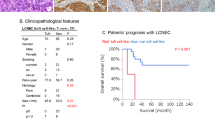
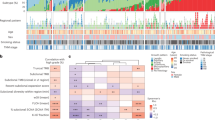
Abstract
Background
Tuft cells are chemosensory epithelial cells playing a role in innate immunity. Recent studies revealed cancers with a tuft cell-like gene expression signature in the thorax. We wondered whether this signature might also occur in extrathoracic cancers.
Methods
We examined mRNA expression of tuft cell markers (POU2F3, GFI1B, TRPM5, SOX9, CHAT, and AVIL) in 19 different types of cancers in multiple extrathoracic organs with The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) (N = 6322). Four different extrathoracic cancers in our local archives (N = 909) were analysed by immunohistochemistry.
Results
Twenty-two (0.35%) extrathoracic tumours with co-expression of POU2F3 and other tuft cell markers were identified in various TCGA datasets. Twelve of the 22 “tuft cell-like tumours” shared poor differentiation and a gene expression pattern, including KIT, anti-apoptotic BCL2, and ionocyte-associated genes. In our archival cases, eleven (1.21%) tumours co-expressing POU2F3, KIT, and BCL2 on immunohistochemistry, i.e., were presumable tuft cell-like cancers. In three among five TCGA cohorts, the tuft cell-like cancer subsets expressed SLFN11, a promising biomarker of PARP inhibitor susceptibility.
Conclusions
Tuft cell-like carcinomas form distinct subsets in cancers of many organs. It appears warranted to investigate their shared gene expression signature as a predictive biomarker for novel therapeutic strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data on TCGA and PanCancer Atlas that support the findings of this study are available in cBioPortal (http://www.cbioportal.org/).
References
von Moltke J, Ji M, Liang HE, Locksley RM. Tuft-cell-derived IL-25 regulates an intestinal ILC2-epithelial response circuit. Nature. 2016;529:221–5.
Howitt MR, Lavoie S, Michaud M, Blum AM, Tran SV, Weinstock JV, et al. Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut. Science. 2016;351:1329–33.
Gerbe F, Sidot E, Smyth DJ, Ohmoto M, Matsumoto I, Dardalhon V, et al. Intestinal epithelial tuft cells initiate type 2 mucosal immunity to helminth parasites. Nature. 2016;529:226–30.
Schneider C, O’Leary CE, Locksley RM. Regulation of immune responses by tuft cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:584–93.
Huang YH, Klingbeil O, He XY, Wu XS, Arun G, Lu B, et al. POU2F3 is a master regulator of a tuft cell-like variant of small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev. 2018;32:915–28.
Schütz B, Ruppert AL, Strobel O, Lazarus M, Urade Y, Büchler MW, et al. Distribution pattern and molecular signature of cholinergic tuft cells in human gastro-intestinal and pancreatic-biliary tract. Sci Rep. 2019;9:17466.
Bornstein C, Nevo S, Giladi A, Kadouri N, Pouzolles M, Gerbe F, et al. Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells. Nature. 2018;559:622–6.
Miller CN, Proekt I, von Moltke J, Wells KL, Rajpurkar AR, Wang H, et al. Thymic tuft cells promote an IL-4-enriched medulla and shape thymocyte development. Nature. 2018;559:627–31.
Nevo S, Kadouri N, Abramson J. Tuft cells: from the mucosa to the thymus. Immunol Lett. 2019;210:1–9.
Goto N, Fukuda A, Yamaga Y, Yoshikawa T, Maruno T, Maekawa H, et al. Lineage tracing and targeting of IL17RB+ tuft cell-like human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:12996–3005.
Nakanishi Y, Seno H, Fukuoka A, Ueo T, Yamaga Y, Maruno T, et al. Dclk1 distinguishes between tumor and normal stem cells in the intestine. Nat Genet. 2013;45:98–103.
DelGiorno KE, Chung CY, Vavinskaya V, Maurer HC, Novak SW, Lytle NK, et al. Tuft cells inhibit pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice by producing prostaglandin D2. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1866.e8–81.e8.
Yamashita J, Ohmoto M, Yamaguchi T, Matsumoto I, Hirota J. Skn-1a/Pou2f3 functions as a master regulator to generate Trpm5-expressing chemosensory cells in mice. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0189340.
Yamada Y, Simon-Keller K, Belharazem-Vitacolonnna D, Bohnenberger H, Kriegsmann M, Kriegsmann K, et al. A tuft cell-like signature is highly prevalent in thymic squamous cell carcinoma and delineates new molecular subsets among the major lung cancer histotypes. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16:1003–16.
Baine MK, Hsieh MS, Lai WV, Egger JV, Jungbluth AA, Daneshbod Y, et al. SCLC subtypes defined by ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1: a comprehensive immunohistochemical and histopathologic characterization. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:1823–35.
Rudin CM, Poirier JT, Byers LA, Dive C, Dowlati A, George J, et al. Molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer: a synthesis of human and mouse model data. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19:289–97.
Gay CM, Stewart CA, Park EM, Diao L, Groves SM, Heeke S, et al. Patterns of transcription factor programs and immune pathway activation define four major subtypes of SCLC with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:346.e7–60.e7.
Yoshino T, Pentheroudakis G, Mishima S, Overman MJ, Yeh KH, Baba E, et al. JSCO-ESMO-ASCO-JSMO-TOS: international expert consensus recommendations for tumour-agnostic treatments in patients with solid tumours with microsatellite instability or NTRK fusions. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:861–72.
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–4.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6:pl1.
George J, Lim JS, Jang SJ, Cun Y, Ozretić L, Kong G, et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2015;524:47–53.
George J, Walter V, Peifer M, Alexandrov LB, Seidel D, Leenders F, et al. Integrative genomic profiling of large-cell neuroendocrine carcinomas reveals distinct subtypes of high-grade neuroendocrine lung tumors. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1048.
Montoro DT, Haber AL, Biton M, Vinarsky V, Lin B, Birket SE, et al. A revised airway epithelial hierarchy includes CFTR-expressing ionocytes. Nature. 2018;560:319–24.
Plasschaert LW, Žilionis R, Choo-Wing R, Savova V, Knehr J, Roma G, et al. A single-cell atlas of the airway epithelium reveals the CFTR-rich pulmonary ionocyte. Nature. 2018;560:377–81.
Coleman N, Zhang B, Byers LA, Yap TA. The role of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) as a predictive biomarker for targeting the DNA damage response. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:857–9.
Winkler C, Armenia J, Jones GN, Tobalina L, Sale MJ, Petreus T, et al. SLFN11 informs on standard of care and novel treatments in a wide range of cancer models. Br J Cancer. 2021;124:951–62.
Rathkey D, Khanal M, Murai J, Zhang J, Sengupta M, Jiang Q, et al. Sensitivity of mesothelioma cells to PARP inhibitors is not dependent on BAP1 but is enhanced by temozolomide in cells with high-Schlafen 11 and low-O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:843–59.
Lok BH, Gardner EE, Schneeberger VE, Ni A, Desmeules P, Rekhtman N, et al. PARP inhibitor activity correlates with SLFN11 expression and demonstrates synergy with temozolomide in small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:523–35.
Pietanza MC, Waqar SN, Krug LM, Dowlati A, Hann CL, Chiappori A, et al. Randomized, double-blind, phase II study of temozolomide in combination with either veliparib or placebo in patients with relapsed-sensitive or refractory small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2386–94.
Polley E, Kunkel M, Evans D, Silvers T, Delosh R, Laudeman J, et al. Small cell lung cancer screen of oncology drugs, investigational agents, and gene and microRNA expression. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108:djw122.
Bautista JL, Cramer NT, Miller CN, Chavez J, Berrios DI, Byrnes LE, et al. Single-cell transcriptional profiling of human thymic stroma uncovers novel cellular heterogeneity in the thymic medulla. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1096.
Huang N, Pérez P, Kato T, Mikami Y, Okuda K, Gilmore RC, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the oral cavity and saliva. Nat Med. 2021;27:892–903.
Skala SL, Wang X, Zhang Y, Mannan R, Wang L, Narayanan SP, et al. Next-generation RNA sequencing-based biomarker characterization of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and related oncocytic neoplasms. Eur Urol. 2020;78:63–74.
Goldfarbmuren KC, Jackson ND, Sajuthi SP, Dyjack N, Li KS, Rios CL, et al. Dissecting the cellular specificity of smoking effects and reconstructing lineages in the human airway epithelium. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2485.
Chan JM, Quintanal-Villalonga Á, Gao VR, Xie Y, Allaj V, Chaudhary O, et al. Signatures of plasticity, metastasis, and immunosuppression in an atlas of human small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:1479–96. e18
Pozo K, Kollipara RK, Kelenis DP, Rodarte KE, Ullrich MS, Zhang X, et al. ASCL1, NKX2-1, and PROX1 co-regulate subtype-specific genes in small-cell lung cancer. iScience. 2021;24:102953.
Radovich M, Pickering CR, Felau I, Ha G, Zhang H, Jo H, et al. The integrated genomic landscape of thymic epithelial tumors. Cancer Cell. 2018;33:244.e10–58.e10.
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Digestive system tumours. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2019.
Murai J, Thomas A, Miettinen M, Pommier Y. Schlafen 11 (SLFN11), a restriction factor for replicative stress induced by DNA-targeting anti-cancer therapies. Pharm Ther. 2019;201:94–102.
Zhu Q, Zhan P, Zhang X, Lv T, Song Y. Clinicopathologic characteristics of patients with ROS1 fusion gene in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4:300–9.
Wu XS, He XY, Ipsaro JJ, Huang YH, Preall JB, Ng D, et al. OCA-T1 and OCA-T2 are coactivators of POU2F3 in the tuft cell lineage. Nature. 2022;607:169–75.
Baine MK, Febres-Aldana CA, Chang JC, Jungbluth AA, Sethi S, Antonescu CR, et al. POU2F3 in SCLC: clinicopathologic and genomic analysis with a focus on its diagnostic utility in neuroendocrine-low SCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2022.06.004.
Funding
Y.Y. is currently receiving a grant, JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP21K06902.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experimental design and idea: YY, HB, AM. Data mining and statistical analysis: YY. Tissue (including tissue microarrays), clinical and molecular data acquisition: HB, MK, KK, PS, NG, YN, HS, HC, RS, GS. Pathology analysis: YY, HB, MK, KK, PS, MF, SM, HH, PS, AM. Manuscript writing: YY, HB, PS, AM. Correction and approval of manuscript: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee II, University of Heidelberg, approval no. 2017-806R-MA and the ethical committee of Kyoto University Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, Y., Bohnenberger, H., Kriegsmann, M. et al. Tuft cell-like carcinomas: novel cancer subsets present in multiple organs sharing a unique gene expression signature. Br J Cancer 127, 1876–1885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-022-01957-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-022-01957-6
This article is cited by
-
POU2F3-expressing intraepithelial small-cell carcinoma with mixed small-cell carcinoma and conventional-type urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder
Virchows Archiv (2024)
-
Expression of FOXI1 and POU2F3 varies among different salivary gland neoplasms and is higher in Warthin tumor
Discover Oncology (2024)
-
An exploratory study for tuft cells in the breast and their relevance in triple-negative breast cancer: the possible relationship of SOX9
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Appearance of tuft cells during prostate cancer progression
Oncogene (2023)