Abstract
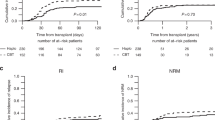
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is a curative procedure in patients with Shwachman–Diamond syndrome (SDS) with bone marrow abnormalities. The results of 74 patients with SDS (6 acute myeloid leukemia, 7 myelodysplastic syndrome, and 61 bone marrow failure) treated with HSCT between 1988 and 2016 are reported. The donor source was: 24% sibling, 8% parent, and 68% unrelated donor. The stem cell source was: 70% bone marrow, 19% peripheral blood stem cells, and 11% cord blood. The conditioning regimen was myeloablative in 54% and reduced intensity in 46%. Neutrophil engraftment was achieved in 84% of patients after a median time of 17.5 days. Graft failure occurred in 15% of HSCTs. Grades I–IV acute and chronic GVHD were observed in 55% and 20% of patients, respectively. After a median follow-up of 7.3 years (95% CI 4.8–10.2), 28 patients died for progression/relapse (7) or toxicity (21). The 5-year overall survival and nonrelapse mortality were 63.3% (95% CI 50.8–73.4) and 19.8% (95% CI 10.8–30.8), respectively. In conclusion, this is the largest series so far reported and confirms that HSCT is a suitable option for patients with SDS. Further efforts are needed to lower transplant-related toxicity and reduce graft failure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0901-x
References
Goobie S, Popovic M, Morrison J, Ellis L, Ginzberg H, Boocock GR, et al. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with exocrine pancreatic dysfunction and bone marrow failure maps to the centromeric region of chromosome 7. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68:1048–54.
Boocock GR, Morrison JA, Popovic M, Richards N, Ellis N, Durie PR, et al. Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman–Diamond syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003;33:97–101.
Dror Y, Donadieu J, Koglmeier J, Dodge J, Toiviainen-Salo S, Makitie O, et al. Draft consensus guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1242:40–55.
Cesaro S, Oneto R, Messina C, Gibson BE, Buzyn A, Steward C, et al. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Shwachman– Diamond disease: a study from the European Group for blood and marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol. 2005;131:231–6.
Donadieu J, Michel G, Merlin E, Bordigoni P, Monteux B, Beaupain B, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Shwachman–Diamond syndrome: experience of the French neutropenia registry. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005;36:787–92.
Isaev AA, Deev RV, Kuliev, Plaxa iL, Stancheva NV, Borovkova AS, et al. First experience of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation treatment of Shwachman–Diamond syndrome using unaffected HLA–matched sibling donor produced through preimplantation HLA typing. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2017;52:1249–52.
Barber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–405.
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51.
Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kroger N. The EBMT Handbook. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy. Springer Open ebook 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02278-5.
Ball LM, Egeler RM. Acute GvHD: pathogenesis and classification. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;41(Suppl 2):S58–64. EBMT Paediatric Working Party.
Dignan FL, Amrolia P, Clark A, Comish J, Jackson G, Mahendra P, et al. Diagnosis and management of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2012;158:46–61.
Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009;15:1628–33.
Tsai PH, Sahdev I, Herry A, Lipton JM. Fatal cyclophosphamide-induced congestive heart failure in a 10-year-old boy with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and severe bone marrow failure treated with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1990;12:472–6.
Barrios N, Kirkpatrick D, Regueira O, Wuttke B, McNeil J, Humbert J. Bone marrow transplant in Shwachman Diamond syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1999;79:337–8.
Seymour JF, Escudier SM. Acute leukemia complicating bone marrow hypoplasia in an adult with Shwachman’s syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 1993;12:131–5.
Smith OP, Chan MY, Evans J, Veys P. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and matched unrelated donor BMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1995;16:717–8.
Smith OP, Hann IM, Chessells JM, Reeves BR, Milla P. Haematological abnormalities in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1996;94:279–84.
Bunin N, Leahey A, Dunn S. Related donor liver transplant for veno-occlusive disease following T-depleted unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation. 1996;61:664–6.
Arseniev L, Diedrich H, Link H. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in a patient with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Ann Hematol. 1996;72:83–4.
Dokal I, Rule S, Chen F, Potter M, Goldman J. Adult onset of acute myeloid leukaemia (M6) in patients with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1997;99:171–3.
Davies SM, Wagner JE, DeFor T, Blazar BR, Katsanis E, Kersey JH, et al. Unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for children and adolescents with aplastic anaemia or myelodysplasia. Br J Haematol. 1997;96:749–56.
Okcu F, Roberts WM, Chan KW. Bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman–Diamond syndrome: report of two cases and review of the literature. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998;21:849–51.
Miano M, Porta F, Locatelli F, Miniero R, La Nasa G, Di Bartolomeo P, et al. Unrelated donor marrow transplantation for inborn errors. Bone Marrow Transpl. 1998;21:S37–41.
Faber J, Lauener R, Wick F, Betts D, Filgueira L, Seger RA, et al. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: early bone marrow transplantation in a high risk patient and new clues to pathogenesis. Eur J Pediatr. 1999;158:995–1000.
Cipolli M, D’Orazio C, Delmarco A, Marchesini C, Miano A, Mastella G. Shwachman’s syndrome: pathomorphosis and long-term outcome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29:265–72.
Cesaro S, Guariso G, Calore E, Gazzola MV, Destro R, Varotto S, et al. Successful unrelated bone marrow transplantation for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2001;27:97–9.
Fleitz J, Rumelhart S, Goldman F, Ambruso D, Sokol RJ, Pacini D, et al. Successful allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002;29:75–9.
Hsu JW, Vogelsang G, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA. Bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002;30:255–8.
Park SY, Chae MB, Kwack YG, Lee MH, Kim I, Kim YS, et al. Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with malignant myeloid transformation. A case report. Korean J Intern Med. 2002;17:204–6.
Cunningham J, Sales M, Pearce A, Howard J, Stallings R, Telford N, et al. Does isochromosome 7q mandate bone marrow transplant in children with Shwachman–Diamond syndrome? Br J Haematol. 2002;119:1062–9.
Mitsui T, Kawakami T, Sendo D, Katsuura M, Shimizu Y, Hayasaka K. Successful unrelated donor bone marrow transplantation for Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2004;79:189–92.
Vibhakar R, Radhi M, Rumelhart S, Tatman T, Goldman F. Successful unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation in children with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2005;36:855–61.
Sauer M, Zeidler C, Meissner B, Rehe K, Hanke A, Welte K, et al. Substitution of cyclophosphamide and busulfan by fludarabine, treosulfan and melphalan in a preparative regimen for children and adolescents with Shwachman–Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2007;39:143–7.
Bhatla D, Davies SM, Shenoy S, Harris RE, Crockett M, Shoultz L, et al. Reduced intensity conditioning is safe and effective for transplantation of patients with Shwachman Diamond syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2008;42:159–65.
Linden T, Ehlert K, Niemeyer CM, Fleischhack G, Jürgens H, Rossig C. Molecular diagnosis of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome in a child with incomplete clinical disease phenotype. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;55:177–9.
Bizzetto R, Bonfim C, Rocha V, Sociè G, Locatelli F, Chan K, et al. Outcomes after related and unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation for hereditary bone marrow failure syndromes other than Fanconi anemia. Haematologica. 2011;96:134–41.
Keogh SJ, McKee S, Smithson SF, Grier D, Steward CG. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: a complex case demonstrating the potential for misdiagnosis as asphyxiating thoracic dystrophy (Jeune syndrome). BMC Pediatr. 2012;12:48.
Bertaina A, Merli P, Rutella S, Pagliara D, Bernardo ME, Masetti R, et al. HLA-haploidentical stem cell transplantation after removal of αβ+T and B cells in children with nonmalignant disorders. Blood. 2014;124:822–6.
Myers KC, Rose SR, Rutter MM, Meha PA, Khoury JC, Cole T, et al. Endocrine evaluation of children with and without Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome genemutations and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. J Pediatr. 2013;162:1235–40.
Myers KC, Bolyard AA, Otto B, Wong TE, Jones AT, Harris RE, et al. Variable clinical presentation of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: update from the North-American Shwachman-Diamond syndrome registry. J Pediatr. 2014;164:866–70.
Delaporta P, Sofocleous C, Economou M, Makis A, Kostaridou S, Kattamis A. The Greek Registry of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: molecular and clinical data. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64:1–4.
Burroughs LM, Shimamura A, Talano JA, Domm JA, Baker KK, Delaney C, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation using treosulfan-based conditioning for treatment of marrow failure disorders. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:1669–77.
Shimosato Y, Tanoshima R, Tsujimoto SI, Takeuchi M, Sakari K, Kajiwara R, et al. Association of isochromosome (7)(q10) in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome with the severity of cytopenia. Clin Case Rep. 2018;6:125–8.
Donadieu J, Fenneteau O, Beaupain B, Beaufils S, Bellanger F, Mahiaoui N, et al. Classification of and risk factors for hematologic complications in a French national cohort of 102 patients with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Haematologica. 2012;97:1312–9.
Lindsley RC, Saber W, Mar BG, Redd R, Wang T, Haagenson MD, et al. Prognostic mutations in myelodysplastic syndrome after stem-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:536–47.
Xia J, Miller CA, Baty J, Ramesh A, Jotte MRM, Fulton RS, et al. Somatic mutations and clonal hematopoiesis in congenital neutropenia. Blood. 2018;131:408–16.
Cremers EM, Van Biezen A, de Wreede LC, Scholten M, Vitek A, Finke J, et al. Prognostic pre-transplant factors in myelodysplastic syndromes primarily treated by high dose allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective study of the MDS subcommittee of the CMWP of the EBMT. Ann Hematol. 2016;95:1971–8.
Bacigalupo A, Socie’ G, Lanino E, Prete A, Locatelli F, Cesaro S, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, antithymocyte globulin, with or without low dose total body irradiation, for alternative donor transplants, in acquired severe aplastic anemia: a retrospective study from the EBMT-SAA Working Party. Haematologica. 2010;95:976–82.
Bardelli D, Dander E, Bugarin C, Cappuzzello C, Pievani A, Fazio G, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells from Shwachman-Diamond syndrome patients fail to recreate a bone marrow niche in vivo and exhibit impaired angiogenesis. Br J Haematol. 2018;182:114–24.
Ciurea SO, Al Malki MM, Kongtim P, Fuchs EJ, Luznik L, Huang XJ, et al. The European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) consensus recommendations for donor selection in haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-019-0499-z.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr Rodney Seddon for reviewing the English style of manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Appendix
Appendix
List of EBMT contributing centers. Center indentifying code (CIC)
CIC 295 Hannover (Christian Kratz, 4), CIC 285 Padova (Marta Pillon, 4), CIC 160 Paris Necker (Benedicte Neven, 4), CIC 301 Marseille (Gerard Michel, 3), CIC 386 Bristol (Stephen Robinson, 3), CIC 424 Montréal (Henrique Bittencourt, 3), CIC 707 Glasgow (Brenda E. Gibson, 3), CIC 234 Brussels (Xavier Poiré, 2),CIC 203 Leiden (Stijn Halkes, 2), CIC 274 Genova (Edoardo Lanino, 2), CIC 207 Paris St. Louis (Regis Peffault de Latour, 2), CIC 422 Barcelona Vall d’Hebron (Cristina Diaz de Heredia, 2), CIC 521 Manchester (Robert Wynn, 2), CIC 796 Rome (Franco Locatelli, 2), CIC 524 Heidelberg (Johann Greil, 2), CIC 243 London (Paul Veys, 2), CIC 775 Paris Saint Antoine (Mohammad Mohty, 1), CIC 246 Rotterdam (Jan Cornelissen, 1), CIC 457 Istanbul (Gülyüz Öztürk, 1), CIC 535 Tübingen (Rupert Handgretinger,1), CIC 539 London (Mickey Koh, 1), CIC 631 Paris Robert Debre (Jean-Hughes Dalle, 1), CIC 751 Athens (Vassiliki Kitra-Rossou, 1), CIC 806 Lyon (Yves Bertrand, 1). CIC 209 Leuven (Anne Uyttebroek,1), CIC 212 Stockholm (Per Ljungman,1), CIC 253 Nantes (Patrice Chevalier, 1), CIC 261 Geneva (Marc Ansari, 1), CIC 260 Barcelona Santa Creu i Sant Pau (Isabel Badell, 1), CIC 208 Zürich (Tayfun Güngör, 1), CIC 501 Liverpool (Salim Rahuman, 1), CIC 513 Munich (Johanna Tischer, 1), CIC 623 Verona (Cristina Tecchio, 1), CIC 717 Nottingham (Nigel Russel, 1), CIC 817 Wroclaw (Alicia Chybicka, 1), CIC 764, Bydgoszcz, (Jan Styczynski, 1), CIC 824 Budapest (Krisztian Kallay, 1), CIC 774 Dublin (Owen Smith, 1), CIC 775 Petach-Tikva (Jerry Stein, 1), CIC 725 St. Petersburg (Boris Afanasyev,1), CIC 676 Nancy (Cécile Pochon, 1), CIC 795 Pisa (Maria Cristina Menconi, 1).
Collaborators
CIC 160 Paris Necker (Benedicte Neven, 4), CIC 301 Marseille (Gerard Michel, 3), CIC 386 Bristol (Stephen Robinson, 3), CIC 424 Montréal (Henrique Bittencourt, 3), CIC 707 Glasgow (Brenda E. Gibson, 3), CIC 234 Brussels (Xavier Poiré, 2), CIC 775 Paris Saint Antoine (Mohammad Mohty, 1), CIC 246 Rotterdam (Jan Cornelissen, 1), CIC 457 Istanbul (Gülyüz Öztürk, 1), CIC 535 Tübingen (Rupert Handgretinger,1), CIC 539 London (Mickey Koh, 1), CIC 631 Paris Robert Debre (Jean-Hughes Dalle, 1), CIC 751 Athens (Vassiliki Kitra-Rossou, 1), CIC 806 Lyon (Yves Bertrand, 1).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cesaro, S., Pillon, M., Sauer, M. et al. Long-term outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Shwachman–Diamond syndrome: a retrospective analysis and a review of the literature by the Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (SAAWP-EBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant 55, 1796–1809 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0863-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-0863-z
This article is cited by
-
Clinical features, epidemiology, and treatment of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: a systematic review
BMC Pediatrics (2023)
-
Second allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with inborn errors of immunity
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Comparable clinical outcomes of haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia and non-hepatitis-associated aplastic anemia
Annals of Hematology (2022)
-
Recent advances in hematopoietic cell transplantation for inherited bone marrow failure syndromes
International Journal of Hematology (2022)