Abstract
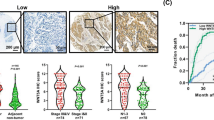
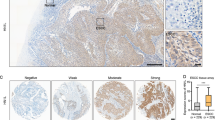
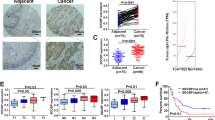
Esophageal squamous cells carcinoma (ESCC) is a major common thoracic tumor characterized by distinctly high incidences and mortality rates. Despite advances in multimodality therapy, the mortality rate of ESCC remains high and understanding of molecular alterations leading to the development and progression of ESCC is still very limited. In this study, a new tumor suppressor candidate, cell adhesion molecule with homology to L1CAM (CHL1), located at 3p26 which was frequently deleted in ESCC was identified. Reduced expression of CHL1 correlated with poor differentiation, increased invasion, and lymph-node metastasis, advanced tumor stage, and decreased overall survival. Methylation-specific PCR and FISH assays revealed that down-regulation of CHL1 in both ESCC cell lines and clinical samples were associated with promoter hypermethylation and loss of heterozygosity. Functional studies using lentiviral-based overexpression and knockdown systems provided direct support of CHL1 to function as an important tumor suppressor with both anti-proliferation and anti-metastasis abilities, through Merlin and SEMA3B-Np1-mediated inhibition of AKT signaling pathway. Further characterization of CHL1 may provide a novel therapeutic target in ESCC treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Li JY. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in China. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1982;62:113–20.
Ke L. Mortality and incidence trends from esophagus cancer in selected geographic areas of China circa 1970–90. Int J Cancer. 2002;102:271–4.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Portale G, Hagen JA, Peters JH, Chan LS, DeMeester SR, Gandamihardja TA, et al. Modern 5-year survival of resectable esophageal adenocarcinoma: single institution experience with 263 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:588–96.
Kwong D, Lam A, Guan X, Law S, Tai A, Wong J, et al. Chromosomal aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma among Chinese: gain of 12p predicts poor prognosis after surgery. Hum Pathol. 2004;35:309–16.
Ogasawara S, Maesawa C, Tamura G, Satodate R. Frequent microsatellite alterations on chromosome 3p in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995;55:891–4.
Yen CC, Chen YJ, Chen JT, Hsia JY, Chen PM, Liu JH, et al. Comparative genomic hybridization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: correlations between chromosomal aberrations and disease progression/prognosis. Cancer. 2001;92:2769–77.
Yen CC, Liang SC, Jong YJ, Chen YJ, Lin CH, Chen YM, et al. Chromosomal aberrations of malignant pleural effusions of lung adenocarcinoma: different cytogenetic changes are correlated with genders and smoking habits. Lung Cancer. 2007;57:292–301.
Knosel T, Schluns K, Dietel M, Petersen I. Chromosomal alterations in lung metastases of colorectal carcinomas: associations with tissue specific tumor dissemination. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2005;22:533–8.
Chan AS, To KF, Lo KW, Mak KF, Pak W, Chiu B, et al. High frequency of chromosome 3p deletion in histologically normal nasopharyngeal epithelia from southern Chinese. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5365–70.
Dalbagni G, Presti J, Reuter V, Fair WR, Cordon-Cardo C. Genetic alterations in bladder cancer. Lancet. 1993;342:469–71.
Presti JC Jr, Reuter VE, Galan T, Fair WR, Cordon-Cardo C. Molecular genetic alterations in superficial and locally advanced human bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 1991;51:5405–9.
Miyoshi Y, Iwao K, Nagasawa Y, Aihara T, Sasaki Y, Imaoka S, et al. Activation of the beta-catenin gene in primary hepatocellular carcinomas by somatic alterations involving exon 3. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2524–7.
Zhang YJ, Ahsan H, Chen Y, Lunn RM, Wang LY, Chen SY, et al. High frequency of promoter hypermethylation of RASSF1A and p16 and its relationship to aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct levels in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2002;35:85–92.
Ackermann S, Kocak H, Hero B, Ehemann V, Kahlert Y, Oberthuer A, et al. FOXP1 inhibits cell growth and attenuates tumorigenicity of neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:840.
Kou C, Zhou T, Han X, Zhuang H, Qian H. LRIG1, a 3p tumor suppressor, represses EGFR signaling and is a novel epigenetic silenced gene in colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464:519–25.
Qin YR, Fu L, Sham PC, Kwong DL, Zhu CL, Chu KK, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism-mass array reveals commonly deleted regions at 3p22 and 3p14.2 associate with poor clinical outcome in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:826–30.
Raju SC, Hauff SJ, Lemieux AJ, Orosco RK, Gross AM, Nguyen LT, et al. Combined TP53 mutation/3p loss correlates with decreased radiosensitivity and increased matrix-metalloproteinase activity in head and neck carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:470–5.
Chen J, Fu L, Zhang LY, Kwong DL, Yan L, Guan XY. Tumor suppressor genes on frequently deleted chromosome 3p in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31:215–22.
Fu L, Qin YR, Xie D, Hu L, Kwong DL, Srivastava G, et al. Characterization of a novel tumor-suppressor gene PLC delta 1 at 3p22 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10720–6.
Zhu C, Qin YR, Xie D, Chua DT, Fung JM, Chen L, et al. Characterization of tumor suppressive function of P300/CBP-associated factor at frequently deleted region 3p24 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2009;28:2821–8.
Uchida K, Oga A, Nakao M, Mano T, Mihara M, Kawauchi S, et al. Loss of 3p26.3 is an independent prognostic factor in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:463–9.
Ognibene M, Pagnan G, Marimpietri D, Cangelosi D, Cilli M, Benedetti MC, et al. CHL1 gene acts as a tumor suppressor in human neuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9:25903–21.
Senchenko VN, Krasnov GS, Dmitriev AA, Kudryavtseva AV, Anedchenko EA, Braga EA, et al. Differential expression of CHL1 gene during development of major human cancers. PLoS One. 2011;6:e15612.
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:401–4.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6:pl1.
Qian CN, Berghuis B, Tsarfaty G, Bruch M, Kort EJ, Ditlev J, et al. Preparing the “soil”: the primary tumor induces vasculature reorganization in the sentinel lymph node before the arrival of metastatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:10365–76.
Yamaguchi H, Condeelis J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:642–52.
Schlatter MC, Buhusi M, Wright AG, Maness PF. CHL1 promotes Sema3A-induced growth cone collapse and neurite elaboration through a motif required for recruitment of ERM proteins to the plasma membrane. J Neurochem. 2008;104:731–44.
Wright AG, Demyanenko GP, Powell A, Schachner M, Enriquez-Barreto L, Tran TS, et al. Close homolog of L1 and neuropilin 1 mediate guidance of thalamocortical axons at the ventral telencephalon. J Neurosci. 2007;27:13667–79.
Loginov VI, Khodyrev DS, Pronina IV, Maliukova AV, Kazubskaia TP, Ermilova VD, et al. [Two CpG-islands of SEMA3B gene: methylation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2009;43:1088–92.
Castro-Rivera E, Ran S, Brekken RA, Minna JD. Semaphorin 3B inhibits the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway through neuropilin-1 in lung and breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8295–303.
Ming XY, Fu L, Zhang LY, Qin YR, Cao TT, Chan KW, et al. Integrin alpha7 is a functional cancer stem cell surface marker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13568.
Li Y, Dowbenko D, Lasky LA. AKT/PKB phosphorylation of p21Cip/WAF1 enhances protein stability of p21Cip/WAF1 and promotes cell survival. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:11352–61.
Ogawara Y, Kishishita S, Obata T, Isazawa Y, Suzuki T, Tanaka K, et al. Akt enhances Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:21843–50.
Rong R, Tang X, Gutmann DH, Ye K. Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) tumor suppressor merlin inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase through binding to PIKE-L. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:18200–5.
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi N, Tobe T. Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer. 1992;69:277–84.
Tao Q, Huang H, Geiman TM, Lim CY, Fu L, Qiu GH, et al. Defective de novo methylation of viral and cellular DNA sequences in ICF syndrome cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:2091–102.
Guan XY, Sham JS, Tang TC, Fang Y, Huo KK, Yang JM. Isolation of a novel candidate oncogene within a frequently amplified region at 3q26 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3806–9.
Xie D, Sham JS, Zeng WF, Lin HL, Che LH, Wu HX, et al. Heterogeneous expression and association of beta-catenin, p16 and c-myc in multistage colorectal tumorigenesis and progression detected by tissue microarray. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:896–902.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1309000), Shenzhen Peacock Team Project (KQTD2015033117210153), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81472250, 81602061, and 81772554), the Hong Kong Research Grant Council grants including GRF (HKU/7668/11 M and 767313), CRF (C7038-14G and C7027-14G), Health and Medical Research Fund (04150826), and Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (182300410376, 182300410297, and 162300410300). Professor XY Guan is Sophie YM Chan Professor in cancer research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Jiang, L., Zhu, C. et al. Loss of cell adhesion molecule L1 like promotes tumor growth and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 38, 3119–3133 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0648-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0648-7
This article is cited by
-
Loss of STARD13 contributes to aggressive phenotype transformation and poor prognosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Endocrine (2023)
-
Melatonin inhibits ESCC tumor growth by mitigating the HDAC7/β-catenin/c-Myc positive feedback loop and suppressing the USP10-maintained HDAC7 protein stability
Military Medical Research (2022)
-
Exosomal miR-338-3p suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cells metastasis by inhibiting CHL1 through the MAPK signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiR-151-3p transferred by cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles promotes osteosarcoma progression through the CHL1/integrin 1β/TGF-β axis
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)
-
StarD13 differentially regulates migration and invasion in prostate cancer cells
Human Cell (2021)