Abstract
Background
While emerging evidence indicates that N6-methyladenosine (m6A) regulators play crucial roles in cancer progression, their clinical significance in gastric cancer (GC) has thus far not been elucidated.
Methods
We investigated the expression of the m6A regulator genes and their prognostic potential in a large clinical cohort of 173 GC patients using qRT-PCR assays. In addition, we undertook a series of in-vitro and in-vivo functional studies to investigate the oncogenic role of FTO.
Results
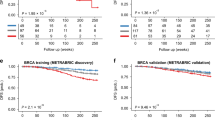
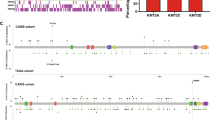
GC patients with low expression of METTL3, METTL14, ALKBH5, WTAP and YTHDF1 demonstrated significantly poor OS, while patients with high FTO expression exhibited markedly worse OS. Furthermore, the cumulative risk-score derived from these gene panel also significantly associated with poor OS, with a corresponding hazard ratio of 5.47 (95% CI: 3.18–9.41, p < 0.0001). We observed that FTO expression was frequently upregulated in GC cell lines, with epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) features. FTO knockdown in HGC27 and AGS cells inhibited cell proliferation and migratory potential, while its overexpression in MKN28 cells resulted in enhanced proliferation and migration. Finally, confirming our in-vitro findings, FTO suppression led to significant tumour growth inhibition in a HGC27 xenograft model.
Conclusions
We demonstrate that m6A regulators may serve as promising prognostic biomarkers in GC. Our functional studies reveal that FTO is an important oncogene and may be a promising therapeutic target associated with EMT-alterations in gastric cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available within the article.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33.
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, Yao Y, Wei Q, Ajani JA. Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:643–55.
Wu HH, Lin WC, Tsai KW. Advances in molecular biomarkers for gastric cancer: miRNAs as emerging novel cancer markers. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2014;16:e1.
Wei CM, Gershowitz A, Moss B. Methylated nucleotides block 5’ terminus of HeLa cell messenger RNA. Cell. 1975;4:379–86.
Bokar JA, Shambaugh ME, Polayes D, Matera AG, Rottman FM. Purification and cDNA cloning of the AdoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase. RNA. 1997;3:1233–47.
Fu Y, Dominissini D, Rechavi G, He C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m(6)A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15:293–306.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;18:31–42.
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6.
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46.
Schwartz S, Agarwala SD, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Mertins P, Shishkin A, et al. High-resolution mapping reveals a conserved, widespread, dynamic mRNA methylation program in yeast meiosis. Cell. 2013;155:1409–21.
Zhao BS, He C. Fate by RNA methylation: m6A steers stem cell pluripotency. Genome Biol. 2015;16:43.
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10:93–95.
Ping XL, Sun BF, Wang L, Xiao W, Yang X, Wang WJ, et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24:177–89.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–7.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma Stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017;18:2622–34.
Zhang S, Zhao BS, Zhou A, Lin K, Zheng S, Lu Z, et al. m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 maintains tumorigenicity of glioblastoma stem-like cells by sustaining FOXM1 expression and cell proliferation program. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:591–606 e596.
Zhang C, Samanta D, Lu H, Bullen JW, Zhang H, Chen I, et al. Hypoxia induces the breast cancer stem cell phenotype by HIF-dependent and ALKBH5-mediated m(6)A-demethylation of NANOG mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E2047–2056.
Zhang C, Zhi WI, Lu H, Samanta D, Chen I, Gabrielson E, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate pluripotency factor expression by ZNF217- and ALKBH5-mediated modulation of RNA methylation in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7:64527–42.
Li Z, Weng H, Su R, Weng X, Zuo Z, Li C, et al. FTO Plays an oncogenic role in acute myeloid leukemia as a N(6)-methyladenosine RNA demethylase. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:127–41.
Kwok CT, Marshall AD, Rasko JE, Wong JJ. Genetic alterations of m(6)A regulators predict poorer survival in acute myeloid leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:39.
Ma JZ, Yang F, Zhou CC, Liu F, Yuan JH, Wang F, et al. METTL14 suppresses the metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma by modulating N(6) -methyladenosine-dependent primary MicroRNA processing. Hepatology. 2017;65:529–43.
Su R, Dong L, Li Y, Gao M, Han L, Wunderlich M, et al. Targeting FTO suppresses cancer stem cell maintenance and immune evasion. Cancer Cell. 2020;38:79–96 e11.
Kandimalla R, Gao F, Li Y, Huang H, Ke J, Deng X, et al. RNAMethyPro: a biologically conserved signature of N6-methyladenosine regulators for predicting survival at pan-cancer level. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2019;3:13.
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9:671–5.
Bartzatt R. Anti-inflammatory drugs and prediction of new structures by comparative analysis. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2012;11:151–60.
Zheng G, Cox T, Tribbey L, Wang GZ, Iacoban P, Booher ME, et al. Synthesis of a FTO inhibitor with anticonvulsant activity. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014;5:658–65.
Huang Y, Yan J, Li Q, Li J, Gong S, Zhou H, et al. Meclofenamic acid selectively inhibits FTO demethylation of m6A over ALKBH5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:373–84.
Wang X, Li Z, Kong B, Song C, Cong J, Hou J, et al. Reduced m(6)A mRNA methylation is correlated with the progression of human cervical cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8:98918–30.
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT, Colman H, et al. FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:427–42.
Li Y, Zhang S, Huang S. FoxM1: a potential drug target for glioma. Future Oncol. 2012;8:223–6.
Xu D, Shao W, Jiang Y, Wang X, Liu Y, Liu X. FTO expression is associated with the occurrence of gastric cancer and prognosis. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:2285–92.
Li Y, Zheng D, Wang F, Xu Y, Yu H, Zhang H. Expression of demethylase genes, FTO and ALKBH1, is associated with prognosis of gastric cancer. Digestive Dis Sci. 2019;64:1503–13.
Zhang C, Zhang M, Ge S, Huang W, Lin X, Gao J, et al. Reduced m6A modification predicts malignant phenotypes and augmented Wnt/PI3K-Akt signaling in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 2019;8:4766–81.
Su Y, Huang J, Hu J. m(6)A RNA methylation regulators contribute to malignant progression and have clinical prognostic impact in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1038.
Guan K, Liu X, Li J, Ding Y, Li J, Cui G, et al. Expression status and prognostic value of M6A-associated Genes in gastric cancer. J Cancer. 2020;11:3027–40.
Zhang J, Piao HY, Wang Y, Meng XY, Yang D, Zhao Y, et al. To develop and validate the combination of RNA methylation regulators for the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020;13:10785–95.
Xu X, Zhou E, Zheng J, Zhang C, Zou Y, Lin J, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of m6A “Eraser” related gene signature in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:631803.
Jing JJ, Zhao X, Li H, Sun LP, Yuan Y. Expression profiles and prognostic roles of m6A writers, erasers and readers in gastric cancer. Future Oncol. 2021;17:2605–20.
Wang D, Qu X, Lu W, Wang Y, Jin Y, Hou K, et al. N(6)-Methyladenosine RNA demethylase FTO promotes gastric cancer metastasis by down-regulating the m6A methylation of ITGB1. Front Oncol. 2021;11:681280.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–90.
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA, Thiery JP. Emt: 2016. Cell. 2016;166:21–45.
Roche, J, Gemmill, RM & Drabkin, HA. Epigenetic regulation of the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2017:9:72.
Liu N, Parisien M, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Pan T. Probing N6-methyladenosine RNA modification status at single nucleotide resolution in mRNA and long noncoding RNA. RNA. 2013;19:1848–56.
Dai Q, Fong R, Saikia M, Stephenson D, Yu YT, Pan T, et al. Identification of recognition residues for ligation-based detection and quantitation of pseudouridine and N6-methyladenosine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35:6322–9.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505:117–20.
Chi KR. The RNA code comes into focus. Nature. 2017;542:503–6.
Helm M, Motorin Y. Detecting RNA modifications in the epitranscriptome: predict and validate. Nat Rev Genet. 2017;18:275–91.
Batista PJ, Molinie B, Wang J, Qu K, Zhang J, Li L, et al. m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15:707–19.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Preethi Ravindranathan, Aki Sakatani, Michael Hsieh, and Kinnari Pankaj Modi for experimental advice, and acknowledge Divya Pasham, Ashley Cao, Maddie Brown, and Anna Wakita for experimental support.
Funding
This work was supported by CA184792, CA187956, CA227602, CA072851 and CA202797, grants from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, and a pilot grant from the Stupid Strong Foundation to A Goel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design: TS, RK and AG; Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: TS, RK; Drafting of the manuscript: TS, RK, YO, MO, YT and AG; Statistical analysis: TS, and RK; Administrative, technical, or material support: TS, YO, MO, YT and AG; Supervision: AG
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All study-related procedures were performed as per the Declarations of Helsinki, wherein a written informed consent was obtained from each patient, and the institutional review boards of all participating institutions involved approved the study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimura, T., Kandimalla, R., Okugawa, Y. et al. Novel evidence for m6A methylation regulators as prognostic biomarkers and FTO as a potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer 126, 228–237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01581-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01581-w
This article is cited by
-
METTL3 and METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SREBF2-AS1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and sorafenib resistance through DNA demethylation of SREBF2
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Clinical significance and functional role of adhesion G-protein-coupled receptors in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
A liquid biopsy signature for predicting early recurrence in patients with gastric cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
m6A modification of AC026356.1 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating the IGF2BP1-IL11 axis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Role of N6-methyladenosine RNA modification in gastric cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2023)