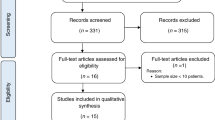
Abstract
Aplastic anemia is a relatively rare but potentially fatal disorder, with a reported higher incidence in developing countries in comparison to the West. There are significant variations in epidemiological as well as etiological factors of bone marrow failure syndromes in the developing countries in comparison to the developed world. Furthermore, the management of bone marrow failure syndromes in resource constraint settings has significant challenges including delayed diagnosis and referral, limited accessibility to healthcare facilities, treatment modalities as well as limitations related to patients who require allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Here we will provide a review of the available evidence related to specific issues of aplastic anemia in the developing countries and we summarize suggested recommendations from the Eastern Mediterranean blood and bone marrow transplantation (EMBMT) group and the severe aplastic anemia working party of the European Society of blood and marrow transplantation (SAAWP of EBMT) related to the diagnosis and therapeutic options in countries with restricted resources.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 December 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01534-0
References
Killick SB, Bown N, Cavenagh J, Dokal I, Foukaneli T, Hill A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;172:187–207.
Kojima S. Why is the incidence of aplastic anemia higher in Asia? Expert Rev Hematol. 2017;10:277–9.
Ally M, Magesa P, Luzzatto L. High frequency of acquired aplastic anemia in Tanzania. Am J Hematol. 2019;94:E86–8.
Peslak SA, Olson T, Babushok DV. Diagnosis and treatment of aplastic anemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017;18:70.
Camitta BM, Storb R, Thomas ED. Aplastic anemia (first of two parts): pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. N Engl J Med. 1982;306:645–52.
Savage SA, Viard M, O’HUigin C, Zhou W, Yeager M, Li SA, et al. Genome-wide Association Study Identifies HLA-DPB1 as a significant risk factor for severe aplastic anemia. Am J Hum Genet. 2020;106:264–71.
Dolberg OJ, Levy Y. Idiopathic aplastic anemia: diagnosis and classification. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:569–73.
Gadalla SM, Savage SA. Telomere biology in hematopoiesis and stem cell transplantation. Blood Rev. 2011;25:261–9.
Young NS, Kaufman DW. The epidemiology of acquired aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2008;93:489–92.
Montané E, Ibáñez L, Vidal X, Ballarín E, Puig R, García N, et al. Epidemiology of aplastic anemia: a prospective multicenter study. Haematologica. 2008;93:518–23.
Ahmed P, Chaudhry QUN, Satti TM, Mahmood SK, Ghafoor T, Shahbaz N, et al. Epidemiology of aplastic anemia: a study of 1324 cases. Hematology. 2020;25:48–54.
Akram Z, Ahmed P, Kajigaya S, Satti TM, Satti HS, Chaudhary QUN, et al. Epidemiological, clinical and genetic characterization of aplastic anemia patients in Pakistan. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:301–12.
Rehman S, Saba N, Naz M, Ahmed P, Munir S, Sajjad S, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of FAS and FASL genes and risk of idiopathic aplastic anemia. Immunol Investig. 2018;47:484–91.
Rehman S, Ahmed P, Saba N, Munir S, Sajjad S, Satti TM, et al. Association of GSTM1 and GSTT1 deletion polymorphisms with Pakistani aplastic anemia patients and controls and meta-analysis. Ann Hematol. 2015;94:1965–71.
Mahapatra M, Singh PK, Agarwal M, Prabhu M, Mishra P, Seth T, et al. Epidemiology, clinico-haematological profile and management of aplastic anaemia: AIIMS experience. J Assoc Physicians India. 2015;63 (3 Suppl):30–5.
Prihartono N, Kriebel D, Woskie S, Thetkhathuek A, Sripaung N, Padungtod C, et al. Risk of aplastic anemia and pesticide and other chemical exposures. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2011;23:369–77.
Young NS, Issaragrasil S, Chieh CW, Takaku F. Aplastic anaemia in the Orient. Br J Haematol. 1986;62:1–6.
Wang L, Liu H. Pathogenesis of aplastic anemia. Hematology. 2019;24:559–66.
Mary JY, Baumelou E, Guiguet M. Epidemiology of aplastic anemia in France: a prospective multicentric study. The French Cooperative Group for Epidemiological Study of Aplastic Anemia. Blood. 1990;75:1646–53.
Shallis RM, Ahmad R, Zeidan AM. Aplastic anemia: Etiology, molecular pathogenesis, and emerging concepts. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101:711–20.
Issaragrisil S, Kaufman DW, Anderson T, Chansung K, Leaverton PE, Shapiro S, et al. The epidemiology of aplastic anemia in Thailand. Blood. 2006;107:1299–307.
Yong AS, Goh AS, Rahman J, Menon J, Purushothaman V. Epidemiology of aplastic anemia in the state of Sabah, Malaysia. Med J Malaysia. 1998;53:59–62.
Ahamed M, Anand M, Kumar A, Siddiqui MKJ. Childhood aplastic anaemia in Lucknow, India: incidence, organochlorines in the blood and review of case reports following exposure to pesticides. Clin Biochem. 2006;39:762–6.
Jeong DC, Chung NG, Kang HJ, Koo HH, Kook H, Kim SK, et al. Epidemiology and clinical long-term outcome of childhood aplastic anemia in Korea for 15 years: retrospective study of the Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology Oncology (KSPHO). J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2011;33:172–8.
Arewa OP, Akinola NO. Survival in primary a plastic anaemia; experience with 20 cases from a tertiary hospital in Nigeria. Afr Health Sci. 2009;9:290–3.
Moore CA, Krishnan K. Aplastic Anemia, in StatPearls. 2021, StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2021, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL).
Adil S, Kakepoto GN, Khurshid M, Burney IA. Epidemiological features of aplastic anaemia in Pakistan. J Pak Med Assoc. 2001;51:443.
Ehrlich P. Ueber einem Fall von Anämie mit Bemerkungen über regenerative Veränderungen des Knochenmarks. Charité-Annalen. 1888;13:301–9.
Smith MT. Overview of benzene-induced aplastic anaemia. Eur J Haematol. 1996;60:107–10.
Aksoy M. Benzene as a leukemogenic and carcinogenic agent. Am J Ind Med. 1985;8:9–20.
Cudillo L. Aplastica anemia and viral hepatitis. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2009;1:e2009026.
Alter BP. Aplastic anemia, pediatric aspects. Oncologist. 1996;1:361–6.
McCahon E, Tang K, Rogers PC, McBride ML, Schultz KR. The impact of Asian descent on the incidence of acquired severe aplastic anaemia in children. Br J Haematol. 2003;121:170–2.
Chen C-H, Ferreira JC, Joshi AU, Stevens MC, Li S-J, Hsu JH-M, et al. Novel and prevalent non-East Asian ALDH2 variants; implications for global susceptibility to aldehydes’ toxicity. EBioMedicine. 2020;55:102753.
Rehman S, Saba N, Khalilullah, Munir S, Ahmed P, Mehmood T. The frequency of HLA class I and II alleles in Pakistani patients with aplastic anemia. Immunol Investig. 2009;38:812–9.
Lee KA, Kim SH, Woo HY, Hong YJ, Cho HC. Increased frequencies of glutathione S-transferase (GSTM1 and GSTT1) gene deletions in Korean patients with acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2001;98:3483–5.
Sleijfer S, Lugtenburg P. Aplastic anaemia: a review. Neth J Med. 2003;61:157–63.
Dutta A, De R, Dolai TK, Mitra PK, Halder A. Comparative study of environmental factors and different addictions in aplastic anaemia patients in Eastern India. J Blood Disord Symptoms Treat. 2019;8:2015–8.
Taj M, Shah T, Aslam SK, Zaheer S, Nawab F, Shaheen S, et al. Environmental determinants of aplastic anemia in Pakistan: a case-control study. J Public Health. 2016;24:453–60.
Marsh JCW. Aplastic anemia: what’s in the environment? Blood. 2006;107:1250.
Akram Z, Ahmed P, Kajigaya S, Satti TM, Satti HS, Gutierrez-Rodrigues F, et al. Epidemiological, clinical and genetic characterization of aplastic anemia patients in Pakistan. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:301–12.
Kook H, Chung NG, Kang HJ, Im HJ. Acquired aplastic anemia in Korean children: treatment guidelines from the Bone Marrow Failure Committee of the Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology Oncology. Int J Hematol. 2016;103:380–6.
Ramzan M, Yadav SP, Zafar MS, Dinand V, Sachdeva A. Outcome of pediatric acquired aplastic anemia: a developing world experience. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2014;31:29–38.
Townsley DM, Dumitriu B, Young NS. Bone marrow failure and the telomeropathies. Blood. 2014;124:2775–83.
Alter BP. Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes: considerations pre- and posttransplant. Blood. 2017;130:2257–64.
Narayanan S. Managing anaemia in bone marrow failure syndromes. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2018;12:538–41.
Young NS. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2013;2013:76–81.
Höchsmann B, Moicean A, Risitano A, Ljungman P, Schrezenmeier H. Supportive care in severe and very severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:168–73.
Han W. Health care system reforms in developing countries. J Public Health Res. 2012;1:199.
Valdez JM, Scheinberg P, Young NS, Walsh TJ. Infections in patients with aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol. 2009;46:269–76.
Young NS. Aplastic Anemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:1643–56.
Zhang Y, Wu L, Mo W, Zhou M, Li Y, Chen X, et al. Comparable outcomes of first-line hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated and matched sibling donors in adult patients with aplastic anemia: a retrospective single-center study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1567–75.
Marsh JC, Risitano AM, Mufti GJ. The case for upfront HLA-matched unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation as a curative option for adult acquired severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:e277–84.
Xu LP, Jin S, Wang SQ, Xia LH, Bai H, Gao SJ, et al. Upfront haploidentical transplant for acquired severe aplastic anemia: registry-based comparison with matched related transplant. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:25.
Chaudhry QUN, Iftikhar R, Satti TM, Mahmood SK, Ghafoor T, Shamshad GU, et al. Outcome of fludarabine-based conditioning in high-risk aplastic anemia patients undergoing matched related donor transplantation: a single-center study from Pakistan. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:2375–82.
Jubelirer SJ. The benefit of the neutropenic diet: fact or fiction? Oncologist. 2011;16:704.
Quillen K, Wong E, Scheinberg P, Young NS, Walsh TJ, Wu CO, et al. Granulocyte transfusions in severe aplastic anemia: an eleven-year experience. Haematologica. 2009;94:1661–8.
Garg A, Gupta A, Mishra A, Singh M, Yadav S, Nityanand S. Role of granulocyte transfusions in combating life-threatening infections in patients with severe neutropenia: experience from a tertiary care centre in North India. PloS ONE. 2018;13:e0209832.
Kallen ME, Dulau-Florea A, Wang W, Calvo KR. Acquired and germline predisposition to bone marrow failure: Diagnostic features and clinical implications. Semin Hematol. 2019;56:69–82.
Townsley DM, Scheinberg P, Winkler T, Desmond R, Dumitriu B, Rios O, et al. Eltrombopag added to standard immunosuppression for aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:1540–50.
Cle DV, Atta EH, Dias DSP, Lima CBL, Bonduel M, Sciuccati G, et al. Rabbit antithymocyte globulin dose does not affect response or survival as first-line therapy for acquired aplastic anemia: a multicenter retrospective study. Ann Hematol. 2018;97:2039–46.
Lum SH, Grainger JD. Eltrombopag for the treatment of aplastic anemia: current perspectives. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:2833–43.
Al-Ghazaly J, Al-Dubai W, Al-Jahafi AK, Abdullah M, Al-Hashdi A. Cyclosporine monotherapy for severe aplastic anemia: a developing country experience. Ann Saudi Med. 2005;25:375–9.
Maschan A, Bogatcheva N, Kryjanovskii O, Shneider M, Litvinov D, Mitiushkina T, et al. Results at a single centre of immunosuppression with cyclosporine A in 66 children with aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1999;106:967–70.
Mandal PK, Baul S, Dolai TK, De R, Chakrabarti P. Outcome of cyclosporine monotherapy in patients of aplastic anemia: experience of a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern India. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2017;33:144–7.
Scheinberg P, Nunez O, Weinstein B, Scheinberg P, Biancotto A, Wu CO, et al. Horse versus rabbit antithymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:430–8.
Marsh JC, Bacigalupo A, Schrezenmeier H, Tichelli A, Risitano AM, Passweg JR, et al. Prospective study of rabbit antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for aplastic anemia from the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party. Blood. 2012;119:5391–6.
Risitano AM, Perna F. Aplastic anemia: immunosuppressive therapy in 2010. Pediatr Rep. 2011;3:14–7.
Feng X, Scheinberg P, Biancotto A, Rios O, Donaldson S, Wu C, et al. In vivo effects of horse and rabbit antithymocyte globulin in patients with severe aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2014;99:1433–40.
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O, Young NS. Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy and survival in severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2009;144:206–16.
Lengline E, Drenou B, Peterlin P, Tournilhac O, Abraham J, Berceanu A, et al. Nationwide survey on the use of eltrombopag in patients with severe aplastic anemia: a report on behalf of the French Reference Center for Aplastic Anemia. Haematologica. 2018;103:212–20.
Ecsedi M, Lengline É, Knol-Bout C, Bosman P, Eikema D-J, Afanasyev B, et al. Use of eltrombopag in aplastic anemia in Europe. Ann Hematol. 2019;98:1341–50.
Konishi A, Nakaya A, Fujita S, Satake A, Nakanishi T, Azuma Y, et al. Evaluation of eltrombopag in patients with aplastic anemia in real-world experience. Leuk Res Rep. 2019;11:11–3.
Zhu Y, Gao Q, Hu J, Liu X, Guan D, Zhang F. Allo-HSCT compared with immunosuppressive therapy for acquired aplastic anemia: a system review and meta-analysis. BMC Immunol. 2020;21:10.
Dufour C, Pillon M, Sociè G, Rovò A, Carraro E, Bacigalupo A, et al. Outcome of aplastic anaemia in children. A study by the severe aplastic anaemia and paediatric disease working parties of the European group blood and bone marrow transplant. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:565–73.
Dufour C, Pillon M, Passweg J, Socie G, Bacigalupo A, Franceschetto G, et al. Outcome of aplastic anemia in adolescence: a survey of the Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica. 2014;99:1574–81.
Georges GE. Consider allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for older, fitpatients with aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:e69–70.
Sheth VS, Potter V, Gandhi SA, Kulasekararaj AG, de Lavallade H, Muus P, et al. Similar outcomes of alemtuzumab-based hematopoietic cell transplantation for SAA patients older or younger than 50 years. Blood Adv. 2019;3:3070–9.
Zhang YY, Mo WJ, Zuo YY, Zhou M, Zhang XH, Wang Y, et al. Comparable survival outcome between transplantation from haploidentical donor and matched related donor or unrelated donor for severe aplastic anemia patients aged 40 years and older: a retrospective multicenter cohort study. Clin Transplant. 2020;34:e13810.
Geng C, Liu X, Chen M, Yang C, Han B. Comparison of frontline treatment with intensive immunosuppression therapy and HLA-haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for young patients with severe aplastic anemia—a meta analysis. Leuk Res. 2020;88:106266.
Prata PH, Eikema DJ, Afansyev B, Bosman P, Smiers F, Diez-Martin JL, et al. Haploidentical transplantation and posttransplant cyclophosphamide for treating aplastic anemia patients: a report from the EBMT Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55:1050–58.
Ciceri F, Lupo-Stanghellini M, Korthof E. Haploidentical transplantation in patients with acquired aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:183–5.
Luo CJ, Chen J, Wang JM, Qin X, Zhang BH, Zhu H, et al. Alternative donor HSCT for 109 children with acquired severe aplastic anemia: a single center retrospective analysis. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41:128–31.
Yoshida N, Kojima S. Updated guidelines for the treatment of acquired aplastic anemia in children. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018;20:67.
Dufour C, Veys P, Carraro E, Bhatnagar N, Pillon M, Wynn R, et al. Similar outcome of upfront‐unrelated and matched sibling stem cell transplantation in idiopathic paediatric aplastic anaemia. A study on behalf of the UK Paediatric BMT Working Party, Paediatric Diseases Working Party and Severe Aplastic Anaemia Working Party of EBMT. Br J Haematol. 2015;171:585–94.
Yue C, Ding Y, Gao Y, Li L, Pang Y, Liu Z, et al. Cotransplantation of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cells and allogeneic bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells as a first-line treatment in very severe aplastic anemia patients with refractory infections. Eur J Haematol. 2018;100:624–9.
Lu Y, Sun RJ, Zhao YL, Xiong M, Cao XY, Zhang JP, et al. Unmanipulated haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation achieved outcomes comparable with matched unrelated donor transplantation in young acquired severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:1881–7.
Li Y, Duan F, Xiao H, Wu X, Wang S, Xu D, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of haploidentical allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with severe aplastic anemia: a multicenter study. Transplantation. 2018;102:1724–31.
Kim H, Lee KH, Sohn SK, Kim I, Kim SH, Park Y, et al. Effect of stem cell source and dose on allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with idiopathic aplastic anemia: data from the korean aplastic anemia trials. Acta Haematol. 2020;143:232–43.
Bacigalupo A, Socie G, Schrezenmeier H, Tichelli A, Locasciulli A, Fuehrer M, et al. Bone marrow versus peripheral blood as the stem cell source for sibling transplants in acquired aplastic anemia: survival advantage for bone marrow in all age groups. Haematologica. 2012;97:1142–8.
Schrezenmeier H, Passweg JR, Marsh JC, Bacigalupo A, Bredeson CN, Bullorsky E, et al. Worse outcome and more chronic GVHD with peripheral blood progenitor cells than bone marrow in HLA-matched sibling donor transplants for young patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2007;110:1397–400.
Kumar R, Kimura F, Ahn KW, Hu Z-H, Kuwatsuka Y, Klein JP, et al. Comparing outcomes with bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells as graft source for matched sibling transplants in severe aplastic anemia across different economic regions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:932–40.
Morton J, Hutchins C, Durrant S. Granulocyte–colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)–primed allogeneic bone marrow: significantly less graft-versus-host disease and comparable engraftment to G-CSF–mobilized peripheral blood stem cells. Blood. 2001;98:3186–91.
Clay J, Kulasekararaj AG, Potter V, Grimaldi F, McLornan D, Raj K, et al. Nonmyeloablative peripheral blood haploidentical stem cell transplantation for refractory severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:1711–6.
Storb R, Etzioni R, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Buckner CD, Bensinger W, et al. Cyclophosphamide combined with antithymocyte globulin in preparation for allogeneic marrow transplants in patients with aplastic anemia. Blood. 1994;84:941–9.
Aljurf M, Al-Zahrani H, Van Lint M, Passweg J. Standard treatment of acquired SAA in adult patients 18–40 years old with an HLA-identical sibling donor. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:178–9.
Iftikhar R, Anwer F, Neupane K, Rafae A, Mahmood SK, Ghafoor T, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in aplastic anemia: current indications and transplant strategies. Blood Rev. 2020;47:100772.
Iftikhar R, Satti TM, Mahmood SK, Ghafoor T, Shamshad GU, Shahbaz N, et al. Comparison of Conventional Cyclophosphamide versus Fludarabine-Based Conditioning in High-Risk Aplastic Anemia Patients Undergoing Matched-Related Donor Transplantation. Clin Hematol Int. 2020;2:82–91.
Aljurf M, Zaidi SZ, El Solh H, Hussain F, Ghavamzadeh A, Mahmoud HK, et al. Special issues related to hematopoietic SCT in the Eastern Mediterranean region and the first regional activity report. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;43:1–12.
Chen JY, Zheng TL, Zhou T, Hu PW, Huang MJ, Xu X, et al. Human cytomegalovirus prevalence and distribution of glycoprotein B, O genotypes among hospitalized children with respiratory infections in West China, 2009–2014. Trop Med Int Health. 2016;21:1428–34.
Tomblyn M, Chiller T, Einsele H, Gress R, Sepkowitz K, Storek J, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: a global perspective. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;44:453–5.
Burroughs LM, Woolfrey AE, Storer BE, Deeg HJ, Flowers ME, Martin PJ, et al. Success of allogeneic marrow transplantation for children with severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2012;158:120–8.
Marsh JC, Gupta V, Lim Z, Ho AY, Ireland RM, Hayden J, et al. Alemtuzumab with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide reduces chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2011;118:2351–7.
Vaht K, Goransson M, Carlson K, Isaksson C, Lenhoff S, Sandstedt A, et al. High graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse/rejection-free survival and similar outcome of related and unrelated allogeneic stem cell transplantation for aplastic anemia: a Nationwide Swedish Cohort Study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:1970–4.
George B, Mathews V, Viswabandya A, Kavitha ML, Srivastava A, Chandy M. Fludarabine and cyclophosphamide based reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens reduce rejection and improve outcome in Indian patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;40:13–8.
Jalili M, Alimoghaddam K, Hamidieh AA, Hamdi A, Jahani M, Bahar B, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with severe acquired aplastic anemia: Iranian experience. Int J Hematol-Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2011;5:22–7.
Atta EH, de Sousa AM, Schirmer MR, Bouzas LF, Nucci M, Abdelhay E. Different outcomes between cyclophosphamide plus horse or rabbit antithymocyte globulin for HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplant in severe aplastic anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:1876–82.
Shin SH, Lee JW. The optimal immunosuppressive therapy for aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. 2013;97:564–72.
Agarwal M, Jijina F, Shah S, Malhotra P, Damodar S, Ross C. Safety and efficacy of indigenous equine antithymocyte globulin along with cyclosporine in subjects with acquired aplastic anemia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2015;31:174–9.
Zheng Y, Liu Y, Chu Y. Immunosuppressive therapy for acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA): a prospective comparison of four different regimens. Exp Hematol. 2006;34:826–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Members on behalf of the Eastern Mediterranean Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EMBMT) Group, Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (SAAWP of EBMT) are listed below.
The original online version of this article was revised: In the original version of this article, the given and family names of Amir Ali Hamidieh were incorrectly structured. The name was displayed correctly in all versions at the time of publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iftikhar, R., Ahmad, P., de Latour, R. et al. Special issues related to the diagnosis and management of acquired aplastic anemia in countries with restricted resources, a report on behalf of the Eastern Mediterranean blood and marrow transplantation (EMBMT) group and severe aplastic anemia working party of the European Society for blood and marrow transplantation (SAAWP of EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 2518–2532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01332-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-021-01332-8
This article is cited by
-
Profile and Predictors of Infection Following Anti-thymocyte Globulin or Anti-lymphocyte Globulin with Cyclosporine in Aplastic Anemia
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2023)