Abstract
Background
Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) is not yet universally accepted due to still limited functional data and some concerns on oncological safety compared to the standard one. We assessed perioperative, pathological and early functional outcomes in patients with clinically localised prostate cancer treated with Retzius-sparing versus standard RARP.
Methods
A single-surgeon cohort of 207 consecutive patients undergoing RARP was analysed. A later study group of 102 patients receiving the Retzius-sparing approach was compared with an earlier control group of 105 patients receiving the standard one. Urinary continence recovery 1 week after catheter removal was the primary study outcome. Urinary continence recovery 1, 2, 3 and 6 months after catheter removal, potency recovery 6 months postoperatively, rate of perioperative complications and positive surgical margins were secondary study outcomes.
Results
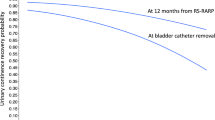
Patients in the study group reported significantly higher urinary continence recovery rates 1 week (91.2% vs. 54.3%, p < 0.001), 1 month (92.2% vs. 66.7%, p < 0.001), 2 months (95.1% vs. 74.3%, p < 0.001), 3 months (96.1% vs. 83.8%, p = 0.01), but not 6 months (97% vs 90.5%, p = 0.09) after catheter removal compared to controls. Potency recovery rates 6 months after catheter removal were significantly higher in the study than the control group (68.2% vs 51.6%, p = 0.03). On multivariable analyses, the Retzius-sparing approach was an independent predictor of 1-week urinary continence recovery, but not of 6-month potency recovery. There were significant differences neither in perioperative complication rate (9.8% in the study vs. 14.3% in the control group, p = 0.28) nor in positive surgical margin rate (9.8% in the study vs. 8.6% in the control group, p = 0.75).
Conclusions
In a comparative study, we observed a significant improvement in immediate urinary continence, but not in early potency recovery, using the Retzius-sparing compared to the standard approach for RARP, with no increase in perioperative complication and positive surgical margin rate.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets created and analyzed in this study are not publicly available. Requests for data can be addressed to the corresponding author (GG).
References
Martini A, Falagario UG, Villers A, Dell’Oglio P, Mazzone E, Autorino R, et al. Contemporary techniques of prostate dissection for robot-assisted prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2020;78:583–91.
Guillonneau B, Vallancien G. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the Montsouris technique. J Urol. 2000;163:1643–9.
Checcucci E, Pecoraro A, De Cillis S, Manfredi M, Amparore D, Aimar R, et al. The importance of anatomical reconstruction for continence recovery after robot assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and pooled analysis from referral centers. Minerva Urol Nephrol. 2021;73:165–77.
Galfano A, Ascione A, Grimaldi S, Petralia G, Strada E, Bocciardi AM. A new anatomic approach for robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy: a feasibility study for completely intrafascial surgery. Eur Urol. 2010;58:457–61.
Gragg P, Sellers CL. Twitter. Law Libr J. 2010;102:325–30.
Checcucci E, Veccia A, Fiori C, Amparore D, Manfredi M, Di Dio M, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy vs the standard approach: a systematic review and analysis of comparative outcomes. BJU Int. 2020;125:8–16.
Barakat B, Othman H, Gauger U, Wolff I, Hadaschik B, Rehme C. Retzius sparing radical prostatectomy versus robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: which technique is more beneficial for prostate cancer patients (MASTER study)? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;8:1060–71.
Liu J, Zhang J, Yang Z, Liu Q, Zhang W, Qing Z, et al. Comparison of Retzius-sparing and conventional robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy regarding continence and sexual function: an updated meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022;25:47–54.
Chung DY, Jung HD, Kim DK, Lee MH, Lee SW, Paick S, et al. Outcomes of Retzius-sparing versus conventional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a KSER update series systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0268182.
Ficarra V, Gan M, Borghesi M, Zattoni F, Mottrie A. Posterior muscolofascial reconstruction incorporated into urethrovescical anastomosis during robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol. 2012;26:1542–5.
Ficarra V, Rossanese M, Crestani A, Alario G, Mucciardi G, Isgrò A, et al. Robot-assisted radical prostatectomy using the novel urethral fixation technique versus standard vesicourethral anastomosis. Eur Urol. 2021;79:530–6.
Briganti A, Larcher A, Abdollah F, Capitanio U, Gallina A, Suardi N, et al. Updated nomogram predicting lymph node invasion in patients with prostate cancer undergoing extended pelvic lymph node dissection: the essential importance of percentage of positive cores. Eur Urol. 2012;61:480–7.
D’Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, Schultz D, Blank K, Broderick GA, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA. 1998;280:969–74.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004;23:322–30.
Wei JT, Dunn RL, Litwin MS, Sandler HM, Sanda MG. Development and validation of the expanded prostate cancer index composite (EPIC) for comprehensive assessment of health-related quality of life in men with prostate cancer. Urology. 2000;56:899–905.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Peña BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999;11:319–26.
Dalela D, Jeong W, Prasad MA, Sood A, Abdollah F, Diaz M, et al. A pragmatic randomized controlled trial examining the impact of the Retzius-sparing approach on early urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2017;72:677–85.
Menon M, Dalela D, Jamil M, Diaz M, Tallman C, Abdollah F, et al. Functional recovery, oncologic outcomes and postoperative complications after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: an evidence-based analysis comparing the retzius sparing and standard approaches. J Urol. 2018;199:1210–7.
Qiu X, Li Y, Chen M, Xu L, Guo S, Marra G, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy improves early recovery of urinary continence: a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial with a 1-year follow-up. BJU Int. 2020;126:633–40.
Asimakopoulos AD, Topazio L, De Angelis M, Agrò EF, Pastore AL, Fuschi A, et al. Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a prospective randomized comparison on immediate continence rates. Surg Endosc. 2018;33:2187–96.
Egan J, Marhamati S, Carvalho FLF, Davis M, O’Neill J, Lee H, et al. Retzius-sparing robot- assisted radical prostatectomy leads to durable improvement in urinary function and quality of life versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy without compromise on oncologic efficacy: single-surgeon series and step-by-step guide. Eur Urol. 2021;79:839–57.
Sayyid RK, Simpson WG, Lu C, Terris MK, Klaassen Z, Madi R. Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: a safe surgical technique with superior continence outcomes. J Endourol. 2017;31:1244–50.
Turkolmez K, Akpinar C, Kubilay E, Suer E. Retzius-Sparing vs modified anatomical structure preserving and Retzius-Repairing Robotic-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy: a prospective randomized comparison on functional outcomes with a 1-year follow-up. J Endourol. 2022;36:1214–22.
Umari P, Eden C, Cahill D, Rizzo M, Eden D, Sooriakumaran P. Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a comparative prospective study of nearly 500 patients. J Urol. 2021;205:780–90.
Deng W, Jiang H, Liu X, Chen L, Liu W, Zhang C, et al. Transvesical Retzius-Sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a retrospective propensity score-adjusted analysis. Front Oncol. 2021;11:687010.
Tahra A, Sen UT, Sobay R, İnkaya A, Kucuk EV, Boylu U. Comparison of Retzius-sparing versus standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. Actas Urol Esp. 2022;46:293–300.
Stonier T, Simson N, Davis J, Challacombe B. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RS-RARP) vs standard RARP: it’s time for critical appraisal. BJU Int. 2019;123:5–7.
Galfano A, Secco S, Dell’Oglio P, Rha K, Eden C, Fransis K, et al. Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: early learning curve experience in three continents. BJU Int. 2021;127:412–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation: VF. Data curation: MR, MG, MF, LM, GM, MM. Investigation: VF. Resources: VF. Formal Analysis: VF. Writing Original draft: VF. Writing Review & Editing: GG. Supervision: VF, GG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ficarra, V., Rossanese, M., Gilante, M. et al. Retzius-sparing vs. standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for clinically localised prostate cancer: a comparative study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 26, 568–574 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00625-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-022-00625-3
This article is cited by
-
Single port robot-assisted radical and simple prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2024)
-
Retzius-sparing vs. posterior urethral suspension: similar early-phase post-robotic radical prostatectomy continence outcomes
Journal of Robotic Surgery (2024)