Abstract
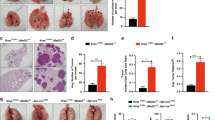
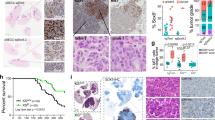
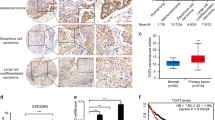
EGFR ligands (e.g., EGF and TGFA) have been shown to be clinically associated with poor survival in lung cancer. Since TGFA itself initiates autochthonous tumors in liver, breast, and pancreas but not in the lung in transgenic mice in vivo, it would appear that an EGFR ligand may not initiate but rather promote lung cancer. However, it has not been proven in vivo whether lung cancer is promoted by an EGFR ligand. Using transgenic mouse models conditionally expressing EGFRL858R or KrasG12D with TGFA (an EGFR ligand) in lung epithelium, we determined that TGFA promoted the growth of EGFRL858R-lung tumors in airway regions but not that of KrasG12D-lung tumors. Analysis of TCGA datasets identified ΔNp63 and AGR2 as potential key tumor-promoting regulators, which were highly induced in the TGFA-induced EGFRL858R-lung tumors. The expression of AGR2 was positively correlated with the expression of TGFA in human EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas. The expression of TGFA in human EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinomas but not in the EGFR wild-type lung adenocarcinoma was associated with poor survival. These results suggest that targeting EGFR ligands may benefit patients who carry EGFR-mutant lung tumors but will not benefit patients with KRAS-mutant lung tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Velu TJ, Beguinot L, Vass WC, Willingham MC, Merlino GT, Pastan I, et al. Epidermal-growth-factor-dependent transformation by a human EGF receptor proto-oncogene. Science. 1987;238:1408–10.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:169–81.
Gazdar AF, Minna JD. Deregulated EGFR signaling during lung cancer progression: mutations, amplicons, and autocrine loops. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008;1:156–60.
Linardou H, Dahabreh IJ, Bafaloukos D, Kosmidis P, Murray S. Somatic EGFR mutations and efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:352–66.
Greulich H, Chen TH, Feng W, Jänne PA, Alvarez JV, Zappaterra M, et al. Oncogenic transformation by inhibitor-sensitive and -resistant EGFR mutants. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e313.
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA, Settleman J. Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 2004;305:1163–7.
Korfhagen TR, Swantz RJ, Wert SE, McCarty JM, Kerlakian CB, Glasser SW, et al. Respiratory epithelial cell expression of human transforming growth factor-alpha induces lung fibrosis in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1994;93:1691–9.
Hardie WD, Le Cras TD, Jiang K, Tichelaar JW, Azhar M, Korfhagen TR. Conditional expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in adult mouse lung causes pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004;286:L741–9.
Jhappan C, Stahle C, Harkins RN, Fausto N, Smith GH, Merlino GT. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990;61:1137–46.
Sandgren EP, Luetteke NC, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL, Lee DC. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990;61:1121–35.
Wagner M, Lührs H, Klöppel G, Adler G, Schmid RM. Malignant transformation of duct-like cells originating from acini in transforming growth factor transgenic mice. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:1254–62.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2014;511:543–50.
Saito M, Shiraishi K, Kunitoh H, Takenoshita S, Yokota J, Kohno T. Gene aberrations for precision medicine against lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:713–20.
Fisher GH, Wellen SL, Klimstra D, Lenczowski JM, Tichelaar JW, Lizak MJ, et al. Induction and apoptotic regression of lung adenocarcinomas by regulation of a K-Ras transgene in the presence and absence of tumor suppressor genes. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3249–62.
Politi K, Zakowski MF, Fan PD, Schonfeld EA, Pao W, Varmus HE. Lung adenocarcinomas induced in mice by mutant EGF receptors found in human lung cancers respond to a tyrosine kinase inhibitor or to down-regulation of the receptors. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1496–510.
Tateishi M, Ishida T, Mitsudomi T, Sugimachi K. Prognostic implication of transforming growth factor alpha in adenocarcinoma of the lung—an immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer. 1991;63:130–3.
Giannou AD, Marazioti A, Kanellakis NI, Giopanou I, Lilis I, Zazara DE, et al. NRAS destines tumor cells to the lungs. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9:672–86.
Green JA, Arpaia N, Schizas M, Dobrin A, Rudensky AY. A nonimmune function of T cells in promoting lung tumor progression. J Exp Med. 2017;214:3565–75.
Rodriguez PC, Popa X, Martínez O, Mendoza S, Santiesteban E, Crespo T, et al. A phase III clinical trial of the epidermal growth factor vaccine CIMAvax-EGF as switch maintenance therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:3782–90.
Perl AK, Zhang L, Whitsett JA. Conditional expression of genes in the respiratory epithelium in transgenic mice: cautionary notes and toward building a better mouse trap. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009;40:1–3.
Siveke JT, Einwächter H, Sipos B, Lubeseder-Martellato C, Klöppel G, Schmid RM. Concomitant pancreatic activation of Kras(G12D) and Tgfa results in cystic papillary neoplasms reminiscent of human IPMN. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:266–79.
Yanagi S, Kishimoto H, Kawahara K, Sasaki T, Sasaki M, Nishio M, et al. Pten controls lung morphogenesis, bronchioalveolar stem cells, and onset of lung adenocarcinomas in mice. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2929–40.
Davé V, Wert SE, Tanner T, Thitoff AR, Loudy DE, Whitsett JA. Conditional deletion of Pten causes bronchiolar hyperplasia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008;38:337–45.
Zhao R, Fallon TR, Saladi SV, Pardo-Saganta A, Villoria J, Mou H, et al. Yap tunes airway epithelial size and architecture by regulating the identity, maintenance, and self-renewal of stem cells. Dev Cell. 2014;30:151–65.
Zhao B, Ye X, Yu J, Li L, Li W, Li S, et al. TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1962–71.
Watanabe H, Ma Q, Peng S, Adelmant G, Swain D, Song W, et al. SOX2 and p63 colocalize at genetic loci in squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:1636–45.
Yoh K, Prywes R. Pathway regulation of p63, a director of epithelial cell fate. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6:51.
Fessart D, Domblides C, Avril T, Eriksson LA, Begueret H, Pineau R. et al. Secretion of protein disulphide isomerase AGR2 confers tumorigenic properties. eLife. 2016;5:e13887
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature. 2012;489:519–25.
Klijn C, Durinck S, Stawiski EW, Haverty PM, Jiang Z, Liu H, et al. A comprehensive transcriptional portrait of human cancer cell lines. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33:306–12.
Li D, Shimamura T, Ji H, Chen L, Haringsma HJ, McNamara K, et al. Bronchial and peripheral murine lung carcinomas induced by T790M-L858R mutant EGFR respond to HKI-272 and rapamycin combination therapy. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:81–93.
Regales L, Balak MN, Gong Y, Politi K, Sawai A, Le C, et al. Development of new mouse lung tumor models expressing EGFR T790M mutants associated with clinical resistance to kinase inhibitors. PLoS ONE. 2007;2:e810.
Zhou W, Ercan D, Chen L, Yun CH, Li D, Capelletti M, et al. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Nature. 2009;462:1070–4.
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:1046–61.
Jia Y, Yun CH, Park E, Ercan D, Manuia M, Juarez J, et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature. 2016;534:129–32.
Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E, Burton L, Chan E, et al. Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature. 2012;487:505–9.
Schneider MR, Dahlhoff M, Herbach N, Renner-Mueller I, Dalke C, Puk O, et al. Betacellulin overexpression in transgenic mice causes disproportionate growth, pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome, and complex eye pathology. Endocrinology. 2005;146:5237–46.
Ji H, Wang Z, Perera SA, Li D, Liang MC, Zaghlul S, et al. Mutations in BRAF and KRAS converge on activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in lung cancer mouse models. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4933–9.
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K, Guimaraes AR, Upadhyay R, et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med. 2008;14:1351–6.
Perera SA, Li D, Shimamura T, Raso MG, Ji H, Chen L, et al. HER2YVMA drives rapid development of adenosquamous lung tumors in mice that are sensitive to BIBW2992 and rapamycin combination therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:474–9.
Chen Z, Sasaki T, Tan X, Carretero J, Shimamura T, Li D, et al. Inhibition of ALK, PI3K/MEK, and HSP90 in murine lung adenocarcinoma induced by EML4-ALK fusion oncogene. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9827–36.
Ceteci F, Xu J, Ceteci S, Zanucco E, Thakur C, Rapp UR. Conditional expression of oncogenic C-RAF in mouse pulmonary epithelial cells reveals differential tumorigenesis and induction of autophagy leading to tumor regression. Neoplasia. 2011;13:1005–18.
Xu C, Buczkowski KA, Zhang Y, Asahina H, Beauchamp EM, Terai H, et al. NSCLC driven by DDR2 mutation is sensitive to dasatinib and JQ1 combination therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14:2382–9.
Huang Q, Schneeberger VE, Luetteke N, Jin C, Afzal R, Budzevich MM, et al. Preclinical modeling of KIF5B-RET fusion lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:2521–9.
Freed DM, Bessman NJ, Kiyatkin A, Salazar-Cavazos E, Byrne PO, Moore JO, et al. EGFR ligands differentially stabilize receptor dimers to specify signaling kinetics. Cell. 2017;171:683–95.
Hogan BL, Barkauskas CE, Chapman HA, Epstein JA, Jain R, Hsia CC, et al. Repair and regeneration of the respiratory system: complexity, plasticity, and mechanisms of lung stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15:123–38.
Tata PR, Mou H, Pardo-Saganta A, Zhao R, Prabhu M, Law BM, et al. Dedifferentiation of committed epithelial cells into stem cells in vivo. Nature. 2013;503:218–23.
Liu J, Cho SN, Akkanti B, Jin N, Mao J, Long W. ErbB2 pathway activation upon Smad4 loss promotes lung tumor growth and metastasis. Cell Rep. 2015;10:1599–1613.
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara K, Kozlowski P, et al. LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature. 2007;448:807–10.
Han X, Li F, Fang Z, Gao Y, Li F, Fang R, et al. Transdifferentiation of lung adenocarcinoma in mice with Lkb1 deficiency to squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3261.
Zhang H, Fillmore Brainson C, Koyama S, Redig AJ, Chen T, Li S, et al. Lkb1 inactivation drives lung cancer lineage switching governed by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14922.
Rusch V, Klimstra D, Venkatraman E, Pisters PW, Langenfeld J, Dmitrovsky E. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor and its ligand transforming growth factor alpha is frequent in resectable non-small cell lung cancer but does not predict tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3:515–22.
Zhang J, Iwanaga K, Choi KC, Wislez M, Raso MG, Wei W, et al. Intratumoral epiregulin is a marker of advanced disease in non-small cell lung cancer patients and confers invasive properties on EGFR-mutant cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2008;1:201–7.
Maeda Y, Tsuchiya T, Hao H, Tompkins DH, Xu Y, Mucenski ML, et al. Kras(G12D) and Nkx2-1 haploinsufficiency induce mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4388–400.
Li B, Dewey CN. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinforma. 2011;12:323.
Maeda Y, Hunter TC, Loudy DE, Davé V, Schreiber V, Whitsett JA. PARP-2 interacts with TTF-1 and regulates expression of surfactant protein-B. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:9600–6.
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Whitsett, H. Varmus, K. Politi, T. Korfhagen, W. Hardie, J. Gokey, and M. Durbin for mice, materials, and discussion.
Funding
This study was supported by the American Lung Association (RG309608), Trustee Award Grant, CF-RDP Pilot & Feasibility Grant, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (YM), the Rotary Foundation Global Grant (KT), AMED (TF), and the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan (TT, TF, YN, and TN)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomoshige, K., Guo, M., Tsuchiya, T. et al. An EGFR ligand promotes EGFR-mutant but not KRAS-mutant lung cancer in vivo. Oncogene 37, 3894–3908 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0240-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0240-1