Abstract
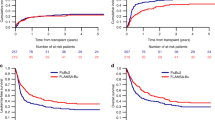
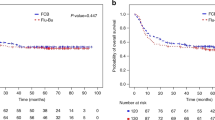
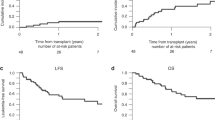
To compare the efficacy and toxicity of a novel regimen called FBA, consisting of fludarabine, busulfan, and cytarabine, with the standard BuCy2 regimen for younger adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia, we conducted a prospective randomized phase II study. Patients in complete remission were randomly assigned to receive either the FBA (n = 56) or the BuCy2 regimen (n = 55). The difference in 100-day transplant-related mortality (TRM) was not statistically significant between the two arms (1.79% for FBA versus 5.45% for BuCy2, P = 0.260), as were the cumulative incidences of relapse, TRM, overall survival (OS) and event-free survival (EFS) at 3 years. However, the 100-day cumulative incidences of grades II–IV and III–IV acute graft-versus-host disease (aGVHD) were lower in the FBA group [(8.93% versus 21.86%, P = 0.032) (1.79% versus 9.09%, P = 0.025)]. The 3-year GVHD and relapse-free survival (GRFS) was 31.20% for the FBA group and 14.96% for the BuCy2 group (P = 0.004). The incidences of diarrhea and severe oral mucositis within the first 30 days post-transplantation were lower in the FBA group [(28.57% versus 65.45%; P < 0.001) (51.79% versus 70.91%; P = 0.039)]. In conclusion, allogenic transplantation with the FBA regimen achieved similar TRM, relapse rate, OS and EFS, as that with the BuCy2 regimen but with less frequent and less severe complications in early stage after transplantation and a trend toward higher GRFS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devine SM, Owzar K, Blum W, Mulkey F, Stone RM, Hsu JW, et al. Phase II study of allogeneic transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network 0502. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:4167–75.
Tanaka Y, Kurosawa S, Tajima K, Tanaka T, Ito R, Inoue Y, et al. Analysis of non-relapse mortality and causes of death over 15 years following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51:553–9.
Holler E, Kolb HJ, Moller A, Kempeni J, Liesenfeld S, Pechumer H, et al. Increased serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha precede major complications of bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1990;75:1011–6.
Kawamura K, Kako S, Mizuta S, Ishiyama K, Aoki J, Yano S, et al. Comparison of conditioning with fludarabine/busulfan and fludarabine/melphalan in allogeneic transplantation recipients 50 years or older. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23:2079–87.
Scott BL, Pasquini MC, Logan BR, Wu J, Devine SM, Porter DL, et al. Myeloablative versus reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:1154–61.
Zeng W, Huang L, Meng F, Liu Z, Zhou J, Sun H. Reduced-intensity and myeloablative conditioning allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7:4357–68.
Rambaldi A, Grassi A, Masciulli A, Boschini C, Micò MC, Busca A, et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine as a preparative regimen for allogeneic haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1525–36.
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ, Plunkett W. Fludarabine potentiates metabolism of cytarabine in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia during therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:116–24.
Ossenkoppele GJ, Graveland WJ, Sonneveld P, Daenen SM, Biesma DH, Verdonck LF, et al. The value of fludarabine in addition to ARA-C and G-CSF in the treatment of patients with high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and AML in elderly patients. Blood. 2004;103:2908–13.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Büchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH, et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4642–9.
Zhang WP, Yang D, Song XM, Ni X, Chen J, Chen L, et al. Allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation is a promising and safe choice for the treatment of refractory/relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia, even with a higher leukemia burden. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19:653–60.
Lu DP1, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W, et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood. 2006;107:3065–73.
Litzow MR, Pérez WS, Klein JP, Bolwell BJ, Camitta B, Copelan EA, et al. Comparison of outcome following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation with cyclophosphamide-total body irradiation versus busulphan-cyclophosphamide conditioning regimens for acute myelogenous leukaemia in first remission. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:1115–24.
Bornhäuser M, Thiede C, Schuler U, Platzbecker U, Freiberg-Richter J, Helwig A, et al. Dose-reduced conditioning for allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation: durable engraftment without antithymocyte globulin. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;26:119–25.
Baronciani D, Rambaldi A, Iori AP, Di Bartolomeo P, Pilo F, Pettinau M, et al. Treosulfan/fludarabine as an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant conditioning regimen for high-risk patients. Am J Hematol. 2008;83:717–20.
Falda M, Busca A, Baldi I, Mordini N, Bruno B, Allione B, et al. Nonmyeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation in elderly patients with hematological malignancies: results from the GITMO (Gruppo Italiano Trapianto Midollo Osseo) multicenter prospective clinical trial. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:863–6.
Holtan SG, DeFor TE, Lazaryan A, Bejanyan N, Arora M, Brunstein CG, et al. Composite end point of graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood. 2015;125:1333–8.
Solh M, Zhang X, Connor K, Brown S, Solomon SR, Morris LE, et al. Factors predicting graft-versus-host disease-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: multivariable analysis from a single center. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22:1403–9.
NCI. Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 4.0, 28 May 2009. https://ctep.cancer.gov.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA-matched sibling donors. Transplant. 1974;18:295–304.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, McDonald GB, Striker G, Sale GE, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980;69:204–17.
Al Ibraheemi AA, Shamoun S. Incidence and risk factors of oral mucositis in patients with breast cancer who receiving chemotherapy in Al-Bashir hospital. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2016;10:217–23.
Stelljes M, Krug U, Beelen DW, Braess J, Sauerland MC, Heinecke A, et al. Allogeneic transplantation versus chemotherapy as postremission therapy for acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective matched pairs analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:288–96.
Giralt S, Estey E, Albitar M, van Besien K, Rondón G, Anderlini P, et al. Engraftment of allogeneic hematopoietic progenitor cells with purine analog-containing chemotherapy: harnessing graft-versus-leukemia without myeloablative therapy. Blood. 1997;89:4531–6.
Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, Wang X, Braunschweig I, Ippolitti C, et al. Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97:631–7.
Savani BN, Labopin M, Kröger N, Finke J, Ehninger G, Niederwieser D, et al. Expanding transplant options to patients over 50 years. Improved outcome after reduced intensity conditioning mismatched-unrelated donor transplantation for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the EBMT. Haematologica. 2016;101:773–80.
Poiré X, Labopin M, Cornelissen JJ, Volin L, Richard Espiga C, Veelken JH, et al. Outcome of conditioning intensity in acute myeloid leukemia with monosomal karyotype in patients over 45 year-old: a study from the acute leukemia working party (ALWP) of the European group of blood and marrow transplantation (EBMT). Am J Hematol. 2015;90:719–24.
Sarmiento MM, Bertín CP, Jara V, Ocqueteau TM, Ramírez VP. Intensity adjustment of hematopoietic alogeneic transplantation in acute leukemia. Rev Med Chil. 2016;144:1112–8.
Sébert M, Porcher R, Robin M, Adès L, Boissel N, Raffoux E, et al. Equivalent outcomes using reduced intensity or conventional myeloablative conditioning transplantation for patients aged 35 years and over with AML. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015;50:74–81.
Gyurkocza B, Sandmaie BM. Conditioning regimens for hematopoietic cell transplantation: one size does not fit all. Blood. 2014;124:344–53.
Iravani M, Evazi MR, Mousavi SA, Shamshiri AR, Tavakoli M, Ashouri A, et al. Fludarabine and busulfan as a myeloablative conditioning regimen for allogeneic stem cell transplantation in high- and standard-risk leukemic patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007;40:105–10.
Shimoni A, Labopin M, Savani B, Volin L, Ehninger G, Kuball J, et al. Long-term survival and late events after allogeneic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched siblings for acute myeloid leukemia with myeloablative compared to reduced-intensity conditioning: a report on behalf of the acute leukemia working party of European group for blood and marrow transplantation. J Hematol Oncol. 2016;9:118.
Abdul Wahid SF, Ismail NA, Mohd-Idris MR, Jamaluddin FW, Tumian N, Sze-Wei EY, et al. Comparison of reduced-intensity and myeloablative conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:2535–52.
Burnett AK, Hills RK, Milligan D, Kjeldsen L, Kell J, Russell NH, et al. Identification of patients with acute myeloblastic leukemia who benefit from the addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin: results of the MRC AML15 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:369–77.
Abrahamsson J, Forestier E, Heldrup J, Jahnukainen K, Jónsson OG, Lausen B, et al. Response-guided induction therapy in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with excellent remission rate. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:310–5.
Kim H, Lee JH, Joo YD, Bae SH, Lee JH, Kim DY, et al. A prospective, multicenter phase II study of continuous infusion of FLAG for patients older than 60 yr with resistant acute myeloid leukemia: a comparison with intensive younger patients’ trial. Eur J Haematol. 2016;96:188–97.
Alwan AF, Matti BF, Naji AS, Jawad AM. The efficacy of fludarabine, high dose cytosine arabinoside with granulocyte colony stimulating factor (FLAG) protocol as salvage therapy for refractory/relapsed acute leukemias in adult Iraqi patients. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2014;30:231–5.
Kaspers GJ, Zimmermann M, Reinhardt D, Gibson BE, Tamminga RY, Aleinikova O, et al. Improved outcome in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: results of a randomized trial on liposomal daunorubicin by the International BFM Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:599–607.
Bacigalupo A, Lamparelli T, Bruzzi P, Guidi S, Alessandrino PE, di Bartolomeo P, et al. Antithymocyte globulin for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis in transplants from unrelated donors: 2 randomized studies from Gruppo Italiano Trapianti Midollo Osseo (GITMO). Blood. 2001;98:2942–7.
Bacigalupo A, Lamparelli T, Barisione G, Bruzzi P, Guidi S, Alessandrino PE, et al. Thymoglobulin prevents chronic graft-versus-host disease, chronic lung dysfunction, and late transplant-related mortality: long-term follow-up of a randomized trial in patients undergoing unrelated donor transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12:560–5.
Wang JM, Hu J, Wang C, Chen HX, Hou J, Zhang WP, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioning with FBA/FBAA regimen is feasible for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia (AML): interim results of a multicenter clinical trial in China. Blood. 2009;114:196.
Horan JT, Logan BR, Agovi-Johnson MA, Lazarus HM, Bacigalupo AA, Ballen KK, et al. Reducing the risk for transplantation-related mortality after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: how much progress has been made? J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:805–13.
Andreyev J, Ross P, Donnellan C, Lennan E, Leonard P, Waters C, et al. Guidance on the management of diarrhoea during cancer chemotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e447–460.
Lee JH, Joo YD, Kim H, Ryoo HM, Kim MK, Lee GW, et al. Randomized trial of myeloablative conditioning regimens: busulfan plus cyclophosphamide versus busulfan plus fludarabine. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:701–9.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC 81530047; 81270638; 81090413) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (08JC1406500; 05DZ19327) to JMW.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W-PZ and J-MW designed the study, contributed to patient enrollment, diagnosis and treatment, and wrote the manuscript. Z-WW collected and verified patient information, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. LC and JC randomly assigned patients to treatment arms. All other authors were involved in protocol discussions and contributed to the diagnosis and treatment of the patients.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, WP., Wang, ZW., Hu, XX. et al. Preconditioning with fludarabine, busulfan and cytarabine versus standard BuCy2 for patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective, randomized phase II study. Bone Marrow Transplant 54, 894–902 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0356-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0356-5
This article is cited by
-
Myeloablative conditioning regimens in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in complete remission: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2023)
-
Cytogenetic evolution predicts a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia patients who relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Chemotherapy vs. allogeneic transplantation as post molecular remission therapy in patients aged less than 60 years with Philadelphia-positive ALL
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
The benefit of chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients with acute myeloid leukemia relapsed after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Annals of Hematology (2019)
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells transplantation improves the survival of intermediate-risk acute myeloid leukemia patients aged less than 60 years
Annals of Hematology (2019)