Abstract
Background
CHK1 is considered an oncogene with overexpression in numerous cancers. However, CHK1 signalling regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear.
Methods
CHEK1 mRNA, protein, pri-miR-195 and miR-195 expression in HCC tissue was determined by qPCR, WB and IF staining assay. Survival analyses in HCC with high- and low-CHEK1 mRNA expression was performed using TCGA database. Relative luciferase activity was investigated in HCC cells transfected with p-CHEK1 3’UTR. Apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay. NK and CD8+ T cells were analysed by flow cytometry.
Results
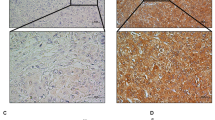
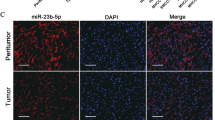
CHK1 is increased in human HCC tumours compared with non-cancerous liver. High CHK1 predicts worse prognosis. IFN-γ suppresses CHK1 via IRF-1 in HCC cells. The molecular mechanism of IRF-1 suppressing CHK1 is post-transcriptional by promoting miR-195 binding to CHEK1 mRNA 3’UTR, which exerts a translational blockade. Upregulated IRF-1 inhibits CHK1, which induces apoptosis of HCC cells. Likewise, CHK1 inhibition augments cellular apoptosis in HCC tumours. This effect may be a result of increased tumour NK cell infiltration. However, IRF-1 expression or CHK1 inhibition also upregulates PD-L1 expression via increased STAT3 phosphorylation.
Conclusions
IRF-1 induces miR-195 to suppress CHK1 protein expression. Both increased IRF-1 and decreased CHK1 upregulate cellular apoptosis and PD-L1 expression in HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre, L. A., Bray, F., Siegel, R. L., Ferlay, J., Lortet-Tieulent, J. & Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65, 87–108 (2015).
Sadeghi, S., Bejjani, A. & Finn, R. S. Systemic therapy for primary liver tumors: cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 28, 695–715 (2019).
Wildi, S., Pestalozzi, B. C., Mccormack, L. & Clavien, P. A. Critical evaluation of the different staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 91, 400–408 (2004).
Clavien, P. A., Lesurtel, M., Bossuyt, P. M., Gores, G. J., Langer, B., Perrier, A. et al. Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an international consensus conference report. Lancet Oncol. 13, e11–e22 (2012).
Montironi, C., Montal, R. & Llovet, J. M. New drugs effective in the systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 14, 56–61 (2019).
Marquardt, J. U., Saborowski, A., Czauderna, C. & Vogel, A. The changing landscape of systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: new targeted agents and immunotherapies. Target Oncol. 14, 115–123 (2019).
Dai, Y. & Grant, S. New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 376–383 (2010).
Zhang, Y. & Hunter, T. Roles of Chk1 in cell biology and cancer therapy. Int. J. Cancer 134, 1013–1023 (2014).
Pouliot, L. M., Chen, Y. C., Bai, J., Guha, R., Martin, S. E., Gottesman, M. M. et al. Cisplatin sensitivity mediated by WEE1 and CHK1 is mediated by miR-155 and the miR-15 family. Cancer Res. 72, 5945–5955 (2012).
Bever, K. M. & Le, D. T. DNA repair defects and implications for immunotherapy. J. Clin. Invest. 128, 4236–4242 (2018).
Shevtsov, M., Sato, H., Multhoff, G. & Shibata, A. Novel approaches to improve the efficacy of immuno-radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 9, 156 (2019).
Sen, T., Rodriguez, B. L., Chen, L., Corte, C. M. D., Morikawa, N., Fujimoto, J. et al. Targeting DNA damage response promotes antitumor immunity through STING-mediated T-cell activation in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 9, 646–661 (2019).
Mouw, K. W. & Konstantinopoulos, P. A. From checkpoint to checkpoint: DNA damage ATR/Chk1 checkpoint signalling elicits PD-L1 immune checkpoint activation. Br. J. Cancer 118, 933–935 (2018).
Sato, H., Niimi, A., Yasuhara, T., Permata, T. B. M., Hagiwara, Y., Isono, M. et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 8, 1751 (2017).
Sen, T., Della Corte, C. M., Milutinovic, S., Cardnell, R. J., Diao, L., Ramkumar, K. et al. Combination treatment of the oral CHK1 inhibitor, SRA737, and low-dose gemcitabine enhances the effect of programmed death ligand 1 blockade by modulating the immune microenvironment in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 14, 2152–2163 (2019).
Hong, J., Hu, K., Yuan, Y., Sang, Y., Bu, Q., Chen, G. et al. CHK1 targets spleen tyrosine kinase (L) for proteolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 2165–2175 (2012).
Myers, K., Gagou, M. E., Zuazua-Villar, P., Rodriguez, R. & Meuth, M. ATR and Chk1 suppress a caspase-3-dependent apoptotic response following DNA replication stress. PLoS Genet. 5, e1000324 (2009).
Tamura, T., Yanai, H., Savitsky, D. & Taniguchi, T. The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 26, 535–584 (2008).
Bowie, M. L., Troch, M. M., Delrow, J., Dietze, E. C., Bean, G. R., Ibarra, C. et al. Interferon regulatory factor-1 regulates reconstituted extracellular matrix (rECM)-mediated apoptosis in human mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 26, 2017–2026 (2007).
Hong, S., Kim, H. Y., Kim, J., Ha, H. T., Kim, Y. M., Bae, E. et al. Smad7 protein induces interferon regulatory factor 1-dependent transcriptional activation of caspase 8 to restore tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 3560–3570 (2013).
Stang, M. T., Armstrong, M. J., Watson, G. A., Sung, K. Y., Liu, Y., Ren, B. et al. Interferon regulatory factor-1-induced apoptosis mediated by a ligand-independent fas-associated death domain pathway in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 26, 6420–6430 (2007).
Kim, P. K., Armstrong, M., Liu, Y., Yan, P., Bucher, B., Zuckerbraun, B. S. et al. IRF-1 expression induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in mouse mammary cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 23, 1125–1135 (2004).
Li, P., Du, Q., Cao, Z., Guo, Z., Evankovich, J., Yan, W. et al. Interferon-gamma induces autophagy with growth inhibition and cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells through interferon-regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1). Cancer Lett. 314, 213–222 (2012).
Carthew, R. W. & Sontheimer, E. J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136, 642–655 (2009).
Lujambio, A. & Lowe, S. W. The microcosmos of cancer. Nature 482, 347–355 (2012).
Bonci, D., Coppola, V., Musumeci, M., Addario, A., Giuffrida, R., Memeo, L. et al. The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat. Med. 14, 1271–1277 (2008).
Cutrona, G., Matis, S., Colombo, M., Massucco, C., Baio, G., Valdora, F. et al. Effects of miRNA-15 and miRNA-16 expression replacement in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implication for therapy. Leukemia 31, 1894–1904 (2017).
Xia, L., Zhang, D., Du, R., Pan, Y., Zhao, L., Sun, S. et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 123, 372–379 (2008).
Zhang, B., Wang, X., Deng, J., Zheng, H., Liu, W., Chen, S. et al. p53-dependent upregulation of miR-16-2 by sanguinarine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 459, 50–58 (2019).
Kim, C., Hong, Y., Lee, H., Kang, H. & Lee, E. K. MicroRNA-195 desensitizes HCT116 human colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Lett. 412, 264–271 (2018).
Bargiela-Iparraguirre, J., Prado-Marchal, L., Fernandez-Fuente, M., Gutierrez-Gonzalez, A., Moreno-Rubio, J., Munoz-Fernandez, M. et al. CHK1 expression in Gastric Cancer is modulated by p53 and RB1/E2F1: implications in chemo/radiotherapy response. Sci. Rep. 6, 21519 (2016).
Yu, X., Zhang, Y., Ma, X. & Pertsemlidis, A. miR-195 potentiates the efficacy of microtubule-targeting agents in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 427, 85–93 (2018).
Yokota, S., Yoshida, O., Dou, L., Spadaro, A. V., Isse, K., Ross, M. A. et al. IRF-1 promotes liver transplant ischemia/reperfusion injury via hepatocyte IL-15/IL-15Ralpha production. J. Immunol. 194, 6045–6056 (2015).
Ueki, S., Dhupar, R., Cardinal, J., Tsung, A., Yoshida, J., Ozaki, K. S. et al. Critical role of interferon regulatory factor-1 in murine liver transplant ischemia reperfusion injury. Hepatology 51, 1692–1701 (2010).
Du, Q., Zhang, X., Liu, Q., Zhang, X., Bartels, C. E. & Geller, D. A. Nitric oxide production upregulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by inhibiting Dickkopf-1. Cancer Res. 73, 6526–6537 (2013).
Lal, A., Navarro, F., Maher, C. A., Maliszewski, L. E., Yan, N., O’day, E. et al. miR-24 Inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to “seedless” 3’UTR microRNA recognition elements. Mol. Cell. 35, 610–625 (2009).
Chandrashekar, D. S., Bashel, B., Balasubramanya, S. A. H., Creighton, C. J., Ponce-Rodriguez, I., Chakravarthi, B. et al. UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19, 649–658 (2017).
Cerami, E., Gao, J., Dogrusoz, U., Gross, B. E., Sumer, S. O., Aksoy, B. A. et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2, 401–404 (2012).
Yan, Y., Zheng, L., Du, Q., Yan, B. & Geller, D. A. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2 regulate PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 69, 1891–1903 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02586-9.
Parmar, K., Kochupurakkal, B. S., Lazaro, J. B., Wang, Z. C., Palakurthi, S., Kirschmeier, P. T. et al. The CHK1 inhibitor prexasertib exhibits monotherapy activity in high-grade serous ovarian cancer models and sensitizes to PARP inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 6127–6140 (2019).
Lowery, C. D., Dowless, M., Renschler, M., Blosser, W., Vanwye, A. B., Stephens, J. R. et al. Broad spectrum activity of the checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitor prexasertib as a single agent or chemopotentiator across a range of preclinical pediatric tumor models. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 2278–2289 (2019).
Garcia-Diaz, A., Shin, D. S., Moreno, B. H., Saco, J., Escuin-Ordinas, H., Rodriguez, G. A. et al. Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. 19, 1189–1201 (2017).
Ding, L., Chen, X., Xu, X., Qian, Y., Liang, G., Yao, F. et al. PARP1 suppresses the transcription of PD-L1 by poly(ADP-Ribosyl)ating STAT3. Cancer Immunol. Res. 7, 136–149 (2019).
Koh, J., Jang, J. Y., Keam, B., Kim, S., Kim, M. Y., Go, H. et al. EML4-ALK enhances programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma via hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and STAT3. Oncoimmunology 5, e1108514 (2016).
Sun, C., Mezzadra, R. & Schumacher, T. N. Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity 48, 434–452 (2018).
Hsu, J., Hodgins, J. J., Marathe, M., Nicolai, C. J., Bourgeois-Daigneault, M. C., Trevino, T. N. et al. Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. J. Clin. Invest. 128, 4654–4668 (2018).
Karnitz, L. M. & Zou, L. Molecular pathways: targeting ATR in cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 21, 4780–4785 (2015).
Angius, G., Tomao, S., Stati, V., Vici, P., Bianco, V. & Tomao, F. Prexasertib, a checkpoint kinase inhibitor: from preclinical data to clinical development. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 85, 9–20 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03950-y.
Tanaka, N., Ishihara, M. & Taniguchi, T. Suppression of c-myc or fosB-induced cell transformation by the transcription factor IRF-1. Cancer Lett. 83, 191–196 (1994).
Kroger, A., Dallugge, A., Kirchhoff, S. & Hauser, H. IRF-1 reverts the transformed phenotype of oncogenically transformed cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 22, 1045–1056 (2003).
Wang, W. J., Wu, S. P., Liu, J. B., Shi, Y. S., Huang, X., Zhang, Q. B. et al. MYC regulation of CHK1 and CHK2 promotes radioresistance in a stem cell-like population of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 73, 1219–1231 (2013).
Yu, W., Liang, X., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Sun, Z., Liu, Y. et al. MicroRNA-195: a review of its role in cancers. Onco Targets Ther. 11, 7109–7123 (2018).
Vivier, E., Raulet, D. H., Moretta, A., Caligiuri, M. A., Zitvogel, L., Lanier, L. L. et al. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science 331, 44–49 (2011).
Lee, M. H., Liu, K. H., Thomas, J. L., Chen, J. R. & Lin, H. Y. Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma with magnetic PD-1 peptide-imprinted polymer nanocomposite and natural killer cells. Biomolecules. 9, 651 (2019).
Zhou, J., Peng, H., Li, K., Qu, K., Wang, B., Wu, Y. et al. Liver-resident NK cells control antiviral activity of hepatic T cells via the PD-1-PD-L1 axis. Immunity 50, 403–17 e4 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Y. and D.A.G. designed the research. Y.Y., L.Z., Q.D., X.C., K.D. and Y.G. performed research and also analysed the data. Y.Y. and D.A.G. wrote the paper. All authors edited and approved the submission of this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Human tissue samples were obtained in accordance with the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Review Board (IRB) approved protocol (No. MOD08010372/PRO08010372). Animal experiments were approved by the University of Pittsburgh Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol No. 18012053).
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Funding information
This work was supported by the NIH Grant (HHSN276201200017C and P30DK120531-01, D.A.G.), and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2017GXNSFAA198014 and 2020GXNSFAA297008, Y.Y.).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., Zheng, L., Du, Q. et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) downregulates Checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1) through miR-195 to upregulate apoptosis and PD-L1 expression in Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Br J Cancer 125, 101–111 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01337-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-021-01337-6
This article is cited by
-
MicroRNAs as regulators of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy: targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4 pathways
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
Noninvasive evaluation of PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer by immunoPET imaging using an acylating agent–modified antibody fragment
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2023)