Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR) in Kawasaki disease (KD) complicated with coronary artery lesions (CALs) and to construct a nomogram prediction model.
Methods
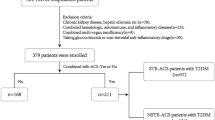
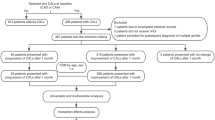
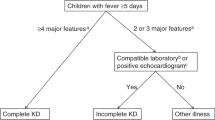
The medical records of KD inpatients diagnosed in the Department of Pediatrics of Lanzhou University Second Hospital from May 2015 to September 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. ROC curves were applied to evaluate the predictive value of MHR in KD complicated with CALs, and logistic regression analysis was used to screen independent risk factors. We constructed a nomogram model and performed internal validation.
Results
A total of 568 KD patients were enrolled in the study. MHR was significantly higher in KD patients complicated with CALs and was identified as an independent risk factor for CALs (OR: 1.604, 95% CI: 1.292–1.990). The area under the ROC curve for MHR in predicting CALs was 0.661. The C-index of the nomogram model constructed by incorporating MHR was 0.725 (95% CI: 0.682–0.768), and the calibration curve revealed good agreement between the predicted and actual probabilities.
Conclusions
MHR may not be suitable as a single biomarker to predict the occurrence of CALs, but the nomogram model constructed in combination with other independent risk factors had acceptable predictive performance.
Impact
-
The inflammatory response plays an important role in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease.
-
The monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio is a novel systemic inflammation marker.
-
The monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio is an independent risk factor for Kawasaki disease complicated with coronary artery lesions.
-
The nomogram established by incorporating the monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio has satisfactory predictive performance for coronary artery lesion formation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Nakamura, Y. Kawasaki disease: epidemiology and the lessons from it. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 21, 16–19 (2018).
McCrindle, B. W. et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a Scientific Statement for Health Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135, e927–e999 (2017).
Kuo, H. C. Preventing coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Biomed. J. 40, 141–146 (2017).
Miura, M. et al. Association of severity of coronary artery aneurysms in patients with Kawasaki disease and risk of later coronary events. JAMA Pediatr. 172, e180030 (2018).
Chang, L. S. et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and scoring system for predicting coronary artery lesions of Kawasaki disease. BMC Pediatr. 20, 398 (2020).
Kanai, T. et al. The combination of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios as a novel predictor of intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in patients with Kawasaki disease: a multicenter study. Heart Vessels 35, 1463–1472 (2020).
Tsai, C. M., Yu, H. R., Tang, K. S., Huang, Y. H. & Kuo, H. C. C-Reactive protein to albumin ratio for predicting coronary artery lesions and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease. Front. Pediatr. 8, 607631 (2020).
Liu, X. et al. Predictive value of the systemic immune-inflammation index for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and cardiovascular complications in Kawasaki disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 711007 (2021).
Wang, H. Y. et al. Assessing the performance of monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio for predicting ischemic stroke: insights from a population-based Chinese cohort. Lipids Health Dis. 18, 127 (2019).
Liu, H. B. et al. Monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio predicts the outcome of acute ischemic stroke. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 27, 959–968 (2020).
Kundi, H. et al. Association of monocyte/HDL-C ratio with syntax scores in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Herz 41, 523–529 (2016).
Enhos, A. et al. Assessment of the relationship between monocyte to high-density lipoprotein ratio and myocardial bridge. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 112, 12–17 (2019).
Newburger, J. W. et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A Statement for Health Professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Pediatrics 114, 1708–1733 (2004).
Dallaire, F. & Dahdah, N. New equations and a critical appraisal of coronary artery Z scores in healthy children. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 24, 60–74 (2011).
Kobayashi, T. et al. A new Z score curve of the coronary arterial internal diameter using the lambda-mu-sigma method in a pediatric population. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 29, 794–801.e729 (2016).
Saundankar, J. et al. The epidemiology and clinical features of Kawasaki disease in Australia. Pediatrics 133, E1009–E1014 (2014).
Shao, S. R. et al. Predictive value of serum lipid for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesion in Kawasaki disease. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 106, E4210–E4220 (2021).
Wu, J. et al. Analysis of epidemiological characteristics of 581 children with Kawasaki disease in Gansu. Chin. Gen. Pract. 24, 4499–4505 (2021).
Lo, M. S. A framework for understanding Kawasaki disease pathogenesis. Clin. Immunol. 214, 108385 (2020).
Takahashi, K., Oharaseki, T. & Yokouchi, Y. Histopathological aspects of cardiovascular lesions in Kawasaki disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 21, 31–35 (2018).
Zhang, D. F., Liu, L. J., Huang, X. P. & Tian, J. Insights into coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Front. Pediatr. 8, 493 (2020).
Nandi, A., Pal, P. & Basu, S. A comparison of serum IL6 and CRP levels with respect to coronary changes and treatment response in Kawasaki disease patients: a prospective study. Rheumatol. Int. 39, 1797–1801 (2019).
Kim, M. K., Song, M. S. & Kim, G. B. Factors predicting resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment and coronary artery lesion in patients with Kawasaki disease: analysis of the Korean nationwide multicenter survey from 2012 to 2014. Korean Circ. J. 48, 71–79 (2018).
Xie, T. et al. Predictors for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 15, 17 (2017).
Williams, H., Mack, C. D., Li, S. C. H., Fletcher, J. P. & Medbury, H. J. Nature versus number: monocytes in cardiovascular disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 9119 (2021).
Armaroli, G. et al. Monocyte-derived interleukin-1 as the driver of S100a12-induced sterile inflammatory activation of human coronary artery endothelial cells: implications for the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 71, 792–804 (2019).
Murphy, A. J. et al. High-density lipoprotein reduces the human monocyte inflammatory response. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 2071–2077 (2008).
Grao-Cruces, E., Lopez-Enriquez, S., Martin, M. E. & Montserrat-de la Paz, S. High-density lipoproteins and immune response: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 195, 117–123 (2022).
Hua, W. et al. A new scoring system to predict Kawasaki disease with coronary artery lesions. Clin. Rheumatol. 38, 1099–1107 (2019).
Ou, C.-Y., Tseng, Y.-F., Lee, C.-L., Chiou, Y.-H. & Hsieh, K.-S. Significant relationship between serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and children with Kawasaki disease and coronary artery lesions. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 108, 719–724 (2009).
Kim, H., Yamaguchi, H., Inamo, K., Okada, T. & Harada, K. Changes in apolipoproteins during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr. Jpn. 37, 672–676 (1995).
Aydin, F. Y. et al. The role of monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in predicting the severity of proteinuria and renal dysfunction in primary nephrotic syndrome. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 13, e20345 (2021).
Xu, H. Z. et al. Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio as an independent risk factor for papillary thyroid carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 35, e24014 (2021).
Liu, H. et al. Monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio predicts the outcome of acute ischemic stroke. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 27, 959–968 (2020).
Demir, F. et al. Usefulness of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in prediction of coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease. Balk. Med. J. 32, 371–376 (2015).
Wang, L. et al. Evaluating the added predictive ability of MMP-9 in serum for Kawasaki disease with coronary artery lesions. J. Investig. Med. 69, 13–19 (2021).
Downie, M. L. et al. Factors associated with development of coronary artery aneurysms after Kawasaki disease are similar for those treated promptly and those with delayed or no treatment. Int. J. Cardiol. 236, 157–161 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Department of Pediatrics of Lanzhou University Second Hospital for providing us with data support. This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (20JR10RA599), Cuiying Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (2020QN-22), and Cuiying Scientific Training Program for Undergraduates of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (CYXZ2021-67).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.Y.: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. Y.Y.: resources, validation, supervision, writing—review and editing. S.C.: investigation, software. Z.M.: investigation, visualization. H.D., J.L., F.D., Y.Z., X.L.: investigation. X.H.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, data curation, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Lanzhou University Second Hospital (No. 2021A-058), and the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Yang, Y., Cao, S. et al. Kawasaki disease coronary artery lesions prediction with monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio. Pediatr Res 94, 246–251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02401-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02401-4
This article is cited by
-
Monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is associated with cerebral small vessel diseases
BMC Neurology (2024)
-
Predictive value of monocyte to HDL-C ratio for coronary artery lesions and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease
European Journal of Pediatrics (2023)