Abstract
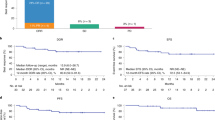
This study reported 2-year efficacy and safety of relma-cel in Chinese patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (B-NHL). In this phase 1 dose-escalating trial, patients received lymphodepleting chemotherapy for 3 days, followed by relma-cel as a single infusion in escalating dose levels (25 × 106, 50 × 106, 100 × 106, and 150 × 106 CAR-T cells). The endpoints included best objective response rate (ORR), best complete response rate (CRR), duration of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. A total of 23 patients were enrolled, including 60.9% with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and 26.1% with follicular lymphoma. Twenty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the best ORR was 85.0% and the best CRR was 75.0%. With a median follow-up of 24.2 months, 6 patients died and 2 had progressive disease, the median DOR, PFS, and OS were all not reached. The 2-year PFS and OS rates were 60.0% and 70.0%, respectively. Any grade and grade ≥ 2 cytokine release syndrome occurred in 18.2% and 13.6% of patients, respectively. Only 1(4.5%) patient had grade 3 CRS lasting 13 days, which was resolved by tocilizumab. No grade ≥ 2 neurotoxicity events or treatment-related deaths occurred. Patients with R/R B-NHL treated with relma-cel achieved durable response with favorable safety profile.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Hamadani M, Habermann TM, Cerhan JR, Macon WR, Maurer MJ, Go RS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtype distribution, geodemographic patterns, and survival in the US: A longitudinal analysis of the National Cancer Data Base from 1998 to 2011. Am J Hematol. 2015;90:790–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24086.
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P. et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109:1857–61. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-08-038257.
International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors P. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N. Engl J Med. 1993;329:987–94. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199309303291402.
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363–85. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565.
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, Van Den Neste E, Kuruvilla J, Westin J, et al. Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood. 2017;130:1800–8. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-03-769620.
Casulo C, Barr PM. How I treat early-relapsing follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2019;133:1540–7. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-08-822148.
Batlevi CL, Sha F, Alperovich A, Ni A, Smith K, Ying Z. et al. Follicular lymphoma in the modern era: survival, treatment outcomes, and identification of high-risk subgroups. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10:74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-020-00340-z.
Abramson JS. Anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Transfus Med Rev. 2020;34:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmrv.2019.08.003.
Ying Z, Song Y, Zhu J. Effectiveness and safety of Anti-CD19 Chimeric antigen receptor-T cell immunotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharm. 2022;13:834113 https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.834113.
Ying Z, Yang H, Guo Y, Li W, Zou D, Zhou D. et al. Relmacabtagene autoleucel (relma-cel) CD19 CAR-T therapy for adults with heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in China. Cancer Med. 2021;10:999–1011. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3686.
Wang W, Hao M, Cheng Y, Gao J, Yang S, Liu Y, et al. JWCAR029 Is a CD19-Targeted CAR T cell product with process and quality controls delivered as a flat dose of CAR T cell to patients with NHL. Blood. 2018;132:5387–5387. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-99-114434.
Ying Z, Xu P, Wang L, Cheng S, Wu W, Wang W, et al. Clinical response in Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) B-NHL treated with the CD19-Directed CAR T-cell product JWCAR029. Blood. 2019;134:2876 https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-127751.
Yan Z-X, Li L, Wang W, OuYang B-S, Cheng S, Wang L. et al. Clinical efficacy and tumor microenvironment influence in a dose-escalation study of Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:6995–7003. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0101.
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E. et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3059–68. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.54.8800.
Li DH, Whitmore JB, Guo W, Ji Y. Toxicity and efficacy probability interval design for phase I adoptive cell therapy dose-finding clinical trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1125.
Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, Miklos DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO. et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(18)30864-7.
Schuster SJ, Tam CS, Borchmann P, Worel N, McGuirk JP, Holte H. et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1403–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(21)00375-2.
Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J. et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396:839–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)31366-0.
Gargett T, Truong N, Ebert LM, Yu W, Brown MP. Optimization of manufacturing conditions for chimeric antigen receptor T cells to favor cells with a central memory phenotype. Cytotherapy. 2019;21:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.03.003.
Ying Z, He T, Jin S, Wang X, Zheng W, Lin N. et al. A durable 4-1BB-based CD19 CAR-T cell for treatment of relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Chin J Cancer Res. 2022;34:53–62. https://doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2022.01.05.
Cappell KM, Sherry RM, Yang JC, Goff SL, Vanasse DA, McIntyre L. et al. Long-term follow-up of anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:3805–15. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.20.01467.
Hirayama AV, Gauthier J, Hay KA, Voutsinas JM, Wu Q, Pender BS. et al. High rate of durable complete remission in follicular lymphoma after CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy. Blood. 2019;134:636–40. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019000905.
Schuster SJ, Svoboda J, Chong EA, Nasta SD, Mato AR, Anak O. et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells in refractory B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl J Med. 2017;377:2545–54. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1708566.
Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, Rives S, Boyer M, Bittencourt H. et al. Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl J Med. 2018;378:439–48. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1709866.
Bishop MR, Dickinson M, Purtill D, Barba P, Santoro A, Hamad N. et al. Second-line tisagenlecleucel or standard care in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl J Med. 2022;386:629–39. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116596.
Itzhaki O, Jacoby E, Nissani A, Levi M, Nagler A, Kubi A. et al. Head-to-head comparison of in-house produced CD19 CAR-T cell in ALL and NHL patients. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e000148. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2019-000148.
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP. et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl J Med. 2019;380:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1804980.
Sesques P, Ferrant E, Safar V, Wallet F, Tordo J, Dhomps A. et al. Commercial anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B cell lymphoma in a European center. Am J Hematol. 2020;95:1324–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25951.
Funding
All funding is provided by JW Therapeutics (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZY: Patient enrollment, data acquisition, patient evaluation, and article preparation. YX, WZ, WL, NL, MT, XW, LP, LD, CZ, MW, FF, TD, YT: Patient enrollment and data acquisition. FS, ZG, JL: Project administration and supervision. YS: Data acquisition, statistical analysis, blood sample collection, patient evaluation, and article review. JZ: Project administration, patient enrollment, data acquisition, and article review.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ying, Z., Xie, Y., Zheng, W. et al. Efficacy and safety of relmacabtagene autoleucel, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cell, in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: 2-year results of a phase 1 trial. Bone Marrow Transplant 58, 288–294 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01888-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-022-01888-z
This article is cited by
-
Recent advances in CAR T-cell therapy for lymphoma in China
Clinical and Translational Oncology (2023)