Abstract
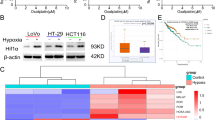
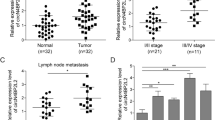
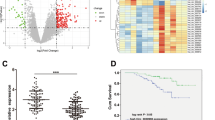
Tumor hypoxia and circular RNAs (circRNAs) are considered to play key roles in tumor progression and malignancy, respectively. Nevertheless, the biological functions and underlying mechanisms of specific circRNAs exposed to hypoxic microenvironments in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain largely elusive. Herein, a novel circRNA, circTDRD3, which is upregulated under hypoxic conditions, was identified. The expression of circTDRD3 was highly expressed in CRC tissues and positively correlated with overall survival, tumor size, lymph node invasion and clinical stage. CircTDRD3 facilitated CRC cell proliferation, migration and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, circTDRD3 promoted HIF1α expression by sponging miR-1231, which facilitated CRC progression. Meanwhile, HIF1α directly combined with TDRD3 promoter to increase the expression of TDRD3 pre-mRNA. Then HIF1a-induced PTBP1 accelerated the formation of circTDRD3. Our findings reveal that circTDRD3 facilitates the proliferation and metastasis of CRC through a positive feedback loop mediated by the HIF1α/PTBP1/circTDRD3/miR-1231/HIF1α axis. Therefore, circTDRD3 may serve as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for patients with CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The previously published sequencing data that were re-analyzed in the current study are available via the accession code GEO126094 and GEO138589. The post-hypoxia database analyzed in this study were shown in Supplementary Table S8.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:145–64.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013;495:333–8.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:453–61.
Barrett SP, Salzman J. Circular RNAs: analysis, expression and potential functions. Development. 2016;143:1838–47.
Zhu Z, Rong Z, Luo Z, Yu Z, Zhang J, Qiu Z, et al. Circular RNA circNHSL1 promotes gastric cancer progression through the miR-1306-3p/SIX1/vimentin axis. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:126.
Wei Y, Chen X, Liang C, Ling Y, Yang X, Ye X, et al. A noncoding regulatory RNAs network driven by Circ-CDYL acts specifically in the early stages hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2020;71:130–47.
Chen T, Wang X, Li C, Zhang H, Liu Y, Han D, et al. CircHIF1A regulated by FUS accelerates triple-negative breast cancer progression by modulating NFIB expression and translocation. Oncogene. 2021;40:2756–71.
Jian X, He H, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Liang X, et al. Hsa_circ_001680 affects the proliferation and migration of CRC and mediates its chemoresistance by regulating BMI1 through miR-340. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:20.
de Heer EC, Jalving M, Harris AL. HIFs, angiogenesis, and metabolism: elusive enemies in breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:5074–87.
Sathornsumetee S, Cao Y, Marcello JE, Herndon JE 2nd, McLendon RE, Desjardins A, et al. Tumor angiogenic and hypoxic profiles predict radiographic response and survival in malignant astrocytoma patients treated with bevacizumab and irinotecan. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:271–8.
Tiwari A, Tashiro K, Dixit A, Soni A, Vogel K, Hall B, et al. Loss of HIF1A from pancreatic cancer cells increases expression of PPP1R1B and degradation of p53 to promote invasion and metastasis. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1882–97.e1885.
Semenza GL. Oxygen sensing, hypoxia-inducible factors, and disease pathophysiology. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014;9:47–71.
Keith B, Johnson RS, Simon MC. HIF1α and HIF2α: sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;12:9–22.
Semenza GL. Defining the role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics. Oncogene. 2010;29:625–34.
Chen Y, Zhang B, Bao L, Jin L, Yang M, Peng Y, et al. ZMYND8 acetylation mediates HIF-dependent breast cancer progression and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2018;128:1937–55.
Zhang J, Zhang Q, Lou Y, Fu Q, Chen Q, Wei T, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/interleukin-1β signaling enhances hepatoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition through macrophages in a hypoxic-inflammatory microenvironment. Hepatology. 2018;67:1872–89.
Xia X, Wang S, Ni B, Xing S, Cao H, Zhang Z, et al. Hypoxic gastric cancer-derived exosomes promote progression and metastasis via MiR-301a-3p/PHD3/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2020;39:6231–44.
Luo Z, Rong Z, Zhang J, Zhu Z, Yu Z, Li T, et al. Circular RNA circCCDC9 acts as a miR-6792-3p sponge to suppress the progression of gastric cancer through regulating CAV1 expression. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:86.
Chen LY, Wang L, Ren YX, Pang Z, Liu Y, Sun XD, et al. The circular RNA circ-ERBIN promotes growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer by miR-125a-5p and miR-138-5p/4EBP-1 mediated cap-independent HIF-1α translation. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:164.
Ren S, Liu J, Feng Y, Li Z, He L, Li L, et al. Knockdown of circDENND4C inhibits glycolysis, migration and invasion by up-regulating miR-200b/c in breast cancer under hypoxia. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:388.
Zeng Z, Zhao Y, Chen Q, Zhu S, Niu Y, Ye Z, et al. Hypoxic exosomal HIF-1α-stabilizing circZNF91 promotes chemoresistance of normoxic pancreatic cancer cells via enhancing glycolysis. Oncogene. 2021;40:5505–17.
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA. 2014;20:1666–70.
Georgilis A, Klotz S, Hanley CJ, Herranz N, Weirich B, Morancho B, et al. PTBP1-mediated alternative splicing regulates the inflammatory secretome and the pro-tumorigenic effects of senescent cells. Cancer Cell. 2018;34:85–102.e109.
Oberstrass FC, Auweter SD, Erat M, Hargous Y, Henning A, Wenter P, et al. Structure of PTB bound to RNA: specific binding and implications for splicing regulation. Science. 2005;309:2054–7.
Rong Z, Luo Z, Fu Z, Zhang P, Li T, Zhang J, et al. The novel circSLC6A6/miR-1265/C2CD4A axis promotes colorectal cancer growth by suppressing p53 signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:324.
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1976;73:3852–6.
Rong Z, Shi S, Tan Z, Xu J, Meng Q, Hua J, et al. Circular RNA CircEYA3 induces energy production to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through the miR-1294/c-Myc axis. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:106.
Li B, Zhu L, Lu C, Wang C, Wang H, Jin H, et al. circNDUFB2 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression via destabilizing IGF2BPs and activating anti-tumor immunity. Nat Commun. 2021;12:295.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–8.
He R, Wen W, Fu B, Zhu R, Chen G, Bai S, et al. CircKIF4A is a prognostic factor and modulator of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma progression. Cancers. 2022;14:4950.
Xu S, Wang J, Jiang J, Song J, Zhu W, Zhang F, et al. TLR4 promotes microglial pyroptosis via lncRNA-F630028O10Rik by activating PI3K/AKT pathway after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:693.
Zheng J, Huang X, Tan W, Yu D, Du Z, Chang J, et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat Genet. 2016;48:747–57.
Harrandah AM, Mora RA, Chan EKL. Emerging microRNAs in cancer diagnosis, progression, and immune surveillance. Cancer Lett. 2018;438:126–32.
Kim S, Bae WJ, Ahn JM, Heo JH, Kim KM, Choi KW, et al. MicroRNA signatures associated with lymph node metastasis in intramucosal gastric cancer. Mod Pathol. 2021;34:672–83.
Li J, Xu J, Cao Z, Du S, Zhang L. MiR-1231 decrease the risk of cancer-related mortality in patients combined with non-small cell lung cancer and diabetes mellitus. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:438.
Schito L, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: master regulators of cancer progression. Trends Cancer. 2016;2:758–70.
Quintero M, Mackenzie N, Brennan PA. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;30:465–8.
Loh XY, Sun QY, Ding LW, Mayakonda A, Venkatachalam N, Yeo MS, et al. RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 suppresses hypoxia and cell-cycle signaling. Cancer Res. 2020;80:219–33.
Yang H, Zhang H, Yang Y, Wang X, Deng T, Liu R, et al. Hypoxia induced exosomal circRNA promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via targeting GEF-H1/RhoA axis. Theranostics. 2020;10:8211–26.
Huan L, Guo T, Wu Y, Xu L, Huang S, Xu Y, et al. Hypoxia induced LUCAT1/PTBP1 axis modulates cancer cell viability and chemotherapy response. Mol Cancer. 2020;19:11.
Chen LL. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:205–11.
Rong Z, Luo Z, Zhang J, Li T, Zhu Z, Yu Z, et al. GINS complex subunit 4, a prognostic biomarker and reversely mediated by Krüppel-like factor 4, promotes the growth of colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:1203–17.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 81772526 and 82072662), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant Support (Grant no. 20191425), Shanghai Jiaotong University Medical Cross Fund (Grant no. YG2017MS28), Three year Action Plan for Clinical Skills and Clinical Innovation in Shanghai level Hospitals (Grant no. SHDC2020CR4022), Shanghai Anticancer Association Eyas Program (Grant no. SACA-CY21C08 to PZ) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant no. 2021M702182 to PZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CH, PZ, BZ and ZF conceived this experiments and revised the manuscript. ZF contributed to the manuscript writing. ZF, PZ, RZ contributed to main experiments. SX and YZ contributed to bioinformatics analysis and experiments. ZF, BZ, YZ and ZL contributed to the raw data gathering and analyzing. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Z., Zhang, P., Zhang, R. et al. Novel hypoxia-induced HIF1α-circTDRD3-positive feedback loop promotes the growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncogene 42, 238–252 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02548-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02548-8
This article is cited by
-
Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates hypoxia-induced proliferation, migration, and inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes via inhibiting the HIF-1α- circCDC42BPB pathway
Advances in Rheumatology (2024)
-
CircRNAs in colorectal cancer: potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Lactate exacerbates lung damage induced by nanomicroplastic through the gut microbiota–HIF1a/PTBP1 pathway
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
PTBP1 as a potential regulator of disease
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
Hypoxia-induced circRTN4IP1 promotes progression and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2023)