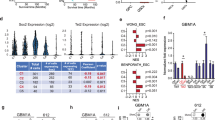
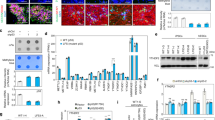
Abstract
Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1), the rate-limiting enzyme in polyamine catabolism, has broad regulatory roles due to near ubiquitous polyamine binding. We describe a novel function of SAT1 as a gene-specific transcriptional regulator through local polyamine acetylation. SAT1 expression is elevated in aggressive brain tumors and promotes resistance to radiotherapy. Expression profiling in glioma cells identified SAT1 target genes that distinguish high- and low-grade tumors, in support of the prognostic utility of SAT1 expression. We further discovered mechanisms of SAT1-driven tumor aggressiveness through promotion of expression of both DNA damage response pathways as well as cell cycle regulatory genes. Mechanistically, SAT1 associates specifically with the promoter of the MELK gene, which functionally controls other SAT1 targets, and leads biologically to maintenance of neurosphere stemness in conjunction with FOXM1 and EZH2. CRISPR knockin mutants demonstrate the essentiality of the polyamine acetyltransferase activity of SAT1 for its function as a transcriptional regulator. Together, the data demonstrate that gene-specific polyamine removal is a major transcriptional regulatory mechanism active in high-grade gliomas that drives poor outcomes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pegg AE, Casero RA Jr. Current status of the polyamine research field. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;720:3–35.
Pegg AE. Spermidine/spermine-N(1)-acetyltransferase: a key metabolic regulator. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;294:E995–1010.
Holst CM, Nevsten P, Johansson F, Carlemalm E, Oredsson SM. Subcellular distribution of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32:39–47.
deHart GW, Jin T, McCloskey DE, Pegg AE, Sheppard D. The alpha9beta1 integrin enhances cell migration by polyamine-mediated modulation of an inward-rectifier potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7188–93.
Uemura T, Yerushalmi HF, Tsaprailis G, Stringer DE, Pastorian KE, Hawel L, et al. Identification and characterization of a diamine exporter in colon epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:26428–35.
Baek JH, Liu YV, McDonald KR, Wesley JB, Zhang H, Semenza GL. Spermidine/spermine N(1)-acetyltransferase-1 binds to hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and RACK1 and promotes ubiquitination and degradation of HIF-1alpha. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:33358–66.
Lee SB, Park JH, Folk JE, Deck JA, Pegg AE, Sokabe M, et al. Inactivation of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) by specific acetylation of its hypusine residue by spermidine/spermine acetyltransferase 1 (SSAT1). Biochem J. 2011;433:205–13.
Yoo J, Kim H, Aksimentiev A, Ha T. Direct evidence for sequence-dependent attraction between double-stranded DNA controlled by methylation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11045.
Veeravalli KK, Ponnala S, Chetty C, Tsung AJ, Gujrati M, Rao JS. Integrin alpha9beta1-mediated cell migration in glioblastoma via SSAT and Kir4.2 potassium channel pathway. Cell Signal. 2012;24:272–81.
Brett-Morris A, Wright BM, Seo Y, Pasupuleti V, Zhang J, Lu J, et al. The polyamine catabolic enzyme SAT1 modulates tumorigenesis and radiation response in GBM. Cancer Res. 2014;74:6925–34.
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, et al. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7011–21.
Ceccarelli M, Barthel FP, Malta TM, Sabedot TS, Salama SR, Murray BA, et al. Molecular profiling reveals biologically discrete subsets and pathways of progression in diffuse glioma. Cell. 2016;164:550–63.
Kim SH, Joshi K, Ezhilarasan R, Myers TR, Siu J, Gu C, et al. EZH2 protects glioma stem cells from radiation-induced cell death in a MELK/FOXM1-dependent manner. Stem Cell Rep. 2015;4:226–38.
Joshi K, Banasavadi-Siddegowda Y, Mo X, Kim SH, Mao P, Kig C, et al. MELK-dependent FOXM1 phosphorylation is essential for proliferation of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells. 2013;31:1051–63.
Wang J, Cheng P, Pavlyukov MS, Yu H, Zhang Z, Kim SH, et al. Targeting NEK2 attenuates glioblastoma growth and radioresistance by destabilizing histone methyltransferase EZH2. J Clin Investig. 2017;127:3075–89.
Chen X, Muller GA, Quaas M, Fischer M, Han N, Stutchbury B, et al. The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 controls cell cycle-dependent gene expression through an atypical chromatin binding mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:227–36.
Sharma V, Malgulwar PB, Purkait S, Patil V, Pathak P, Agrawal R, et al. Genome-wide ChIP-seq analysis of EZH2-mediated H3K27me3 target gene profile highlights differences between low- and high-grade astrocytic tumors. Carcinogenesis. 2017;38:152–61.
Coleman CS, Huang H, Pegg AE. Structure and critical residues at the active site of spermidine/spermine-N1-acetyltransferase. Biochem J. 1996;316(Pt 3):697–701.
Huang L, Chen K, Cai ZP, Chen FC, Shen HY, Zhao WH, et al. DEPDC1 promotes cell proliferation and tumor growth via activation of E2F signaling in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490:707–12.
Santos JS, Fonseca NA, Vieira CP, Vieira J, Casares F. Phylogeny of the teashirt-related zinc finger (tshz) gene family and analysis of the developmental expression of tshz2 and tshz3b in the zebrafish. Dev Dyn. 2010;239:1010–8.
Takeuchi H, Saito H, Noda T, Miyamoto T, Yoshinaga T, Terahara K, et al. Phosphorylation of the HIV-1 capsid by MELK triggers uncoating to promote viral cDNA synthesis. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006441.
Krieg AJ, Hammond EM, Giaccia AJ. Functional analysis of p53 binding under differential stresses. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:7030–45.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by P30CA125123 (CJC); and R01CA187053 (SMW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakur, V.S., Aguila, B., Brett-Morris, A. et al. Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 is a gene-specific transcriptional regulator that drives brain tumor aggressiveness. Oncogene 38, 6794–6800 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0917-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0917-0
This article is cited by
-
Metabolomic profiling of cancer-related fatigue involved in cachexia and chemotherapy
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Forkhead box transcription factors (FOXOs and FOXM1) in glioma: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Abundant expression of ferroptosis-related SAT1 is related to unfavorable outcome and immune cell infiltration in low-grade glioma
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Adaptive Changes Allow Targeting of Ferroptosis for Glioma Treatment
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Ferroptosis Markers Predict the Survival, Immune Infiltration, and Ibrutinib Resistance of Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma
Inflammation (2022)