Abstract
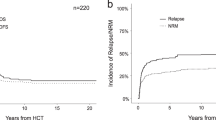
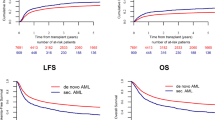
Posttransplant relapse represents the greatest obstacle to the success of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). This study investigated clinical features and outcomes of posttransplant relapse of AML based on data for 1265 patients with AML suffering relapse after allogeneic HCT conducted during complete remission (CR). Relapse occurred at a median of 6.1 months. The incidence rate of relapse peaked at 29.0 per 100 patient-years during the first 3–6 months period post transplant, after which the rate declined over time, and after 3 years remained consistently at less than 1 per 100 patient-years. The probability of overall survival (OS) after posttransplant relapse was 19% at 2 years, with 68% of deaths being attributed to leukemia. The interval from transplantation to relapse was identified as the strongest indicator for OS. Donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) and second allogeneic HCT (HCT2) were administered to 152 (12%) and 481 (38%) patients, respectively. Landmark analyses showed some signs of survival benefit when these procedures were performed during CR, but no benefit was gained when performed during non-CR. Our findings clarify clinical features of posttransplant relapse of AML, and indicate the urgent need for developing effective bridging to cellular therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanada M, Takami A, Yamasaki S, Arai Y, Konuma T, Uchida N, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adults with acute myeloid leukemia conducted in Japan during the past quarter century. Ann Hematol. 2020;99:1351–60.
Schmid C, Labopin M, Nagler A, Niederwieser D, Castagna L, Tabrizi R, et al. Treatment, risk factors, and outcome of adults with relapsed AML after reduced intensity conditioning for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2012;119:1599–606.
Bejanyan N, Weisdorf DJ, Logan BR, Wang HL, Devine SM, de Lima M, et al. Survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: a Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research study. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015;21:454–9.
Lim ABM, Curley C, Fong CY, Bilmon I, Beligaswatte A, Purtill D, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia relapsing after allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplantation: prognostic factors and impact of initial therapy of relapse. Intern Med J. 2018;48:276–85.
Atsuta Y. Introduction of Transplant Registry Unified Management Program 2 (TRUMP2): scripts for TRUMP data analyses, part I (variables other than HLA-related data). Int J Hematol. 2016;103:3–10.
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J, Davis TE, McFadden ET, et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982;5:649–55.
Yanada M, Mori J, Aoki J, Harada K, Mizuno S, Uchida N, et al. Effect of cytogenetic risk status on outcomes for patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing various types of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: an analysis of 7812 patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2018;59:601–09.
Schlenk RF, Dohner K, Mack S, Stoppel M, Kiraly F, Gotze K, et al. Prospective evaluation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation from matched related and matched unrelated donors in younger adults with high-risk acute myeloid leukemia: German-Austrian trial AMLHD98A. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4642–8.
Schmid C, Labopin M, Nagler A, Bornhauser M, Finke J, Fassas A, et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion in the treatment of first hematological relapse after allogeneic stem-cell transplantation in adults with acute myeloid leukemia: a retrospective risk factors analysis and comparison with other strategies by the EBMT Acute Leukemia Working Party. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4938–45.
Takami A, Yano S, Yokoyama H, Kuwatsuka Y, Yamaguchi T, Kanda Y, et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion for the treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a retrospective analysis by the Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2014;20:1785–90.
Miyamoto T, Fukuda T, Nakashima M, Henzan T, Kusakabe S, Kobayashi N, et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion for relapsed hematological malignancies after unrelated allogeneic bone marrow transplantation facilitated by the Japan Marrow Donor Program. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017;23:938–44.
Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Labopin M, Polge E, Nishihori T, Bazarbachi A, Finke J, et al. Association of Second Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplant vs Donor Lymphocyte Infusion With Overall Survival in Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia Relapse. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1245–53.
Christopeit M, Kuss O, Finke J, Bacher U, Beelen DW, Bornhauser M, et al. Second allograft for hematologic relapse of acute leukemia after first allogeneic stem-cell transplantation from related and unrelated donors: the role of donor change. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3259–71.
Maeda Y, Ugai T, Kondo E, Ikegame K, Murata M, Uchida N, et al. HLA discrepancy between graft and host rather than that graft and first donor impact the second transplant outcome. Haematologica. 2019;104:1055–61.
Craddock C, Labopin M, Robin M, Finke J, Chevallier P, Yakoub-Agha I, et al. Clinical activity of azacitidine in patients who relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 2016;101:879–83.
Metzelder SK, Schroeder T, Lubbert M, Ditschkowski M, Gotze K, Scholl S, et al. Long-term survival of sorafenib-treated FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukaemia patients relapsing after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Cancer. 2017;86:233–39.
Schroeder T, Rautenberg C, Kruger W, Platzbecker U, Bug G, Steinmann J, et al. Treatment of relapsed AML and MDS after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with decitabine and DLI-a retrospective multicenter analysis on behalf of the German Cooperative Transplant Study Group. Ann Hematol. 2018;97:335–42.
Xuan L, Wang Y, Chen J, Jiang E, Gao L, Wu B, et al. Sorafenib therapy is associated with improved outcomes for FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 internal tandem duplication acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019;25:1674–81.
Platzbecker U, Wermke M, Radke J, Oelschlaegel U, Seltmann F, Kiani A, et al. Azacitidine for treatment of imminent relapse in MDS or AML patients after allogeneic HSCT: results of the RELAZA trial. Leukemia. 2012;26:381–9.
Platzbecker U, Middeke JM, Sockel K, Herbst R, Wolf D, Baldus CD, et al. Measurable residual disease-guided treatment with azacitidine to prevent haematological relapse in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukaemia (RELAZA2): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1668–79.
Tsirigotis P, Byrne M, Schmid C, Baron F, Ciceri F, Esteve J, et al. Relapse of AML after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: methods of monitoring and preventive strategies. A review from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016;51:1431–38.
Spyridonidis A. How I treat measurable (minimal) residual disease in acute leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2020;135:1639–49.
Pusic I, Choi J, Fiala MA, Gao F, Holt M, Cashen AF, et al. Maintenance therapy with decitabine after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2015;21:1761–9.
Brunner AM, Li S, Fathi AT, Wadleigh M, Ho VT, Collier K, et al. Haematopoietic cell transplantation with and without sorafenib maintenance for patients with FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission. Br J Haematol. 2016;175:496–504.
Battipaglia G, Ruggeri A, Massoud R, El Cheikh J, Jestin M, Antar A, et al. Efficacy and feasibility of sorafenib as a maintenance agent after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer. 2017;123:2867–74.
de Lima M, Oran B, Champlin RE, Papadopoulos EB, Giralt SA, Scott BL, et al. CC-486 maintenance after stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018;24:2017–24.
Guillaume T, Malard F, Magro L, Labopin M, Tabrizi R, Borel C, et al. Prospective phase II study of prophylactic low-dose azacitidine and donor lymphocyte infusions following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019;54:1815–26.
Schmid C, Labopin M, Schaap N, Veelken H, Schleuning M, Stadler M, et al. Prophylactic donor lymphocyte infusion after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute leukaemia—a matched pair analysis by the Acute Leukaemia Working Party of EBMT. Br J Haematol. 2019;184:782–87.
Burchert A, Bug G, Fritz LV, Finke J, Stelljes M, Rollig C, et al. Sorafenib maintenance after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia with FLT3-internal tandem duplication mutation (SORMAIN). J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:2993–3002.
Zeiser R, Vago L. Mechanisms of immune escape after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2019;133:1290–97.
Shimoni A, Labopin M, Finke J, Ciceri F, Deconinck E, Kroger N, et al. Donor selection for a second allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML patients relapsing after a first transplant: a study of the Acute Leukemia Working Party of EBMT. Blood. Cancer J. 2019;9:88.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Practical Research Project for Allergic Diseases and Immunology (Research Technology of Medical Transplantation) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), grant number: 18ek0510023h0002, and a grant from the Aichi Cancer Research Foundation, grant number: 2020-1-11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yanada, M., Konuma, T., Yamasaki, S. et al. Relapse of acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: clinical features and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant 56, 1126–1133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-01163-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-020-01163-z
This article is cited by
-
Recurrent DDX41 mutation in very late relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Leukemia (2024)
-
A novel risk model for predicting early relapse in acute myeloid leukemia patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Overcoming relapse: prophylactic or pre-emptive use of azacitidine or FLT3 inhibitors after allogeneic transplantation for AML or MDS
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Outcomes of third allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in relapsed/refractory acute leukemia after a second transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2022)
-
A retrospective single-center analysis of G-CSF-mobilized donor lymphocyte infusion in hematologic malignancies after unmanipulated allogenic PBSCT
International Journal of Hematology (2022)