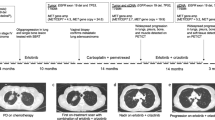
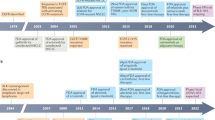
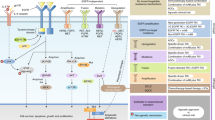
Abstract
EGFR mutations account for the majority of druggable targets in lung adenocarcinoma. Over the past decades the optimization of EGFR inhibitors revolutionized the treatment options for patients suffering from this disease. The pace of this development was largely dictated by the inevitable emergence of resistance mutations during drug treatment. As a result, a rapid understanding of the structural and molecular biology of the individual mutations is the key for the development of next-generation inhibitors. Currently, the field faces an unprecedented number of combinations of activating mutations with distinct resistance mutations in parallel to the approval of osimertinib as a first-line drug for EGFR-mutant lung cancer. In this review, we present a survey of the diverse landscape of EGFR resistance mechanisms with a focus on new insights into on-target EGFR kinase mutations. We discuss array of mutations, their structural effects on the EGFR kinase domain as well as the most promising strategies to overcome the individual resistance profiles found in lung cancer patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piotrowska Z, Isozaki H, Lennerz JK, Gainor JF, Lennes IT, Zhu VW, et al. Landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib in. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1529–39.
Ercan D, Choi HG, Yun CH, Capelletti M, Xie T, Eck MJ, et al. EGFR mutations and resistance to irreversible pyrimidine-based EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:3913–23.
Ho CC, Liao WY, Lin CA, Shih JY, Yu CJ, Yang JC. Acquired BRAF V600E mutation as resistant mechanism after treatment with osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:567–72.
Offin M, Somwar R, Rekhtman N, Benayed R, Chang JC, Plodkowski A et al. Acquired ALK and RET gene fusions as mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancers. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018;2. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.18.00126.
Leonetti A, Sharma S, Minari R, Perego P, Giovannetti E, Tiseo M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:725–37.
Ortiz-Cuaran S, Scheffler M, Plenker D, Dahmen L, Scheel AH, Fernandez-Cuesta L, et al. Heterogeneous mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:4837–47.
Niederst MJ, Hu H, Mulvey HE, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Piotrowska Z, et al. The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:3924–33.
Foster SA, Whalen DM, Ozen A, Wongchenko MJ, Yin J, Yen I, et al. Activation mechanism of oncogenic deletion mutations in BRAF, EGFR, and HER2. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:477–93.
Wagener-Ryczek S, Heydt C, Süptitz J, Michels S, Falk M, Alidousty C, et al. Mutational spectrum of acquired resistance to reversible versus irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:408.
Takezawa K, Pirazzoli V, Arcila ME, Nebhan CA, Song X, de Stanchina E, et al. HER2 amplification: a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:922–33.
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Gale CM, Lifshits E, Gonzales AJ, Shimamura T, et al. PF00299804, an irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor, is effective in lung cancer models with EGFR and ERBB2 mutations that are resistant to gefitinib. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11924–32.
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, Riely G, Viale A, Wang L, et al. MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:20932–7.
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:75ra26.
Sos ML, Koker M, Weir BA, Heynck S, Rabinovsky R, Zander T, et al. PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3256–61.
Walter AO, Sjin RT, Haringsma HJ, Ohashi K, Sun J, Lee K, et al. Discovery of a mutant-selective covalent inhibitor of EGFR that overcomes T790M-mediated resistance in NSCLC. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:1404–15.
Janne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW, Planchard D, Ohe Y, Ramalingam SS, et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl J Med. 2015;372:1689–99.
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:1046–61.
Sequist LV, Rolfe L, Allen AR. Rociletinib in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl J Med. 2015;373:578–9.
Zhai X, Ward RA, Doig P, Argyrou A. Insight into the therapeutic selectivity of the irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib through enzyme kinetic studies. Biochemistry. 2020;59:1428–41.
Thress KS, Paweletz CP, Felip E, Cho BC, Stetson D, Dougherty B, et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat Med. 2015;21:560–2.
Niederst MJ, Hu H, Mulvey HE, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Piotrowska Z, et al. The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:3924–33.
Zhao ZR, Lin YB, Ng CSH, Zhang R, Wu X, Ou Q, et al. Mutation profile of resected EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma by next-generation sequencing. Oncologist. 2019;24:1368–74.
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl J Med. 2018;378:113–25.
Yang Z, Yang N, Ou Q, Xiang Y, Jiang T, Wu X, et al. Investigating novel resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:3097–107.
Oxnard GR, Hu Y, Mileham KF, Husain H, Costa DB, Tracy P, et al. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1527–34.
Lee J, Kim HS, Lee B, Kim HK, Sun JM, Ahn JS et al. Genomic landscape of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR T790M-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2020;126:2704–12.
Mehlman C, Cadranel J, Rousseau-Bussac G, Lacave R, Pujals A, Girard N, et al. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentric retrospective French study. Lung Cancer. 2019;137:149–56.
Minari R, Mazzaschi G, Bordi P, Gnetti L, Alberti G, Altimari A et al. Detection of EGFR-activating and T790M mutations using liquid biopsy in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer whose disease has progressed during treatment with first- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a multicenter real-life retrospective study. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020;21:30072–3.
Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, Lee CK, Kurata T, Kim DW, John T, et al. Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:841–9.
Schoenfeld AJ, Chan JM, Kubota D, Sato H, Rizvi H, Daneshbod Y et al. Tumor analyses reveal squamous transformation and off-target alterations as early resistance mechanisms to first-line osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:2654–63.
Roper N, Brown AL, Wei JS, Pack S, Trindade C, Kim C et al. Clonal evolution and heterogeneity of osimertinib acquired resistance mechanisms in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Cell Rep Med. 2020;1–13.
Bennouna J, Girard N, Audigier-Valette C, le Thuaut A, Gervais R, Masson P, et al. Phase II study evaluating the mechanisms of resistance on tumor tissue and liquid biopsy in patients with EGFR-mutated non-pretreated advanced lung cancer receiving osimertinib until and beyond radiologic progression: the MELROSE trial. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020;21:e10–4.
Starrett JH, Guernet AA, Cuomo ME, Poels KE, van Alderwerelt van Rosenburgh IK, Nagelberg A, et al. Drug sensitivity and allele-specificity of first-line osimertinib resistance EGFR mutations. Cancer Res. 2020;80:2017–30.
Nishino M, Suda K, Kobayashi Y, Ohara S, Fujino T, Koga T, et al. Effects of secondary EGFR mutations on resistance against upfront osimertinib in cells with EGFR-activating mutations in vitro. Lung Cancer. 2018;126:149–55.
Oztan A, Fischer S, Schrock AB, Erlich RL, Lovly CM, Stephens PJ, et al. Emergence of EGFR G724S mutation in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma post progression on osimertinib. Lung Cancer. 2017;111:84–87.
Peled N, Roisman LC, Miron B, Pfeffer R, Lanman RB, Ilouze M, et al. Subclonal therapy by two EGFR TKIs guided by sequential plasma cell-free DNA in EGFR-mutated lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:e81–4.
Zhang Y, He B, Zhou D, Li M, Hu C. Newly emergent acquired EGFR exon 18 G724S mutation after resistance of a T790M specific EGFR inhibitor osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer: a case report. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:51–6.
Fassunke J, Muller F, Keul M, Michels S, Dammert MA, Schmitt A, et al. Overcoming EGFR(G724S)-mediated osimertinib resistance through unique binding characteristics of second-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2018;9:4655.
Brown BP, Zhang YK, Westover D, Yan Y, Qiao H, Huang V, et al. On-target resistance to the mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor osimertinib can develop in an allele-specific manner dependent on the original EGFR-activating mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:3341–51.
Bersanelli M, Minari R, Bordi P, Gnetti L, Bozzetti C, Squadrilli A, et al. L718Q mutation as new mechanism of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:e121–3.
Callegari D, Ranaghan KE, Woods CJ, Minari R, Tiseo M, Mor M, et al. L718Q mutant EGFR escapes covalent inhibition by stabilizing a non-reactive conformation of the lung cancer drug osimertinib. Chem Sci. 2018;9:2740–9.
Shan Y, Eastwood MP, Zhang X, Kim ET, Arkhipov A, Dror RO, et al. Oncogenic mutations counteract intrinsic disorder in the EGFR kinase and promote receptor dimerization. Cell. 2012;149:860–70.
Banno E, Togashi Y, Nakamura Y, Chiba M, Kobayashi Y, Hayashi H, et al. Sensitivities to various epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors of uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations L861Q and S768I: What is the optimal epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor? Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1134–40.
Leventakos K, Kipp BR, Rumilla KM, Winters JL, Yi ES, Mansfield AS. S768I mutation in EGFR in patients with lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:1798–801.
Chen K, Zhou F, Shen W, Jiang T, Wu X, Tong X, et al. Novel mutations on EGFR Leu792 potentially correlate to acquired resistance to osimertinib in advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:e65–8.
Ou SI, Cui J, Schrock AB, Goldberg ME, Zhu VW, Albacker L, et al. Emergence of novel and dominant acquired EGFR solvent-front mutations at Gly796 (G796S/R) together with C797S/R and L792F/H mutations in one EGFR (L858R/T790M) NSCLC patient who progressed on osimertinib. Lung Cancer. 2017;108:228–31.
Fairclough SR, Kiedrowski LA, Lin JJ, Zelichov O, Tarcic G, Stinchcombe TE, et al. Identification of osimertinib-resistant. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019;8:24.
Klempner SJ, Mehta P, Schrock AB, Ali SM, Ou SI. -oriented solvent-front EGFR G796S mutation in tissue and ctDNA in a patient progressing on osimertinib: a case report and review of the literature. Lung Cancer. 2017;8:241–7.
Zheng D, Hu M, Bai Y, Zhu X, Lu X, Wu C, et al. EGFR G796D mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib. Oncotarget. 2017;8:49671–9.
Sutto L, Gervasio FL. Effects of oncogenic mutations on the conformational free-energy landscape of EGFR kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:10616–21.
Shan Y, Arkhipov A, Kim ET, Pan AC, Shaw DE. Transitions to catalytically inactive conformations in EGFR kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:7270–5.
Liu B, Bernard B, Wu JH. Impact of EGFR point mutations on the sensitivity to gefitinib: insights from comparative structural analyses and molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins. 2006;65:331–46.
Liu Y, Li Y, Ou Q, Wu X, Wang X, Shao YW, et al. Acquired EGFR L718V mutation mediates resistance to osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer but retains sensitivity to afatinib. Lung Cancer. 2018;118:1–5.
Fang W, Huang Y, Gan J, Zheng Q, Zhang L. Emergence of EGFR G724S after progression on osimertinib responded to afatinib monotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2020;15:e36–7.
Yang X, Huang C, Chen R, Zhao J. Resolving resistance to osimertinib therapy with afatinib in an NSCLC patient with EGFR L718Q mutation. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020;21:e258–60.
Ma L, Chen R, Wang F, Ma LL, Yuan MM, Chen RR, et al. L718Q mutation occurs without T790M mutation in a lung adenocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to osimertinib. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7:207.
Kobayashi Y, Azuma K, Nagai H, Kim YH, Togashi Y, Sesumi Y, et al. Characterization of EGFR T790M, L792F, and C797S mutations as mechanisms of acquired resistance to afatinib in lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017;16:357–64.
Zhang Q, Zhang XC, Yang JJ, Yang ZF, Bai Y, Su J, et al. EGFR L792H and G796R: two novel mutations mediating resistance to the third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13:1415–21.
Arulananda S, Do H, Musafer A, Mitchell P, Dobrovic A, John T. Combination osimertinib and gefitinib in C797S and T790M EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:1728–32.
Uchibori K, Inase N, Araki M, Kamada M, Sato S, Okuno Y, et al. Brigatinib combined with anti-EGFR antibody overcomes osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14768.
Chen Y, Wu J, Wang A, Qi Z, Jiang T, Chen C, et al. Discovery of N-(5-((5-chloro-4-((2-(isopropylsulfonyl)phenyl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)-4-met hoxy-2-(4-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl)phenyl)acrylamide (CHMFL-ALK/EGFR-050) as a potent ALK/EGFR dual kinase inhibitor capable of overcoming a variety of ALK/EGFR associated drug resistant mutants in NSCLC. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;139:674–97.
Wang X, Zhou L, Yin JC, Wu X, Shao YW, Gao B. Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR 19del/C797S/T790M triple mutations responds to brigatinib and anti-EGFR antibody combination therapy. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14:e85–8.
Jia Y, Yun CH, Park E, Ercan D, Manuia M, Juarez J, et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature. 2016;534:129–32.
To C, Jang J, Chen T, Park E, Mushajiang M, De Clercq DJH, et al. Single and dual targeting of mutant EGFR with an allosteric inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:926–43.
Engelhardt H, Bose D, Petronczki M, Scharn D, Bader G, Baum A, et al. Start selective and rigidify: the discovery path toward a next generation of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2019;62:10272–93.
Guibert N, Hu Y, Feeney N, Kuang Y, Plagnol V, Jones G. et al. Amplicon-based next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA for detection of driver and resistance mutations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:1049–55.
Acknowledgements
We thank all members of the Sos Lab for fruitful comments, especially Johannes Brägelmann and Katia Garbert. This work was supported by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (e:Med initative; 01ZX1901A), a research grant by the Thyssen Foundation (10.19.2.025MN), the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the collaborative research center 1399 and the Deutsche Krebshilfe (70112888).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MLS is a founder and shareholder of PearlRiver Bio GmbH and receives a research grant from PearlRiver Bio GmbH. HLT is a consultant for PearlRiver Bio GmbH.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tumbrink, H.L., Heimsoeth, A. & Sos, M.L. The next tier of EGFR resistance mutations in lung cancer. Oncogene 40, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01510-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01510-w
This article is cited by
-
A destabilizing Y891D mutation in activated EGFR impairs sensitivity to kinase inhibition
npj Precision Oncology (2024)
-
Tenovin 3 induces apoptosis and ferroptosis in EGFR 19del non small cell lung cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Correlation of MRI quantitative perfusion parameters with EGFR, VEGF and EGFR gene mutations in non-small cell cancer
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Toward the next generation EGFR inhibitors: an overview of osimertinib resistance mediated by EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Targeting the up-regulated CNOT3 reverses therapeutic resistance and metastatic progression of EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Death Discovery (2023)