tbx3. Cell Rep. 2015;12:1594–605.
Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Munoz X, Bonet C, Garcia N, Vencesla A, Yiannakouris N, et al. Genetic association of gastric cancer with miRNA clusters including the cancer-related genes MIR29, MIR25, MIR93 and MIR106: results from the EPIC-EURGAST study. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:2065–76.
Wang L, Wang Q, Li HL, Han LY. Expression of MiR200a, miR93, metastasis-related gene RECK and MMP2/MMP9 in human cervical carcinoma-relationship with prognosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2113–8.
Otsuka M, Jing Q, Georgel P, New L, Chen J, Mols J, et al. Hypersusceptibility to vesicular stomatitis virus infection in Dicer1-deficient mice is due to impaired miR24 and miR93 expression. Immunity. 2007;27:123–34.
Wu B, Yao H, Wang S, Xu R. DAPK1 modulates a curcumin-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis by regulating STAT3, NF-kappaB, and caspase-3 activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434:75–80.
Pulling LC, Grimes MJ, Damiani LA, Juri DE, Do K, Tellez CS, et al. Dual promoter regulation of death-associated protein kinase gene leads to differentially silenced transcripts by methylation in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:2023–30.
Martoriati A, Doumont G, Alcalay M, Bellefroid E, Pelicci PG, Marine JC. dapk1, encoding an activator of a p19ARF-p53-mediated apoptotic checkpoint, is a transcription target of p53. Oncogene. 2005;24:1461–6.
Chen CH, Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Tsai HC, Lin JR, Chang ZF, et al. Bidirectional signals transduced by DAPK-ERK interaction promote the apoptotic effect of DAPK. EMBO J. 2005;24:294–304.
Llambi F, Lourenco FC, Gozuacik D, Guix C, Pays L, Del Rio G, et al. The dependence receptor UNC5H2 mediates apoptosis through DAP-kinase. EMBO J. 2005;24:1192–201.
Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, Lang YD, Lin CJ, Huang J, et al. miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3631–41.
Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S, Shao Z, Gallagher PJ. A death-associated protein kinase (DAPK)-interacting protein, DIP-1, is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis and regulates the cellular levels of DAPK. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:46980–6.
Guo C, Yang G, Khun K, Kong X, Levy D, Lee P, et al. Activation of Stat3 in renal tumors. Am J Transl Res. 2009;1:283–90.
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Marumo K, Murai MSTAT3. but not ERKs, mediates the IL-6-induced proliferation of renal cancer cells, ACHN and 769P. Kidney Int. 2002;61:926–38.
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Shimada T, Uchida A, Marumo K, Murai M. Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in renal cell carcinoma: a study of incidence and its association with pathological features and clinical outcome. J Urol. 2002;168:762–5.
Shanmugam R, Gade P, Wilson-Weekes A, Sayar H, Suvannasankha A, Goswami C, et al. A noncanonical Flt3ITD/NF-kappaB signaling pathway represses DAPK1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:360–9.
Chuang YT, Fang LW, Lin-Feng MH, Chen RH, Lai MZ. The tumor suppressor death-associated protein kinase targets to TCR-stimulated NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol. 2008;180:3238–49.
Nakav S, Cohen S, Feigelson SW, Bialik S, Shoseyov D, Kimchi A, et al. Tumor suppressor death-associated protein kinase attenuates inflammatory responses in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012;46:313–22.
Acknowledgements
We are particularly grateful to Professor Xueshan Qiu for his timely help.
Fundings
This work was supported by Shenyang Plan Project of Science and Technology (Grant No. F19-112-4-098), National key R & D plan key research projects of precision medicine (2017YFC0908000), China Medical University’s 2018 discipline promotion program. Funding agency did not participate in the design of the study and collection, analysis and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YD designed, performed the experiments, organized data and wrote the paper. CK acquired funding, established the urology laboratory, provided the required equipment and instruments, supervised assays, contributed to the critical reading of the paper, generated the figures, and gave final approval of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Kong, C. STAT3 regulates miR93-mediated apoptosis through inhibiting DAPK1 in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 502–513 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00235-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00235-y
This article is cited by
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: microRNA-15b-5p encapsulated by M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promotes gastric cancer metastasis by targeting BRMS1 and suppressing DAPK1 transcription
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2022)