Abstract
Emerging clinical and histologic evidence is challenging the long-established dogma that root canal treatment (RCTx) is the only therapeutic option for preservation of vital mature permanent teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposure. Vital pulp therapy procedures like pulpotomy are not only technically simpler and more economical, but also afford patients a host of other benefits over conventional RCTx. This narrative review provides an update on the contemporary understanding of pulp pathophysiology and defence mechanisms, the proposed new diagnostic terminologies for pulpal inflammation, and how the biological characteristics of hydrophilic calcium silicate cements have enabled consistent successful outcomes for pulpotomy-treated mature teeth. The paper also details the evidence base from clinical trials and systematic reviews conducted over the past decade and outlines the practical treatment considerations for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth.
Key points
-
Provides a contemporary update on pulp pathophysiology and defence mechanisms.
-
Presents proposed new diagnostic terminologies for pulpitis.
-
Details the most recent evidence base for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth.
-
Outlines treatment considerations for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction: a new era for minimally invasive endodontics
Dogmas in medicine and dentistry are often cherished with implicit faith, despite the lack of high-quality evidence. Paradigm shifts from existing treatment practices often generate great resistance, even at the risk of delivering poor-quality care to patients. One such closely held belief is that a vital mature permanent tooth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis will require root canal treatment (RCTx) for long-term preservation of the tooth. Less invasive vital pulp therapy (VPT) procedures like pulpotomy were restricted to immature permanent teeth, with the goal of ensuring completion of their root formation (apexogenesis). However, there is now growing evidence to suggest that irrespective of whether the permanent teeth are mature or immature, if the pulpal infection and inflammation can be controlled, even ‘irreversibly' inflamed pulp tissue appear capable of healing, thus allowing for the conservative management of such teeth.1,2 Recent position statements from the American Association of Endodontists and the European Society of Endodontology (ESE) have concluded that ‘pre-treatment diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis is not necessarily an indication for pulpectomy',3,4 heralding a new era for minimally invasive VPT in mature permanent teeth. This paradigm shift suggests the need for dentists to consider offering pulpotomy as a definitive treatment modality for managing mature permanent teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposures. The rationale, evidence base and treatment considerations for successful pulpotomy in vital mature permanent teeth are presented in this paper.
Pulp defence mechanisms
Historically, the dental pulp was believed to be very vulnerable to tissue insult from bacterial carious attack and the resulting inflammation. The low compliance dentinal walls and lack of collateral circulation was thought to limit the ability of pulp tissue to accommodate increases in intra-pulpal pressure or effectively deliver humoral and cellular immune components to the injured site. The diagnostic consensus was that cariously exposed pulp in mature permanent teeth should be considered irreversibly inflamed based on the rationale that the underlying inflammation has spread throughout the pulp tissue and the restricted blood supply through the closed apices of mature teeth would not be enough to promote healing, even if the tissue insult is removed.2 However, studies have shown that dental pulp can not only accommodate moderate increases in intra-pulpal pressure during inflammation,5,6 but that the dental pulp also has an effective immune defence response.7,8,9
Contemporary understanding of dental pulp pathophysiology and defence mechanisms have confirmed early studies that showed the innate ability of pulp tissue to heal itself if the insult is removed.10 The abundant fibroblast cells in the pulpal tissue are the only non-immune cells in the body capable of activating the complement system and play a central role in modulating the repair and healing potential of pulp.11 Besides pulp fibroblasts, adult dental pulp stem cells also contribute to the regenerative potential of pulp in mature permanent teeth. Recent data have suggested that pulp defence mechanisms are mediated via the following pathways: i) complement activation by pulp fibroblasts expresses significant anti-inflammatory potential and also contributes to tissue regeneration by recruiting pulp progenitors;12 ii) pulp fibroblasts can directly induce lysis of cariogenic bacteria;13 iii) chemokines released from injured pulp tissue attract mesenchymal dental pulp stem cells that can differentiate into odontoblast-like cells and induce reparative dentine formation;14 and iv) synthesis and release of antimicrobial peptides by dental pulp stem cells.9
Histopathologic and histobacteriologic studies have shown that, in teeth with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposures, there is a bacterially colonised necrotic area of varying dimensions in the pulp chamber.15 However, few millimetres away from the bacterially colonised necrotic tissue, it is not unusual to find the healthy pulpal architecture that is generally free from inflammation and bacteria.16,17 Innate and adaptive immune defence mechanisms equip the pulp to limit the spread of bacterial infection.18,19 If no treatment is rendered to eliminate the infected pulp, the pulp infection at the carious exposure site will gradually spread to involve the entire coronal pulp, although the radicular pulp can still remain free from infection.15 In theory, if the infected coronal pulp is completely removed, a favourable environment can be created for radicular pulpal healing as the immunoinflammatory cells get eliminated by apoptosis and the odontoblast-like cells induce dentine bridge formation. Taken together, the histological picture of a severely inflamed pulp may not always be a sign of irreversibility in terms of infection.
Thus, the current interpretation of pulp inflammation includes the understanding that ‘irreversible' pulpitis need not to be seen as a one-way route towards pulp cell impairment and subsequent necrosis, but as a ‘double-edged sword', where a so-called wanted inflammation, given the right balance, can result in pulpal repair and healing. On the other hand, if the pulpal inflammation is sustained and uncontrolled, it will inevitably lead to an infected pulp cavity and tissue necrosis.20,21 However, the demarcation point at which pulpal inflammation becomes truly irreversible is difficult to determine based solely on patient symptoms and currently available diagnostic tests.2
New diagnostic terminology for pulpitis
Traditionally, identifying reversible/irreversible pulpitis relied on a patient's subjective description of symptoms and pulp sensibility tests. However, the simple dichotomous way of describing inflamed vital pulp as reversible or irreversible pulpitis does not match the current understanding of pulp biology and the defensive response of the pulp complex.22 With histologic evidence showing that there is no discrete boundary that would render a pulp irreversibly inflamed and beyond repair, it may be better to consider pulpitis as a temporally and spatially graded disease.3 The contemporary understanding of pulpal inflammation and healing have led to calls to revise the existing diagnostic nomenclature.23,24 Wolters and co-workers expanded the classification of pulpitis based on patient symptoms and possible histologic picture and related them to different VPT modalities (Table 1).24 The ESE proposed the term ‘partial irreversible pulpitis' as possibly a more accurate clinical reflection of the histological picture,4 while others have suggested that the diagnostic term for pulpal inflammation should be confined to ‘pulpitis' without any further designation.2 In the context of practising minimally invasive endodontics, the terms ‘reversible' and ‘irreversible' are considered obsolete, especially considering our improved understanding of the pulp biology and the importance of preserving vital pulp.25 The proposed new diagnostic terminologies can guide clinicians in choosing more conservative therapeutic options when treating patients with caries-induced pulpal inflammation.
Why pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth?
Full pulpectomy and RCTx of vital mature permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposure can be considered as a prophylactic procedure to prevent further pulpal infection and subsequent development of apical periodontitis (AP).1 There is no doubt that a correctly performed RCTx can achieve high success rates.26,27 Unfortunately, cross-sectional studies from across the world have shown that up to 40% of root filled teeth are technically inadequate with persistent AP.28,29,30,31,32 Managing irreversible pulpitis in mature permanent teeth with pulpotomy could potentially have a number of advantages over conventional RCTx: i) treatment procedure is technically less challenging, avoiding the complications associated with difficult root canal anatomy; ii) it preserves the proprioceptive sensation of the tooth; iii) biological immune response from the retained pulp tissue can prevent infection of the apical area; iv) regenerative and repair potential of the pulp is retained; v) structural integrity of the tooth is maintained, lowering the risk of fracture; vi) there is significant reduction in pain and discomfort to the patient; and vii) it saves time and cost for both the patient and public health systems.
A potential concern after full pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth is the occurrence of pulp canal obliteration leading to AP. However, the development of AP in pulpotomised permanent teeth is a sequela of pulp infection, either due to coronal restoration microleakage or incomplete pulp disinfection during the pulpotomy procedure, and not due to the pulp canal obliteration itself.1 Canal calcification in pulpotomised teeth without pulp infection will not lead to AP and further treatment intervention should not be required.33
Contemporary pulpotomy medicaments
The pulpotomy medicament to be placed directly over the remaining pulp tissue should ideally be able to provide a good seal against long-term bacterial leakage, stimulate healing and repair of the remnant pulp tissue, and promote dentinogenesis.34 Calcium hydroxide (CH) was among the earliest and most popular medicaments used for VPT based on its high alkalinity and ability to stimulate reparative dentine formation. However, CH also induced several healing complications when placed directly over vital pulp, with studies showing the success rates of CH VPT significantly declining over time.35 The drawbacks of using CH for VPT included: i) tunnel defects in the newly formed dentine resulting in an ineffective seal; ii) high solubility of CH in oral fluids; and iii) poor adhesion to pulp floor due to its hydrophobicity. These healing complications could be the reason why CH demonstrated a lower range of clinical success (34-92%) when used as the pulpotomy medicament in mature permanent teeth.36,37,38,39 Despite its lower costs, the use of CH as a pulpotomy medicament in mature teeth can no longer be recommended.
Recent decades have seen the development of bioactive hydrophilic calcium silicate cements (CSCs), such as mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium-enriched mixture, Biodentine, and bioceramics for use in VPT procedures. These hydrophilic CSCs have demonstrated more consistent clinical success (85-100%) when used as the pulpotomy medicament in mature permanent teeth.40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47 The contrast in clinical outcomes was especially stark when direct comparisons were made between CH and CSCs for VPT.39,48,49 New-generation bioactive CSCs are not only dimensionally stable with excellent sealing abilities, but also have beneficial biocompatible, immunomodulatory and osteogenic properties.50,51 Recent studies have shown that CSCs can induce the release of regenerative dentine-bound growth factors, upregulate angiogenesis, and stimulate cellular differentiation of dentine-forming cells.52,53 These biological properties provide for better pulpal healing and improved quality of the mineralised dentine bridge over the pulp, contributing towards successful pulpotomy outcomes even in mature permanent teeth.
State of evidence
Pulpotomy has traditionally not been part of the treatment considerations for mature permanent teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis. However, there is now increasing evidence from retrospective studies,54,55,56 prospective cohort studies40,41,47,57,58,59,60 and randomised controlled trials,39,42,43,44,45,46,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70 showing high success rates for pulpotomy in treating mature permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposures (online Supplementary Table 1). Systematic reviews, meta-analyses and recent umbrella reviews (Table 2) have also concluded that pulpotomy could be a prospective substitute to conventional RCTx in managing vital mature permanent teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis or carious pulp exposure.71,72,73,74,75,76
Treatment considerations for pulpotomy in mature teeth
While the pulpotomy procedure is technically less challenging than conventional RCTx, it still requires strict adherence to procedural guidelines to achieve long-term success. Parameters like correct diagnosis of initial pulp status; strict aseptic operative technique; disinfection and haemostasis of remanent pulp; use of bioactive hydrophilic pulpotomy medicaments; and provision of immediate definitive coronal restorations will influence pulpotomy outcomes in mature permanent teeth. Treatment considerations for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth, based on a synthesis of evidence from successful clinical studies, are detailed below.
Diagnosis: symptoms, sensibility tests and radiographs
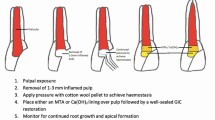
Despite its limitations, pre-operative diagnosis of pulpitis based on clinical signs and symptoms and response to pulp sensibility tests can serve as an initial guide in choosing the best therapeutic option for mature permanent teeth with pulpal inflammation (see decision tree in Fig. 1).77 The radical change in the available treatment options is that full pulpotomy is now indicated even for mature teeth with symptoms typical of irreversible pulpitis (severe spontaneous or continuous pain with exaggerated lingering responses to sensibility tests). Furthermore, full pulpotomy can also be performed in vital mature teeth with signs of AP (pain on percussion) or with periapical lesions on the radiograph. Carious pulp exposures in vital mature teeth without signs and symptoms of irreversible pulpitis or AP can initially be treated even more conservatively with partial pulpotomy, progressing to full pulpotomy if haemostasis is not achieved. However, VPT is contraindicated in mature teeth diagnosed with pulpal necrosis (confirmed by negative response to sensibility tests or intra-operatively by the lack of pulpal bleeding).
Decision tree for inflamed vital pulp in mature permanent teeth. Reproduced with permission from Yong et al., ‘Conservative pulp therapy in the management of reversible and irreversible pulpitis', Australian Dental Journal, 2021, Australian Dental Association77
Aseptic operative technique
Successful outcomes for pulpotomy are contingent on strict adherence to an aseptic operative technique. These measures include: i) mandatory rubber dam isolation; ii) pre-operative crown disinfection before caries excavation with 2% chlorhexidine (CHX) or 5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl); iii) minimising further bacterial contamination of pulp by the removal of all carious tissues, starting at the periphery of the cavity and then progressively over the pulp chamber roof; and iv) mandatory use of a fresh sterile bur (different from the caries excavation bur) when de-roofing the pulp chamber.
Pulp amputation and haemostasis
Pulpotomy outcomes will depend on the severity of pulp inflammation and ability to obtain haemostasis after the removal of inflamed tissue. Once the pulp is exposed, flushing the cavity with CHX or NaOCl can minimise the bacterial load and prevent lodgement of dentinal debris into pulpal tissue. Pulp amputation should be carried out with sterile high-speed rotatory bur under copious water irrigation. Another critical step after pulp exposure is the intra-operative assessment of pulp vitality. Direct visualisation of pulp tissue (preferably under magnification) during and after haemostasis not only provides additional diagnostic information about degree of pulp inflammation, but can also help identify potential necrotic tissues that require removal before application of the pulpotomy medicament.3 Healthy vital pulp will present as uniformly red vascular tissue, while non-vital necrotic pulp presents as dark avascular tissue with minimal bleeding or as yellowish liquefied areas or with calcific debris embedded in the pulp tissue.77
Haemostasis and disinfection of the resected pulp tissue is achieved either by placement of a NaOCl-soaked sterile cotton pellet over the amputated pulp or by passive NaOCl irrigation. NaOCl in concentrations ranging from 0.5-5% can be used in direct contact with pulpal tissues without compromising pulp cell recruitment, cytodifferentiation, and reparative dentine formation.34,78,79 Besides haemostatic effects, NaOCl also disinfects the dentine-pulp interface and removes adherent biofilms.78 Although physiologic saline has been used in place of NaOCl for haemostasis, it lacks disinfection properties, possibly resulting in poorer outcomes when compared with NaOCl haemostasis.80 The use of more effective haemostatic agents (for example, ferric sulphate or hydrogen peroxide) should be avoided as they tend to mask the true inflammatory status of the pulp.4
The time taken to achieve haemostasis after pulp amputation has been used as an indicator for the degree of pulpal inflammation and as a prognostic factor for procedural success of VPT.81 However, a retrospective study that investigated the ‘time to stop bleeding' after pulpotomy in vital mature teeth with carious pulp exposures concluded that bleeding time had no effect on treatment outcomes55 and clinical studies have reported successful outcomes for bleeding times ranging from 1-25 minutes.79 Recent reviews suggest that bleeding duration may not be a true indicator of pulpal inflammatory status82,83 and therefore achieving immediate haemostasis need not be a determining factor for successful pulpotomy outcomes. Nevertheless, persistent bleeding beyond ten minutes, despite attempts at haemostasis, should be considered as a contraindication for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth and RCTx or extraction should be preferred in these cases.2
Pulpotomy medicament and coronal restoration
Probably the most critical factor in achieving favourable pulpotomy outcomes is adequate sealing of the remnant pulp tissue with the bioactive medicament and a definitive coronal restoration. Once haemostasis is achieved, 2-3 mm of a hydrophilic CSC should be directly adapted over the pulp stumps, ensuring that there is no porosity or excess cement on the pulp chamber walls. Immediate placement of a definitive coronal restoration is also recommended to prevent microleakage, protect the bioactive medicament, reduce post-operative sensitivity, and establish foundation for future cuspal coverage restoration, should it be required.3 The data on placing full coverage crowns on pulpotomy-treated teeth are limited, with a couple of studies reporting that placing crowns on such teeth had higher success rates compared to resin composite or amalgam restorations.54,60 In addition, 100% success rates have been demonstrated following placement of stainless steel crowns in pulpotomised permanent molars of children.47 A 3-6 month waiting period has been suggested before additional tooth preparation for cuspal coverage, as early endodontic failures tend to occur within this period.59 If clinical and radiographic outcomes of the pulpotomy treatment are successful after this waiting period, a full coverage restoration should be strongly considered for long-term survival of the pulpotomised tooth.3,77
Follow-up and prognosis
The ESE recommends that teeth that receive VPT should be assessed with clinical, radiographic and sensibility testing at 6 and 12 months post-operatively, and thereafter at yearly intervals for up to four years.4 The clinical outcome measures for success are an asymptomatic functional tooth, no tenderness to percussion or palpation, and no swelling or sinus tract associated with the treated tooth. Radiographically, there should be no signs of internal root resorption, evident healing of any pre-operative periapical lesions, and no new periapical pathologies. Sensibility tests should elicit a normal response in teeth that receive pulp capping or partial pulpotomy. However, teeth that have undergone full pulpotomy will not be responsive to sensibility tests and in these cases, radicular pulp is considered normal unless there are clinical or radiographic signs of failure.2
Recent clinical trials suggest that early failures of pulpotomy-treated mature teeth (that is, those that fail within 3-6 months of treatment) are mostly due to endodontic causes (for example, inaccurate assessment of inflammatory status of pulp), while later failures tend to reflect restorative causes (for example, pulp space reinfection due to poorly sealed coronal restorations).59,60 Clinical trials have shown that age, sex, previous restorations, site of carious exposure, and presence of pre-operative periapical lesions do not appear to be significant factors in deciding prognosis of pulpotomy-treated mature teeth.42,58,59 The only potential prognostic predictive factors found in clinical studies of pulpotomy in mature teeth were pre-operative pain (for early failures) and the type of definitive coronal restoration used (for late failures).59,60
Conclusions
The drive to practise minimally invasive endodontics, improved understanding of dentine-pulp defence mechanisms, introduction of bioactive pulp medicaments, and accumulating evidence from clinical and radiographic outcome studies have resulted in pulpotomy being increasingly considered as a therapeutic alternative to traditional RCTx, even in mature teeth. Pulpotomy could be an especially attractive option for patients who do not have access to specialist endodontic care or cannot afford its costs. The ESE position statement, while cautiously recommending such treatments, suggests the need for more robust long-term evidence before pulpotomy can be routinely recommended as a substitute for RCTx.4 Attempts to collate further high-quality clinical evidence on the long-term effectiveness of pulpotomy in treating mature teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis are currently underway around the world (Table 3). Within the UK, three clinical trials on pulpotomy in permanent teeth are in progress, including the National Institute of Health Research-funded multi-centre primary care PIP trial and the Northern Ireland Public Health Agency funded REFORM trial. The day is probably not too far when pulpotomy can be routinely offered as the first line of treatment for vital mature permanent teeth diagnosed with irreversible pulpitis.
References
Lin L M, Ricucci D, Saoud T M, Sigurdsson A, Kahler B. Vital pulp therapy of mature permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis from the perspective of pulp biology. Aust Endod J 2020; 46: 154-166.
Taha N A, About I, Sedgley C M, Messer H H. Conservative management of mature permanent teeth with carious pulp exposure. J Endod 2020; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.06.025.
Anonymous. AAE Position Statement on Vital Pulp Therapy. J Endod 2021; 47: 1340-1344.
Duncan H F, Galler K M, Tomson P L et al. European Society of Endodontology position statement: Management of deep caries and the exposed pulp. Int Endod J 2019; 52: 923-934.
Van Hassel H J. Physiology of the human dental pulp. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1971; 32: 126-134.
Heyeraas K J, Berggreen E. Interstitial fluid pressure in normal and inflamed pulp. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 1999; 10: 328-336.
Jontell M, Okiji T, Dahlgren U, Bergenholtz G. Immune defence mechanisms of the dental pulp. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 1998; 9: 179-200.
Farges J C, Alliot-Licht B, Renard E et al. Dental Pulp Defence and Repair Mechanisms in Dental Caries. Mediators Inflamm 2015; 2015: 230251.
Lundy F T, Irwin C R, McLean D F, Linden G J, El Karim I A. Natural Antimicrobials in the Dental Pulp. J Endod 2020; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.06.021.
Mjör I A, Tronstad L. The healing of experimentally induced pulpitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1974; 38: 115-121.
Jeanneau C, Lundy F T, El Karim I A, About I. Potential Therapeutic Strategy of Targeting Pulp Fibroblasts in Dentin-Pulp Regeneration. J Endod 2017; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2017.06.007.
Chmilewsky F, Jeanneau C, Laurent P, About I. Pulp fibroblasts synthesize functional complement proteins involved in initiating dentin-pulp regeneration. Am J Pathol 2014; 184: 1991-2000.
Jeanneau C, Rufas P, Rombouts C, Giraud T, Dejou J, About I. Can Pulp Fibroblasts Kill Cariogenic Bacteria? Role of Complement Activation. J Dent Res 2015; 94: 1765-1772.
Dimitrova-Nakov S, Baudry A, Harichane Y, Kellermann O, Goldberg M. Pulp stem cells: implication in reparative dentin formation. J Endod 2014; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.01.011.
Ricucci D, Loghin S, Siqueira Jr J F. Correlation between clinical and histologic pulp diagnoses. J Endod 2014; 40: 1932-1939.
Ricucci D, Siqueira Jr J F, Li Y, Tay F R et al. Vital pulp therapy: histopathology and histobacteriology-based guidelines to treat teeth with deep caries and pulp exposure. J Dent 2019; 86: 41-52.
Ricucci D, Siqueira Jr J F, Loghin S, Lin L M. Pulp and apical tissue response to deep caries in immature teeth: a histologic and histobacteriologic study. J Dent 2017; 56: 19-32.
Hahn C-L, Liewehr F R. Innate immune responses of the dental pulp to caries. J Endod 2007; 33: 643-651.
Hahn C-L, Liewehr F R. Update on the adaptive immune responses of the dental pulp. J Endod 2007; 33: 773-781.
Cooper P R, Holder M J, Smith A J. Inflammation and regeneration in the dentin-pulp complex: a double-edged sword. J Endod 2014; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2014.01.021.
Cooper P R, Takahashi Y, Graham L W, Simon S, Imazato S, Smith A J. Inflammation-regeneration interplay in the dentine-pulp complex. J Dent 2010; 38: 687-697.
Krastl G, Galler K, Dammaschke T, Schäfer E. Is pulpotomy a valid treatment option for irreversible pulpitis? Dtsch Zahnärztl Z Int 2021; 3: 80-87.
Rechenberg D-K, Zehnder M. Call for a review of diagnostic nomenclature and terminology used in endodontics. Int Endod J 2020; 53: 1315-1317.
Wolters W J, Duncan H F, Tomson P L et al. Minimally invasive endodontics: a new diagnostic system for assessing pulpitis and subsequent treatment needs. Int Endod J 2017; 50: 825-829.
Galicia J C, Peters O A. Proposal for a new diagnostic terminology to describe the status of the dental pulp. Int Endod J 2021; 54: 1415-1416.
Farzaneh M, Abitbol S, Lawrence H P, Friedman S, Study T. Treatment outcome in endodontics - the Toronto study. Phase II: initial treatment. J Endod 2004; 30: 302-309.
Friedman S, Abitbol S, Lawrence H P. Treatment outcome in endodontics: the Toronto study. Phase 1: initial treatment. J Endod 2003; 29: 787-793.
El Merini H, Amarir H, Lamzawaq A, Hamza M. Periapical Status and Quality of Root Canal Fillings in a Moroccan Subpopulation. Int J Dent 2017; 2017: 1068982.
Frisk F, Hugoson A, Hakeberg M. Technical quality of root fillings and periapical status in root filled teeth in Jönköping, Sweden. Int Endod J 2008; 41: 958-968.
Di Filippo G, Sidhu S K, Chong B S. Apical periodontitis and the technical quality of root canal treatment in an adult sub-population in London. Br Dent J 2014; DOI: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.404.
Dugas N N, Lawrence H P, Teplitsky P E, Pharoah M J, Friedman S. Periapical health and treatment quality assessment of root-filled teeth in two Canadian populations. Int Endod J 2003; 36: 181-192.
Peters L B, Lindeboom J A, Elst M E, Wesselink P R. Prevalence of apical periodontitis relative to endodontic treatment in an adult Dutch population: a repeated cross-sectional study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2011; 111: 523-528.
McCabe P S, Dummer P M H. Pulp canal obliteration: an endodontic diagnosis and treatment challenge. Int Endod J 2012; 45: 177-197.
Witherspoon D E. Vital pulp therapy with new materials: new directions and treatment perspectives - permanent teeth. J Endod 2008; DOI: 10.1016/j.joen.2008.02.030.
Barthel C R, Rosenkranz B, Leuenberg A, Roulet J F. Pulp capping of carious exposures: treatment outcome after 5 and 10 years: a retrospective study. J Endod 2000; 26: 525-528.
Calişkan M K. Pulpotomy of carious vital teeth with periapical involvement. Int Endod J 1995; 28: 172-176.
Santini A H. Intraoral comparison of calcium hydroxide (Calnex) alone and in combination with Ledermix in first permanent mandibular molars using two direct inspection criteria. J Dent 1985; 13: 52-59.
Bjørndal L, Reit C, Bruun G et al. Treatment of deep caries lesions in adults: randomized clinical trials comparing stepwise vs. direct complete excavation, and direct pulp capping vs. partial pulpotomy. Eur J Oral Sci 2010; 118: 290-297.
Taha N A, Khazali M A. Partial Pulpotomy in Mature Permanent Teeth with Clinical Signs Indicative of Irreversible Pulpitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Endod 2017; 43: 1417-1421.
Taha N A, Abdelkhader S Z. Outcome of full pulpotomy using Biodentine in adult patients with symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis. Int Endod J 2018; 51: 819-828.
Taha N A, Ahmad M B, Ghanim A. Assessment of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth with carious exposures. Int Endod J 2017; 50: 117-125.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J, Fazlyab M, Baghban A A, Ghoddusi J. Five-year results of vital pulp therapy in permanent molars with irreversible pulpitis: a non-inferiority multicentre randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 2015; 19: 335-341.
Awawdeh L, Al-Qudah A, Hamouri H, Chakra R J. Outcomes of Vital Pulp Therapy Using Mineral Trioxide Aggregate or Biodentine: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. J Endod 2018; 44: 1603-1609.
Uesrichai N, Nirunsittirat A, Chuveera P, Srisuwan T, Sastraruji T, Chompu-Inwai P. Partial pulpotomy with two bioactive cements in permanent teeth of 6-to 18-year-old patients with signs and symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis: a noninferiority randomized controlled trial. Int Endod J 2019; 52: 749-759.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J, Shahravan A, Saberi E, Baghban A A, Parhizkar A. Outcomes of root canal therapy or full pulpotomy using two endodontic biomaterials in mature permanent teeth: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Investig 2022; 26: 3287-3297.
Koli B, Chawla A, Logani A, Kumar V, Sharma S. Combination of Nonsurgical Endodontic and Vital Pulp Therapy for Management of Mature Permanent Mandibular Molar Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis and Apical Periodontitis. J Endod 2021; 47: 374-381.
Qudeimat M A, Alyahya A, Hasan A A. Mineral trioxide aggregate pulpotomy for permanent molars with clinical signs indicative of irreversible pulpitis: a preliminary study. Int Endod J 2017; 50: 126-134.
Li Z, Cao L, Fan M, Xu Q. Direct Pulp Capping with Calcium Hydroxide or Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A Meta-Analysis. J Endod 2015; 41: 1412-1417.
Kundzina R, Stangvaltaite L, Eriksen H M, Kerosuo E. Capping carious exposures in adults: a randomized controlled trial investigating mineral trioxide aggregate versus calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J 2017; 50: 924-932.
Bakland L K, Andreasen J O. Will mineral trioxide aggregate replace calcium hydroxide in treating pulpal and periodontal healing complications subsequent to dental trauma? A review. Dent Traumatol 2012; 28: 25-32.
Parirokh M, Torabinejad M, Dummer P M. Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview - part I: vital pulp therapy. Int Endod J 2018; 51: 177-205.
Smith A J, Duncan H F, Diogenes A, Simon S, Cooper P R. Exploiting the Bioactive Properties of the Dentin-Pulp Complex in Regenerative Endodontics. J Endod 2016; 42: 47-56.
Tomson P L, Lumley P J, Smith A J, Cooper P R. Growth factor release from dentine matrix by pulp-capping agents promotes pulp tissue repair-associated events. Int Endod J 2017; 50: 281-292.
Kunert G G, Kunert I R, da Costa Filho L C, de Figueiredo J A P. Permanent teeth pulpotomy survival analysis: retrospective follow-up. J Dent 2015; 43: 1125-1131.
Linsuwanont P, Wimonsutthikul K, Pothimoke U, Santiwong B. Treatment Outcomes of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Pulpotomy in Vital Permanent Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure: The Retrospective Study. J Endod 2017; 43: 225-230.
Eggmann F, Gasser T J, Hecker H, Amato M, Weiger R, Zaugg L K. Partial pulpotomy without age restriction: a retrospective assessment of permanent teeth with carious pulp exposure. Clin Oral Investig 2022; 26: 365-373.
Guan X, Zhou Y, Yang Q et al. Vital Pulp Therapy in Permanent Teeth with Irreversible Pulpitis Caused by Caries: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Pers Med 2021; 11: 1125.
Rechithra R, Aravind A, Kumar V, Sharma S, Chawla A, Logani A. Influence of occlusal and proximal caries on the outcome of full pulpotomy in permanent mandibular molar teeth with partial irreversible pulpitis: a prospective study. Int Endod J 2021; 54: 1699-1707.
Taha N A, Al-Khatib H. 4-Year Follow-Up of Full Pulpotomy in Symptomatic Mature Permanent Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure Using a Stainproof Calcium Silicate-Based Material. J Endod 2022; 48: 87-95.
Tan S Y, Yu V S H, Lim K C et al. Long-Term Pulpal and Restorative Outcomes of Pulpotomy in Mature Permanent Teeth. J Endod 2020; 46: 383-390.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J. The effect of pulpotomy using a calcium-enriched mixture cement versus one-visit root canal therapy on postoperative pain relief in irreversible pulpitis: a randomized clinical trial. Odontology 2010; 98: 126-133.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J, Ghoddusi J. Two-year results of vital pulp therapy in permanent molars with irreversible pulpitis: an ongoing multicentre randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 2014; 18: 635-641.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J, Ghoddusi J, Yazdani S. One-year results of vital pulp therapy in permanent molars with irreversible pulpitis: an ongoing multicentre, randomized, non-inferiority clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 2013; 17: 431-439.
Asgary S, Hassanizadeh R, Torabzadeh H, Eghbal M J. Treatment Outcomes of 4 Vital Pulp Therapies in Mature Molars. J Endod 2018; 44: 529-535.
Galani M, Tewari S, Sangwan P, Mittal S, Kumar V, Duhan J. Comparative Evaluation of Postoperative Pain and Success Rate after Pulpotomy and Root Canal Treatment in Cariously Exposed Mature Permanent Molars: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Endod 2017; 43: 1953-1962.
Kumar V, Juneja R, Duhan J, Sangwan P, Tewari S. Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin, mineral trioxide aggregate, and calcium hydroxide as pulpotomy agents in permanent molars with irreversible pulpitis: A randomized controlled trial. Contemp Clin Dent 2016; 7: 512-518.
Alqaderi H E, Al-Mutawa S A, Qudeimat M A. MTA pulpotomy as an alternative to root canal treatment in children's permanent teeth in a dental public health setting. J Dent 2014; 42: 1390-1395.
Eghbal M J, Haeri A, Shahravan A et al. Post-Endodontic Pain after Pulpotomy or Root Canal Treatment in Mature Teeth with Carious Pulp Exposure: A Multicentre Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Res Manag 2020; DOI: 10.1155/2020/5853412.
Asgary S, Eghbal M J, Bagheban A A. Long-term outcomes of pulpotomy in permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis: a multi-centre randomized controlled trial. Am J Dent 2017; 30: 151-155.
Taha N A, Al-Rawash M H, Imran Z A. Outcome of full pulpotomy in mature permanent molars using 3 calcium silicate-based materials: a parallel, double blind, randomized controlled trial. Int Endod J 2022; 55: 416-429
Alqaderi H, Lee C-T, Borzangy S, Pagonis T C. Coronal pulpotomy for cariously exposed permanent posterior teeth with closed apices: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent 2016; 44: 1-7.
Cushley S, Duncan H F, Lappin M J et al. Pulpotomy for mature carious teeth with symptoms of irreversible pulpitis: A systematic review. J Dent 2019; 88: 103158.
Leong D J, Yap A U. Vital pulp therapy in carious pulp-exposed permanent teeth: an umbrella review. Clin Oral Investig 2021; 25: 6743-6756.
Li Y, Sui B, Dahl C et al. Pulpotomy for carious pulp exposures in permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent 2019; 84: 1-8.
Santos J M, Pereira J F, Marques A, Sequeira D B, Friedman S. Vital Pulp Therapy in Permanent Mature Posterior Teeth with Symptomatic Irreversible Pulpitis: A Systematic Review of Treatment Outcomes. Medicina (Kaunas) 2021; 57: 573.
Elmsmari F, Ruiz X F, Miró Q, Feijoo-Pato N, Durán-Sindreu F, Olivieri J G. Outcome of Partial Pulpotomy in Cariously Exposed Posterior Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis. J Endod 2019; 45: 1296-1306.
Yong D, Cathro P. Conservative pulp therapy in the management of reversible and irreversible pulpitis. Aust Dent J 2021; DOI: 10.1111/adj.12841.
Hafez A A, Cox C F, Tarim B, Otsuki M, Akimoto N. An in vivo evaluation of haemorrhage control using sodium hypochlorite and direct capping with a one-or two-component adhesive system in exposed nonhuman primate pulps. Quintessence Int 2002; 33: 261-272.
Bogen G, Kim J S, Bakland L K. Direct pulp capping with mineral trioxide aggregate: an observational study. J Am Dent Assoc 2008; 139: 305-315.
Tüzüner T, Alacam A, Altunbas D A, Gokdogan F G, Gundogdu E. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of direct pulp capping therapy in primary molar teeth following haemostasis with various antiseptics: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Paediatr Dent 2012; 13: 289-292.
Matsuo T, Nakanishi T, Shimizu H, Ebisu S. A clinical study of direct pulp capping applied to carious-exposed pulps. J Endod 1996; 22: 551-516.
Zanini M, Hennequin M, Cousson P Y. Which procedures and materials could be applied for full pulpotomy in permanent mature teeth? A systematic review. Acta Odontol Scand 2019; 77: 541-551.
Asgary S, Parhizkar A. Importance of ‘Time' on ‘Haemostasis' in Vital Pulp Therapy - Letter to the Editor. Eur Endod J 2021; 6: 128-129.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by the Qatar National Library
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nebu Philip reviewed the literature and drafted the manuscript. Bharat Suneja conceived and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.© The Author(s) 2022
About this article
Cite this article
Philip, N., Suneja, B. Minimally invasive endodontics: a new era for pulpotomy in mature permanent teeth. Br Dent J 233, 1035–1041 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-022-5316-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-022-5316-1