Abstract
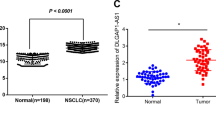
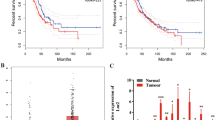
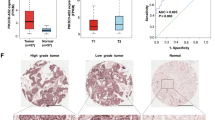
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are emerging as a new class of regulators for a variety of biological processes and have been suggested to play pivotal roles in cancer development and progression. Our current study found that a lncRNA, designated enhancing IL-6/STAT3 signaling activation (LEISA, ENST00000603468), functioned as an oncogenic lncRNA in lung adenocarcinoma (LAD), a major form of non-small cell lung carcinoma, which is one of the most frequently diagnosed malignancies with high morbidity and mortality worldwide, and was involved in the regulation of STAT3 induced IL-6 transcription. Our data showed that LEISA was highly expressed in, and correlated with the clinical progression and prognosis of LAD. Ectopic expression of LEISA promoted the proliferation and suppressed apoptosis of LAD cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that LEISA recruited STAT3 to bind the promoter of IL-6 and upregulated IL-6 expression. Taken together, our work identifies LEISA as a potential diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for LAD.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer J clinicians. 2018;68:394–424.
Liu WJ, Du Y, Wen R, Yang M, Xu J. Drug resistance to targeted therapeutic strategies in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacol therapeutics. 2020;206:107438.
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Akerley W, Bazhenova LA, Borghaei H, Camidge DR, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer, version 6.2015. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw: JNCCN. 2015;13:515–24.
Hess KR, Varadhachary GR, Taylor SH, Wei W, Raber MN, Lenzi R, et al. Metastatic patterns in adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2006;106:1624–33.
Batista PJ, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell. 2013;152:1298–307.
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A, Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature. 2012;489:101–8.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL. Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 2009;23:1494–504.
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, et al. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Sci (N. Y, NY). 2010;329:689–93.
Lai F, Orom UA, Cesaroni M, Beringer M, Taatjes DJ, Blobel GA, et al. Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature. 2013;494:497–501.
Fang L, Wu S, Zhu X, Cai J, Wu J, He Z, et al. MYEOV functions as an amplified competing endogenous RNA in promoting metastasis by activating TGF-β pathway in NSCLC. Oncogene. 2019;38:896–912.
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT. Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics. 2013;193:651–69.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3965–81.
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36:5661–7.
Guan H, Zhu T, Wu S, Liu S, Liu B, Wu J, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00673-v4 promotes aggressiveness of lung adenocarcinoma via activating WNT/β-catenin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:14019–28.
Silva A, Bullock M, Calin G. The clinical relevance of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Cancers. 2015;7:2169–82.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Gao SP, Mark KG, Leslie K, Pao W, Motoi N, Gerald WL, et al. Mutations in the EGFR kinase domain mediate STAT3 activation via IL-6 production in human lung adenocarcinomas. The. J Clin Investig. 2007;117:3846–56.
Jones SA, Jenkins BJ. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:773–89.
Calabrese LH, Rose-John S. IL-6 biology: implications for clinical targeting in rheumatic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:720–7.
Tanaka T, Kishimoto T. The biology and medical implications of interleukin-6. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2:288–94.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Brichory FM, Misek DE, Yim AM, Krause MC, Giordano TJ, Beer DG, et al. An immune response manifested by the common occurrence of annexins I and II autoantibodies and high circulating levels of IL-6 in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:9824–9.
Song L, Rawal B, Nemeth JA, Haura EB. JAK1 activates STAT3 activity in non-small-cell lung cancer cells and IL-6 neutralizing antibodies can suppress JAK1-STAT3 signaling. Mol cancer therapeutics. 2011;10:481–94.
Vinocha A, Grover RK, Deepak R. Clinical significance of interleukin-6 in diagnosis of lung, oral, esophageal, and gall bladder carcinomas. J cancer Res therapeutics. 2018;14:S758–s60.
Yu H, Jove R. The STATs of cancer-new molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:97–105.
Kang S, Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. Targeting Interleukin-6 Signaling in Clinic. Immunity. 2019;50:1007–23.
Johnson DE, O’Keefe RA, Grandis JR. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:234–48.
Taniguchi K, Karin M. IL-6 and related cytokines as the critical lynchpins between inflammation and cancer. Semin Immunol. 2014;26:54–74.
Lederle W, Depner S, Schnur S, Obermueller E, Catone N, Just A, et al. IL-6 promotes malignant growth of skin SCCs by regulating a network of autocrine and paracrine cytokines. Int J cancer. 2011;128:2803–14.
Yoon S, Woo SU, Kang JH, Kim K, Kwon MH, Park S, et al. STAT3 transcriptional factor activated by reactive oxygen species induces IL-6 in starvation-induced autophagy of cancer cells. Autophagy. 2010;6:1125–38.
Yoon S, Woo SU, Kang JH, Kim K, Shin HJ, Gwak HS, et al. NF-κB and STAT3 cooperatively induce IL-6 in starved cancer cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:3467–81.
Chang R, Song L, Xu Y, Wu Y, Dai C, Wang X, et al. Loss of Wwox drives metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer by JAK2/STAT3 axis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:3486.
Matsushita K, Takeuchi O, Standley DM, Kumagai Y, Kawagoe T, Miyake T, et al. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature. 2009;458:1185–90.
Uehata T, Iwasaki H, Vandenbon A, Matsushita K, Hernandez-Cuellar E, Kuniyoshi K, et al. Malt1-induced cleavage of regnase-1 in CD4(+) helper T cells regulates immune activation. Cell. 2013;153:1036–49.
Wang X, Sun W, Shen W, Xia M, Chen C, Xiang D, et al. Long non-coding RNA DILC regulates liver cancer stem cells via IL-6/STAT3 axis. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1283–94.
Wang J, Zhou J, Jiang C, Zheng J, Namba H, Chi P, et al. LNRRIL-6, a novel long noncoding RNA, protects colorectal cancer cells by activating the IL-6-STAT3 pathway. Mol Oncol. 2019;13:2344–60.
Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43:904–14.
Hung T, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNA in genome regulation: prospects and mechanisms. RNA Biol. 2010;7:582–5.
Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018;172:393–407.
Engreitz JM, Haines JE, Perez EM, Munson G, Chen J, Kane M, et al. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature. 2016;539:452–5.
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL, Xu X, Brugmann SA, et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129:1311–23.
Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:452–63.
Gong C, Maquat LE. lncRNAs transactivate STAU1-mediated mRNA decay by duplexing with 3ʹ UTRs via Alu elements. Nature. 2011;470:284–8.
Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, Li R, Yuan J, Yang Y, et al. miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5402–15.
Iioka H, Loiselle D, Haystead TA, Macara IG. Efficient detection of RNA-protein interactions using tethered RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:e53.
Xing YH, Yao RW, Zhang Y, Guo CJ, Jiang S, Xu G, et al. SLERT regulates DDX21 rings associated with Pol I transcription. Cell. 2017;169:664–78. e16.
Deng SJ, Chen HY, Zeng Z, Deng S, Zhu S, Ye Z, et al. Nutrient stress-dysregulated antisense lncRNA GLS-AS impairs GLS-mediated metabolism and represses pancreatic cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2019;79:1398–412.
Lee TI, Johnstone SE, Young RA. Chromatin immunoprecipitation and microarray-based analysis of protein location. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:729–48.
Ying Z, Tian H, Li Y, Lian R, Li W, Wu S, et al. CCT6A suppresses SMAD2 and promotes prometastatic TGF-β signaling. The. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:1725–40.
Cai J, Li R, Xu X, Zhang L, Lian R, Fang L, et al. CK1α suppresses lung tumour growth by stabilizing PTEN and inducing autophagy. Nat cell Biol. 2018;20:465–78.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0106300) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81972170, 81820108025, 81621004, 81672296, 81922050, 81772473, 81802274); the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou City (201803010039); the Guangdong MEPP Fund (NO. GDOE [2019]A21); the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2019A1515011174); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (19ykpy162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Liu, B., Zhang, Y. et al. Long non-coding RNA LEISA promotes progression of lung adenocarcinoma via enhancing interaction between STAT3 and IL-6 promoter. Oncogene 40, 3449–3459 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01769-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01769-7
This article is cited by
-
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes growth and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by repressing VHL through a non-canonical function of EZH2
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Long non-coding RNAs and cancer mechanisms: Immune cells and inflammatory cytokines in the tumor microenvironment
Medical Oncology (2022)
-
LncRNA RCAT1 promotes tumor progression and metastasis via miR-214-5p/E2F2 axis in renal cell carcinoma
Cell Death & Disease (2021)